Introduction
Heavy ion radiation therapy began in the 1970s in
the USA as a more efficient radiation therapy compared with
classical X-ray therapy (1,2). Heavy ion therapy is gaining prevalence,
and has been increasingly utilized in Japan, China, Germany and
Italy (1,2). Heavy ions exhibit three advantageous
cancer cell killing characteristics when compared with X-rays.
Heavy ions exhibit a more efficient dose distribution in cancer
tissues due to the Bragg peak. The phenomenon allows for the
majority of the dose to be deposited within the cancer tissues,
avoiding unnecessary radiation exposure to normal tissues. In
addition, heavy ions form complex DNA lesions within the cell due
to the large amount of energy deposited during particle/DNA
interactions. Heavy ions are able to produce more complex DNA
lesions compared with X-rays and gamma-rays (1,2). Complex
DNA damage lesions are more difficult to repair, compared with the
simple DNA damage lesions frequently observed following irradiation
with X-rays and gamma-rays (3).
Furthermore, heavy ions have a low oxygen enhancement ratio
(3). Heavy ions are more effective at
cell killing under hypoxic conditions when compared with X-rays and
protons (4).
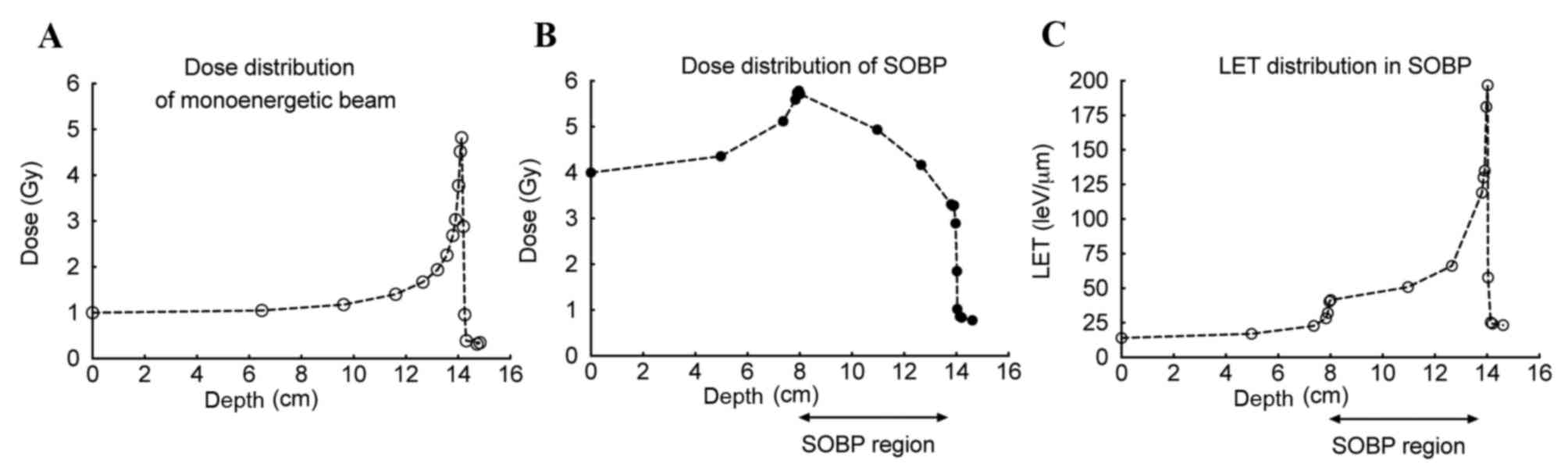
Currently, spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) C ions are
used in heavy ion radiation therapy (1,2). An SOBP
beam consists of various monoenergetic Bragg peak beams to extend
the Bragg peak region to effectively cover the entire cancerous
area and lead to tumor cell death (5). SOBP C ions have been demonstrated to be
effective in the clinic (1,2); however, the biological effect of the
beam track has not been well-studied. In particular, the linear
energy transfer (LET) values in the SOBP region are increased
compared with conventionally used radiation, including X-rays and
gamma-rays, and these values increase with the depth of the beam
track (1,2). Due to this, the quality of the DNA
lesion at each depth point is regarded as being distinct (1,2). It has
been reported that high LET irradiation requires distinct DNA
repair mechanisms compared with low LET irradiation, and these
differences are specifically observed in the two primary DNA double
strand breaks (DSB) repair pathways: Homologous recombination (HR)
and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) (6,7). However,
the differences between high and low LET irradiation remain to be
completely elucidated.
In the present study, the radiosensitivities of four
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines to SOBP C ions were
evaluated to investigate how assorted DNA repair proteins responded
to various LET values, and the subsequent effect on NHEJ, HR and
single strand break repair (8,9). The
present study utilized the OptiCell™ system, previously established
by the authors (10,11), to investigate the effects of distinct
LET-induced radiosensitivities. The OptiCell system enables the
biological effect to be perceived at each depth point of the beam
path, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the SOBP beam. It
was observed that only the single strand break repair deficient
cells demonstrated LET-dependent radiosensitivity in the SOBP
region. The results of the present study may affect the future
development of heavy ion radiation therapy.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
The CHO10B2 (wild-type), V3 (protein kinase
DNA-activated catalytic polypeptide deficient) (12) and PADR9 [poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
(PARP) deficient] (13,14) cells were donated by Dr Joel Bedford
(Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA). The 51D1 (RAD51
paralog D deficient) cells were donated by Dr Larry Thompson
(Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA)
(15). All cell lines were grown in
minimum essential medium α (Wako Pure Chemical Indsutries, Ltd.,
Osaka, Japan) supplemented with 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal
bovine serum (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany),
and 1% penicillin, streptomycin and Fungizone solution
(antibiotic-antimycotic; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5%
CO2. Exponentially growing log phase cells were used in
the present study.
Irradiation
Irradiation with gamma-rays was performed at
Colorado State University using a J.L. Shepherd Model Mark I-68
nominal 6000 Ci 137Cs irradiator (J.L. Shepherd and
Associates, San Fernando, CA, USA) at room temperature and at a
dose rate of 2.5 Gy/min (16). Heavy
ion irradiation was performed at the National Institute of
Radiological Sciences (Chiba, Japan). C ions and Fe ions were
accelerated to 290 and 500 MeV/n, respectively, using the Heavy Ion
Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC). Dose rates for C ions and Fe
ions were set at 1 Gy/min. C ions and Fe ions had LET values of 13
and 200 keV/µm upon entrance. For monoenergetic beam irradiation,
13 and 70 keV/µm C ions, and 200 keV/µm Fe ions, were used.
Monoenergetic C ions with an LET of 70 keV/µm were obtained by
Lucite attenuation (17). For
OptiCell (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) irradiation, C ions were
accelerated to 290 MeV/n initial energy and spread out with a ridge
filter to produce an SOBP of width 6 cm (18).
Cell survival assay using standard
cell culture dishes
Cell survival assay using standard cell culture
dishes was performed as follows. For the gamma-ray irradiated cell
survival assay, exponentially growing cultured cells were
irradiated as described above and plated onto P-60 cell culture
dishes at a density designed to yield ~100 viable colony-forming
cells per P-60 dish. For the heavy ion irradiated cell survival
assay, 4 ml culture medium containing 500 cells was plated onto
each P-60 dish ~3 h prior to irradiation with C and Fe ions, as
described above. All samples were incubated at 37°C for between 7
and 8 days, until cells had formed substantially sized colonies
visible by eye. Surviving colonies were rinsed with 0.9% NaCl,
fixed with 100% ethanol and stained using 0.1% crystal violet at
room temperature. Each colony consisting of >50 cells was scored
as a surviving colony. Cell survival curves were constructed using
GraphPad Prism software (version 6; GraphPad Software, Inc., La
Jolla, CA, USA) and linear quadratic regression. Three independent
experiments were conducted. The D10 values, which represent doses
required to achieve 10% survival, were obtained from each survival
curve using GraphPad Prism software.
Cell survival assay using OptiCell
culture chamber
The cell survival assay using OptiCell culture
chambers was performed as described previously (10,11). For
the OptiCell survival assay following irradiation with SOBP C ions,
10 ml of culture medium containing between 400 and 600 cells was
added to each chamber ~3 h prior to irradiation. In order to
deliver a uniform cell killing effect to each cell line, 4 Gy was
delivered to CHO10B2 and PADR9 cells, 2 Gy was delivered to V3
cells, and 3 Gy was delivered to 51D1 cells at a depth of 0 cm.
Immediately following irradiation, all samples were incubated for
between 7 and 8 days as described above. Each colony consisting of
>50 cells was scored as a surviving colony. At least two
independent experiments were performed using each cell line. The
SOBP slope values, which represent the isobiological cell killing
effect of SOBP irradiation, were calculated as a linear regression
with survival fraction data at depths of between 8 and 14 cm. The
proximal and distal SOBP regions were defined as between 8 and 11
cm, and 11 and 14 cm, respectively, and used in the comparison of
cell killing effects.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism
software. Values are presented as the mean ± standard error of the
means. Statistical comparison was performed using an unpaired two
tailed t-test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
Cell survival in low and high
LET-irradiated DNA repair deficient-CHO cell lines
Cell survival in DNA repair deficient-CHO cell lines
was evaluated to assess the response to gamma-rays, C ions (LET, 13
and 70 keV/µm) and Fe ions (LET, 200 keV/µm; Fig. 1). CHO10B2 and PADR9 cells were
observed to be radioresistant cells. The survival curves following
gamma-ray irradiation were linear quadratic. Although CHO10B2 and
PADR9 exhibited moderate sensitivity to C ions (LET, 13 keV/µm),
they exhibited increased sensitivity to C ions (LET, 70 keV/µm) and
Fe ions (LET, 200 keV/µm) compared with gamma-rays. At the high LET
radiation exposure, the cell survival curves of CHO10B2 and PADR9
cells were exponential. V3 cells were the most radiosensitive cells
among tested cell lines and exhibited exponential cell survival
curves. The radiosensitivities of V3 cells were similar for the low
LET and high LET radiation. 51D1 cells exhibited intermediate
radiosensitivity compared with the four cell lines. 51D1 cells
exhibited relatively increased radiosensitivity to C ions (LET, 13
keV/µm) compared with the other cells.
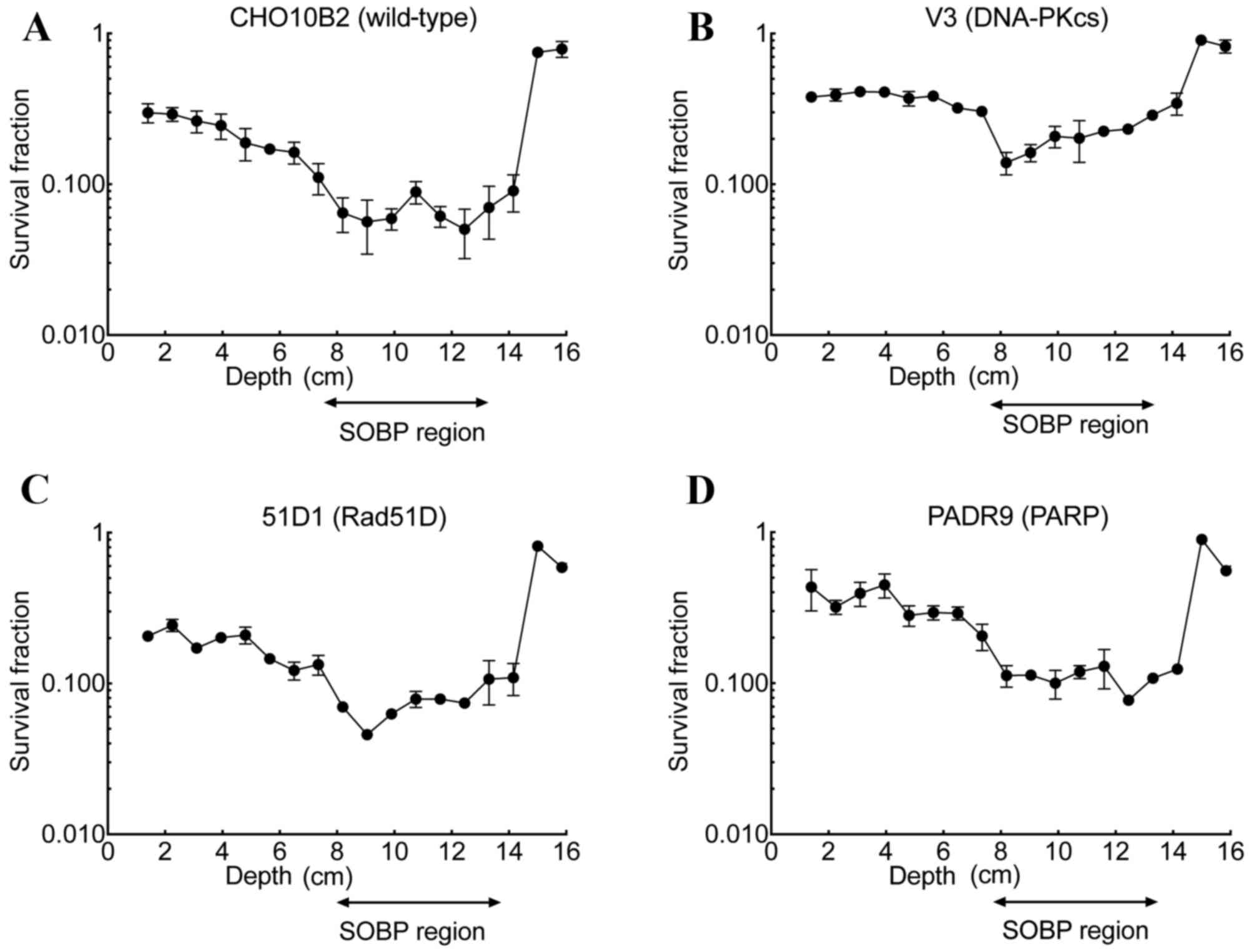
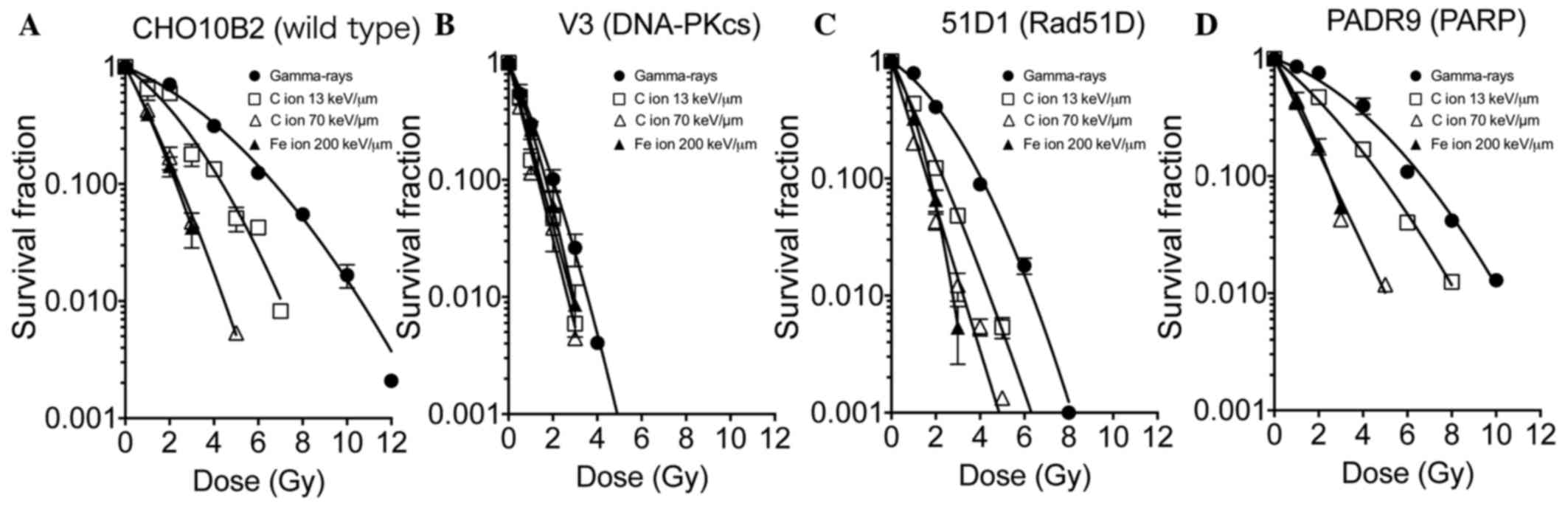 | Figure 1.Cell survival in DNA repair
deficient-CHO cell lines. The survival fractions of (A) CHO10B2,
(B) V3, (C) 51D1 and (D) PADR9 cells, following irradiation with
gamma-rays, C ions (LET, 13 and 70 keV/µm) and Fe ions (LET, 200
keV/µm), were determined using colony formation assays. Closed
circles indicate gamma-rays, open squares indicate C ions LET 13
keV/µm, open triangles indicate C ions LET 70 keV/µm, and closed
triangles indicate Fe ions 200 keV/µm. Values are presented as the
mean ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments.
CHO, Chinese hamster ovary; LET, linear energy transfer; DNA-PKcs,
protein kinase DNA-activated catalytic polypeptide; Rad51D, RAD51
paralog D; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. |
In order to quantitatively evaluate the responses,
the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of the 290 MeV/n
C ions (LET, 13 and 70 keV/µm) and 500 MeV/n Fe ions were
calculated based on the D10 values (Table
I). Gamma-rays were adopted as the standard radiation. The C
(LET, 13 and 70 keV/µm) and Fe ions exhibited an RBE of 1.54, 2.76
and 2.93 in CHO10B2 cells, 1.37, 1.50 and 1.19 in V3 cells, 1.73,
2.50 and 2.31 in 51D1 cells, and 1.38, 2.66 and 2.66 in PADR9
cells, respectively. The cell lines exhibited similar
radiosensitivity, in terms of RBE values, following irradiation
with 70 keV/µm C ions compared with irradiation with the Fe
ions.
 | Table I.RBE values calculated from
D10 values for CHO wild type and DNA repair deficient
mutants. |
Table I.
RBE values calculated from
D10 values for CHO wild type and DNA repair deficient
mutants.
|
| Cell line, RBE
value |
|---|
| Heavy ion | CHO10B2 | V3 | 51D1 | PADR9 |
|---|
| C ions (13
keV/µm) | 1.54 | 1.37 | 1.73 | 1.38 |
| C ions (70
keV/µm) | 2.76 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 2.66 |
| Fe ions (200
keV/µm) | 2.93 | 1.19 | 2.31 | 2.66 |
Cell survival following irradiation
with SOBP C ions compared with depth
The cell survival assay using the OptiCell™ culture
system following irradiation with SOBP C ions was performed in
CHO10B2, V3, 51D1 and PADR9 cells. SOBP C ions were delivered at
depths of between 8 and 14 cm (Fig.
2). At a depth of 1.4 cm, the survival fraction was 0.30 for
CHO10B2, 0.37 for V3, 0.21 for 51D1 and 0.43 for PADR9. As observed
in all cell lines, the survival fraction decreased gradually from
1.4 cm to a depth of 8 cm and rapidly increased at a depth of 14
cm. In the SOBP region, the minimum survival fraction was 0.050 for
CHO10B2, 0.140 for V3, 0.048 for 51D1 and 0.077 for PADR9. When
compared with the entrance region, the SOBP region exhibited
between a 5- and 6-fold increase in cell death in the CHO10B2
(P=0.002) and PADR9 (P=0.037) cells, and an ~2.7-fold increase in
cell death in the V3 (P=0.023) and 51D1 cells (P=0.001; Fig. 3).
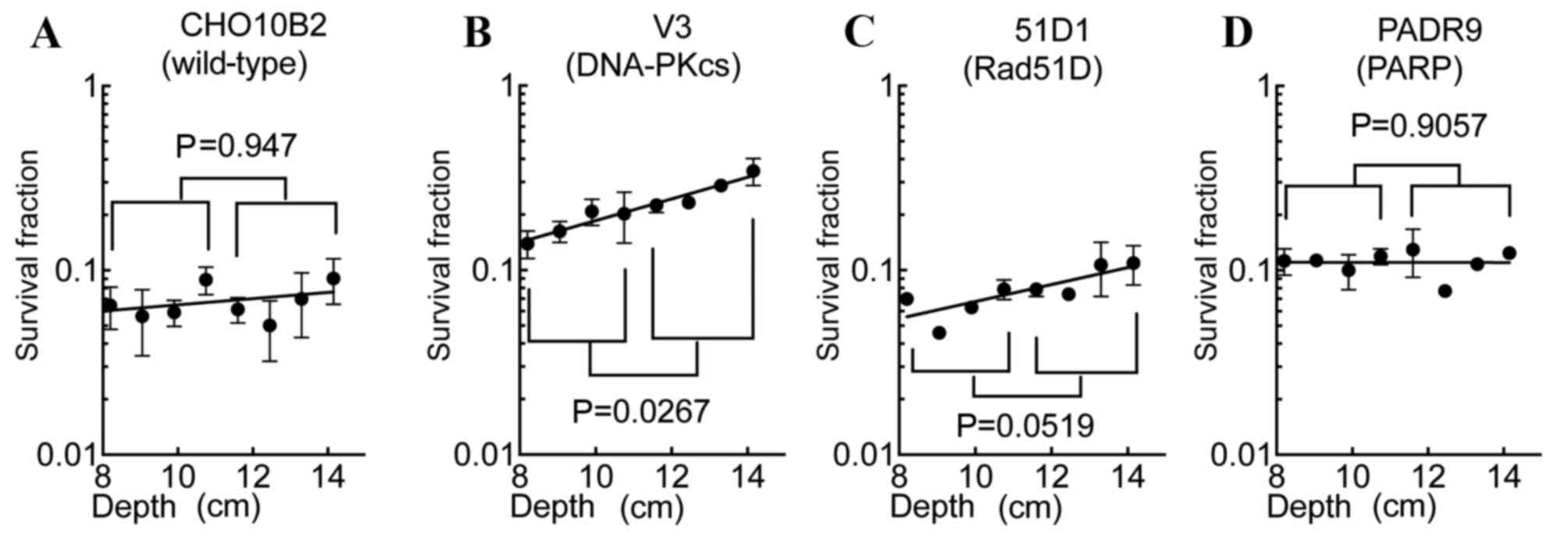
SOBP slope values in the SOBP
region
Comparing the profile of the SOBP region survival
fractions of CHO10B2 and PADR9 cells with those of V3 and 51D1
cells, the V3 and 51D1 cells exhibited increased survival at the
distal SOBP region. In order to evaluate the cytotoxic efficiency
of the SOBP region, SOBP slope values were calculated (Fig. 4). The values of each cell line were
0.017 (CHO10B2), 0.059 (V3), 0.046 (51D1) and ~0 (PADR9). SOBP
slope values nearing 0 suggest isobiological cell death within the
SOBP region. Only the V3 cells exhibited a statistically
significant increase in cell death to proximal SOBP compared with
distal SOBP (P=0.027; Fig. 4B). 51D1
cells exhibited a marked trend of increased radioresistance to
distal SOBP compared with proximal SOBP (P=0.052; Fig. 4C). CHO10B2 (P=0.947; Fig. 4A) and PADR9 (P=0.906; Fig. 4D) did not exhibit significant
differences between proximal and distal SOBP cytotoxicity.
Discussion
In the present study, the biological effect of
irradiation with the SOBP beam region of C ions was assessed using
the OptiCell™ culture system, as reported previously (10,11), and
used to construct a three-dimensional geometric in vitro
experiment. The results of the present study demonstrated that a 6
cm wide SOBP C beam consists of various monoenergetic Bragg peak
beams, which cause rapid build-up of radiation dosage at a depth of
8 cm, a gradual decrease until the proximal boundary and a rapid
decrease at 14 cm. Conversely, LET gradually increases up to a
depth of 14 cm. The combination of these dosages and LET
distributions enables the isobiological killing of cells within the
SOBP region. However, the LET distribution in the SOBP region is
wider compared with monoenergetic beams (5). The biological effects from irradiation
with monoenergetic ions and SOBP with the identical average LET
were distinct (5). Therefore,
monoenergetic ions cannot be used to estimate the biological
effects of irradiation with SOBP with identical average LET
values.
LET-dependent radiosensitivities were studied in
wild-type and DNA repair deficient-CHO cell lines in the present
study. Following the construction of cell survival curves,
wild-type and DNA repair deficient-cell lines exhibited distinct
biological effects when exposed to high LET radiation. RBE values
were demonstrated to increase as LET increases in wild-type cells,
while this association between LET level and RBE value was not
observed in V3 cells. It was confirmed that radiosensitivity is
dose-dependent in NHEJ-deficient cells but not LET-dependent, as
was previously demonstrated (17,19).
Therefore, disruption of NHEJ repair may not be the optimum
strategy for the enhancement of tumor control using high LET
radiation. The 51D1 cells exhibited increased radiosensitivity to
irradiation with 13 keV/µm C ions, which represents the entrance
region of the C ion beam. C ions with LET of 13 keV/µm may be
exposed to the normal tissues that surround tumor tissues. Unless
tumors are selectively targeted by HR inhibitors, it may cause
certain side effects in normal tissues. Conversely, as PADR9 cells
exhibited a shift in sensitivity to high LET radiation from 13 to
70 keV/µm C ions, elevated side effects in normal tissues from PARP
inhibition may be limited. This high LET-specific sensitivity is an
attractive target for C ion radiotherapy. In particular, PARP is a
repair protein associated with single strand break repair (8,9). It has
also been reported that PARP may serve a role in DSB repair
(20). As high LET radiation produces
complex types of DNA damage, which are a mixture of single strand
break and DSB, PARP may be a promising therapeutic target (21–23). The
results of the present study appear to be in accordance with the
PARP inhibitor-induced sensitization with high LET radiation
(24), and indicate PARP inhibition
may be a potential target for heavy ion radiation therapy.
The SOBP beam was originally designed to achieve
uniform cytotoxicity in human salivary gland (HSG) cells (25). In the present study, CHO wild-type
cells exhibited similar isobiological cell killing effects within
the SOBP region compared with HSG cells (25). The SOBP region had distinct impacts on
each cell line and the SOBP slopes between depths of 8 and 14 cm
were calculated. Compared with the slope value of the wild-type
cells, the decreased slope values of the other cell lines
demonstrated that the cells were sensitive to radiation in an
LET-dependent manner. These results indicated that DNA repair
deficiency selectively sensitizes cells to high LET radiation. The
SOBP slope value of PADR9 cells was the lowest (~0) followed by
that of CHO10B2 (0.017), 51D1 (0.046) and V3 (0.059) cells
(Fig. 4). The order of slope values
and differences in RBE values among the cell lines were associated.
As hypothesized following the construction of cell survival curves,
V3 cells exhibited the highest slope value among the cell lines due
to their low RBE value following irradiation to high LET radiation.
HR-deficient 51D1 cells exhibited increased slope values compared
with the wild-type cells. Multiple reports suggested that damage
produced by high LET radiation is repaired by HR with partial
suppression of the NHEJ signaling pathway (6,7). The
results of the present study suggested that inhibiting NHEJ or HR
may lead to non-uniform cytotoxicity within the C ion 6 cm SOBP
region. Although disruptions of these signaling pathways will
result in increased cytotoxicity in the SOBP region, the current
SOBP design obtained from the HSG cell results cannot be directly
applied clinically to radiotherapy. Conversely, PADR9 cells
exhibited isobiological cell killing effects within the SOBP
region. The results of the present study suggest that PARP is an
effective inhibitory target to complement radiotherapy.
In conclusion, the radiosensitivity of DNA repair
deficient-CHO cell lines to high and low LET was investigated, and
the isobiological cell killing effects in the SOBP region of the
radiation beam were evaluated using an OptiCell system. PARP
inhibition was identified to potentially be an optimal target to
complement radiotherapy, and the results of the present study may
contribute to the development of more effective heavy ion radiation
therapies.
Acknowledgements
The authors of the present study would like to thank
Mr. T. Inoue and Mr. Y. Hao (The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan)
for technical assistance, and support from National Institute of
Radiological Sciences-HIMAC. The present study was partially
supported by the Dr Akiko M. Ueno Radiobiology Fund, the Japan
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (grant
no. 15H05935) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
research fellowship (grant no. 15J09331).
References
|
1
|
Durante M and Loeffler JS: Charged
particles in radiation oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:37–43. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marx V: Cancer treatment: Sharp shooters.
Nature. 508:133–138. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okayasu R: Repair of DNA damage induced by
accelerated heavy ions-A mini review. Int J Cancer. 130:991–1000.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirayama R, Furusawa Y, Fukawa T and Ando
K: Repair Kinetics of DNA-DSB induced by X-rays or C Ions under
oxic and hypoxic conditions. J Radiat Res. 46:325–332. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Belli M, Bettega D, Calzolari P, Cherubini
R, Cuttone G, Durante M, Esposito G, Furusawa Y, Gerardi S,
Gialanella G, et al: Effectiveness of monoenergetic and spread-out
bragg peak carbon-ions for inactivation of various normal and
tumour human cell lines. J Radiat Res. 49:597–607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Okayasu R, Okada M, Okabe A, Noguchi M,
Takakura K and Takahashi S: Repair of DNA damage induced by
accelerated heavy ions in mammalian cells proficient and deficient
in the non-homologous end-joining pathway. Radiat Res. 165:59–67.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yajima H, Fujisawa H, Nakajima NI,
Hirakawa H, Jeggo PA, Okayasu R and Fujimori A: The complexity of
DNA double strand breaks is a critical factor enhancing
end-resection. DNA Repair (Amst). 12:936–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Benjamin RC and Gill DM: Poly(ADP-ribose)
synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA
molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem.
255:10502–10508. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benjamin RC and Gill DM: ADP-ribosylation
in mammalian cell ghosts. Dependence of poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis
on strand breakage in DNA. J Biol Chem. 255:10493–10501.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Genet SC, Maeda J, Fujisawa H, Yurkon CR,
Fujii Y, Romero AM, Genik PC, Fujimori A, Kitamura H and Kato TA:
Comparison of cellular lethality in DNA repair-proficient or
-deficient cell lines resulting from exposure to 70 MeV/n protons
or 290 MeV/n C ions. Oncol Rep. 28:1591–1596. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujisawa H, Genik PC, Kitamura H, Fujimori
A, Uesaka M and Kato TA: Comparison of human chordoma cell-kill for
290 MeV/n C ions versus 70 MeV protons in vitro. Radiat Oncol.
8:912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Whitmore GF, Varghese AJ and Gulyas S:
Cell cycle responses of two X-ray sensitive mutants defective in
DNA repair. Int J Radiat Biol. 56:657–665. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
MacLaren RA, Witmer MV, Richardson E and
Stamato TD: Isolation of Chinese hamster ovary cells with reduced
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. Mutat Res. 231:265–274. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Witmer MV, Aboul-Ela N, Jacobson MK and
Stamato TD: Increased sensitivity to DNA-alkylating agents in CHO
mutants with decreased poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. Mutat
Res. 314:249–260. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hinz JM, Tebbs RS, Wilson PF, Nham PB,
Salazar EP, Nagasawa H, Urbin SS, Bedford JS and Thompson LH:
Repression of mutagenesis by Rad51D-mediated homologous
recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:1358–1368. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sunada S, Fujisawa H, Cartwright IM, Maeda
J, Brents CA, Mizuno K, Aizawa Y, Kato TA and Uesaka M:
Monoglucosyl-rutin as a potential radioprotector in mammalian
cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:10–14. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mcmillan DD, Maeda J, Bell JJ, Genet MD,
Phoonswadi G, Mann KA, Kraft SL, Kitamura H, Fujimori A, Yoshii Y,
et al: Validation of 64 Cu-ATSM damaging DNA via high-LET Auger
electron emission. J Radiat Res. 56:784–791. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maeda J, Cartwright IM, Haskins JS, Fujii
Y, Fujisawa H, Hirakawa H, Uesaka M, Kitamura H, Fujimori A, Thamm
DH and Kato TA: Relative biological effectiveness in canine
osteosarcoma cells irradiated with accelerated charged particles.
Oncol Lett. 12:1597–1601. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weyrather WK, Ritter S, Scholz M and Kraft
G: RBE for carbon track-segment irradiation in cell lines of
differing repair capacity. Int J Radiat Biol. 75:1357–1364. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Beck C, Robert I, Reina-San-Martin B,
Schreiber V and Dantzer F: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases in
double-strand break repair: Focus on PARP1, PARP2 and PARP3. Exp
Cell Res. 329:18–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Urushibara A, Shikazono N, O'Neill P,
Fujii K, Wada S and Yokoya A: LET dependence of the yield of
single-, double-strand breaks and base lesions in fully hydrated
plasmid DNA films by 4He(2+) ion irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol.
84:23–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taucher-Scholz G and Kraft G: Influence of
radiation quality on the yield of DNA strand breaks in SV40 DNA
irradiated in solution. Radiat Res. 151:595–604. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taucher-Scholz G, Stanton JA, Schneider M
and Kraft G: Induction of DNA breaks in SV40 by heavy ions. Adv
Space Res. 12:73–80. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirai T, Shirai H, Fujimori H, Okayasu R,
Sasai K and Masutani M: Radiosensitization effect of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition in cells exposed to low and
high liner energy transfer radiation. Cancer Sci. 103:1045–1050.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kagawa K, Murakami M, Hishikawa Y, Abe M,
Akagi T, Yanou T, Kagiya G, Furusawa Y, Ando K, Nojima K, et al:
Preclinical biological assessment of proton and carbon ion beams at
Hyogo ion beam medical center. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
54:928–938. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|