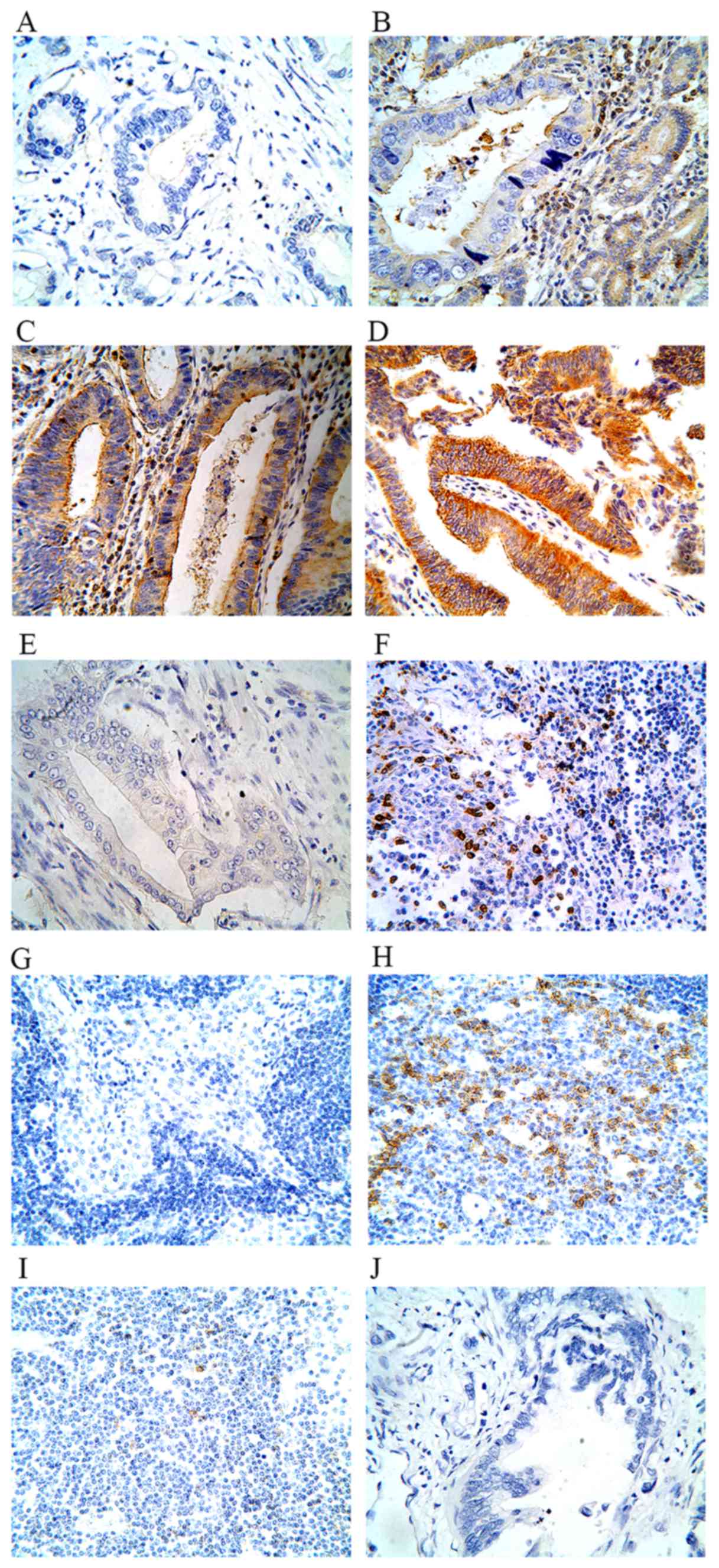
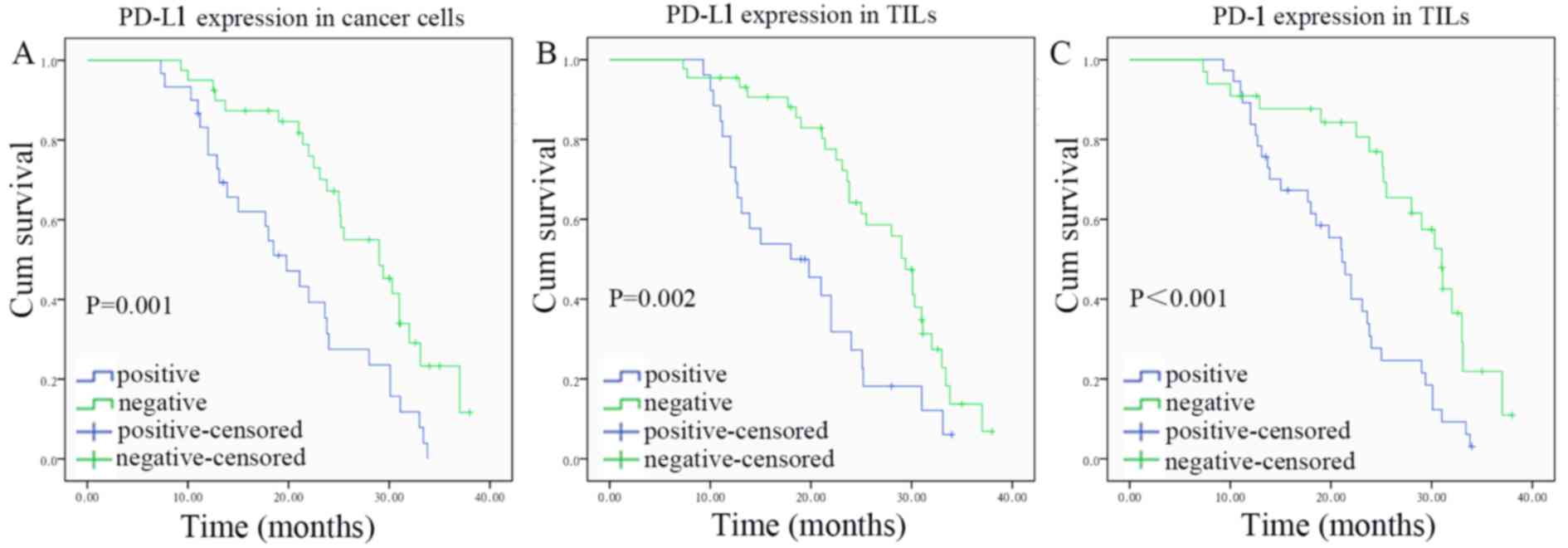
|
1
|
Nakamura H, Arai Y, Totoki Y, Shirota T,
Elzawahry A, Kato M, Hama N, Hosoda F, Urushidate T, Ohashi S, et
al: Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat Genet.
47:1003–1010. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aljiffry M, Walsh MJ and Molinari M:
Advances in diagnosis, treatment and palliation of
cholangiocarcinoma: 1990–2009. World J Gastroenterol. 15:4240–4262.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murakami Y, Uemura K, Sudo T, Hayashidani
Y, Hashimoto Y, Nakamura H, Nakashima A and Sueda T: Adjuvant
gemcitabine plus S-1 chemotherapy improves survival after
aggressive surgical resection for advanced biliary carcinoma. Ann
Surg. 250:950–956. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bordon Y: Tumour immunology: Checkpoint
parley. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:52015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zang X and Allison JP: The B7 family and
cancer therapy: Costimulation and coinhibition. Clin Cancer Res.
13:5271–5279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zou W and Chen L: Inhibitory B7-family
molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:467–477. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Godwin JL, Zibelman M, Plimack ER and
Geynisman DM: Immune checkpoint blockade as a novel
immunotherapeutic strategy for renal cell carcinoma: A review of
clinical trials. Discov Med. 18:341–350. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG and
Xu N: Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1
ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical
significance. Acta histochem. 108:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ghebeh H, Mohammed S, Al-Omair A, Qattan
A, Lehe C, Al-Qudaihi G, Elkum N, Alshabanah M, Bin Amer S, Tulbah
A, et al: The B7-H1 (PD-L1) T lymphocyte-inhibitory molecule is
expressed in breast cancer patients with infiltrating ductal
carcinoma: Correlation with important high-risk prognostic factors.
Neoplasia. 8:190–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki
T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, Higuchi T, Yagi H, Takakura K, Minato N,
et al: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8+
T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 3360–3365. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang W, Chen PW, Li H, Alizadeh H and
Niederkorn JY: PD-L1: PD-1 interaction contributes to the
functional suppression of T-cell responses to human uveal melanoma
cells in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:2518–2525. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong
H, Lohse CM, Webster WS, Sengupta S, Frank I, Parker AS, Zincke H,
et al: Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell
carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res.
66:3381–3385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Geng L, Huang D, Liu J, Qian Y, Deng J, Li
D, Hu Z, Zhang J, Jiang G and Zheng S: B7-H1 up-regulated
expression in human pancreatic carcinoma tissue associates with
tumor progression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:1021–1027. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo
A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M and
Nakajima Y: Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the
programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2151–2157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xylinas E, Robinson BD, Kluth LA, Volkmer
BG, Hautmann R, Küfer R, Zerbib M, Kwon E, Thompson RH, Boorjian SA
and Shariat SF: Association of T-cell co-regulatory protein
expression with clinical outcomes following radical cystectomy for
urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur J Surg Oncol. 40:121–127.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakanishi J, Wada Y, Matsumoto K, Azuma M,
Kikuchi K and Ueda S: Overexpression of B7-H1 (PD-L1) significantly
associates with tumor grade and postoperative prognosis in human
urothelial cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:1173–1182. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inman BA, Sebo TJ, Frigola X, Dong H,
Bergstralh EJ, Frank I, Fradet Y, Lacombe L and Kwon ED: PD-L1
(B7-H1) expression by urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and
BCG-induced granulomata: Associations with localized stage
progression. Cancer. 109:1499–1505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H and Nishimura M: B7-H1 expression on non-small
cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5094–5100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye Y, Zhou L, Xie X, Jiang G, Xie H and
Zheng S: Interaction of B7-H1 on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
cells with PD-1 on tumor-infiltrating T cells as a mechanism of
immune evasion. J Surg Oncol. 100:500–504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y,
Hamada K, Ikeda N, Mizuno T, Yoriki R, Kashizuka H, Yane K, et al:
Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed
death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2947–2953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Huang S, Gong D, Qin Y and Shen
Q: Programmed death-1 upregulation is correlated with dysfunction
of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes in human non-small cell
lung cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. 7:389–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lyford-Pike S, Peng S, Young GD, Taube JM,
Westra WH, Akpeng B, Bruno TC, Richmon JD, Wang H, Bishop JA, et
al: Evidence for a role of the PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in immune
resistance of HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 73:1733–1741. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sfanos KS, Bruno TC, Meeker AK, de Marzo
AM, Isaacs WB and Drake CG: Human prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T
lymphocytes are oligoclonal and PD-1+. Prostate. 69:1694–1703.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ahmadzadeh M, Johnson LA, Heemskerk B,
Wunderlich JR, Dudley ME, White DE and Rosenberg SA: Tumor
antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high
levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood. 114:1537–1544.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Blank C, Brown I, Peterson AC, Spiotto M,
Iwai Y, Honjo T and Gajewski TF: PD-L1/B7H-1 inhibits the effector
phase of tumor rejection by T cell receptor (TCR) transgenic CD8+ T
cells. Cancer Res. 64:1140–1145. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flemming A: Cancer: PD1 makes waves in
anticancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:6012012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th. Springer;
New York, NY: pp. 66–71. 2010
|
|
34
|
Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S, Donnem T, Persson
M, Bremnes RM and Busund LT: The prognostic value of
intraepithelial and stromal innate immune system cells in non-small
cell lung carcinoma. Histopathology. 55:301–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sunshine J and Taube JM: PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 23:32–38. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee J, Kefford R and Carlino M: PD-1 and
PD-L1 inhibitors in melanoma treatment: Past success, present
application and future challenges. Immunotherapy. 8:733–746. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Muenst S, Soysal SD, Gao F, Obermann EC,
Oertli D and Gillanders WE: The presence of programmed death 1
(PD-1)-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with
poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
139:667–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Parsa AT, Waldron JS, Panner A, Crane CA,
Parney IF, Barry JJ, Cachola KE, Murray JC, Tihan T, Jensen MC, et
al: Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7-H1
expression and immunoresistance in glioma. Nat Med. 13:84–88. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marzec M, Zhang Q, Goradia A, Raghunath
PN, Liu X, Paessler M, Wang HY, Wysocka M, Cheng M, Ruggeri BA and
Wasik MA: Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression
of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:pp. 20852–20857. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Curiel TJ, Wei S, Dong H, Alvarez X, Cheng
P, Mottram P, Krzysiek R, Knutson KL, Daniel B, Zimmermann MC, et
al: Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated
antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 9:562–567. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR, Sullivan EL,
Munoz O, Wood CR, Greenfield EA and Freeman GJ: Blockade of
programmed death-1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell
activation and cytokine production. J Immunol. 170:1257–1266. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|