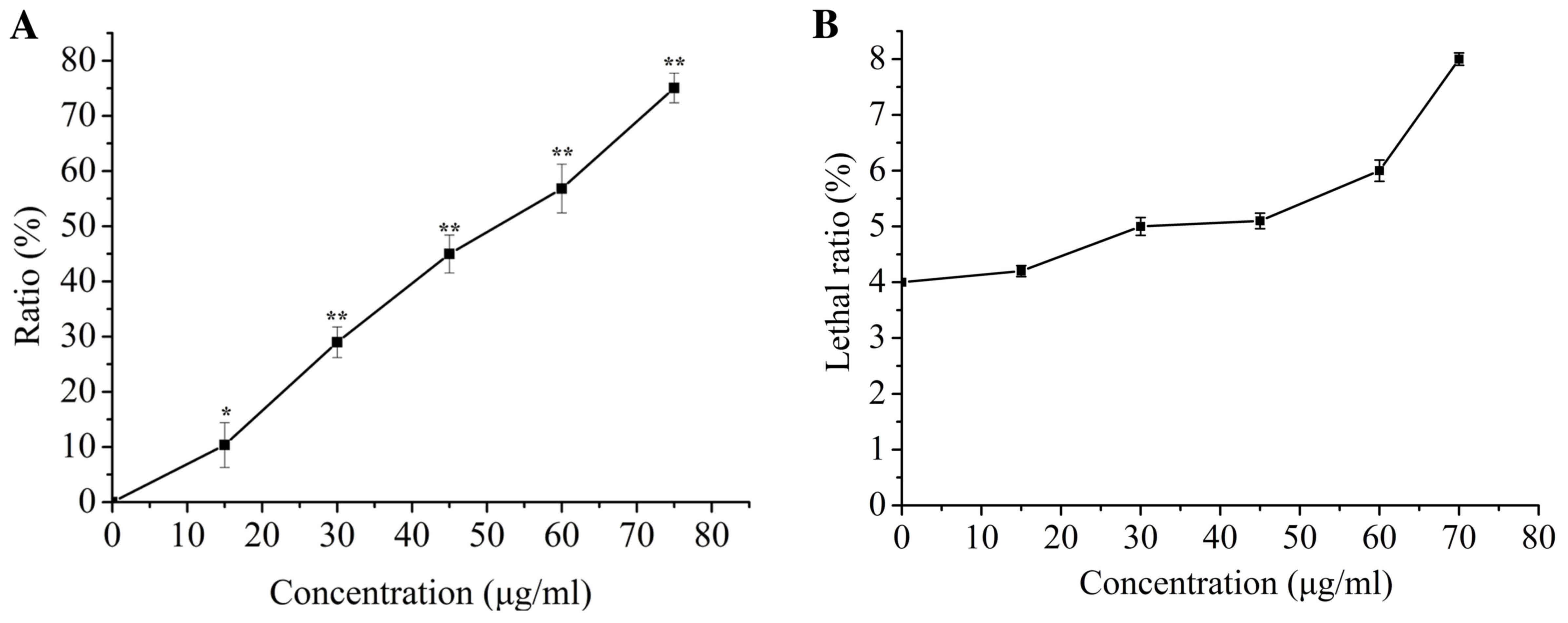
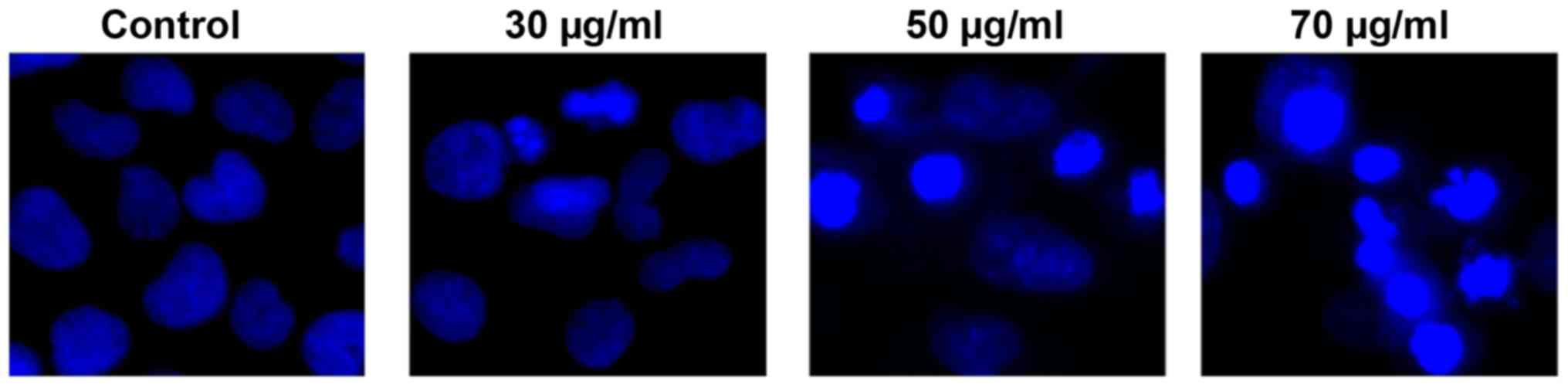
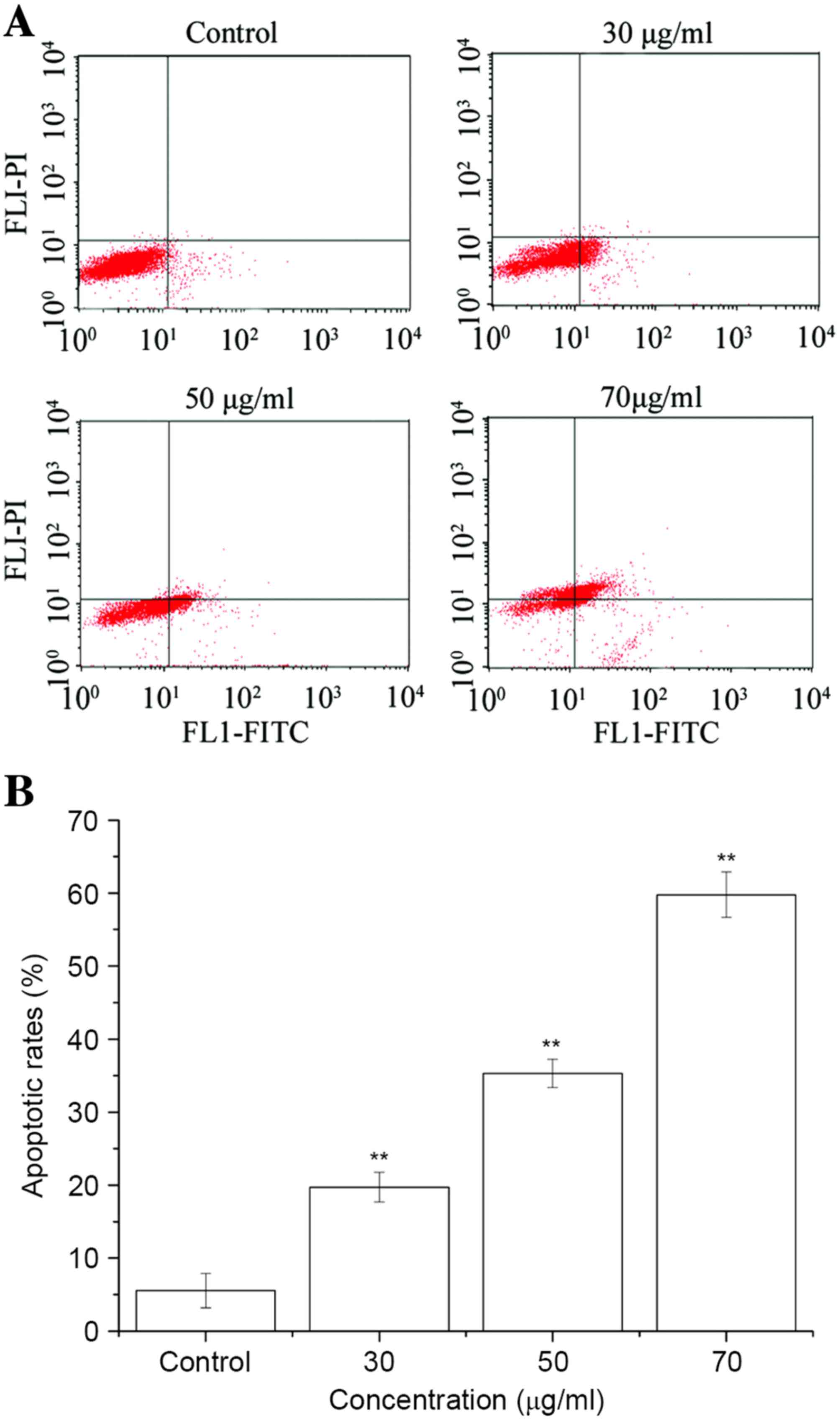
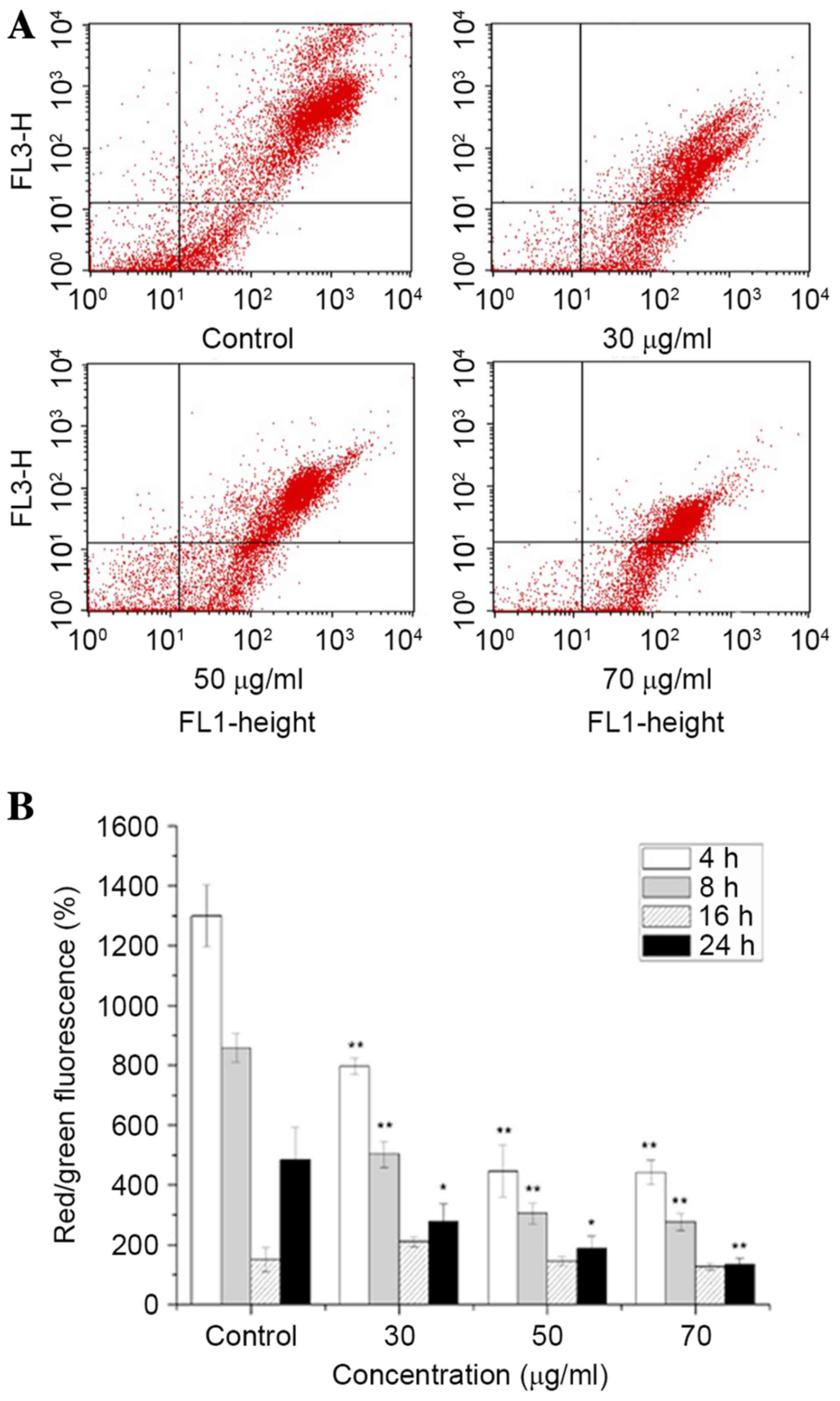
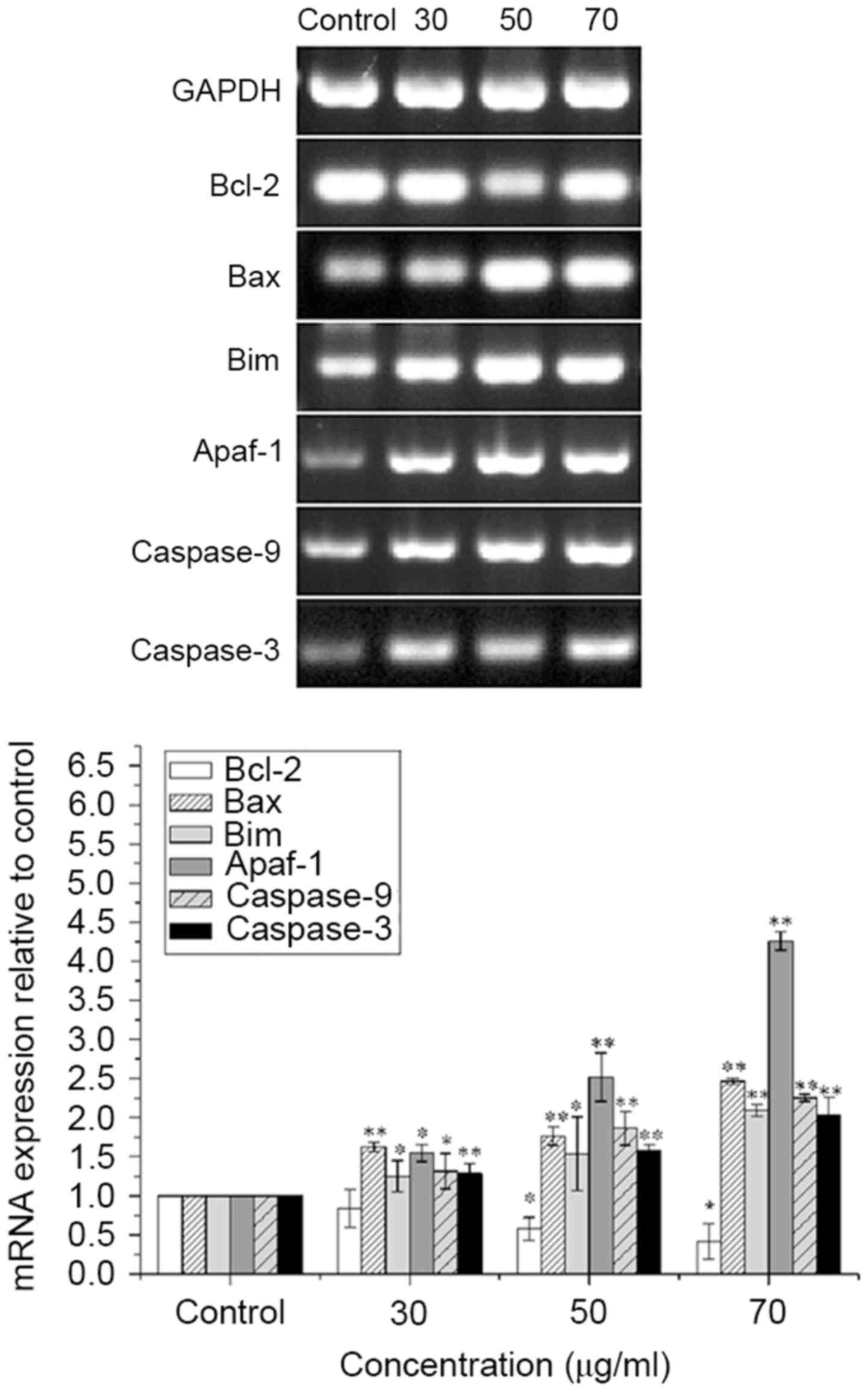
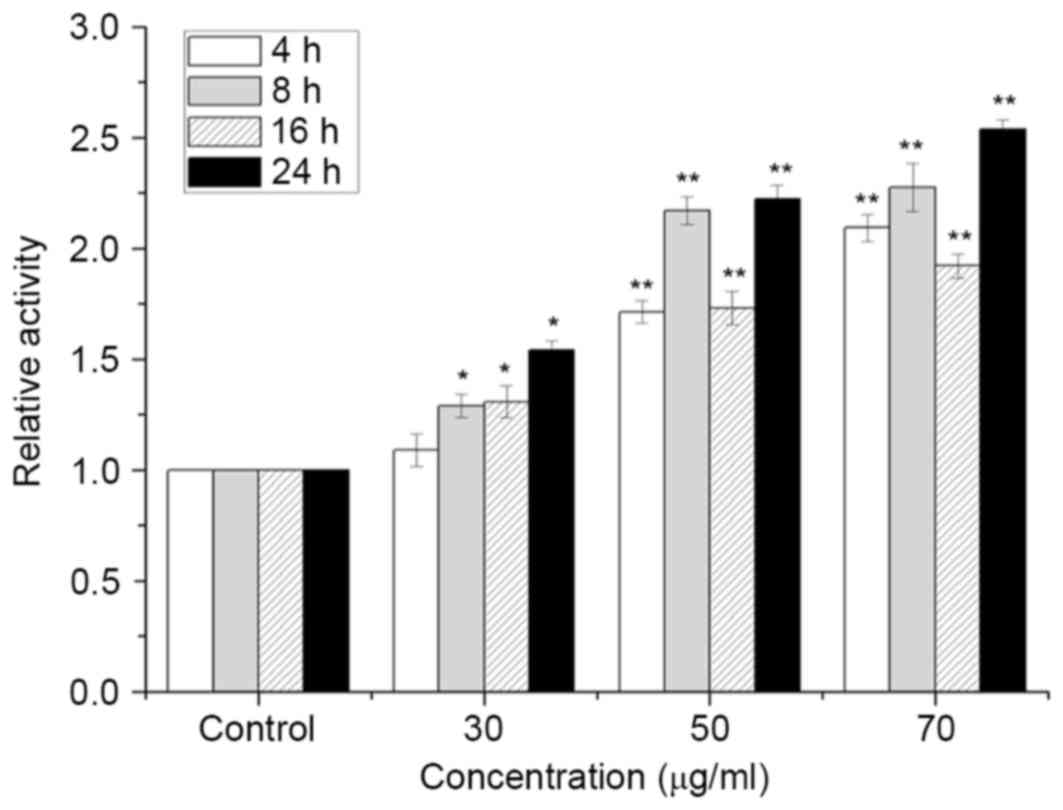
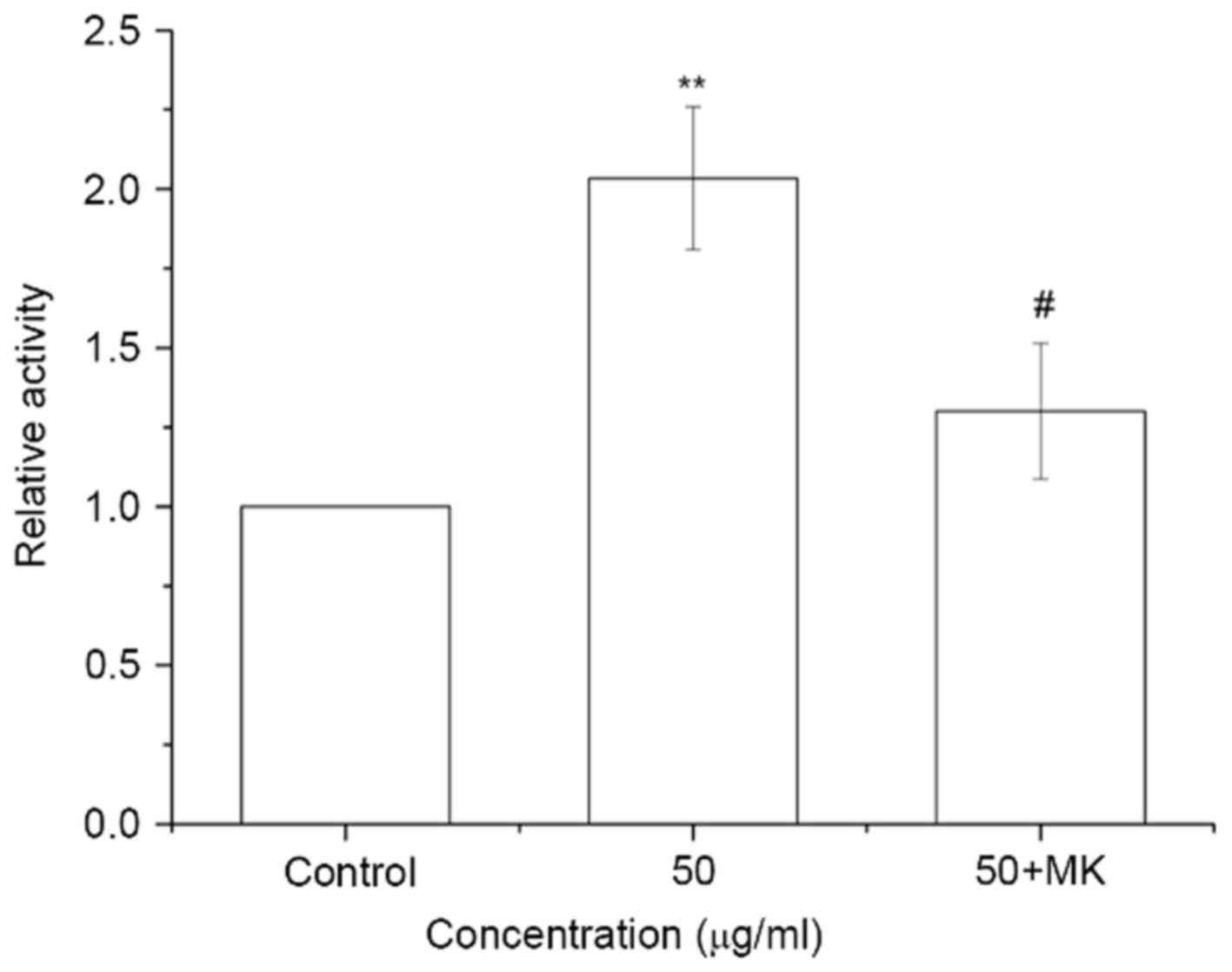
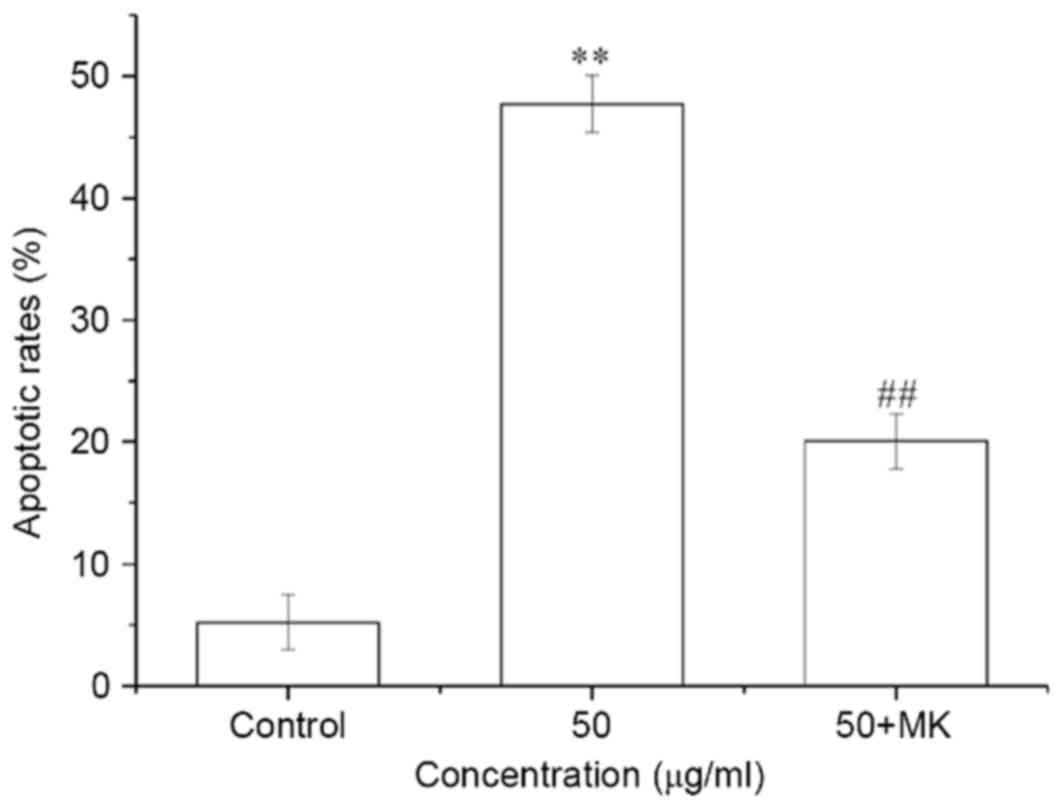
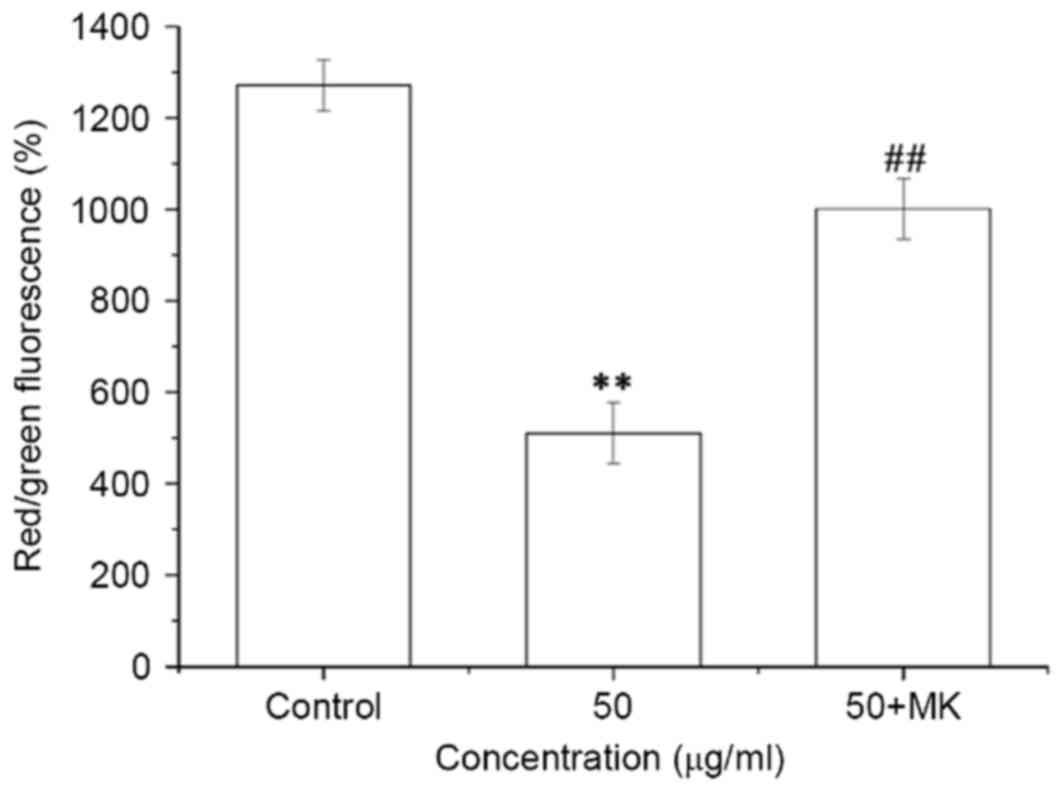
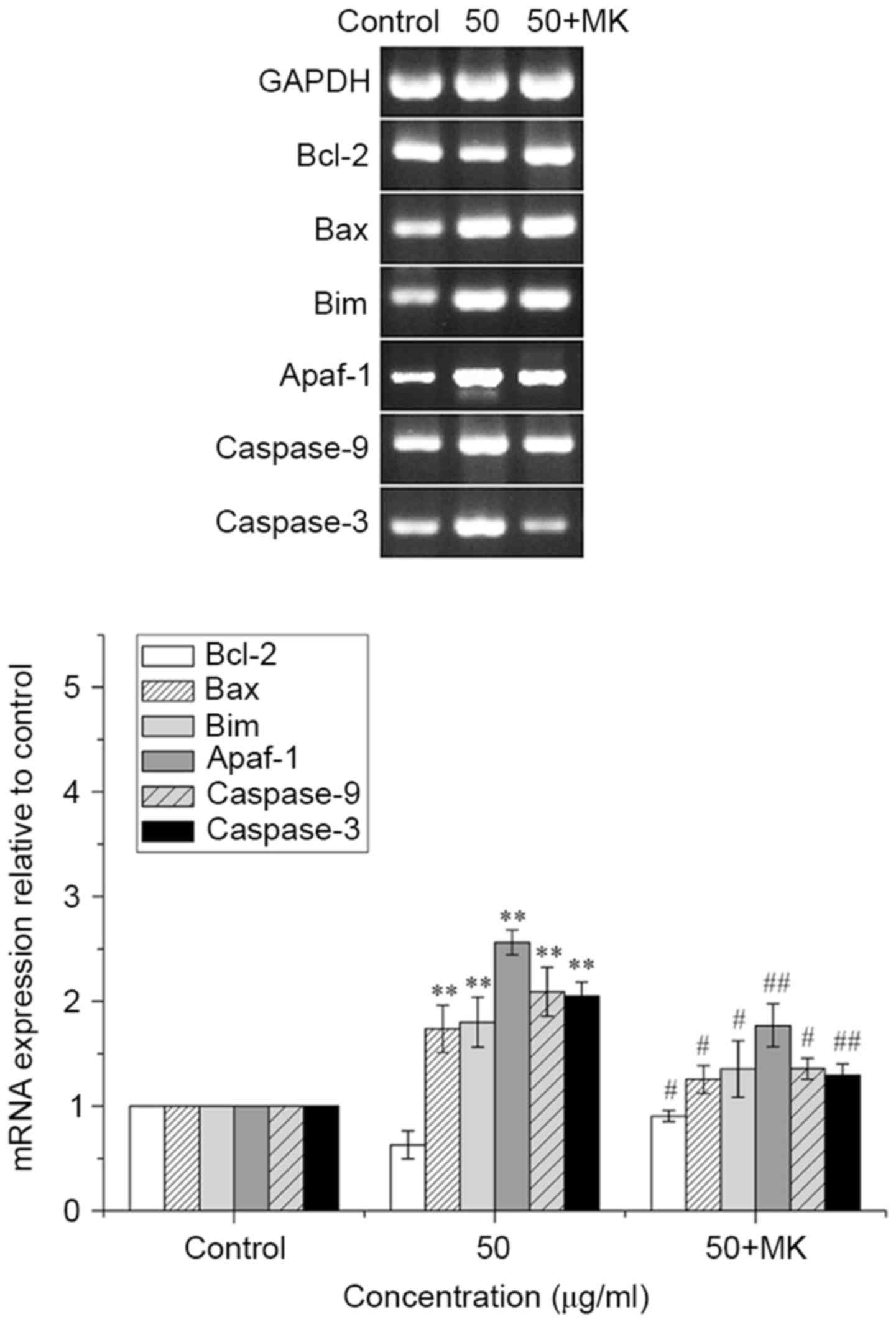
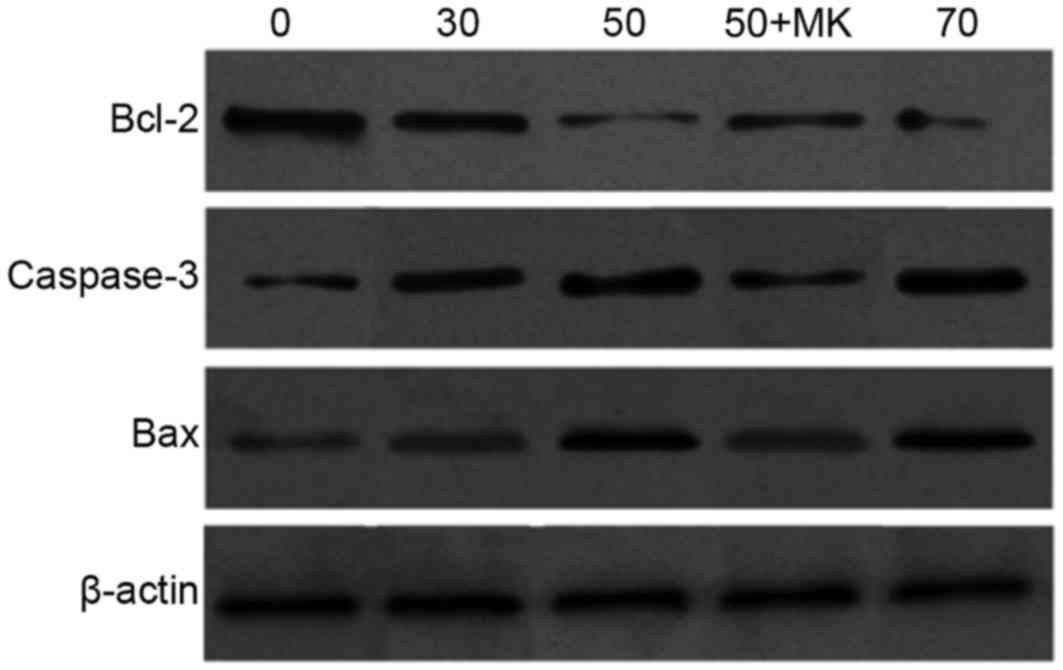
|
1
|
Huang W, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Yu Z, Mou
L, Wu H, Zhao L, Long T, Qin D and Gui Y: Roles of ERβ and GPR30 in
proliferative response of human bladder cancer cell to estrogen.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:2517802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yee DS, Ishill NM, Lowrance WT, Herr HW
and Elkin EB: Ethnic differences in bladder cancer survival.
Urology. 78:544–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM: International variation.
Oncogene. 23:6329–6340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Braithwaite D, Demb J, Henderson LM,
Mandelblatt JS and Kerlikowske K: American Cancer Society: Cancer
Facts & Figures. 2016.
|
|
5
|
Douglass L and Schoenberg M: The future of
intravesical drug delivery for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer. 2:285–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang J, Yuan X, Zhao H, Yan X, Sun X and
Zheng Q: Licochalcone A inhibiting proliferation of bladder cancer
T24 cells by inducing reactive oxygen species production. Biomed
Mater Eng. 24:1019–1025. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stein JP and Skinner DG: Radical
cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results of a
standard procedure. World J Urol. 24:296–304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng C, Zeng W, Su J, Kuang Y, He Y, Zhao
S, Zhang J, Ma W, Bode AM, Dong Z and Chen X: Cyclin-dependent
kinase 2 (CDK2) is a key mediator for EGF-induced cell
transformation mediated through the ELK4/c-Fos signaling pathway.
Oncogene. 35:1170–1179. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu JW, Sun P, Zhang DX, Xiong WJ and Mi J:
Hexokinase 2 regulates G1/S checkpoint through CDK2 in
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Signal. 26:2210–2216. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin YH, Yim H, Park JH and Lee SK: Cdk2
activity is associated with depolarization of mitochondrial
membrane potential during apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
305:974–980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kinghorn AD, Pan L, Fletcher JN and Chai
H: The relevance of higher plants in lead compound discovery
programs. J Nat Prod. 74:1539–1555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fintelmann V: Modern phytotherapy and its
uses in gastrointestinal conditions. Planta Med. 57 Suppl
7:S48–S52. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Madak-Erdogan Z, Gong P, Zhao YC, Xu L,
Wrobel KU, Hartman JA, Wang M, Cam A, Iwaniec UT, Turner RT, et al:
Dietary licorice root supplementation reduces diet-induced weight
gain, lipid deposition, and hepatic steatosis in ovariectomized
mice without stimulating reproductive tissues and mammary gland.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 60:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fukai T, Marumo A, Kaitou K, Kanda T,
Terada S and Nomura T: Anti-Helicobacter pylori flavonoids from
licorice extract. Life Sci. 71:1449–1463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Funakoshi-Tago M, Nakamura K, Tsuruya R,
Hatanaka M, Mashino T, Sonoda Y and Kasahara T: The fixed structure
of Licochalcone A by alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone is necessary
for anti-inflammatory activity through the inhibition of NF-kappaB
activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:562–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, Ba Q, Li M, Ni
SJ, Wang LS and Du X: Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric
cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YM, Kim TH, Kim YW, Yang YM, Ryu DH,
Hwang SJ, Lee JR, Kim SC and Kim SG: Inhibition of liver X
receptor-α-dependent hepatic steatosis by isoliquiritigenin, a
licorice antioxidant flavonoid, as mediated by JNK1 inhibition.
Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1722–1734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yadav VR, Prasad S, Sung B and Aggarwal
BB: The role of chalcones in suppression of NF-κB-mediated
inflammation and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:295–309. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chin YW and Kinghorn AD: Structural
characterization, biological effects, and synthetic studies on
xanthones from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana), a popular
botanical dietary supplement. Mini Rev Org Chem. 5:355–364. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Liu P, Chen Q, Situ H, Xie
T, Zhang J, Peng C, Lin Y and Chen J: MicroRNA-25 regulates
chemoresistance-associated autophagy in breast cancer cells, a
process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer
isoliquiritigenin. Oncotarget. 5:7013–7026. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao H, Yuan X, Li D, Chen H, Jiang J,
Wang Z, Sun X and Zheng Q: Isoliquiritigen enhances the antitumour
activity and decreases the genotoxic effect of cyclophosphamide.
Molecules. 18:8786–8798. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haraguchi H, Ishikawa H, Mizutani K,
Tamura Y and Kinoshita T: Antioxidative and superoxide scavenging
activities of retrochalcones in Glycyrrhiza inflata. Bioorg Med
Chem. 6:339–347. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fukai T, Satoh K, Nomura T and Sakagami H:
Preliminary evaluation of antinephritis and radical scavenging
activities of glabridin from Glycyrrhiza glabra. Fitoterapia.
74:624–629. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yokota T, Nishio H, Kubota Y and Mizoguchi
M: The inhibitory effect of glabridin from licorice extracts on
melanogenesis and inflammation. Pigment Cell Res. 11:355–361. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Inoue H, Mori T, Shibata S and Koshihara
Y: Modulation by glycyrrhetinic acid derivatives of TPA-induced
mouse ear oedema. Br J Pharmacol. 96:204–210. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gerber B, Scholz C, Reimer T, Briese V and
Janni W: Complementary and alternative therapeutic approaches in
patients with early breast cancer: A systematic review. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 95:199–209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kushman ME, Kabler SL, Ahmad S, Doehmer J,
Morrow CS and Townsend AJ: Protective efficacy of hGSTM1-1 against
B[a]P and (+)- or (−)-B[a]P-7,8-dihydrodiol cytotoxicity,
mutagenicity, and macromolecular adducts in V79 cells coexpressing
hCYP1A1. Toxicol Sci. 99:51–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Soriano J, García-Díaz M, Mora M, Sagristá
ML, Nonell S, Villanueva A, Stockert JC and Cañete M: Liposomal
temocene (m-THPPo) photodynamic treatment induces cell death by
mitochondria-independent apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1830:4611–4620. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blix ES, Irish JM, Husebekk A, Delabie J,
Forfang L, Tierens AM, Myklebust JH and Kolstad A: Phospho-specific
flow cytometry identifies aberrant signaling in indolent B-cell
lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 12:4782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Song X, Zhang Z, Guo M, Jiang H,
Wang W, Cao Y, Zhu L and Zhang N: Stevioside inhibits inflammation
and apoptosis by regulating TLR2 and TLR2-related proteins in S.
aureus-infected mouse mammary epithelial cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 22:192–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Zhang B, Yuan X, Yang F, Liu J,
Zhao H, Liu L, Wang Y, Wang Z and Zheng Q:
Isoliquiritigenin-induced differentiation in mouse melanoma B16F0
cell line. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:5349342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin LT and Lin CC:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis
in human hepatoma cells. Planta Med. 71:130–134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim DC, Ramachandran S, Baek SH, Kwon SH,
Kwon KY, Cha SD, Bae I and Cho CH: Induction of growth inhibition
and apoptosis in human uterine leiomyoma cells by
isoliquiritigenin. Reprod Sci. 15:552–558. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jung JI, Chung E, Seon MR, Shin HK, Kim
EJ, Lim SS, Chung WY, Park KK and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin (ISL)
inhibits ErbB3 signaling in prostate cancer cells. Biofactors.
28:159–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takahashi T, Takasuka N, Iigo M, Baba M,
Nishino H, Tsuda H and Okuyama T: Isoliquiritigenin, a flavonoid
from licorice, reduces prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide, causes
apoptosis, and suppresses aberrant crypt foci development. Cancer
Sci. 95:448–453. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou GS, Song LJ and Yang B:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of
U87 human glioma cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 7:531–536.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Choi JS, Shin S, Jin YH, Yim H, Koo KT,
Chun KH, Oh YT, Lee WH and Lee SK: Cyclin-dependent protein kinase
2 activity is required for mitochondrial translocation of Bax and
disruption of mitochondrial transmembrane potential during
etoposide-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 12:1229–1241. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Darvin P, Baeg SJ, Joung YH, Sp N, Kang
DY, Byun HJ, Park JU and Yang YM: Tannic acid inhibits the
Jak2/STAT3 pathway and induces G1/S arrest and mitochondrial
apoptosis in YD-38 gingival cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
47:1111–1120. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Harbour JW, Luo RX, Dei Santi A, Postigo
AA and Dean DC: Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential
intramolecular interactions that progressively block Rb functions
as cells move through G1. Cell. 98:859–869. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Adon AM, Zeng X, Harrison MK, Sannem S,
Kiyokawa H, Kaldis P and Saavedra H: Cdk2 and Cdk4 regulate the
centrosome cycle and are critical mediators of centrosome
amplification in p53-null cells. Mol Cell Biol. 30:694–710. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu L, Ma J, Han J, Wang B, Chen X, Gao C,
Li D and Zheng Q: Licochalcone B arrests cell cycle progression and
induces apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 Cells. Recent Pat
Anticancer Drug Discov. 11:444–452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang J, Lv C, Hu M and Zhong G: The
mitochondria-mediate apoptosis of Lepidopteran cells induced by
azadirachtin. PLoS One. 8:e584992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Priyadarsini RV, Murugan RS, Sripriya P,
Karunagaran D and Nagini S: The neem limonoids azadirachtin and
nimbolide induce cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. Free Radic Res.
44:624–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|