|
1
|
Russell DW and Spremulli LL: Mechanism of
action of the wheat germ ribosome dissociation factor: Interaction
with the 60 S subunit. Arch Biochem Biophys. 201:518–526. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Finch AJ, Hilcenko C, Basse N, Drynan LF,
Goyenechea B, Menne TF, González Fernández A, Simpson P, D'Santos
CS, Arends MJ, et al: Uncoupling of GTP hydrolysis from eIF6
release on the ribosome causes Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Genes
Dev. 25:917–929. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gartmann M, Blau M, Armache JP, Mielke T,
Topf M and Beckmann R: Mechanism of eIF6-mediated inhibition of
ribosomal subunit joining. J Biol Chem. 285:14848–14851. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miluzio A, Beugnet A, Grosso S, Brina D,
Mancino M, Campaner S, Amati B, de Marco A and Biffo S: Impairment
of cytoplasmic eIF6 activity restricts lymphomagenesis and tumor
progression without affecting normal growth. Cancer Cell.
19:765–775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
García-Márquez A, Gijsbers A, de la Mora E
and Sánchez-Puig N: Defective guanine nucleotide exchange in the
Elongation Factor-Like 1 (EFL1) GTPase by mutations in the
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome protein. J Biol Chem. 290:17669–17678.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanvito F, Vivoli F, Gambini S,
Santambrogio G, Catena M, Viale E, Veglia F, Donadini A, Biffo S
and Marchisio PC: Expression of a highly conserved protein, p27BBP,
during the progression of human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
60:510–516. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Biffo S, Sanvito F, Costa S, Preve L,
Pignatelli R, Spinardi L and Marchisio PC: Isolation of a novel
beta4 integrin-binding protein (p27 (BBP)) highly expressed in
epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 272:30314–30321. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanvito F, Piatti S, Villa A, Bossi M,
Lucchini G, Marchisio PC and Biffo S: The beta4 integrin interactor
p27 (BBP/eIF6) is an essential nuclear matrix protein involved in
60S ribosomal subunit assembly. J Cell Biol. 144:823–837. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gandin V, Miluzio A, Barbieri AM, Beugnet
A, Kiyokawa H, Marchisio PC and Biffo S: Eukaryotic initiation
factor 6 is rate-limiting in translation, growth and
transformation. Nature. 455:684–688. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brina D, Grosso S, Miluzio A and Biffo S:
Translational control by 80S formation and 60S availability: The
central role of eIF6, a rate limiting factor in cell cycle
progression and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle. 10:3441–3446. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pinzaglia M, Montaldo C, Polinari D,
Simone M, La Teana A, Tripodi M, Mancone C, Londei P and Benelli D:
EIF6 over-expression increases the motility and invasiveness of
cancer cells by modulating the expression of a critical subset of
membrane-bound proteins. BMC Cancer. 15:1312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
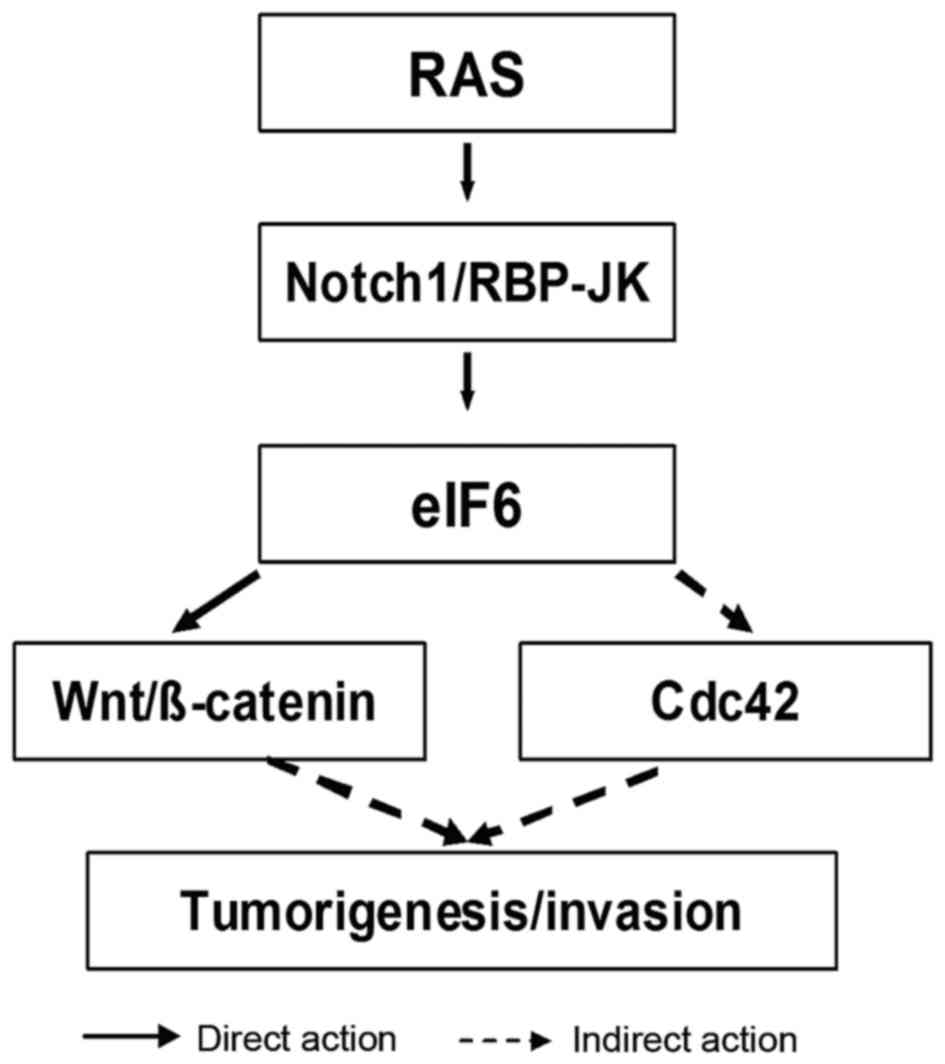
Benelli D, Cialfi S, Pinzaglia M, Talora C
and Londei P: The translation factor eIF6 is a Notch-dependent
regulator of cell migration and invasion. PLos One. 7:e320472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosso P, Cortesina G, Sanvito F, Donadini
A, Di Benedetto B, Biffo S and Marchisio PC: Overexpression of
p27BBP in head and neck carcinomas and their lymph node metastases.
Head Neck. 26:408–417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang CL, Yuan SZ, Yang HP, Wang QL and
Zhang R: Expression and significance of P311 and ITGB4BP in
non-small lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 32:526–528.
2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flavin RJ, Smyth PC, Finn SP, Laios A,
O'Toole SA, Barrett C, Ring M, Denning KM, Li J, Aherne ST, et al:
Altered eIF6 and Dicer expression is associated with
clinicopathological features in ovarian serous carcinoma patients.
Mod Pathol. 21:676–684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ceci M, Gaviraghi C, Gorrini C, Sala LA,
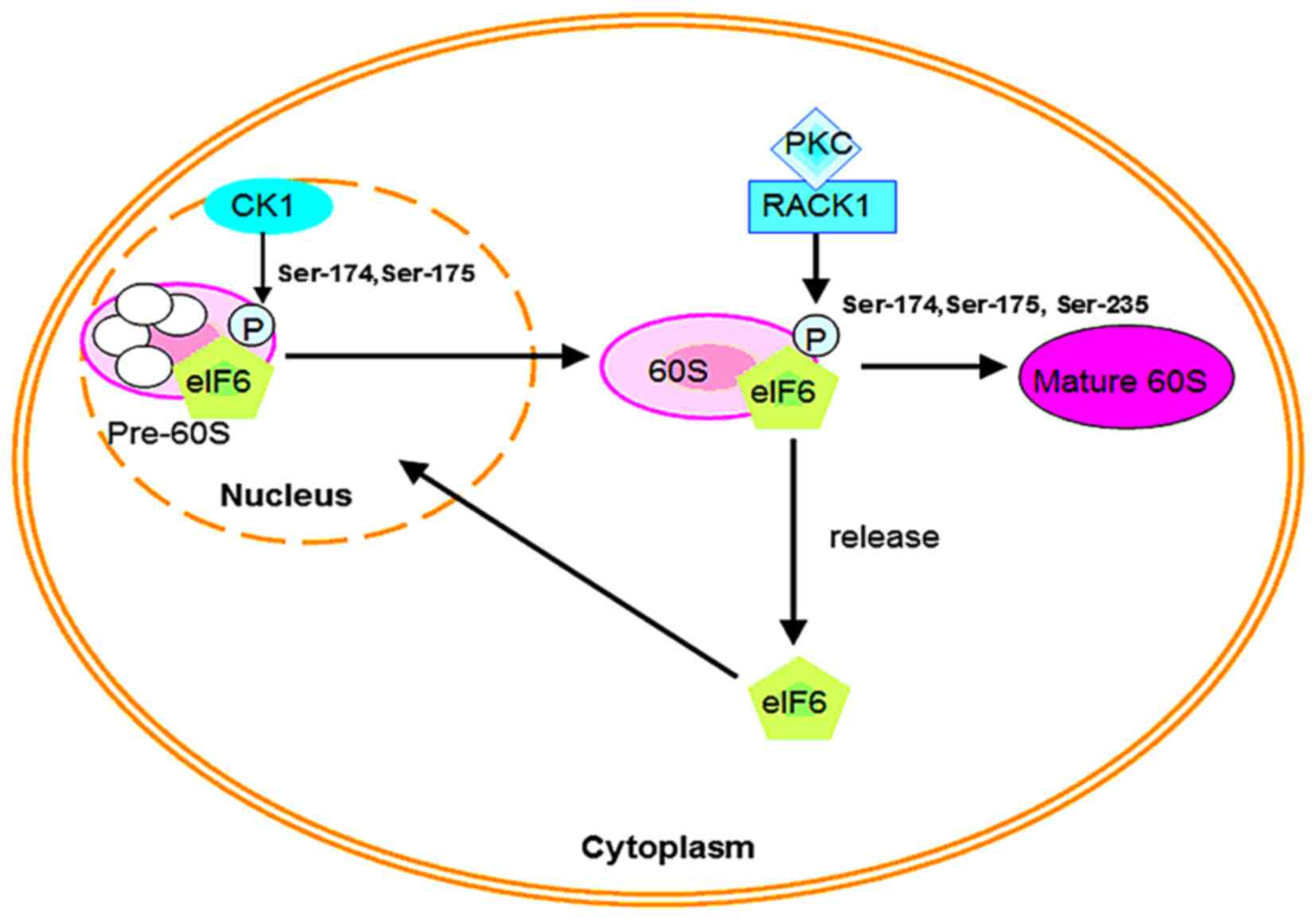
Offenhäuser N, Marchisio PC and Biffo S: Release of eIF6 (p27BBP)
from the 60S subunit allows 80S ribosome assembly. Nature.
426:579–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Biswas A, Mukherjee S, Das S, Shields D,
Chow CW and Maitra U: Opposing action of casein kinase 1 and
calcineurin in nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of mammalian
translation initiation factor eIF6. J Biol Chem. 286:3129–3138.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miluzio A, Beugnet A, Volta V and Biffo S:
Eukaryotic initiation factor 6 mediates a continuum between 60S
ribosome biogenesis and translation. EMBO Rep. 10:459–465. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cruciat CM: Casein kinase 1 and
Wnt/b-catenin signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 31:46–55. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schittek B and Sinnberg T: Biological
functions of casein kinase 1 isoforms and putative role in
tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer. 13:2312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Knippschild U, Kruger M, Richter J, Xu P,
García-Reyes B, Peifer C, Halekotte J, Bakulev V and Bischof J: The
CK1 family: Contribution to cellular stress response and its role
in carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 4:962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Marco N, Iannone L, Carotenuto R, Biffo
S, Vitale A and Campanella C: p27 (BBP)/eIF6 acts as an
anti-apoptotic factor upstream of Bcl-2 during Xenopus laevis
development. Cell Death Differ. 17:360–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Marco N, Tussellino M, Vitale A and
Campanella C: Eukaryotic initiation factor 6 (eif6) overexpression
affects eye development in Xenopus laevis. Differentiation.
82:108–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Silvera D, Formenti SC and Schneider RJ:
Translational control in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:254–266. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Atallah AM, Tabll AA, El-Nashar E,
El-Bakry KA, El-Sadany M, Ibrahim T and El-Dosoky I: AgNORs count
and DNA ploidy in liver biopsies from patients with schistosomal
liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Biochem.
42:1616–1620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gottwald L, Danilewic M, Fendler W, Suzin
J, Spych M, Piekarski J, Tylinski W, Chalubinska J,
Topczewska-Tylinska K and Cialkowska-Rysz A: The AgNORs count in
predicting long-term survival in serous ovarian cancer. Arch Med
Sci. 10:84–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lewinska A, Adamczyk J, Pajak J, Stoklosa
S, Kubis B, Pastuszek P, Slota E and Wnuk M: Curcumin-mediated
decrease in the expression of nucleolar organizer regions in
cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ
Mutagen. 771:43–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Winzer KJ, Bellach J and Hufnagl P:
Long-term analysis to objectify the tumour grading by means of
automated microscopic image analysis of the nucleolar organizer
regions (AgNORs) in the case of breast carcinoma. Diagn Pathol.
8:562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gupta V, Garg M, Chaudhry M, Singh S, Sen
R, Gill M and Sangwaiya A: Role of cyclin D1 immunoreactivity and
AgNOR staining in the evaluation of benign and malignant lesions of
the prostate. Prostate Int. 2:90–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raĭkhlin NT, Bukaeva IA, Smirnova EA,
Pavlovskaia AI, Brzhezovskiĭ VZh, Bogatyrev VN and Ponomareva MV:
Prognistic value of a study of the expression of argyrophilic
nucleolar organizer region associated proteins in case of papillary
thyroid cancer. Arkh Patol. 72:49–52. 2010.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mondal NK, Roychoudhury S and Ray MR:
Higher AgNOR expression in metaplastic and dysplastic airway
epithelial cells predicts the risk of developing lung cancer in
women chronically exposed to biomass smoke. J Environ Pathol
Toxicol Oncol. 34:35–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alaeddini M, Khalili M, Tirgary F and
Etemad-Moghadam S: Argyrophylic proteins of nucleolar organizer
regions (AgNORs) in salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma and its
relation to histological grade. Oral Surg Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 105:758–762. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Duvvuri U and Myers JN: Cancer of the head
and neck is the sixth most common cancer worldwide. Curr Probl
Surg. 46:114–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ferreira MB, De Souza JA and Cohen EE:
Role of molecular markers in the management of head and neck
cancers. Curr Opin Oncol. 23:259–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Peters S, Adjei AA, Gridelli C, Reck M,
Kerr K and Felip E; ESMO Guidelines Working Group, : Metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice
Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
23:vii56–vii64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cetin K, Ettinger DS, Hei YJ and O'Malley
CD: Survival by histologic subtype in stage IV nonsmall cell lung
cancer based on data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End
Results Program. Clin Epidemiol. 3:139–48. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang J, Zhang J, Cui X, Yang Y, Li M, Qu
J, Li J and Wang J: FoxM1: A novel tumor biomarker of lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:3136–3140. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Diaz LK, Zhou X, Welch K, Sahin A and
Gilcrease MZ: Chromogenic in situ hybridization for alpha6beta4
integrin in breast cancer: Correlation with protein expression. J
Mol Diagn. 6:10–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karlsen MA, Høgdall EV, Christensen IJ,
Borgfeldt C, Kalapotharakos G, Zdrazilova-Dubska L, Chovanec J, Lok
CA, Stiekema A, Mutz-Dehbalaie I, et al: A novel diagnostic index
combining HE4, CA125 and age may improve triage of women with
suspected ovarian cancer-An international multicenter study in
women with an ovarian mass. Gynecol Oncol. 138:640–646. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tanner MM, Grenman S, Koul A, Johannsson
O, Meltzer P, Pejovic T, Borg A and Isola JJ: Frequent
amplification of chromosomal region 20q12-q13 in ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 6:1833–1839. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Katz B, Tropé CG, Reich R and Davidson B:
MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer. Hum Pathol. 46:1245–1256. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Berns EM and
Wiemer EA: MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer biology and therapy
resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1282–1290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chong GO, Jeon HS, Han HS, Son JW, Lee YH,
Hong DG, Lee YS and Cho YL: Differential microRNA expression
profiles in primary and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.
Anticancer Res. 35:2611–2617. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Donadini A, Giacopelli F, Ravazzolo R,
Gandin V, Marchisio PC and Biffo S: GABP complex regulates
transcription of eIF6 (p27BBP), an essential trans-acting factor in
ribosome biogenesis. FEBS Lett. 580:1983–1987. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ristevski S, O'Leary DA, Thornell AP, Owen
MJ, Kola I and Hertzog PJ: The ETS transcription factor GABPalpha
is essential for early embryogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 24:5844–5849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ristola M, Arpiainen S, Shimokawa T, Ra C,
Tienari J, Saleem MA, Holthöfer H and Lehtonen S: Regulation of
nephrin gene by the Ets transcription factor, GA-binding protein.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 28:846–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu S, Cui K, Jothi R, Zhao DM, Jing X,
Zhao K and Xue HH: GABP controls a critical transcription
regulatory module that is essential for maintenance and
differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood.
117:2166–2178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and intergration in development.
Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Radtke F, MacDonald HR and
Tacchini-Cottier F: Regulation of innate andadaptive immunity by
Notch. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:427–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin JT, Chen MK, Yeh KT, Chang CS, Chang
TH, Lin CY, Wu YC, Su BW, Lee KD and Chang PJ: Association of high
levels of Jagged-1 and Notch-1 expression with poor prognosis in
head and neck cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:2976–2983. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bell D, Hanna EY, Miele L, Roberts D,
Weber RS and El-Naggar AK: Expression and significance of notch
signaling pathway in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Ann Diagn
Pathol. 18:10–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zardawi SJ, Zardawi I, McNeil CM, Millar
EK, McLeod D, Morey AL, Crea P, Murphy NC, Pinese M, Lopez-Knowles
E, et al: High Notch1 protein expression is an early event in
breast cancer development and is associated with the HER-2
molecular subtype. Histopathology. 56:286–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Arya M, Thrasivoulou C, Henrique R, Millar
M, Hamblin R, Davda R, Aare K, Masters JR, Thomson C, Muneer A, et
al: Targets of Wnt/ß-catenin transcription in penile carcinoma.
PLos One. 10:e01243952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/b-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Polakis P: Drugging Wnt signaling in
cancer. EMBO J. 31:2737–2746. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY,
Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi
T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin
degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 149:1245–1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Niehrs C and Acebron SP: Mitotic and
mitogenic Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 31:2705–2713. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Higgs MR, Lerat H and Pawlotsky JM:
Hepatitis C virus-induced activation of β-catenin promotes c-Myc
expression and a cascade of pro-carcinogenetic events. Oncogene.
32:4683–4693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang H, Wang H, Makki MS, Wen J, Dai Y,
Shi Q, Liu Q, Zhou X and Wang J: Overexpression of β-catenin and
cyclinD1 predicts a poor prognosis in ovarian serous carcinomas.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:264–271. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ji Y, Shah S, Soanes K, Islam MN, Hoxter
B, Biffo S, Heslip T and Byers S: Eukaryoticinitiation factor 6
selectively regulates Wnt signaling and beta-catenin protein
synthesis. Oncogene. 27:755–762. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sahai E and Marshall CJ: Rho GTPases and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:133–142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pedersen E and Brakebusch C: Rho GTPase
function in development: How in vivo models change our view. Exp
Cell Res. 318:1779–1787. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Reymond N, Riou P and Ridley AJ: Rho
GTPases and cancer cell transendothelial migration. Methods Mol
Biol. 827:123–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Stengel K and Zheng Y: Cdc42 in oncogenic
transformation, invasion, and tumorigenesis. Cell Signal.
23:1415–1423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Bray K, Gillette M, Young J, Loughran E,
Hwang M, Sears JC and Vargo-Gogola T: Cdc42 overexpression induces
hyperbranching in the developing mammary gland by enhancing cell
migration. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Weijzen S, Rizzo P, Braid M, Vaishnav R,
Jonkheer SM, Zlobin A, Osborne BA, Gottipati S, Aster JC, Hahn WC,
et al: Activation of Notch-1 signaling maintains the neoplastic
phenotype in human Ras-transformed cells. Nat Med. 8:979–986. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH,
Yoshida K, Brueschke A, Petroulakis E, Robichaud N, Pollak M,
Gaboury LA, et al: eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and
is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:pp. 14134–14139. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cope CL, Gilley R, Balmanno K, Sale MJ,
Howarth KD, Hampson M, Smith PD, Guichard SM and Cook SJ:
Adaptation to mTOR kinase inhibitors by amplification of eIF4E to
maintain cap-dependent translation. J Cell Sci. 127:788–800. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Grosso S, Pesce E, Brina D, Beugnet A,
Loreni F and Biffo S: Sensitivity of global translation to mTOR
inhibition in REN cells depends on the equilibrium between eIF4E
and 4E-BP1. PLoS One. 6:e291362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|