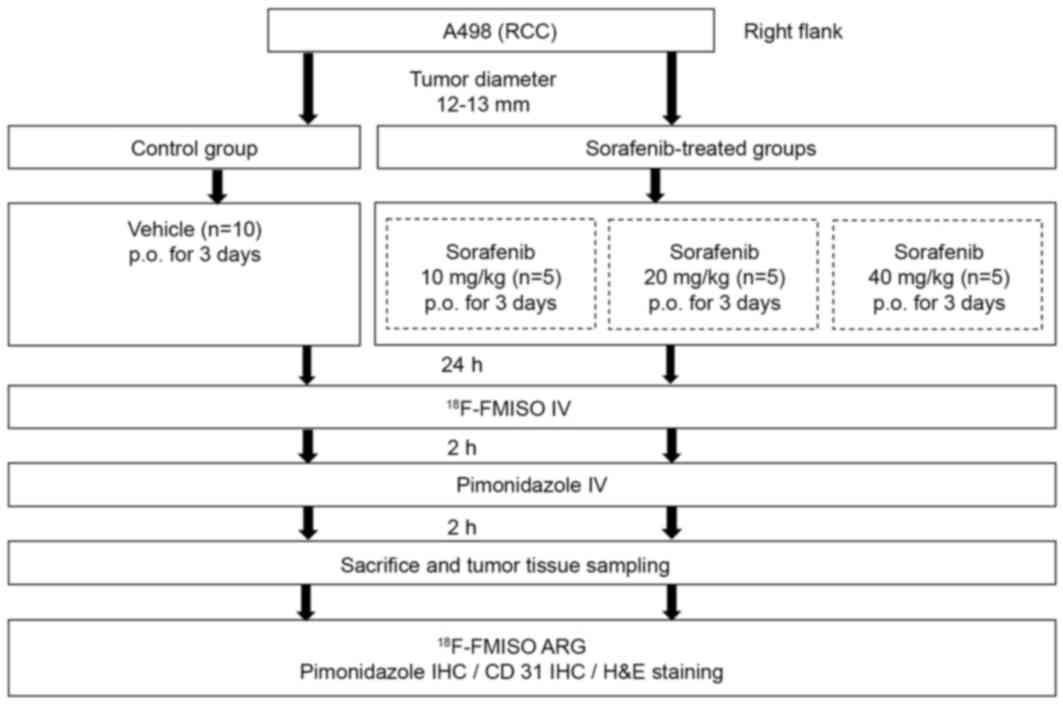
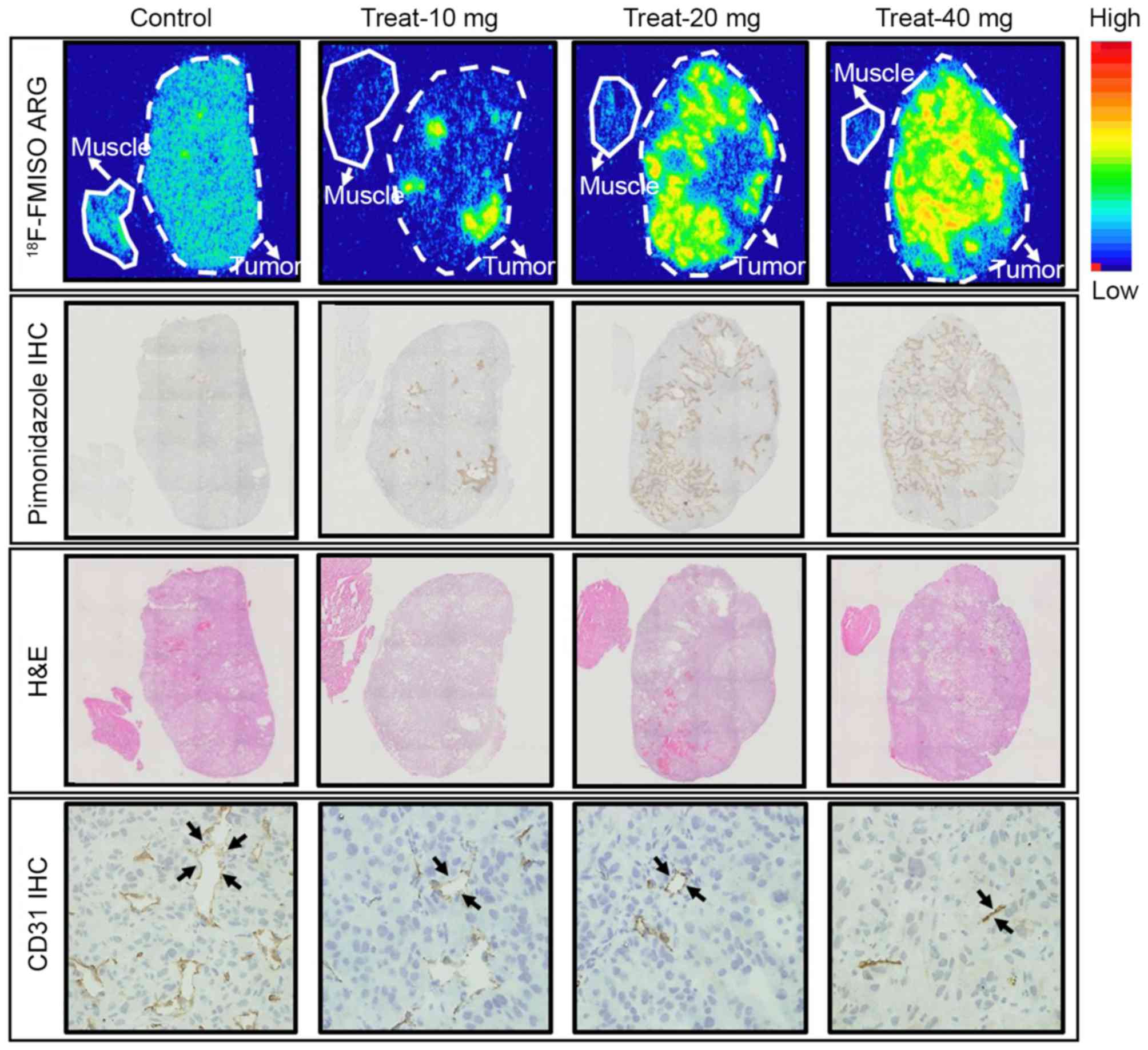
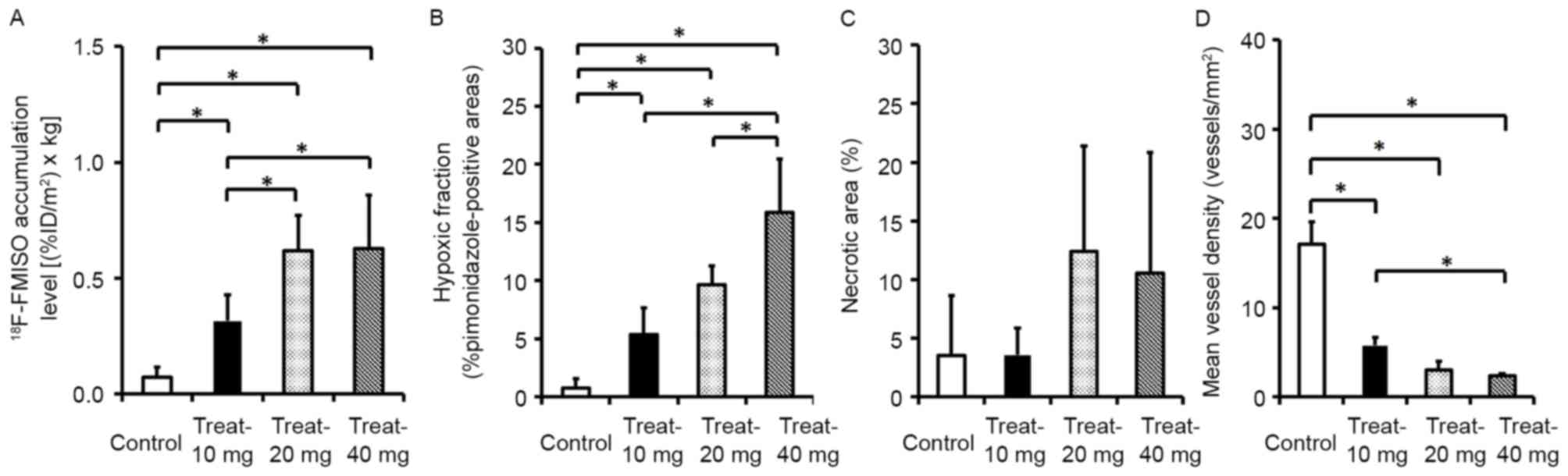
|
1
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma J and Waxman DJ: Combination of
antiangiogenesis with chemotherapy for more effective cancer
treatment. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3670–3684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takimoto CH and Awada A: Safety and
anti-tumor activity of sorafenib (Nexavar) in combination with
other anti-cancer agents: A review of clinical trials. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 61:535–548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y,
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Normalization of the vasculature for
treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev. 91:1071–1121.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Offermanns S and Rosenthal W: Encyclopedia
of Molecular Pharmacology. 2nd. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2008,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Oehler C, O'Donoghue JA, Russell J,
Zanzonico P, Lorenzen S, Ling CC and Carlin S: 18F-fluomisonidazole
PET imaging as a biomarker for the response to
5,6-dimethylx-anthenone-4-acetic acid in colorectal xenograft
tumors. J Nucl Med. 52:437–444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lawrentschuk N, Poon AM, Foo SS, Putra LG,
Murone C, Davis ID, Bolton DM and Scott AM: Assessing regional
hypoxia in human renal tumors using 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron
emission tomography. BJU Int. 96:540–546. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eschmann SM, Paulsen F, Reimold M,
Dittmann H, Welz S, Reischl G, Machulla HJ and Bares R: Prognostic
impact of hypoxia imaging with 18F-misonidazole PET in non-small
lung cancer and head and neck cancer before radiotherapy. J Nucl
Med. 46:253–260. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murakami M, Zhao S, Zhao Y, Chowdhury NF,
Yu W, Nishijima K, Takiguchi M, Tamaki N and Kuge Y: Evaluation of
changes in the tumor microenvironment after sorafenib therapy by
sequential histology and 18F-fluoromisonidazole hypoxia imaging in
renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:1593–1600. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang G, Wang M, Tang X, Gan M and Luo L:
Fully automated one-pot synthesis of [18F] fluoromisonidazole. Nucl
Med Biol. 32:553–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oh SJ, Chi DY, Mosdzianowski C, Kim JY,
Gil HS, Kang SH, Ryu JS and Moon DH: Fully automated synthesis of
[18F] fluoromisonidazole using a conventional [18F] FDG module.
Nucl Med Biol. 32:899–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao S, Kuge Y, Mochizuki T, Takahashi T,
Nakada K, Sato M, Takei T and Tamaki N: Biologic correlates of
intratumoral heterogeneity in 18F-FDG distribution with regional
expression of glucose transporters and hexokinase-II in
experimental tumor. J Nucl Med. 46:675–682. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown RS, Leung JY, Fisher SJ, Frey KA,
Ethier SP and Wahl RL: Intratumoral distribution of tritiated
fluorodeoxyglucose in breast carcinoma. I. Are inflammatory cells
important? J Nucl Med. 36:1854–1861. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Toyama H, Ichise M, Liow JS, Modell KJ,
Vines DC, Esaki T, Cook M, Seidel J, Sokoloff L, Green MV and Innis
RB: Absolute quantification of regional cerebral glucose
utilization in mice by 18F-FDG small animal PET scanning and
2-14C-DG autoradiography. J Nucl Med. 45:1398–1405. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shinojima T, Oya M, Takayanagi A, Mizuno
R, Shimizu N and Murai M: Renal cancer cells lacking hypoxia
inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha expression maintain vascular
endothelial growth factor expression through HIF-2alpha.
Carcinogenesis. 28:529–536. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iliopoulos O, Kibel A, Gray S and Kaelin
WG Jr: Tumour suppression by the human von Hippel-Lindau gene
product. Nat Med. 1:822–826. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kaelin WG Jr: Molecular basis of the VHL
hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:673–682. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|