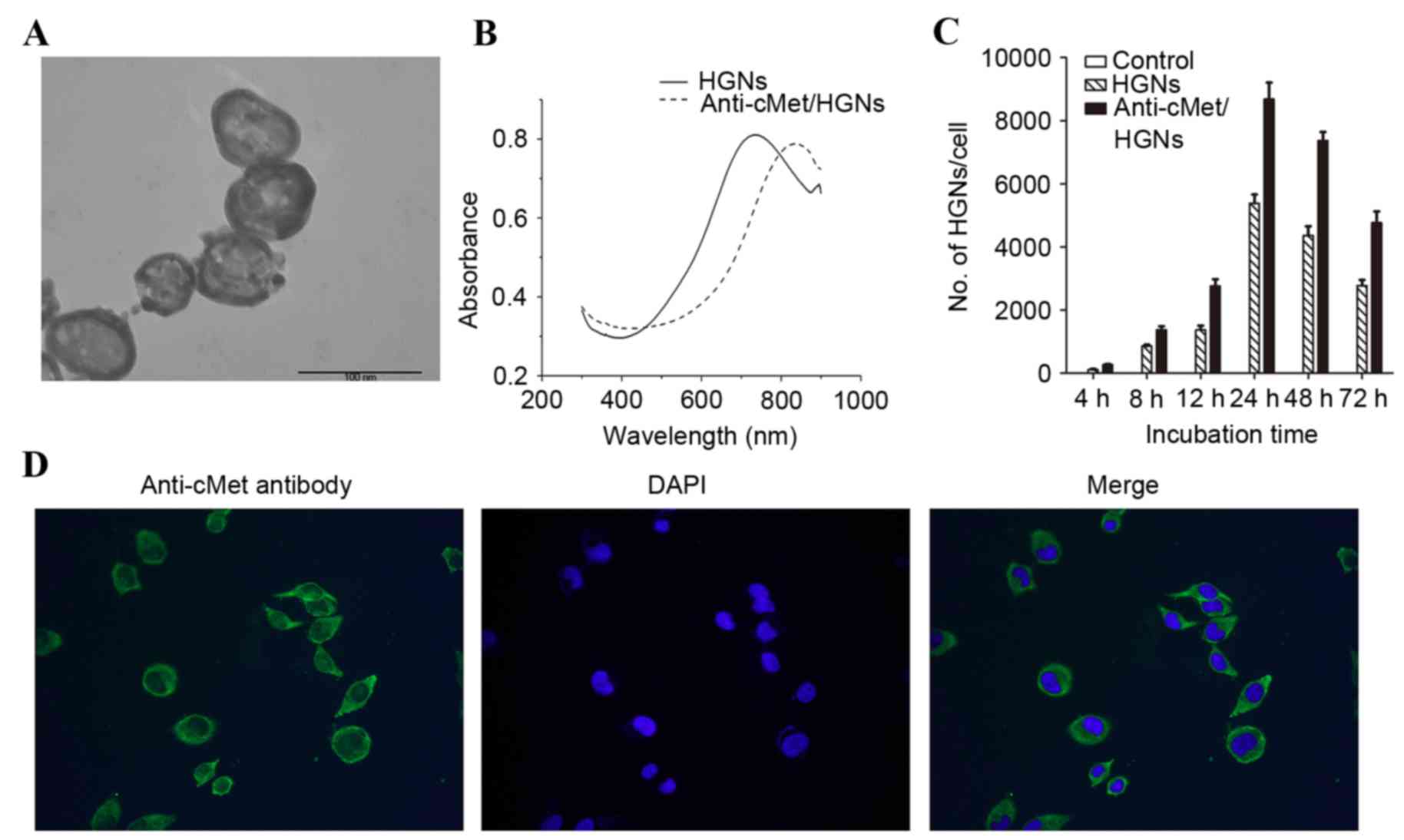
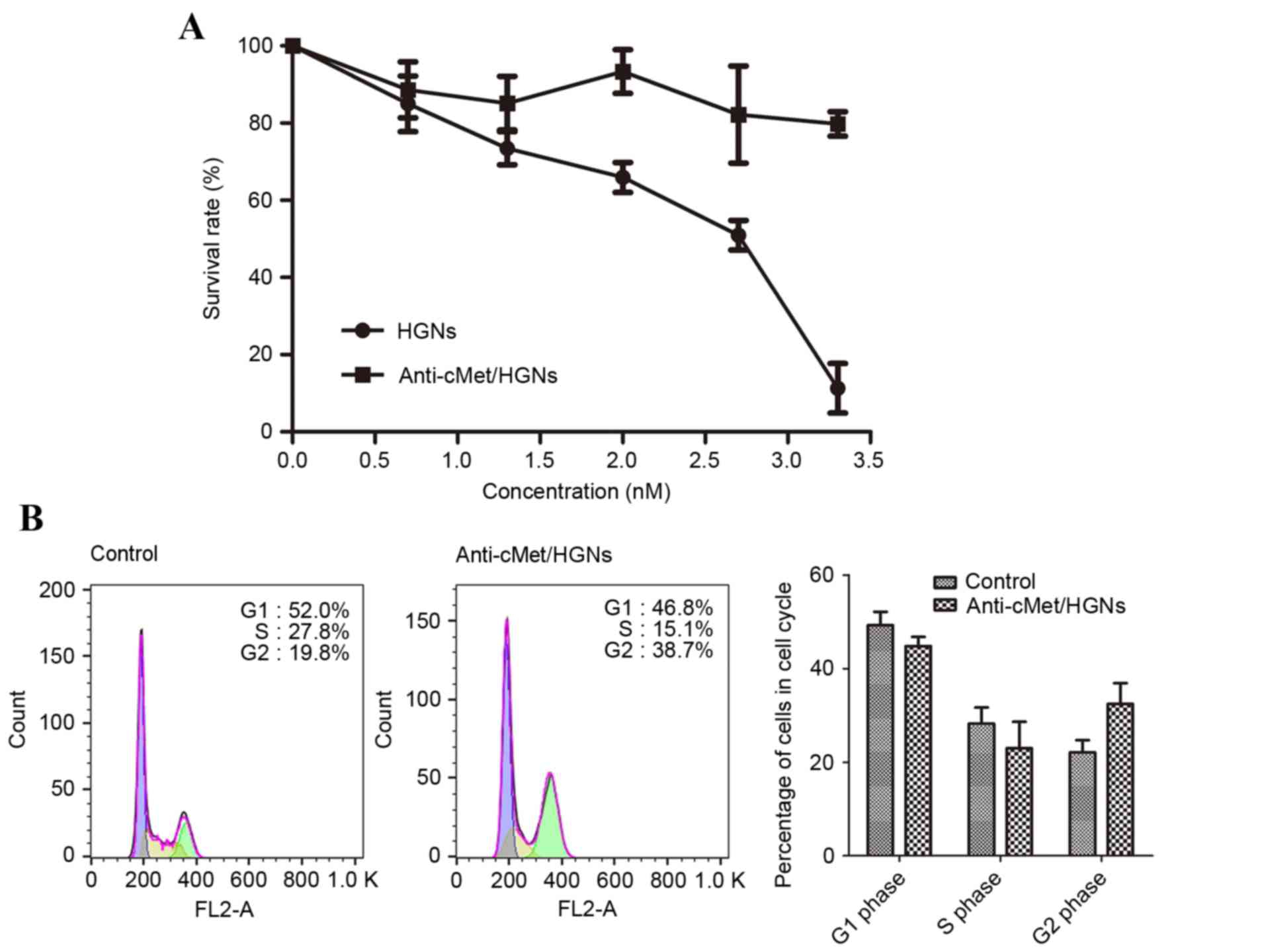
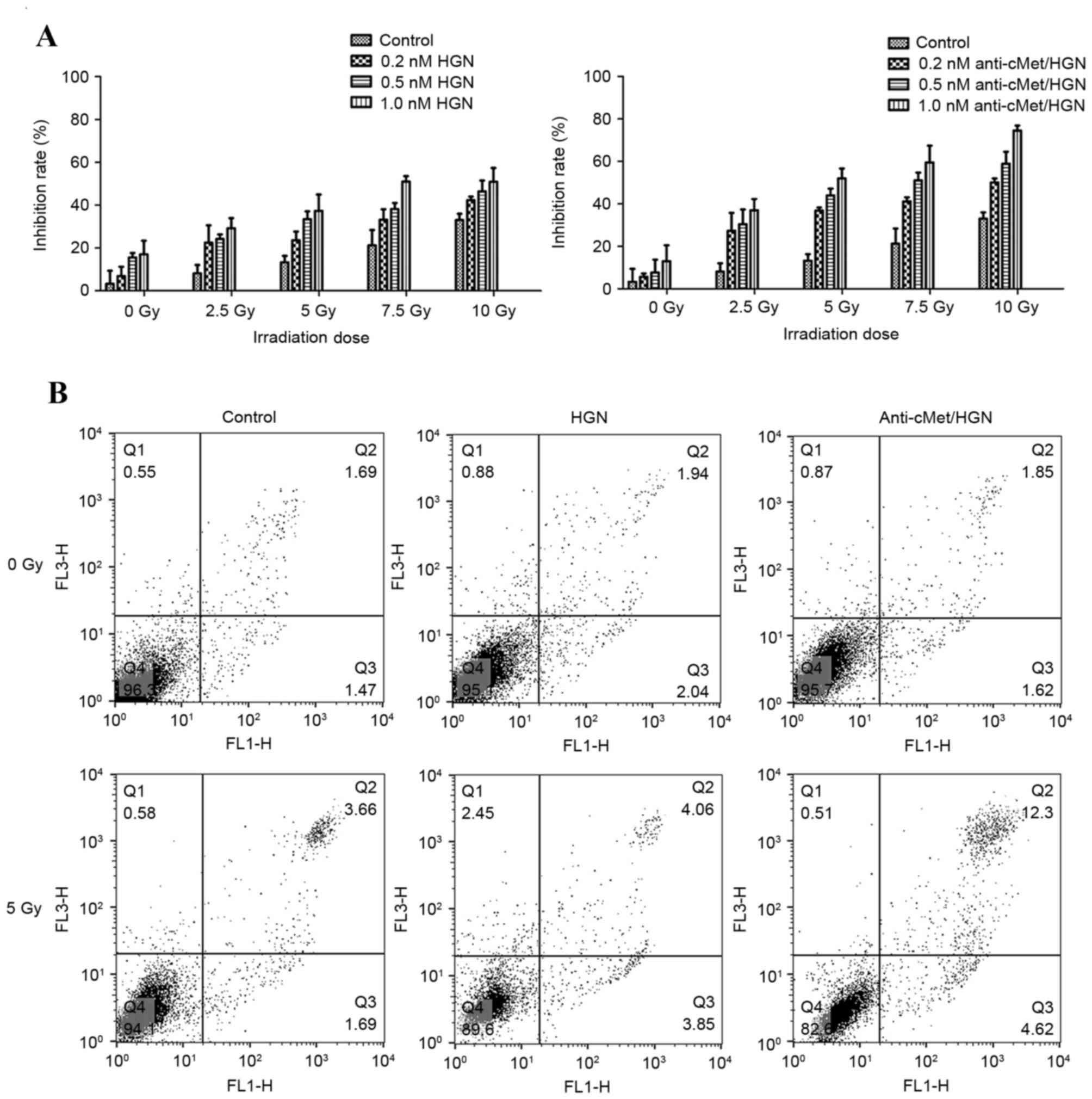
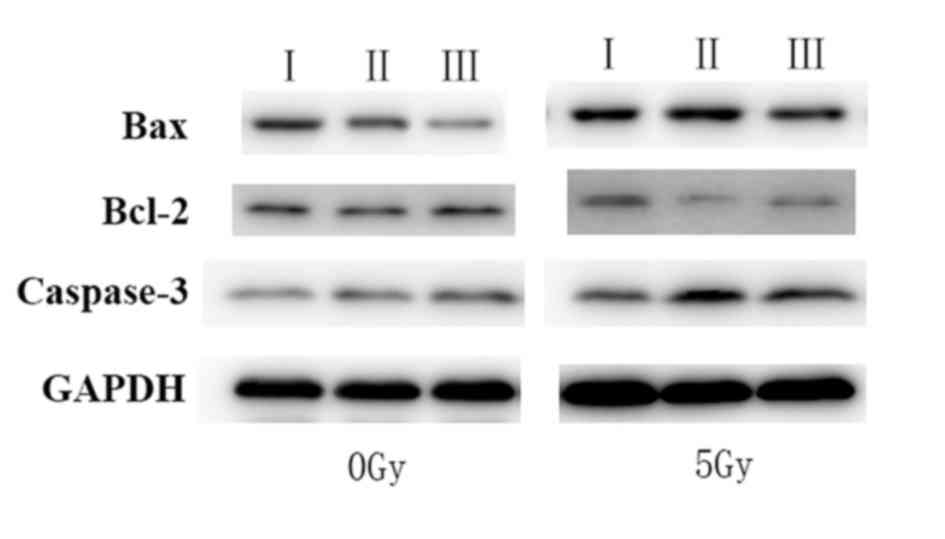
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Daniel MC and Astruc D: Gold
Nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry,
quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology,
catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev. 104:293–346. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahman WN, Bishara N, Ackerly T, He CF,
Jackson P, Wong C, Davidson R and Geso M: Enhancement of radiation
effects by gold nanoparticles for superficial radiation therapy.
Nanomedicine. 5:136–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kong T, Zeng J, Wang X, Yang X, Yang J,
McQuarrie S, McEwan A, Roa W, Chen J and Xing JZ: Enhancement of
radiation cytotoxicity in breast-cancer cells by localized
attachment of gold nanoparticles. Small. 4:1537–1543. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chithrani DB, Jelveh S, Jalali F, van
Prooijen M, Allen C, Bristow RG, Hill RP and Jaffray DA: Gold
nanoparticles as radiation sensitizers in cancer therapy. Radiat
Res. 173:719–728. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM,
Kmiecik TE, Woude GF Vande and Aaronson SA: Identification of the
hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene
product. Science. 251:802–804. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Woude GF Vande: Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baykal C and Ayhan A, Al A, Yüce K and
Ayhan A: Overexpression of the c-Met/HGF receptor and its
prognostic significance in uterine cervix carcinomas. Gynecol
Oncol. 88:123–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang L, Lofton C, Popp M and Tan W: Using
luminescent nanoparticles as staining probes for Affymetrix
GeneChips. Bioconjug Chem. 18:610–613. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Zhao W and Tan W: Bioconjugated
silica nanoparticles: Development and applications. Nano Res.
1:992008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tsai SW, Chen YY and Liaw JW: Compound
cellular imaging of laser scanning confocal microscopy by using
gold nanoparticles and dyes. Sensors (Basel). 8:2306–2316. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mizuno S and Nakamura T: HGF-MET cascade,
a key target for inhibiting cancer metastasis: The impact of NK4
discovery on cancer biology and therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci.
14:888–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turner J, Koumenis C, Kute TE, Planalp RP,
Brechbiel MW, Beardsley D, Cody B, Brown KD, Torti FM and Torti SV:
Tachpyridine, a metal chelator, induces G2 cell-cycle arrest,
activates checkpoint kinases, and sensitizes cells to ionizing
radiation. Blood. 106:3191–3199. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Petignat P and Roy M: Diagnosis and
management of cervical cancer. BMJ. 335:765–768. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dorsey JF, Sun L, Joh DY, Witztum A, Kao
GD, Alonso-Basanta M, Avery S, Hahn SM, Al Zaki A and Tsourkas A:
Gold nanoparticles in radiation research: Potential applications
for imaging and radiosensitization. Transl Cancer Res. 2:280–291.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geng F, Song K, Xing JZ, Yuan C, Yan S,
Yang Q, Chen J and Kong B: Thio-glucose bound gold nanoparticles
enhance radio-cytotoxic targeting of ovarian cancer.
Nanotechnology. 22:2851012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roa W, Zhang X, Guo L, Shaw A, Hu X, Xiong
Y, Gulavita S, Patel S, Sun X, Chen J, et al: Gold nanoparticle
sensitize radiotherapy of prostate cancer cells by regulation of
the cell cycle. Nanotechnology. 20:3751012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jain S, Hirst DG and O'Sullivan JM: Gold
nanoparticles as novel agents for cancer therapy. Br J Radiol.
85:101–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA and Chan WC:
Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle
uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 6:662–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Osaki F, Kanamori T, Sando S, Sera T and
Aoyama Y: A quantum dot conjugated sugar ball and its cellular
uptake. On the size effects of endocytosis in the subviral region.
J Am Chem Soc. 126:6520–6521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilson GD: Radiation and the cell cycle,
revisited. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 23:209–225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garnica-Garza HM: Contrast-enhanced
radiotherapy: Feasibility and characteristics of the physical
absorbed dose distribution for deep-seated tumors. Phys Med Biol.
54:5411–5425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krammer PH: CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated
apoptosis: Live and let die. Adv Immunol. 71:163–210. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Slot KA, Voorendt M, de Boer-Brouwer M,
van Vugt HH and Teerds KJ: Estrous cycle dependent changes in
expression and distribution of Fas, Fas ligand, Bcl-2, Bax, and
pro- and active caspase-3 in the rat ovary. J Endocrinol.
188:179–192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|