Introduction
Breast cancer is a malignant cancer with the highest
morbidity rate worldwide, and its onset age is decreasing (1). Each year, ~1.2 million females are
diagnosed with breast cancer all over the world, among which the
majority succumb at 40–45 years old (2). According to its degree of infiltration,
breast cancer may be divided in to pre-invasive and invasive
carcinoma (3). Clinically, breast
cancer originates from the breast ductal epithelium (4). The probability of being affected by
breast cancer for each woman may be as high as 10% (4). High incidence areas of breast cancer lie
in Europe and America, while the morbidity rate in Asia, Africa and
Latin America is relatively low (5).
Newly detected cases globally reach 1.2 million every year, and
over one-third of patients with breast cancer succumb to the
disease (6).
An increasing number of studies have become focused
on investigating the association between the abnormity of cancer
suppressor genes, particularly tumor protein p53 (TP53), which acts
independently, and the occurrence and progression of breast cancer
(7). A previous study revealed that
estrogen receptor (ER), apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53, Noxa
protein, ras gene and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 may
affect the progression of breast cancer through the p53 pathway
(8). Therefore, novel therapeutic
methods for breast cancer may be identified by studying the p53
pathway.
TP53 is the vital cancer suppressor gene in tumors.
Under the stimulus of DNA damage or other stress signals, TP53 is
activated and launches waterfall biological responses, resulting in
cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis to block the
occurrence and progress of tumors (9). The variation of TP53 may lead to the
loss of its tumor suppressor functions and cause
poorly-differentiated abnormal cells to survive and/or proliferate
(10). Tumors carrying variant P53
genes may exhibit increased invasiveness and be more resistant to
radiotherapy and chemotherapy, with a poorer prognosis (11).
Liriodenine has been extracted from plants and found
to be an alkaloid with extensive pharmacological activities
(12). Liriodenine is widely spread
at low levels among different natural plants of various genera and
families (13). Liriodenine
demonstrates wide pharmacological activities with regard to
antitumor, anti-bacteria, anti-fungus and anti-senile dementia
functions (12,14,15). The
planar construction of liriodenine provides significant
antineoplastic activity (16). The
aim of the present study was to investigate the anticancer effect
of liriodenine on the cell growth and apoptosis of human breast
cancer, in order to evaluate whether it may present a potential
antitumor drug for the treatment of the disease.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and cell culture
The MCF-7 human breast cancer cell was obtained from
the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
(Shanghai, China). MCF-7 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified
Eagle's medium containing 100 µg/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml
streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum (all from Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at 37°C in a humidified
CO2 atmosphere until use.
MTT assay
In total, 1–1.5×104 MCF-7 cells/well were
seeded onto 96-well plates and treated with liriodenine (0, 0.1, 1
and 10 µM) for 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. MCF-7 cells were cultured with
50 µl MTT (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) for 4 h. Dimethyl
sulfoxide (150 µl) was the added to the cells for 30 min to
dissolve the formazan. The absorbance was measured in each well
with a plate reader (Synergy-HY, BioTek Instruments GmbH,
Friedrichshall, Germany) at 550 nm.
Apoptosis assay and DAPI staining
In total, 1×106 MCF-7 cells/well were
seeded onto 6-well plates and treated with liriodenine (0, 0.1, 1
and 10 µM) for 48 h. The cells were stained with 10 µl Annexin V
for 30 min in the dark (KGI Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd.,
Nanjing, China) and stained with 10 µl propidium iodide (KGI
Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd.) for 5 min in the dark.
Apoptotic rate was analyzed using the Guava EasyCyte™ flow
cytometer (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
MCF-7 cells/well (1×106) were then seeded
onto 6-well plates and treated with liriodenine (0, 0.1, 1 and 10
µM) for 48 h. DAPI stain (50 µg/ml; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology, Haimen, China) was added to the cells for 20 min,
which were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline. Images were
captured using a DP70 fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×10;
Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and analyzed using Quantity One
software (version 3.0; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA,
USA).
Caspase-3 activity
In total, 1–1.5×104 MCF-7 cells/well were
seeded onto 96-well plates and treated with liriodenine (0, 0.1, 1
and 10 µM) for 48 h. Caspase-3 activity was measured using
Caspase-3 Activity assay kit (Beyotime, Jiangsu, China).
Ac-DEVD-pNA (Beyotime) was added to each well and incubated for 30
min at 37°C. The absorbance was measured in each well with a plate
reader (Synergy-HY; BioTek Instruments GmbH) at 405 nm.
Western blot analysis
In total, 1×106 MCF-7 cells/well were
seeded onto 6-well plates and treated with liriodenine (0, 0.1, 1
and 10 µM) for 48 h. According to the manufacturer's protocol, the
cells were lysed using radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer
(Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The protein concentrations
were determined using a bicinchoninic acid kit (Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology). Total protein (50 µg) was isolated with 10%
SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The
nitrocellulose membrane was blocked with 5% skimmed milk powder in
Tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 (TBST) for 1 h at room
temperature, and incubated with antibodies against B-cell
lymphoma-2 protein (dilution, 1:500; Bcl-2; sc-783), cyclin D1
(dilution, 1:500; sc-717), p53 (dilution, 1:500; sc-6243), vascular
endothelial growth factor (dilution, 1:500; VEGF; sc-13083) and
β-actin (dilution, 1:500; sc-7210; all Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane
was washed with TBST and incubated with secondary antibody mouse
anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (sc-2357, dilution, 1:3,000; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc.) at 37°C for 1 h, and then assessed by an
BeyoECL Plus (P0018; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The
optical density was analyzed using Quantity One software (version
3.0; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error by
SPSS software (version 20; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Comparisons were made using ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test
for multiple comparisons. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Liriodenine suppresses MCF-7 cell
viability
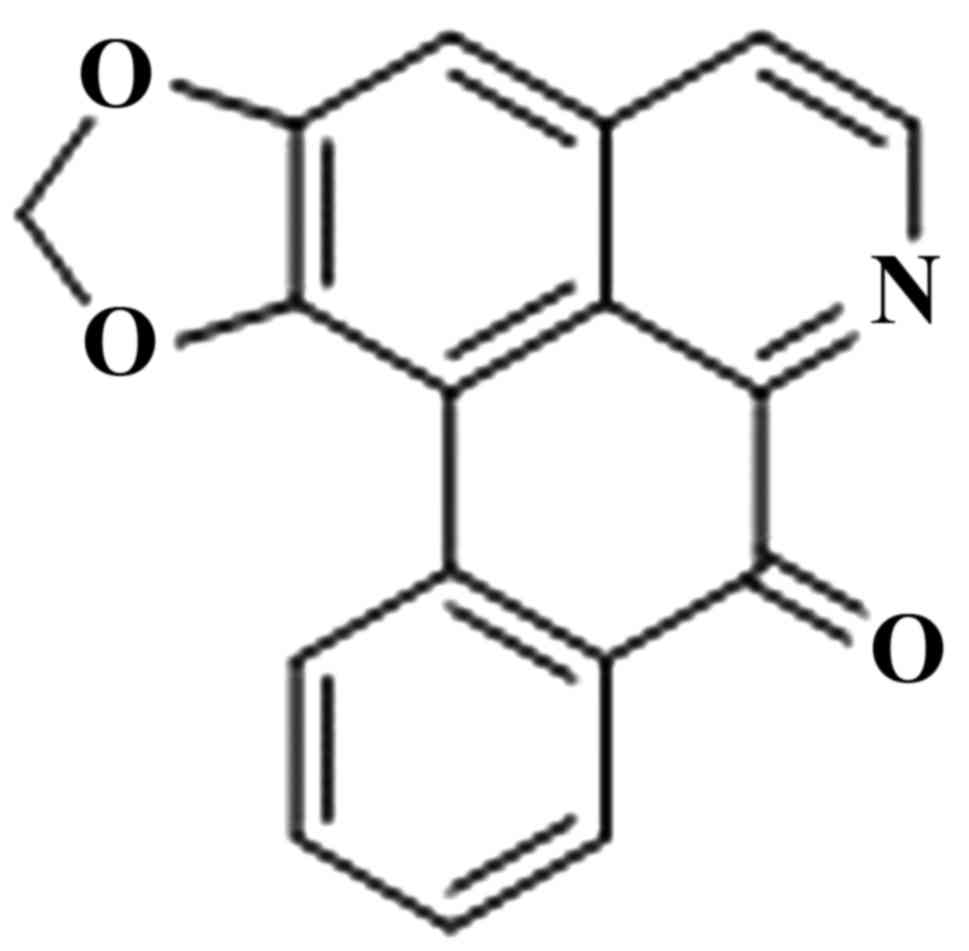
The chemical structure of liriodenine is presented
in Fig. 1. In order to investigate
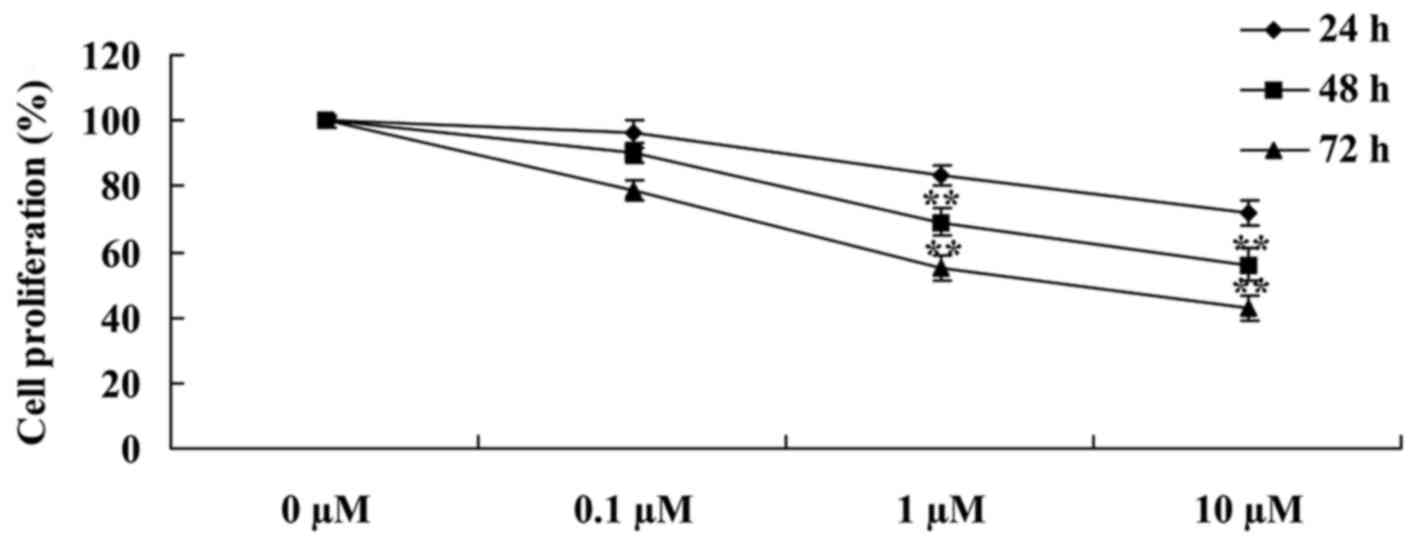
the effects of liriodenine on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells, an
MTT assay was performed to analyze the cellular viability.
Following a 24, 48 or 72 h treatment, liriodenine induced a
dose-dependent decrease in the cellular viability of the MCF-7
cells. Particularly, following a 48- or 72-h treatment, liriodenine
(1 or 10 µM) significantly decreased the cellular viability of the
MCF-7 cells (Fig. 2).
Liriodenine induces apoptosis of MCF-7
cells
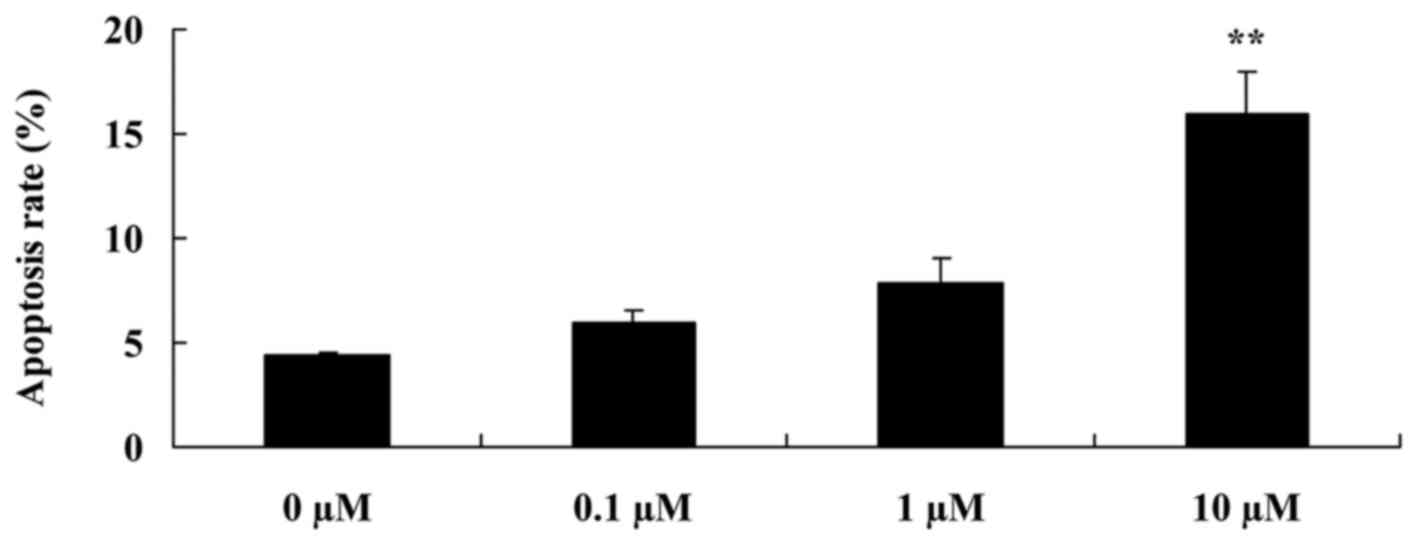
In order to detect whether liriodenine affects the
apoptotic rate of MCF-7 cells, flow cytometry was performed on the
cells. As shown in Fig. 3, following
a 48-h treatment, 10 µM liriodenine significantly increased the
apoptotic rate of the MCF-7 cells compared with the control group
(0 µM liriodenine).
Liriodenine induces apoptotic nucleoli
in MCF-7 cells
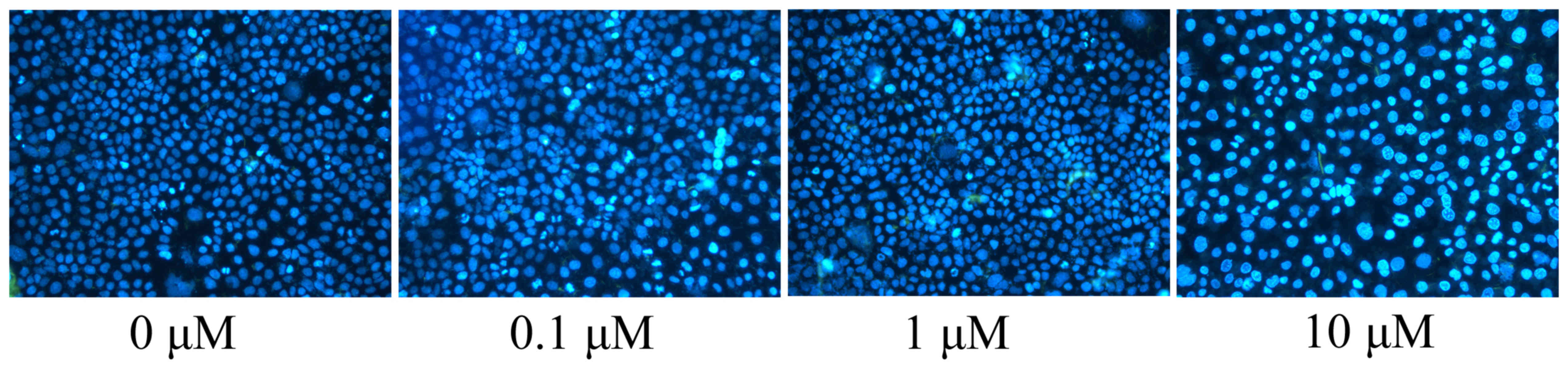
In the present study, apoptotic nucleoli of the
MCF-7 cells, as induced by liriodenine, were observed. DAPI was
used to stain the apoptotic nucleoli of the MCF-7 cells. A
concentration of 10 µM liriodenine significantly increased the
formation of the apoptotic nucleoli of the MCF-7 cells compared
with the control group (0 µM liriodenine) (Fig. 4).
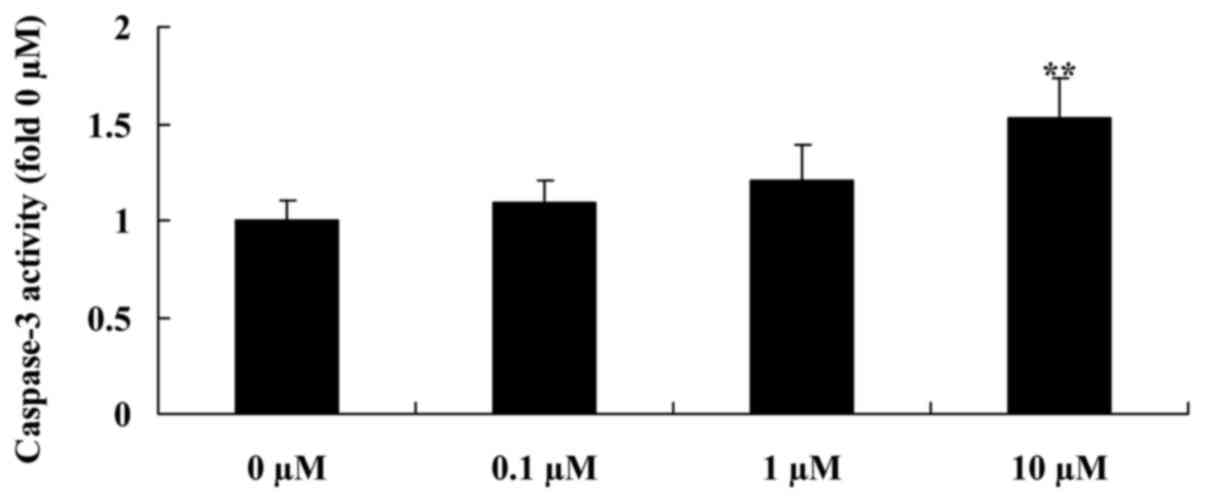
Liriodenine activates caspase-3
activity of MCF-7 cells
In order to detect whether liriodenine affects
thecaspase-3 activity of MCF-7 cells, a Caspase 3 Activity Assay
Kit was used to analyse the caspase-3 activity of MCF-7 cells
treated with liriodenine. A concentration of 10 µM liriodenine
significantly increased the caspase-3 activity of the MCF-7 cells
following a 48-h treatment compared with the control group (0 µM
liriodenine) (Fig. 5).
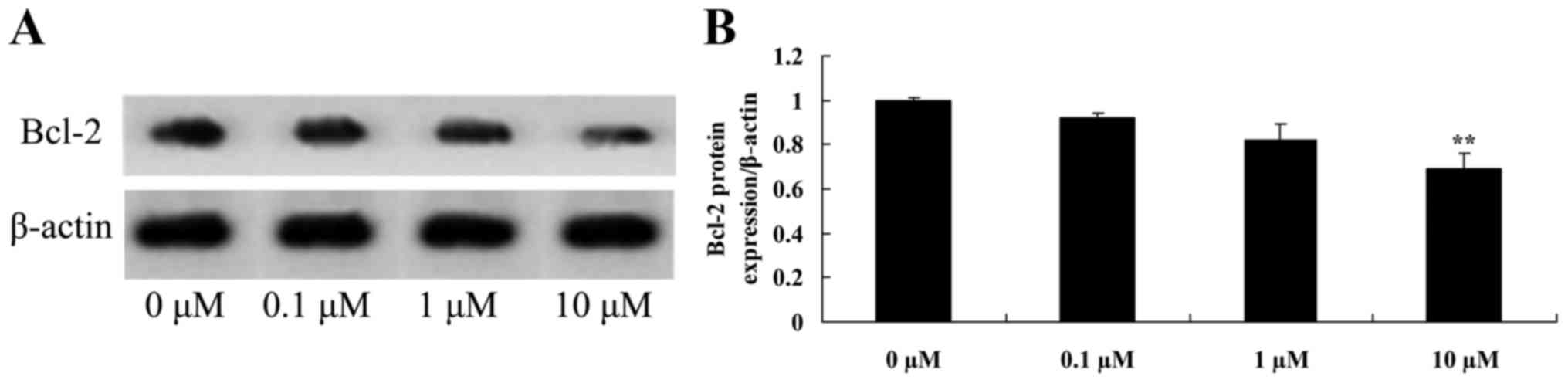
Liriodenine inhibits Bcl-2 protein
expression in MCF-7 cells
The present study investigated the mechanism of
liriodenine on MCF-7 cells. Bcl-2 protein is an important protein
for apoptosis. Bcl-2 protein expression was significantly
suppressed by 10 µM liriodenine in MCF-7 cells following a 48-h
treatment compared with the control group (0 µM liriodenine)
(Fig. 6).
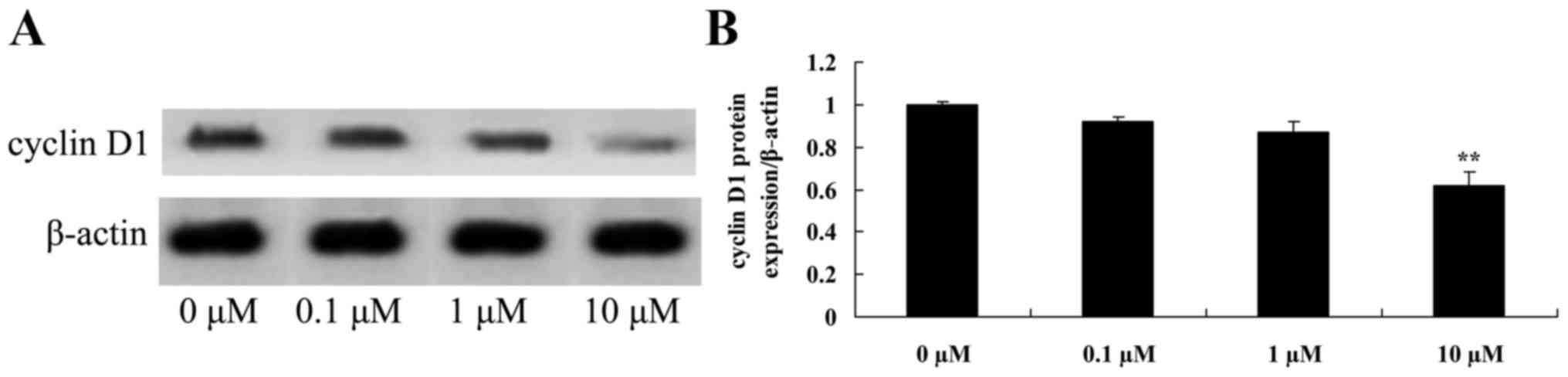
Liriodenine inhibits cyclin D1 protein
expression in MCF-7 cells
In order to investigate the possible effects of
liriodenine on apoptosis of MCF-7 cells, cyclin D1 protein
expression was measured using western blot analysis. As shown in
Fig. 7, cyclin D1 protein expression
in the MCF-7 cells was significantly inhibited by 10 µM liriodenine
following a 48-h treatment compared with the control group (0 µM
liriodenine).
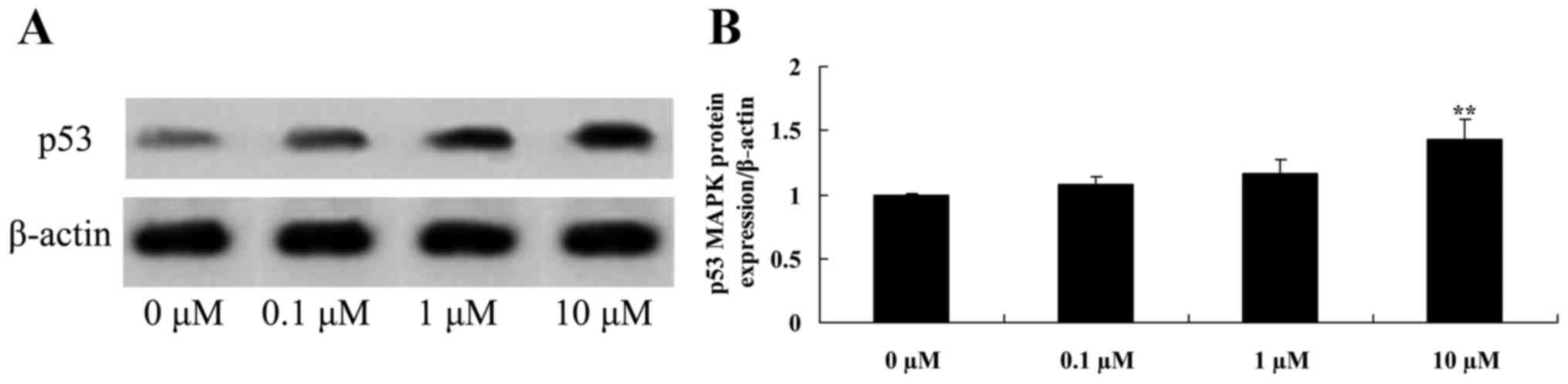
Liriodenine promotes p53 protein
expression in MCF-7 cells
To investigate the effect of liriodenine on p53
protein expression in MCF-7 cells, western blot analysis was
performed. As shown in Fig. 8, 10 µM
liriodenine significantly activated the p53 protein expression of
MCF-7 cells compared with the control group (0 µM liriodenine).
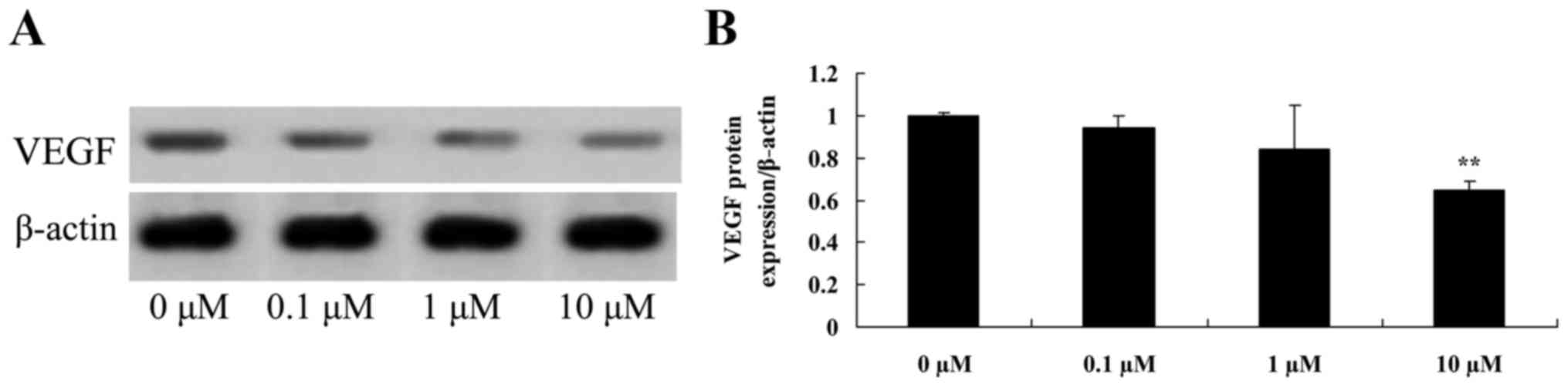
Liriodenine promotes VEGF protein
expression in MCF-7 cells
To investigate the effects of liriodenine on the
VEGF protein expression of MCF-7 cells, VEGF protein expression was
measured using western blot analysis. As shown in Fig. 9, VEGF protein expression in MCF-7
cells was significantly suppressed by 10 µM liriodenine compared
with the control group (0 µM liriodenine).
Discussion
Breast cancer is a common malignant cancer that
greatly threatens the health of women. During the occurrence and
progression of breast cancer, there are numerous factors affecting
the biological behavior of tumor cells (5). The development, metastasis and prognosis
of breast cancer are associated with the mutation and abnormal
expression of oncogenes (17). As
tumor suppressor genes are often mutated in cancer cells, p53 may
be divided into wild-type and mutant-type. Studies have
demonstrated that the genetic mutation of p53 is associated with
the resistance of breast cancer (8,18). The
present study demonstrated that liriodenine significantly decreased
cellular viability, induced the apoptotic rate, increased the
formation of apoptotic nucleoli and increased the caspase-3
activity of MCF-7 cells. Some study reported that liriodenine
exerts anticancer effects on human lung cancer cells (19) and human ovarian cancer cells (13).
As a biological marker of breast cancer, increased
expression of cyclin D1 predicts a poor prognosis (20). Clinical studies have revealed that in
tissues positive for cyclin D1, it has increased expression in
aging cells, indicating that cyclin D1 may promote the cell cycle
by increasing the speed of the G1 stage (21). Overexpression and amplification of
cyclin D1 has no association with tumor size, lymphatic metastasis
or amplification (22). With the
exception of cyclin D1, the development of breast cancer may be
associated with synergistic effects between other oncogenes and
cancer suppressor genes, including Rb, Bcl-2 and ER (23). In the present study, it was revealed
that liriodenine significantly suppressed Bcl-2 and cyclin D1
protein expression in MCF-7 cells. Nordin et al indicated
that liriodenine inhibits proliferation of human ovarian cancer
cells through suppression of Bcl-2 and cytochrome c
(13). Therefore, the effect of
liriodenine on MCF-7 cells may be associated with Bcl-2 and cyclin
D1 expression.
The classical cytological function of p53 is as a
transcription factor that has low expression under physiological
status of non-stimulus, and may respond to various physiological
stimulation pathology stimuli in order to be activated (24). Through regulating these processes,
injured cells may be repaired and the apoptosis of badly damaged
cells may be promoted. Thus, cell carcinogenesis triggered by the
accumulation of DNA injury may be avoided. p53 may perform a
braking function in vicious transformation, subsequently blocking
injured cells from entering into the cell cycle and promoting the
apoptosis of injured cells (25). It
has also been identified that liriodenine significantly activates
p53 protein expression in MCF-7 cells. Hsieh et al reported
that liriodenine inhibited cell proliferation and mediated the
activation of p53 expression in human hepatoma cells (12). The duration of the effect of
liriodenine on MCF-7 cells may also contribute to p53 protein
expression in in vitro experiments.
Studies on breast cancer have proposed that
follicle-stimulating hormone may facilitate the expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor-α and promotes the synthesis of VEGF
(26,27). VEGF can significantly facilitate the
proliferation, invasion, migration and lumen formation in cancer
cell (26). The present study
identified that 10 µM liriodenine significantly suppressed the VEGF
protein expression of MCF-7 cells. Li et al proposed that
liriodenine induces apoptosis through the down regulation of VEGF
expression in human laryngo carcinoma cells (16). Therefore, VEGF expression may perform
a crucial role in the liriodenine-induced apoptosis of MCF-7
cells.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that
liriodenine significantly decreased cellular viability, induced the
apoptotic rate, increased the formation of apoptotic nucleoli and
increased the caspase-3 activity of MCF-7 cells. The potential
mechanism underlying the antitumor effects of liriodenine may
result from inhibition of Bcl-2, cyclin D1 and VEGF expression, and
up regulation of p53 expression, which ultimately induces cellular
apoptosis. Therefore, the present study indicated that liriodenine
may be a potential novel drug for the treatment of breast
cancer.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81260389) and the
Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangxi Province (grant
no. 1228).
References
|
1
|
Metzger-Filho O, de Azambuja E, Bradbury
I, Saini KS, Bines J, Simon SD, Dooren VV, Aktan G, Pritchard KI,
Wolff AC, et al: Analysis of regional timelines to set up a global
phase III clinical trial in breast cancer: The adjuvant lapatinib
and/or trastuzumab treatment optimization experience. Oncologist.
18:134–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bower JE, Greendale G, Crosswell AD, Garet
D, Sternlieb B, Ganz PA, Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Arevalo J and Cole
SW: Yoga reduces inflammatory signaling in fatigued breast cancer
survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Psychoneuroendocrinology.
43:20–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buckley A, McQuaid S, Johnson P and Buggy
DJ: Effect of anaesthetic technique on the natural killer cell
anti-tumour activity of serum from women undergoing breast cancer
surgery: A pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 113 Suppl 1:i56–i62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ansari M, Porouhan P, Mohammadianpanah M,
Omidvari S, Mosalaei A, Ahmadloo N, Nasrollahi H and Hamedi SH:
Efficacy of ginger in control of chemotherapy induced nausea and
vomiting in breast cancer patients receiving doxorubicin-based
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3877–3880.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mrózek E, Layman R, Ramaswamy B, Lustberg
M, Vecchione A, Knopp MV and Shapiro CL: Phase II trial of
neoadjuvant weekly nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel,
carboplatin, and biweekly bevacizumab therapy in women with
clinical stage II or III HER2-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast
Cancer. 14:228–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pu Z, Zhang X, Chen Q, Yuan X and Xie H:
Establishment of an expression platform of OATP1B1 388GG and 521CC
genetic polymorphism and the therapeutic effect of tamoxifen in
MCF-7 cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2420–2428. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu D, Su C, Jiang M, Shen Y, Shi A, Zhao
F, Chen R, Shen Z, Bao J and Tang W: Fenofibrate inhibited
pancreatic cancer cells proliferation via activation of p53
mediated by upregulation of LncRNA MEG3. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 471:290–295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shokouh TZ, Ezatollah A and Barand P:
Interrelationships Between Ki67, HER2/neu, p53, ER, and PR status
and their associations with tumor grade and lymph node involvement
in breast carcinoma subtypes: Retrospective-observational
analytical study. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Antony ML, Kim SH and Singh SV: Critical
role of p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis in benzyl
isothiocyanate-induced apoptotic cell death. PLoS One.
7:e322672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wong FC, Woo CC, Hsu A and Tan BK: The
anti-cancer activities of Vernonia amygdalina extract in human
breast cancer cell lines are mediated through caspase-dependent and
p53-independent pathways. PLoS One. 8:e780212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ali A, Shah AS and Ahmad A:
Gain-of-function of mutant p53: Mutant p53 enhances cancer
progression by inhibiting KLF17 expression in invasive breast
carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 354:87–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh TJ, Liu TZ, Chern CL, Tsao DA, Lu
FJ, Syu YH, Hsieh PY, Hu HS, Chang TT and Chen CH: Liriodenine
inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines by blocking
cell cycle progression and nitric oxide-mediated activation of p53
expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:1117–1126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nordin N, Majid NA, Hashim NM, Rahman MA,
Hassan Z and Ali HM: Liriodenine, an aporphine alkaloid from
Enicosanthellum pulchrum, inhibits proliferation of human ovarian
cancer cells through induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial
signaling pathway and blocking cell cycle progression. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:1437–1448. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hufford CD, Sharma AS and Oguntimein BO:
Antibacterial and antifungal activity of liriodenine and related
oxoaporphine alkaloids. J Pharm Sci. 69:1180–1183. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De la Cruz-Chacón I, González-Esquinca AR,
Fefer P Guevara and Garcia LF Jimenez: Liriodenine, early
antimicrobial defence in Annona diversifolia. Z Naturforsch C.
66:377–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Xu Y and Wang B: Liriodenine induces
the apoptosis of human laryngocarcinoma cells via the upregulation
of p53 expression. Oncol Lett. 9:1121–1127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zuo S, Liu C, Wang J, Wang F, Xu W, Cui S,
Yuan L, Chen X, Fan W, Cui M and Song G: IGFBP-rP1 induces p21
expression through a p53-independent pathway, leading to cellular
senescence of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:1045–1055. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verma S and Rao BJ: p53 suppresses
BRCA2-stimulated ATPase and strand exchange functions of human
RAD51. J Biochem. 154:237–248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang HC, Chang FR, Wu YC and Lai YH:
Anti-cancer effect of liriodenine on human lung cancer cells.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 20:365–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saxena NK, Vertino PM, Anania FA and
Sharma D: Leptin-induced growth stimulation of breast cancer cells
involves recruitment of histone acetyltransferases and mediator
complex to CYCLIN D1 promoter via activation of Stat3. J Biol Chem.
282:13316–13325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feldt M, Bjarnadottir O, Kimbung S,
Jirström K, Bendahl PO, Veerla S, Grabau D, Hedenfalk I and
Borgquist S: Statin-induced anti-proliferative effects via cyclin
D1 and p27 in a window-of-opportunity breast cancer trial. J Transl
Med. 13:1332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mohammadizadeh F, Hani M, Ranaee M and
Bagheri M: Role of cyclin D1 in breast carcinoma. J Res Med Sci.
18:1021–1025. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gonzalez-Sarrias A, Ma H, Edmonds ME and
Seeram NP: Maple polyphenols, ginnalins A-C, induce S- and
G2/M-cell cycle arrest in colon and breast cancer cells mediated by
decreasing cyclins A and D1 levels. Food Chem. 136:636–642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coates AS, Millar EK, O'Toole SA, Molloy
TJ, Viale G, Goldhirsch A, Regan MM, Gelber RD, Sun Z,
Castiglione-Gertsch M, et al: Prognostic interaction between
expression of p53 and estrogen receptor in patients with
node-negative breast cancer: Results from IBCSG Trials VIII and IX.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1432012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, Qi LW, Calway T,
He TC, Du W and Yuan CS: Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 43:289–296. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S and Qian W: Need for clarification
of data in a recent meta-analysis on vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) and risk of breast cancer. Cytokine. 60:5962012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Groves MD, Hess KR, Puduvalli VK, Colman
H, Conrad CA, Gilbert MR, Weinberg J, Cristofanilli M, Yung WK and
Liu TJ: Biomarkers of disease: Cerebrospinal fluid vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stromal cell derived factor
(SDF)-1 levels in patients with neoplastic meningitis (NM) due to
breast cancer, lung cancer and melanoma. J Neurooncol. 94:229–234.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|