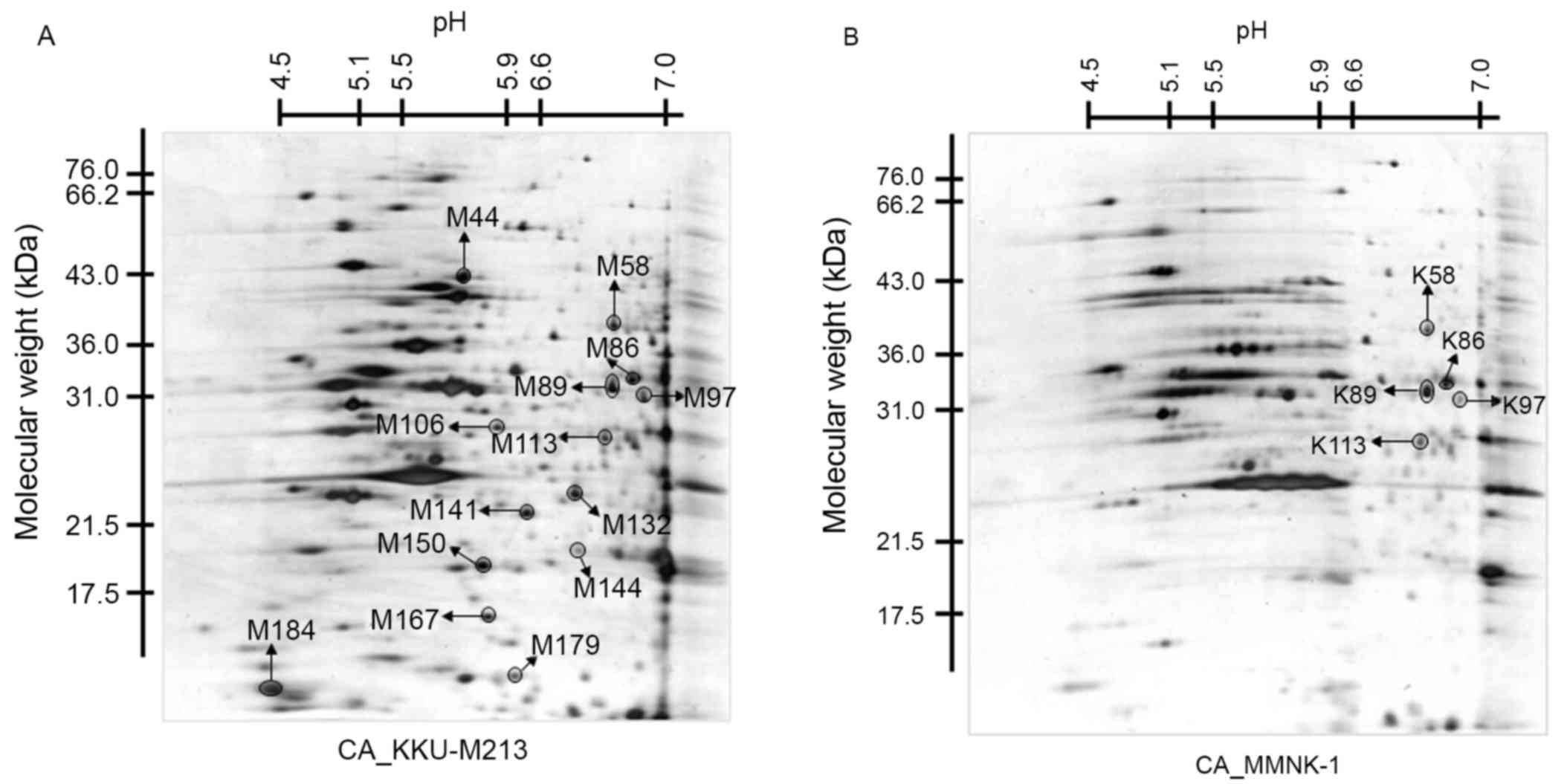
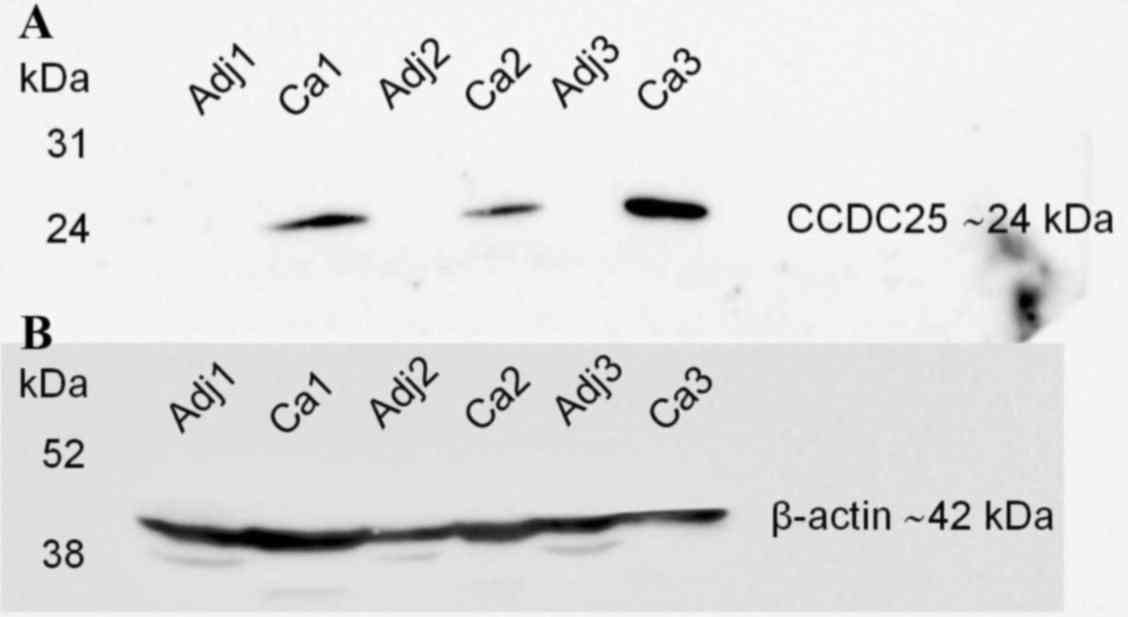
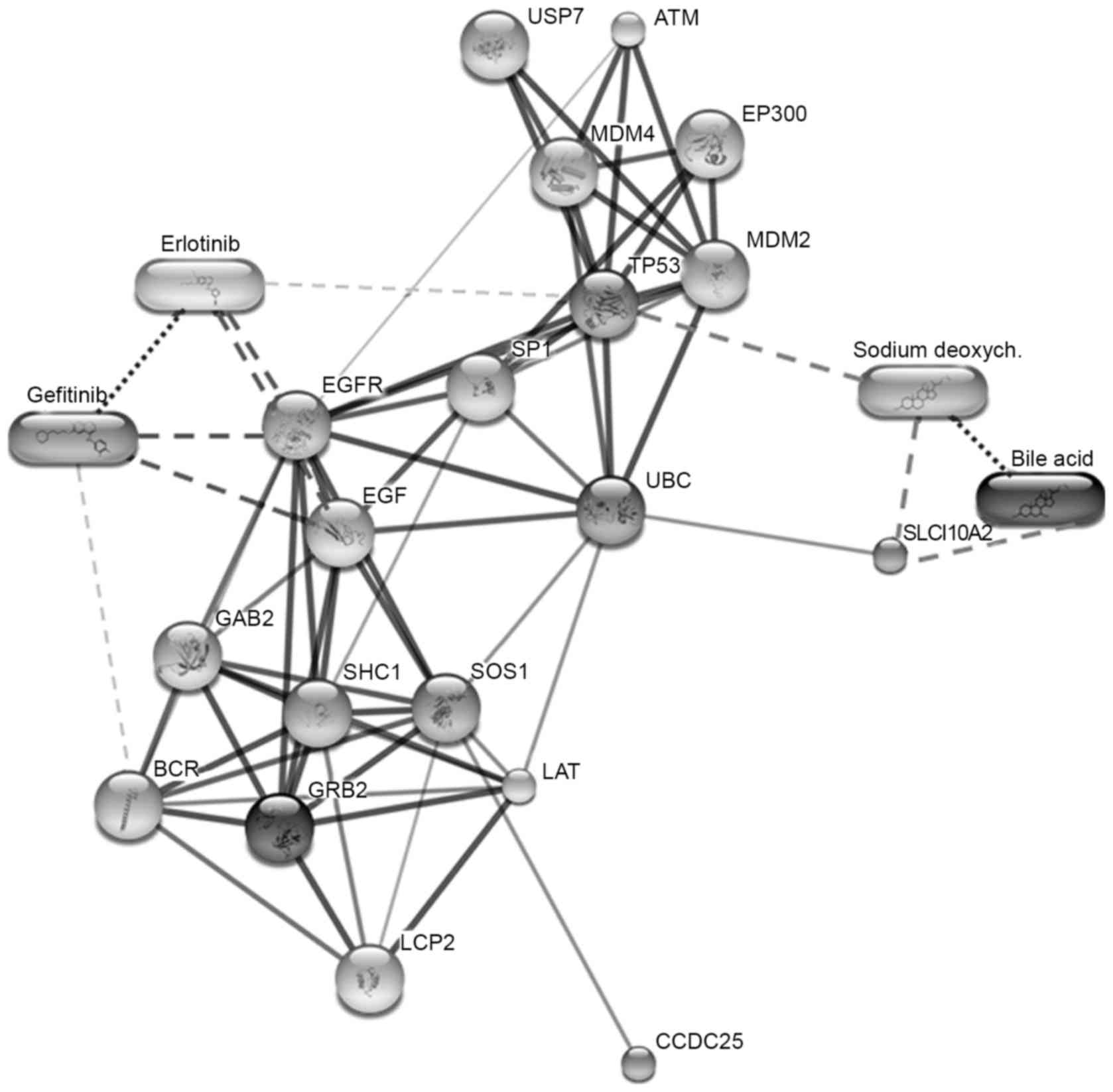
|
1
|
Malaguarnera G, Paladina I, Giordano M,
Malaguarnera M, Bertino G and Berretta M: Serum markers of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Dis Markers. 34:219–228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lazaridis KN and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 128:1655–1667. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sirica AE: Cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular
targeting strategies for chemoprevention and therapy. Hepatology.
41:5–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoon JH, Higuchi H, Werneburg NW, Kaufmann
SH and Gores GJ: Bile acids induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression via
the epidermal growth factor receptor in a human cholangiocarcinoma
cell line. Gastroenterology. 122:985–993. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoon JH, Werneburg NW, Higuchi H, Canbay
AE, Kaufmann SH, Akgul C, Edwards SW and Gores GJ: Bile acids
inhibit Mcl-1 protein turnover via an epidermal growth factor
receptor/Raf-1-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 62:6500–6505.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gupta RA and Dubois RN: Colorectal cancer
prevention and treatment by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Nat Rev
Cancer. 1:11–21. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gores GJ: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current
concepts and insights. Hepatology. 37:961–969. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoon JH, Canbay AE, Werneburg NW, Lee SP
and Gores GJ: Oxysterols induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
cholangiocytes: Implications for biliary tract carcinogenesis.
Hepatology. 39:732–738. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lamireau T, Zoltowska M, Levy E, Yousef I,
Rosenbaum J, Tuchweber B and Desmoulière A: Effects of bile acids
on biliary epithelial cells: Proliferation, cytotoxicity, and
cytokine secretion. Life Sci. 72:1401–1411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fukase K, Ohtsuka H, Onogawa T, Oshio H,
Ii T, Mutoh M, Katayose Y, Rikiyama T, Oikawa M, Motoi F, et al:
Bile acids repress E-cadherin through the induction of Snail and
increase cancer invasiveness in human hepatobiliary carcinoma.
Cancer Sci. 99:1785–1792. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sripa B, Leungwattanawanit S, Nitta T,
Wongkham C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Sripa C and Miwa M:
Establishment and characterization of an opisthorchiasis-associated
cholangiocarcinoma cell line (KKU-100). World J Gastroenterol.
11:3392–3397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maruyama M, Kobayashi N, Westerman KA,
Sakaguchi M, Allain JE, Totsugawa T, Okitsu T, Fukazawa T, Weber A,
Stolz DB, et al: Establishment of a highly differentiated
immortalized human cholangiocyte cell line with SV40T and hTERT.
Transplantation. 77:446–451. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Werneburg NW, Yoon JH, Higuchi H and Gores
GJ: Bile acids activate EGF receptor via a TGF-alpha-dependent
mechanism in human cholangiocyte cell lines. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 285:G31–G36. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perkins DN, Pappin DJ, Creasy DM and
Cottrell JS: Probability-based protein identification by searching
sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis.
20:3551–3567. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuhn M, Szklarczyk D, Pletscher-Frankild
S, Blicher TH, von Mering C, Jensen LJ and Bork P: STITCH 4:
Integration of protein-chemical interactions with user data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database Issue): D401–D407. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pai R, Tarnawski AS and Tran T:
Deoxycholic acid activates beta-catenin signaling pathway and
increases colon cell cancer growth and invasiveness. Mol Biol Cell.
15:2156–2163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Debruyne PR, Bruyneel EA, Karaguni IM, Li
X, Flatau G, Müller O, Zimber A, Gespach C and Mareel MM: Bile
acids stimulate invasion and haptotaxis in human colorectal cancer
cells through activation of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways.
Oncogene. 21:6740–6750. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Perez MJ and Briz O: Bile-acid-induced
cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1677–1689.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Powell AA, LaRue JM, Batta AK and Martinez
JD: Bile acid hydrophobicity is correlated with induction of
apoptosis and/or growth arrest in HCT116 cells. Biochem J.
356:481–486. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Milovic V, Teller IC, Murphy GM, Caspary
WF and Stein J: Deoxycholic acid stimulates migration in colon
cancer cells. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:945–949. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roessler S, Long EL, Budhu A, Chen Y, Zhao
X, Ji J, Walker R, Jia HL, Ye QH, Qin LX, et al: Integrative
genomic identification of genes on 8p associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma progression and patient survival.
Gastroenterology. 142957–966. (e12)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|