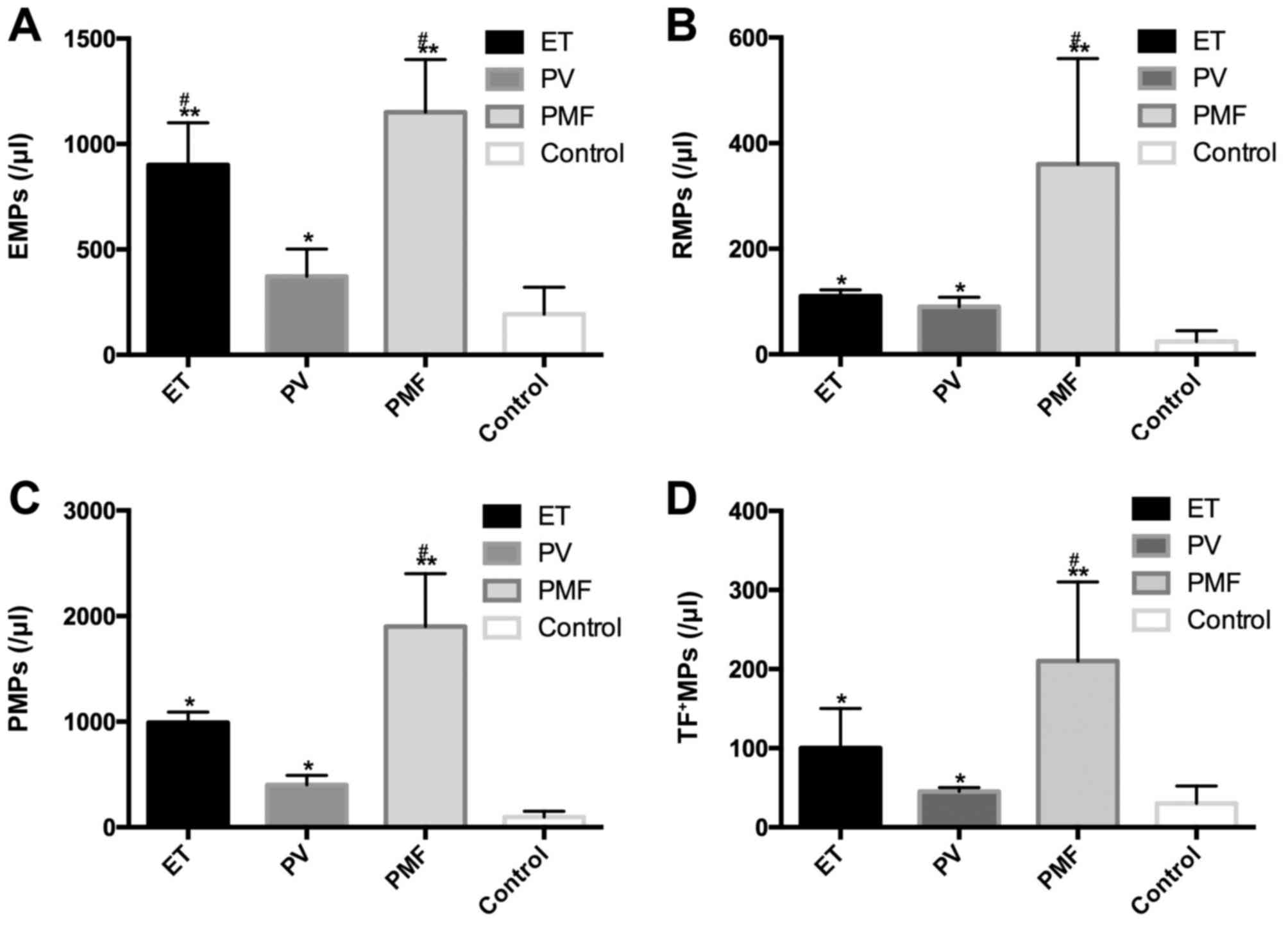
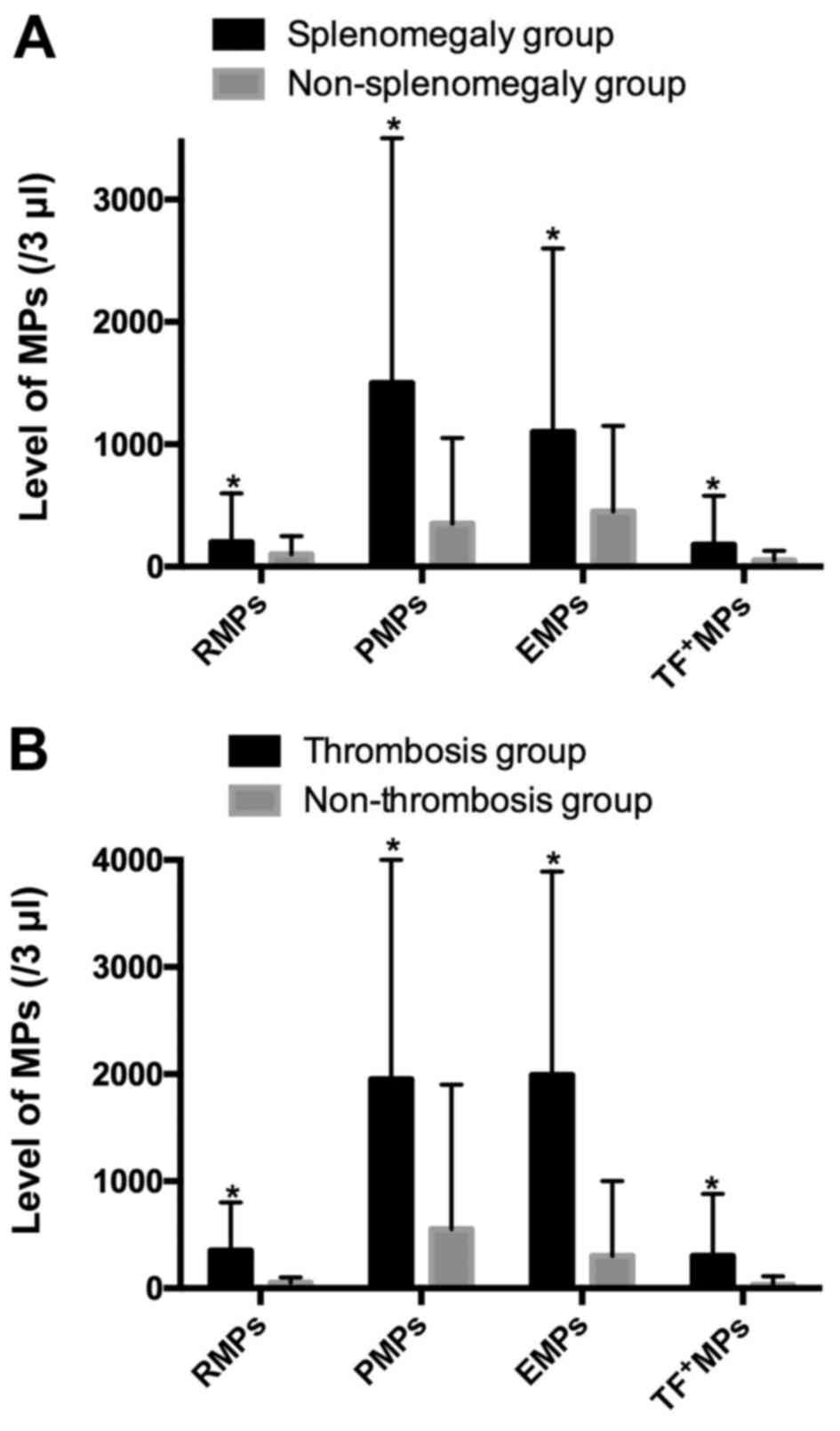
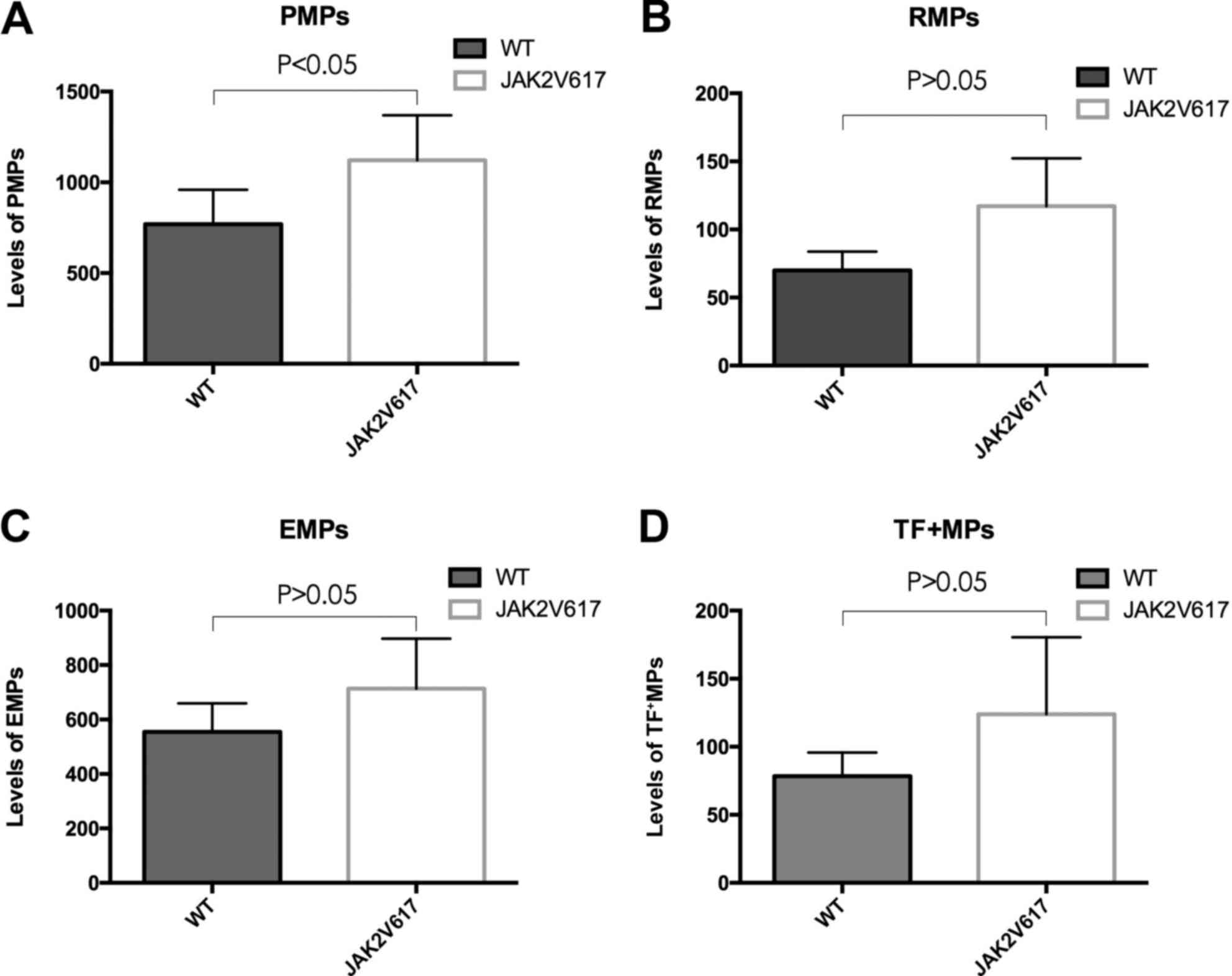
|
1
|
Tefferi A and Vardiman JW: Classification
and diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms: The 2008 World
Health Organization criteria and point-of-care diagnostic
algorithms. Leukemia. 22:14–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barrio S, Gallardo M, Arenas A, Ayala R,
Rapado I, Rueda D, Jimenez A, Albizua E, Burgaleta C, Gilsanz F and
Martinez-Lopez J: Inhibition of related JAK/STAT pathways with
molecular targeted drugs shows strong synergy with ruxolitinib in
chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm. Br J Haematol. 161:667–676.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL,
Wernig G, Huntly BJ, Boggon TJ, Wlodarska I, Clark JJ, Moore S, et
al: Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia
vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with
myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 7:387–397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C,
Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N,
et al: Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human
myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 365:1054–1061. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tefferi A: Polycythemi a vera and
essential thrombocythemia: 2012 update on diagnosis, risk
stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 87:285–293. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barbui T, Carobbio A, Cervantes F,
Vannucchi AM, Guglielmelli P, Antonioli E, Alvarez-Larrán A,
Rambaldi A, Finazzi G and Barosi G: Thrombosis in primary
myelofibrosis: Incidence and risk factors. Blood. 115:778–782.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheung B, Radia D, Pantelidis P,
Yadegarfar G and Harrison C: The presence of the JAK2 V617F
mutation is associated with a higher haemoglobin and increased risk
of thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia. Br J Haematol.
132:244–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Finazzi G, Rambaldi A, Guerini V, Carobbo
A and Barbui T: Risk of thrombosis in patients with essential
thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera according to JAK2 V617F
mutation status. Haematologica. 92:135–136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Willms A, Müller C, Julich H, Klein N,
Schwab R, Güsgen C, Richardsen I, Schaaf S, Krawczyk M, Krawczyk M,
et al: Tumour-associated circulating microparticles: A novel liquid
biopsy tool for screening and therapy monitoring of colorectal
carcinoma and other epithelial neoplasia. Oncotarget.
7:30867–30875. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tseng CC, Wang CC, Hsiao CC, Lu HI, Leu S,
Chang HC, Huang KT, Fang WF, Chen YM, Liu SF, et al: Time courses
and value of circulating microparticles in patients with operable
stage non-small cell lung cancer undergoing surgical intervention.
Tumour Biol. 37:11873–11882. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Campello E, Zanetto A, Spiezia L, Radu CM,
Gavasso S, Ferrarese A, Farinati F, Senzolo M and Simioni P:
Hypercoagulability detected by circulating microparticles in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis. Thromb Res.
143:118–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Owens AP III and Mackman N: Microparticles
in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res. 108:1284–1297. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zwicker JI, Liebman HA, Neuberg D, Lacroix
R, Bauer KA, Furie BC and Furie B: Tumor-derived tissue
factor-bearing microparticles are associated with venous
thromboembolic events in malignancy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6830–6840.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morel O, Luca F, Grunebaum L, Jesel L,
Meyer N, Desprez D, Robert S, Dignat-George F, Toti F, Simon C and
Goichot B: Short-term very low-calorie diet in obese females
improves the haemostatic balance through the reduction of leptin
levels, PAI-1 concentrations and a diminished release of platelet
and leukocyte-derived microparticles. Int J Obes (Lond).
35:1479–1486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C,
Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N,
et al: Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human
myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 365:1054–1061. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boulanger CM, Amabile N and Tedgui A:
Circulating microparticles: A potential prognostic marker for
atherosclerotic vascular disease. Hypertension. 48:180–186. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu JL, May L, Lhotak V, Shahrzad S,
Shirasawa S, Weitz JI, Coomber BL, Mackman N and Rak JW: Oncogenic
events regulate tissue factor expression in colorectal cancer
cells: Implications for tumor progression and angiogenesis. Blood.
105:1734–1741. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davila M, Amirkhosravi A, Coll E, Desai H,
Robles L, Colon J, Baker CH and Francis JL: Tissue factor-bearing
microparticles derived from tumor cells: Impact on coagulation
activation. J Thromb Haemost. 6:1517–1524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomas GM, Panicot-Dubois L, Lacroix R,
Dignat-George F, Lombardo D and Dubois C: Cancer cell-derived
microparticles bearing P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 accelerate
thrombus formation in vivo. J Exp Med. 206:1913–1927. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weiss HJ: Scott syndrome: A disorder of
platelet coagulant activity. Semin Hematol. 31:312–319.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hron G, Kollars M, Weber H, Sagaster V,
Quehenberger P, Eichinger S, Kyrle PA and Weltermann A: Tissue
factor-positive microparticles: Cellular origin and association
with coagulation activation in patients with colorectal cancer.
Thromb Haemost. 97:119–123. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rodriguez P Garcia, Eikenboom HC,
Tesselaar ME, Huisman MV, Nijkeuter M, Osanto S and Bertina RM:
Plasma levels of microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in
patients with clinically suspected pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res.
126:345–349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma G, Liu F, Lv L, Gao Y and Su Y:
Increased promyelocytic-derived microparticles: A novel potential
factor for coagulopathy in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann
Hematol. 92:645–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tesselaar ME, Romijn FP, van der Linden
IK, Prins FA, Bertina RM and Osanto S: Microparticle-associated
tissue factor activity: A link between cancer and thrombosis? J
Thromb Haemost. 5:520–527. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trappenburg MC, van Schilfgaarde M,
Marchetti M, Spronk HM, ten Cate H, Leyte A, Terpstra WE and
Falanga A: Elevated procoagulant microparticles expressing
endothelial and platelet markers in essential thrombocythemia.
Haematologica. 94:911–918. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duchemin J, Ugo V, Ianotto JC, Lecucq L,
Mercier B and Abgrall JF: Increased circulating procoagulant
activity and thrombin generation in patients with
myeloproliferative neoplasms. Thromb Res. 126:238–242. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Campello E, Spiezia L, Radu CM, Bulato C,
Castelli M, Gavasso S and Simioni P: Endothelial, platelet, and
tissue factor-bearing microparticles in cancer patients with and
without venous thromboembolism. Thromb Res. 127:473–477. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Randhawa J, Ostojic A, Vrhovac R, Atallah
E and Verstovsek S: Splenomegaly in myelofibrosis-new options for
therapy and the therapeutic potential of Janus kinase 2 inhibitors.
J Hematol Oncol. 5:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee HS, Park LC, Lee EM, Lee SJ, Shin SH,
Im H, Do KM, Kim EJ, Ye BJ, Song MK, et al: Incidence rates and
risk factors for vascular events in patients with essential
thrombocythemia: A multicenter study from Korea. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 12:70–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lussana F, Caberlon S, Pagani C,
Kamphuisen PW, Büller HR and Cattaneo M: Association of V617F Jak2
mutation with the risk of thrombosis among patients with essential
thrombocythaemia or idiopathic myelofibrosis: A systematic review.
Thromb Res. 124:409–417. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Poli G,
Bogani C, Pancrazzi A, Longo G, Ponziani V, Tozzi L, Pieri L and
Santini V: Influence of JAK2V617F allele burden on phenotype in
essential thrombocythemia. Haematologica. 93:41–48. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marchetti M, Tartari CJ, Russo L,
Panova-Noeva M, Leuzzi A, Rambaldi A, Finazzi G, Woodhams B and
Falanga A: Phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity is highly
expressed by circulating microparticles in patients with essential
thrombocythemia. Am J Hematol. 89:68–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|