|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pivot X: Adjuvant chemotherapy for local
relapse breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 15:125–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shen J, Stass SA and Jiang F: MicroRNAs as
potential biomarkers in human solid tumors. Cancer Lett.
329:125–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Asghari F, Haghnavaz N, Baradaran B,
Hemmatzadeh M and Kazemi T: Tumor suppressor microRNAs: Targeted
molecules and signaling pathways in breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 81:305–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng F, Xiong L, Tang H, Peng C and Chen
J: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
microRNAs: Clinical and biological significance of microRNAs in
breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:14463–14477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo L, Yuan J, Xie N, Wu H, Chen W, Song S
and Wang X: miRNA-411 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA
via the downregulation of specificity protein 1 in breast cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 14:2975–2982. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao L and Zheng XY: MicroRNA-490 inhibits
tumorigenesis and progression in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
9:4505–4516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao H, Kang X, Xia X, Wo L, Gu X, Hu Y,
Xie X, Chang H, Lou L and Shen X: miR-145 suppresses breast cancer
cell migration by targeting FSCN-1 and inhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Transl Res. 8:3106–3114.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tian J, Hu X, Gao W, Zhang J, Chen M,
Zhang X, Ma J and Yuan H: Identification a novel tumor-suppressive
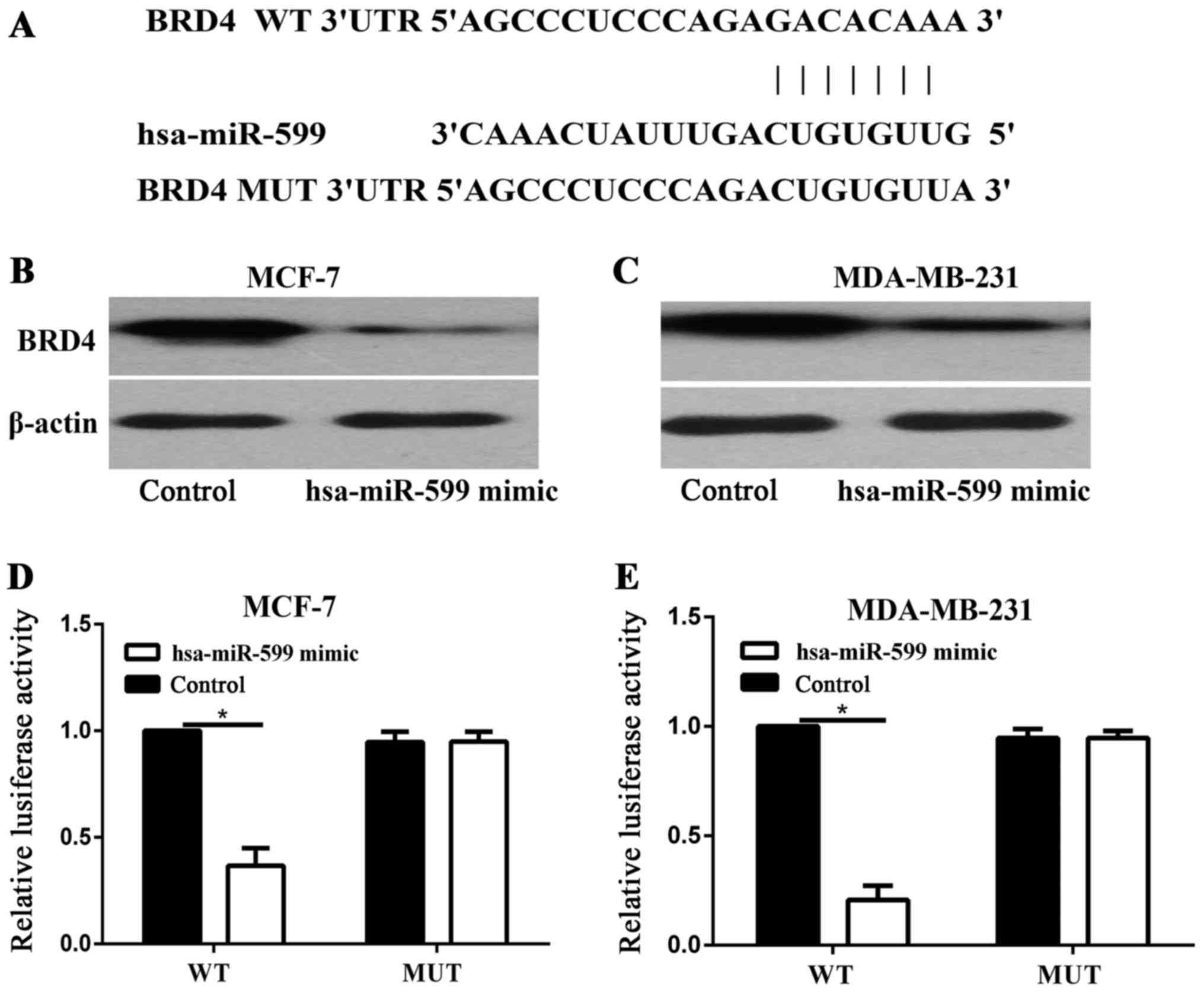
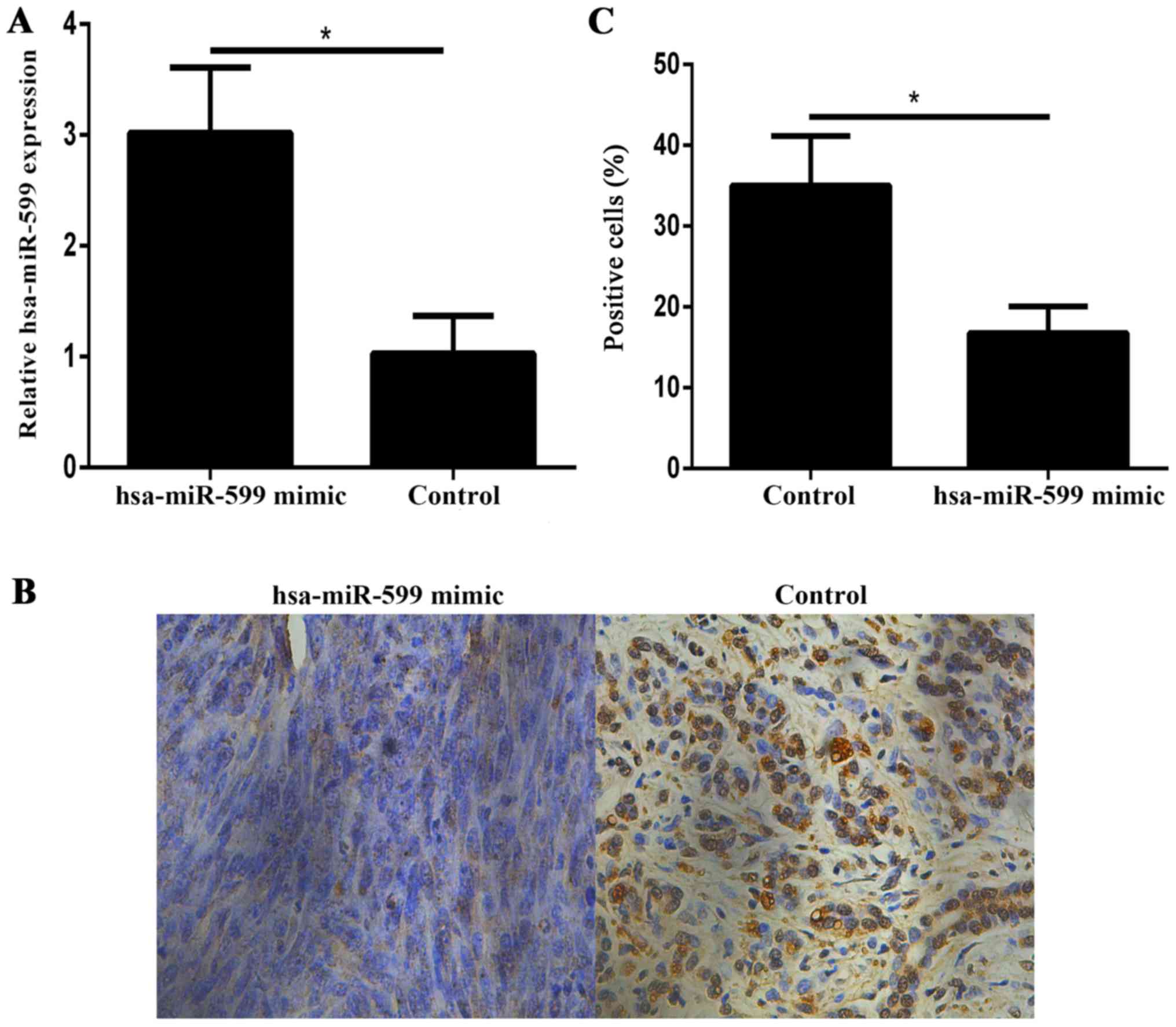
hsa-miR-599 regulates cells proliferation, migration and invasion
by targeting oncogenic MYC in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl
Res. 8:2575–2584. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Joyce DP, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM:
Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast
cancer. Int J Cancer. 139:1443–1448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Z, He N and Zhou Q: Brd4 recruits
P-TEFb to chromosomes at late mitosis to promote G1 gene expression
and cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:967–976. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang YH, Sui YN, Yan K, Wang LS, Wang F
and Zhou JH: BRD4 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell
proliferation and enhances gemcitabine resistance. Oncol Rep.
33:1699–1706. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Segura MF, Fontanals-Cirera B,
Gaziel-Sovran A, Guijarro MV, Hanniford D, Zhang G, González-Gomez
P, Morante M, Jubierre L, Zhang W, et al: BRD4 sustains melanoma
proliferation and represents a new target for epigenetic therapy.
Cancer Res. 73:6264–6276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Puissant A, Frumm SM, Alexe G, Bassil CF,
Qi J, Chanthery YH, Nekritz EA, Zeid R, Gustafson WC, Greninger P,
et al: Targeting MYCN in neuroblastoma by BET bromodomain
inhibition. Cancer Discov. 3:308–323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng Z, Gong Y, Ma Y, Lu K, Lu X, Pierce
LA, Thompson RC, Muller S, Knapp S and Wang J: Inhibition of BET
bromodomain targets genetically diverse glioblastoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:1748–1759. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang YH, Sui XM, Sui YN, Zhu QW, Yan K,
Wang LS, Wang F and Zhou JH: BRD4 induces cell migration and
invasion in HCC cells through MMP-2 and MMP-9 activation mediated
by the Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 10:2227–2232.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lockwood WW, Zejnullahu K, Bradner JE and
Varmus H: Sensitivity of human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines to
targeted inhibition of BET epigenetic signaling proteins. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:19408–19413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patel AJ, Liao CP, Chen Z, Liu C, Wang Y
and Le LQ: BET bromodomain inhibition triggers apoptosis of
NF1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors through Bim
induction. Cell Rep. 6:81–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Andrieu G, Tran AH, Strissel KJ and Denis
GV: BRD4 regulates breast cancer dissemination through
Jagged1/Notch1 signaling. Cancer Res. 76:6555–6567. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pritchard CC, Cheng HH and Tewari M:
MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat Rev Genet.
13:358–369. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie B, Zhang C, Kang K and Jiang S:
miR-599 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and
migration by targeting TGFB2. PLoS One. 10:e01415122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|