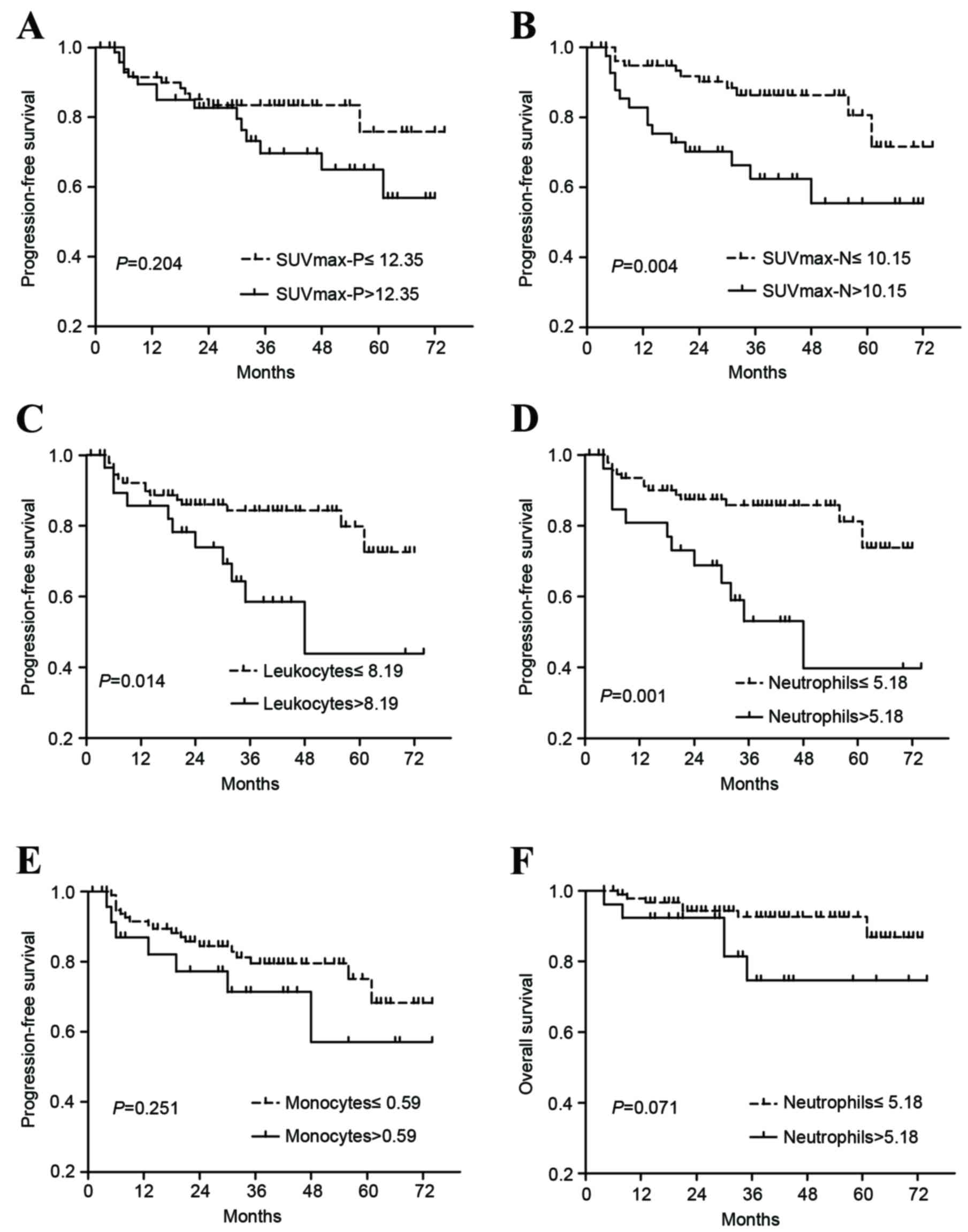
|
1
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao SM, Simons MJ and Qian CN: The
prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China.
Chin J Cancer. 30:114–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Simons MJ: The origin of genetic risk for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A commentary on: Is nasopharyngeal cancer
really a ‘Cantonese cancer’? Chin J Cancer. 29:527–537. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen L, Mao YP, Xie FY, Liu LZ, Sun Y,
Tian L, Tang LL, Lin AH, Li L and Ma J: The seventh edition of the
UICC/AJCC staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma is
prognostically useful for patients treated with intensity-modulated
radiotherapy from an endemic area in China. Radiother Oncol.
104:331–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ludwig JA and Weinstein JN: Biomarkers in
cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:845–856. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weissleder R: Molecular imaging in cancer.
Science. 312:1168–1171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mohandas A, Marcus C, Kang H, Truong MT
and Subramaniam RM: FDG PET/CT in the management of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 203:W146–W157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakamura H, Hirata T, Kitamura H and
Nishikawa J: Correlation of the standardized uptake value in
FDG-PET with the expression level of cell-cycle-related molecular
biomarkers in resected non-small cell lung cancers. Ann Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 15:304–310. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Imamura Y, Azuma K, Kurata S, Hattori S,
Sasada T, Kinoshita T, Okamoto M, Kawayama T, Kaida H, Ishibashi M
and Aizawa H: Prognostic value of SUVmax measurements obtained by
FDG-PET in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving
chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 71:49–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao W, Xu A, Han F, Lin X, Lu L, Shen G,
Huang S, Fan W, Deng X and Zhao C: Positron emission
tomography-computed tomography before treatment is highly
prognostic of distant metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
patients after intensity-modulated radiotherapy treatment: A
prospective study with long-term follow-up. Oral Oncol. 51:363–369.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hung TM, Wang HM, Kang CJ, Huang SF, Liao
CT, Chan SC, Ng SH, Chen IH, Lin CY, Fan KH and Chang JT:
Pretreatment (18)F-FDG PET standardized uptake value of primary
tumor and neck lymph nodes as a predictor of distant metastasis for
patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 49:169–174.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chan SC, Chang JT, Lin CY, Ng SH, Wang HM,
Liao CT, Chang CJ, Lin SY and Yen TC: Clinical utility of 18F-FDG
PET parameters in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Predictive role for different survival endpoints and impact on
prognostic stratification. Nucl Med Commun. 32:989–996. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moore MM, Chua W, Charles KA and Clarke
SJ: Inflammation and cancer: Causes and consequences. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 87:504–508. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmidt H, Suciu S, Punt CJ, Gore M, Kruit
W, Patel P, Lienard D, von der Maase H, Eggermont AM, Keilholz U,
et al: Pretreatment levels of peripheral neutrophils and leukocytes
as independent predictors of overall survival in patients with
American Joint Committee on Cancer Stage IV Melanoma: Results of
the EORTC 18951 Biochemotherapy Trial. J Clin Oncol. 25:1562–1569.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teramukai S, Kitano T, Kishida Y, Kawahara
M, Kubota K, Komuta K, Minato K, Mio T, Fujita Y, Yonei T, et al:
Pretreatment neutrophil count as an independent prognostic factor
in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: An analysis of Japan
multinational trial organisation LC00-03. Eur J Cancer.
45:1950–1958. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamanaka T, Matsumoto S, Teramukai S,
Ishiwata R, Nagai Y and Fukushima M: The baseline ratio of
neutrophils to lymphocytes is associated with patient prognosis in
advanced gastric cancer. Oncology-Basel. 73:215–220. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shankar A, Wang JJ, Rochtchina E, Yu MC,
Kefford R and Mitchell P: Association between circulating white
blood cell count and cancer mortality: A population-based cohort
study. Arch Intern Med. 166:188–194. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He JR, Shen GP, Ren ZF, Qin H, Cui C,
Zhang Y, Zeng YX and Jia WH: Pretreatment levels of peripheral
neutrophils and lymphocytes as independent prognostic factors in
patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck. 34:1769–1776.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun W, Zhang L, Luo M and Hu G, Mei Q, Liu
D, Long G and Hu G: Pretreatment hematologic markers as prognostic
factors in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio. Head
Neck. 38 Suppl 1:E1332–E1340. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K,
Tamahashi N and Ido T: Intratumoral distribution of
fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in vivo: High accumulation in
macrophages and granulation tissues studied by
microautoradiography. J Nucl Med. 33:1972–1980. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brown RS, Leung JY, Fisher SJ, Frey KA,
Ethier SP and Wahl RL: Intratumoral distribution of tritiated
fluorodeoxyglucose in breast carcinoma: I. Are inflammatory cells
important? J Nucl Med. 36:1854–1861. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cottone L, Valtorta S, Capobianco A,
Belloli S, Rovere-Querini P, Fazio F, Manfredi AA and Moresco RM:
Evaluation of the role of tumor-associated macrophages in an
experimental model of peritoneal carcinomatosis using (18)F-FDG
PET. J Nucl Med. 52:1770–1777. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Delbeke D, Coleman RE, Guiberteau MJ,
Brown ML, Royal HD, Siegel BA, Townsend DW, Berland LL, Parker JA,
Hubner K, et al: Procedure guideline for tumor imaging with 18F-FDG
PET/CT 1.0. J Nucl Med. 47:885–895. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ren YY, Li YC, Wu HB, Wang QS, Han YJ,
Zhou WL and Li HS: Whole-body 18F-FDG PET/CT for M staging in the
patient with newly diagnosed nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Who needs?
Eur J Radiol. 89:200–207. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Pierce LA II, Alessio AM and
Kinahan PE: The impact of respiratory motion on tumor
quantification and delineation in static PET/CT imaging. Phys Med
Biol. 54:7345–7362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP and Chan AT:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O'Neill LA and Hardie DG: Metabolism of
inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature.
493:346–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mochizuki T, Tsukamoto E, Kuge Y, Kanegae
K, Zhao S, Hikosaka K, Hosokawa M, Kohanawa M and Tamaki N: FDG
uptake and glucose transporter subtype expressions in experimental
tumor and inflammation models. J Nucl Med. 42:1551–1555.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu C, Li F, Niu G and Chen X: PET imaging
of inflammation biomarkers. Theranostics. 3:448–466. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vaidyanathan S, Patel CN, Scarsbrook AF
and Chowdhury FU: FDG PET/CT in infection and inflammation-current
and emerging clinical applications. Clin Radiol. 70:787–800. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chan WK, Kwong DL, Yeung DW, Huang B and
Khong PL: Prognostic impact of standardized uptake value of F-18
FDG PET/CT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med.
36:1007–1011. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Inokuchi H, Kodaira T, Tachibana H,
Nakamura T, Tomita N, Nakahara R, Takada A, Mizoguchi N, Tamaki T
and Fuwa N: Clinical usefulness of [18F] fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose
uptake in 178 head-and-neck cancer patients with nodal metastasis
treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy: Consideration of its
prognostic value and ability to provide guidance for optimal
selection of patients for planned neck dissection. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 79:747–755. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liao CT, Wang HM, Chang JT, Lin CY, Ng SH,
Huang SF, Chen IH, Hsueh C, Lee LY, Lin CH, et al: Influence of
pathological nodal status and maximal standardized uptake value of
the primary tumor and regional lymph nodes on treatment plans in
patients with advanced oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:421–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kubicek GJ, Champ C, Fogh S, Wang F, Reddy
E, Intenzo C, Dusing RW and Machtay M: FDG-PET staging and
importance of lymph node SUV in head and neck cancer. Head Neck
Oncol. 2:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GA, Meijer C
and Mulder NH: Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the
neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular
endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis. 6:283–287. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fondevila C, Metges JP, Fuster J, Grau JJ,
Palacín A, Castells A, Volant A and Pera M: p53 and VEGF expression
are independent predictors of tumour recurrence and survival
following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
90:206–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoshizaki T, Kondo S, Murono S, Endo K,
Tsuji A, Nakanishi Y, Nakanishi S, Sugimoto H, Hatano M, Ueno T and
Wakisaka N: Progress and controversy for the role of chemotherapy
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 45:244–247. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, Leclercq J,
Ng WT, Ma J, Chan AT, Huang PY, Benhamou E, Zhu G, et al:
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An
update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 16:645–655.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|