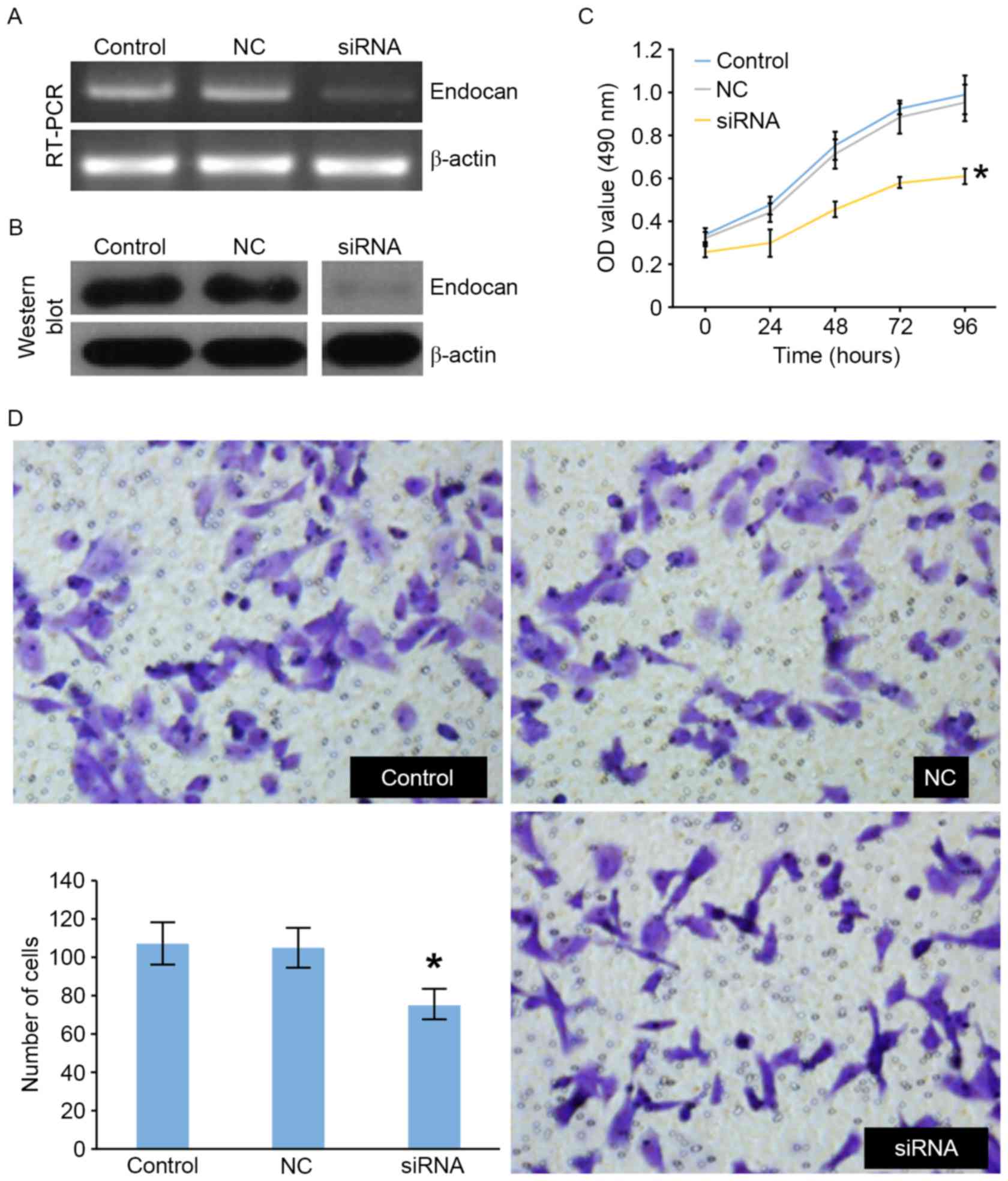
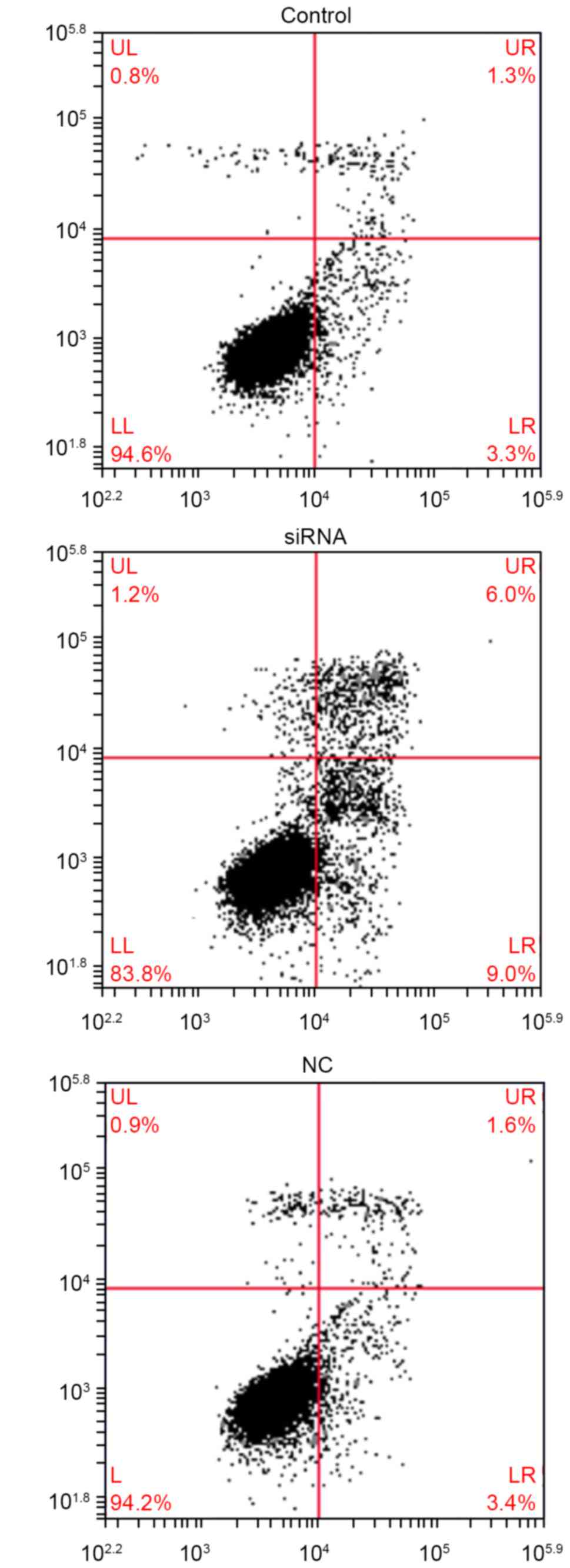
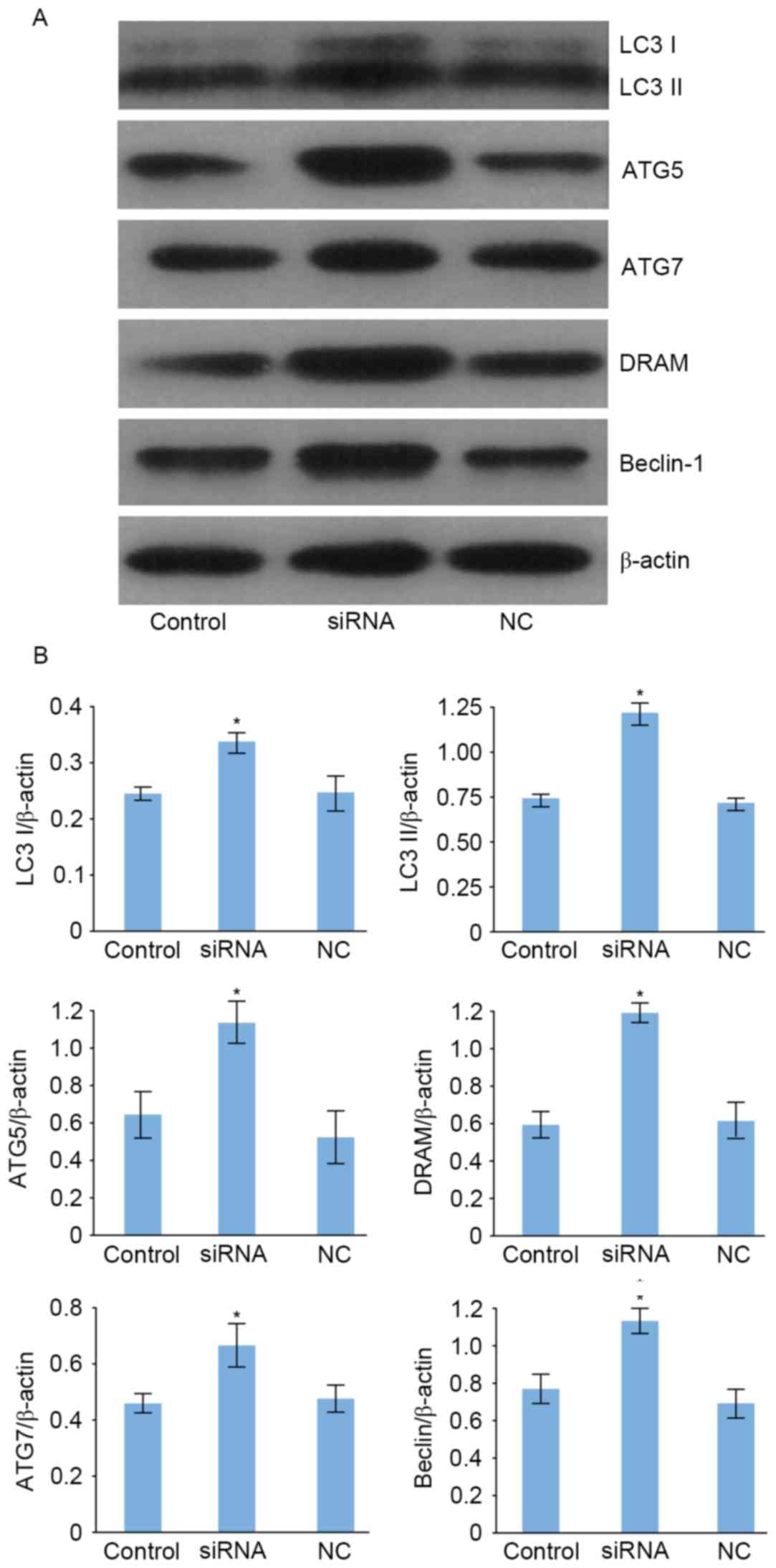
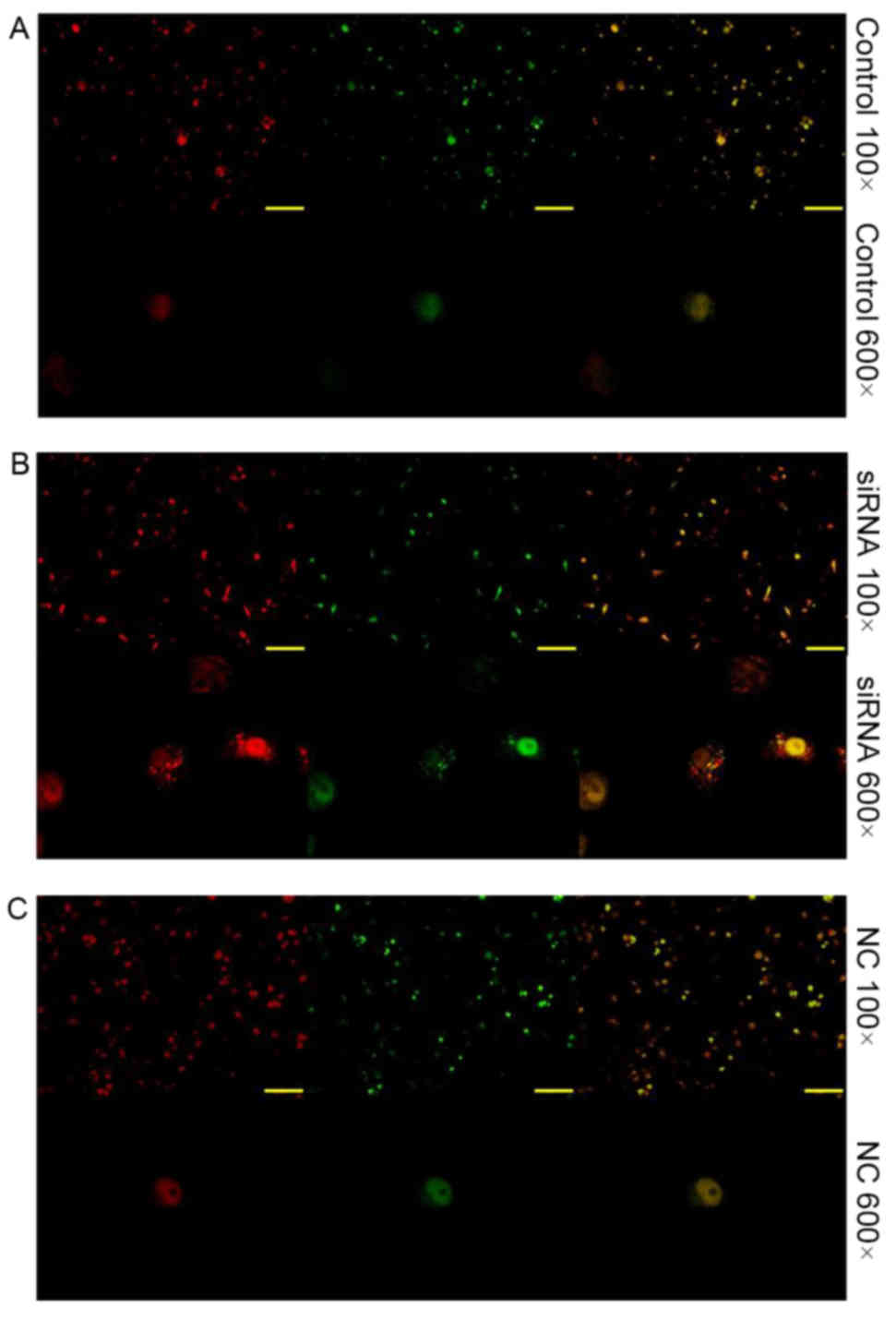
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Song MJ and Bae SH: Newer treatments for
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Intern Med. 29:149–155.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abid MR, Yi XJ, Yano K, Shih SC and Aird
WC: Vascular endocan is preferentially expressed in tumor
endothelium. Microvasc Res. 72:136–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maurage CA, Adam E, Minéo JF, Sarrazin S,
Debunne M, Siminski RM, Baroncini M, Lassalle P, Blond S and
Delehedde M: Endocan expression and localization in human
glioblastomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 68:633–641. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ziol M, Sutton A, Calderaro J, Barget N,
Aout M, Leroy V, Blanc JF, Sturm N, Bioulac-Sage P, Nahon P, et al:
ESM-1 expression in stromal cells is predictive of recurrence after
radiofrequency ablation in early hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Hepatol. 59:1264–1270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oltean S, Pullerits R, Flodén A, Olausson
M and Oltean M: Increased resistin in brain dead organ donors is
associated with delayed graft function after kidney
transplantation. J Transl Med. 11:2332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leroy X, Aubert S, Zini L, Franquet H,
Kervoaze G, Villers A, Delehedde M, Copin MC and Lassalle P:
Vascular endocan (ESM-1) is markedly overexpressed in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 56:180–187. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zuo L, Zhang SM, Hu RL, Zhu HQ, Zhou Q,
Gui SY, Wu Q and Wang Y: Correlation between expression and
differentiation of endocan in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:4562–4568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scherpereel A, Gentina T, Grigoriu B,
Sénéchal S, Janin A, Tsicopoulos A, Plénat F, Béchard D, Tonnel AB
and Lassalle P: Overexpression of endocan induces tumor formation.
Cancer Res. 63:6084–6089. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang YH, Ji NY, Lee CI, Lee HG, Kim JW,
Yeom YI, Kim DG, Yoon SK, Kim JW, Park PJ and Song EY: ESM-1
silencing decreased cell survival, migration, and invasion and
modulated cell cycle progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Amino
Acids. 40:1003–1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen LY, Liu X, Wang SL and Qin CY:
Over-expression of the Endocan gene in endothelial cells from
hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with angiogenesis and tumour
invasion. J Int Med Res. 38:498–510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang GW, Tao YM and Ding X: Endocan
expression correlated with poor survival in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 54:389–394. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gerritsen ME, Tomlinson JE, Zlot C, Ziman
M and Hwang S: Using gene expression profiling to identify the
molecular basis of the synergistic actions of hepatocyte growth
factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in human endothelial
cells. Br J Pharmacol. 140:595–610. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JH, Park MY, Kim CN, Kim KH, Kang HB,
Kim KD and Kim JW: Expression of endothelial cell-specific
molecule-1 regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in human colon
carcinoma: Impact of ESM-1 on prognosis and its correlation with
clinicopathological features. Oncol Rep. 28:1701–1708. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kepp O, Galluzzi L, Lipinski M, Yuan J and
Kroemer G: Cell death assays for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 10:221–237. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jardon MA, Rothe K, Bortnik S, Vezenkov L,
Jiang X, Young RN, Lum JJ and Gorski SM: Autophagy: From structure
to metabolism to therapeutic regulation. Autophagy. 9:2180–2182.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang R and Liu W: Identifying an
essential role of nuclear LC3 for autophagy. Autophagy. 11:852–853.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lai SC and Devenish RJ: LC3-associated
phagocytosis (LAP): Connections with host autophagy. Cells.
1:396–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Atg5: More than
an autophagy factor. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1045–1047. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang X, Qi Q, Hua X, Li X, Zhang W, Sun
H, Li S, Wang X and Li B: Beclin 1, an autophagy-related gene,
augments apoptosis in U87 glioblastoma cells. Oncology Rep.
31:1761–1767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Criollo A, Dessen P and Kroemer G: DRAM: A
phylogenetically ancient regulator of autophagy. Cell Cycle.
8:2319–2320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu X, Nesic-Taylor O, Qiu J, Rea HC,
Fabian R, Rassin DK and Perez-Polo JR: Activation of nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling pathway by interleukin-1 after
hypoxia/ischemia in neonatal rat hippocampus and cortex. J
Neurochem. 93:26–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karin M, Yamamoto Y and Wang QM: The IKK
NF-kappa B system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 3:17–26. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tato CM and Hunter CA: Host-pathogen
interactions: Subversion and utilization of the NF-kappa B pathway
during infection. Infect Immun. 70:3311–3317. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bai X, Feldman NE, Chmura K, Ovrutsky AR,
Su WL, Griffin L, Pyeon D, McGibney MT, Strand MJ, Numata M, et al:
Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation decreases survival
of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human macrophages. PLoS One.
8:e619252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loeuillet C, Martinon F, Perez C, Munoz M,
Thome M and Meylan PR: Mycobacterium tuberculosis subverts innate
immunity to evade specific effectors. J Immunol. 177:6245–6255.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW:
NF-kappaB in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:301–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukuda M, Kusama K and Sakashita H:
Cimetidine inhibits salivary gland tumor cell adhesion to neural
cells and induces apoptosis by blocking NCAM expression. BMC
Cancer. 8:3762008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Djavaheri-Mergny M, Amelotti M, Mathieu J,
Besançon F, Bauvy C, Souquère S, Pierron G and Codogno P: NF-kappaB
activation represses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy.
J Biol Chem. 281:30373–30382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peri S, Devarajan K, Yang DH, Knudson AG
and Balachandran S: Meta-analysis identifies NF-κB as a therapeutic
target in renal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e767462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Orlowski RZ and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB
as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 8:385–389. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|