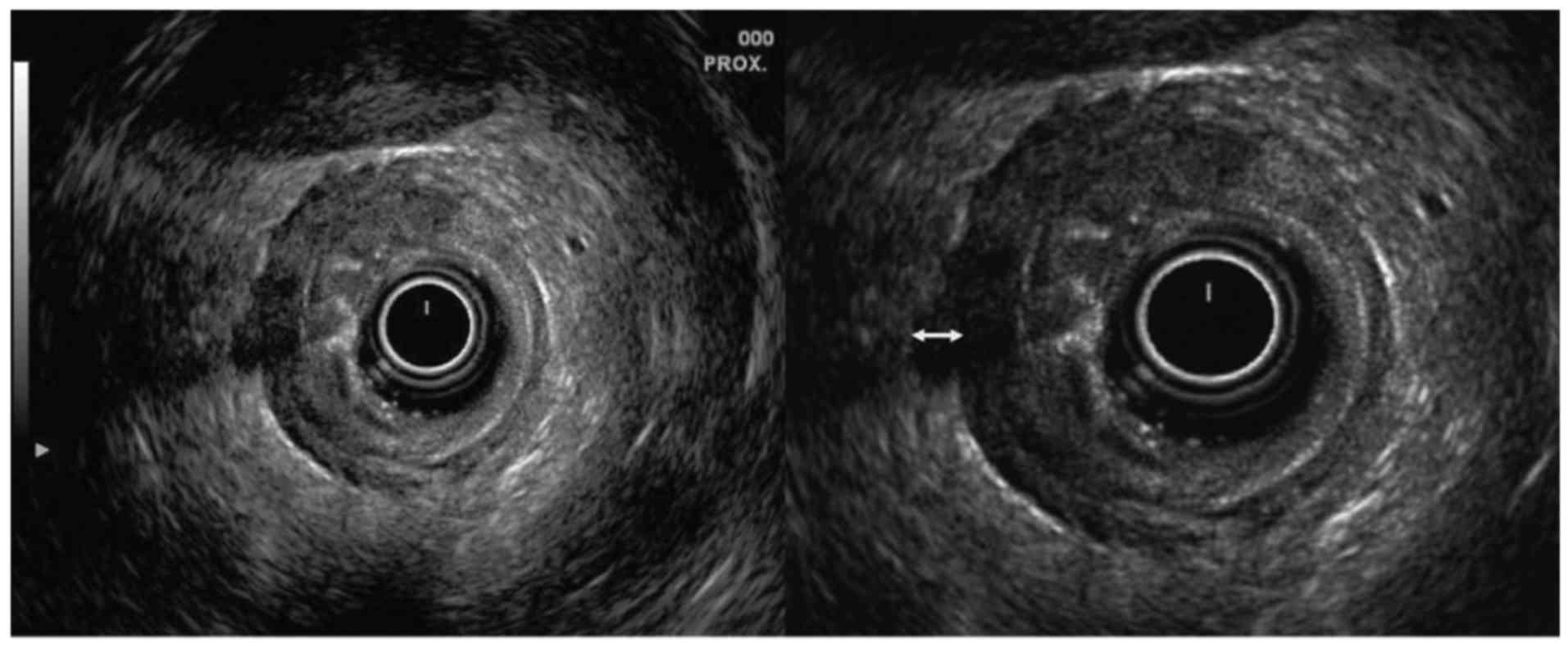
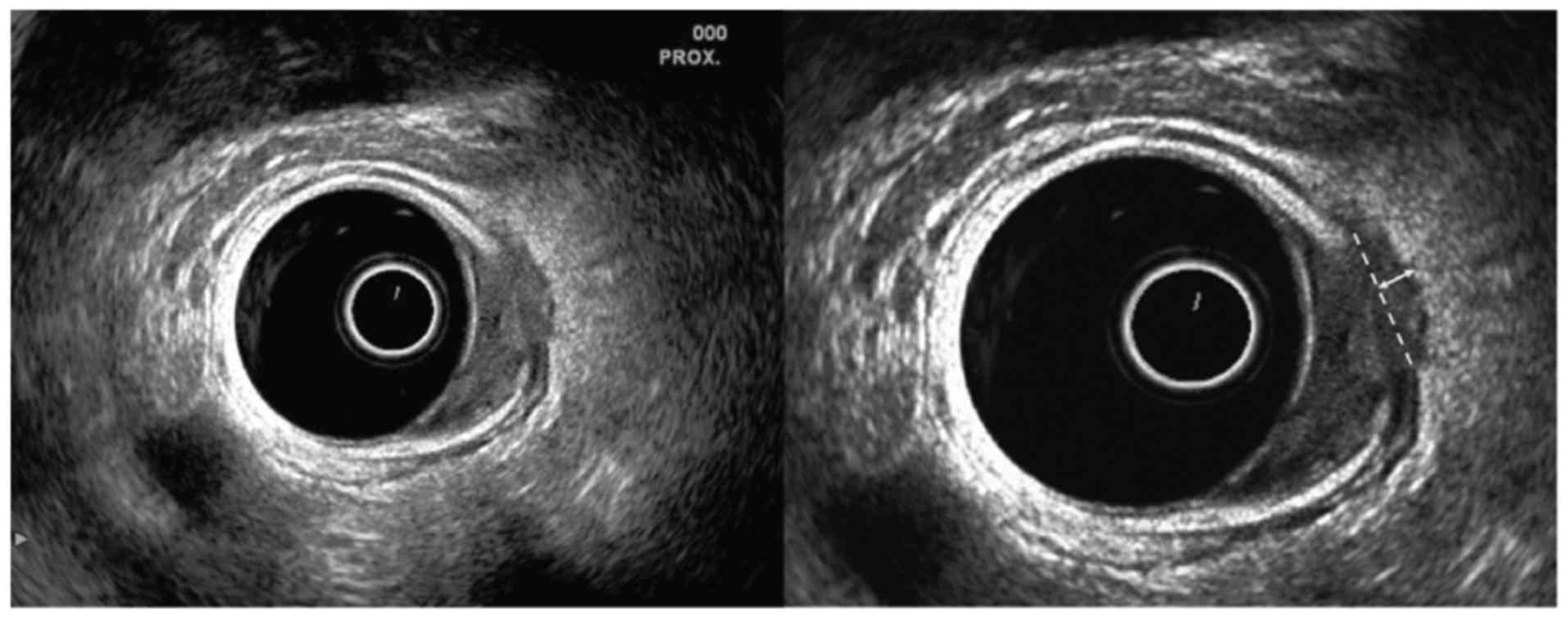
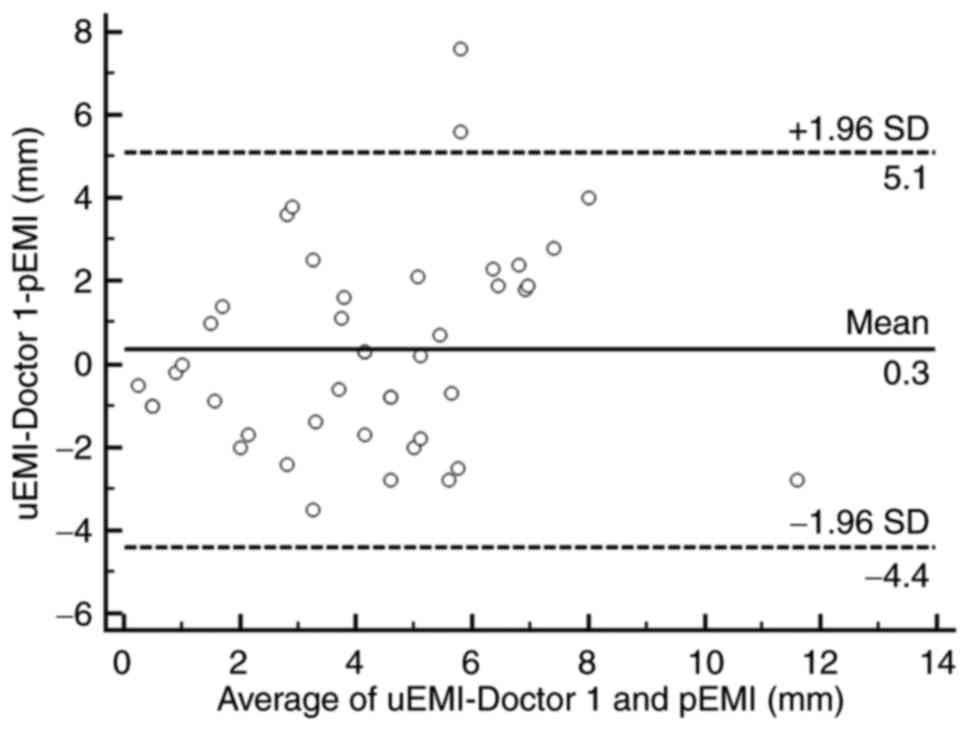
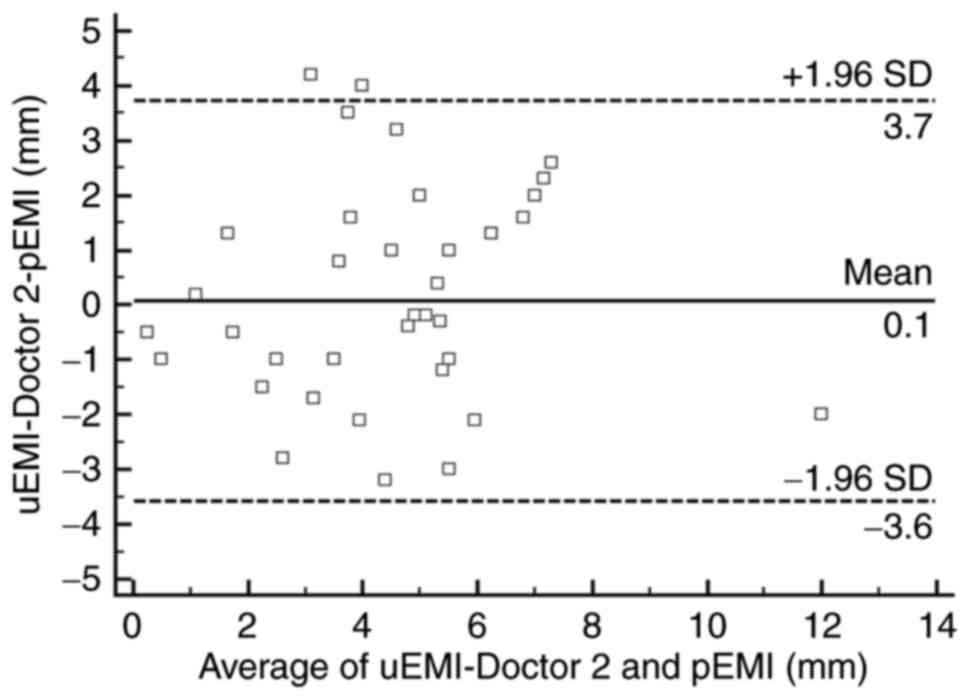
|
1
|
Berardi R, Maccaroni E, Onofri A, Morgese
F, Torniai M, Tiberi M, Ferrini C and Cascinu S: Locally advanced
rectal cancer: The importance of a multidisciplinary approach.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:17279–17287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marks J, Nassif G, Schoonyoung H, DeNittis
A, Zeger E, Mohiuddin M and Marks G: Sphincter-sparing surgery for
adenocarcinoma of the distal 3 cm of the true rectum: Results after
neoadjuvant therapy and minimally invasive radical surgery or local
excision. Surg Endosc. 27:4469–4477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loos M, Quentmeier P, Schuster T, Nitsche
U, Gertler R, Keerl A, Kocher T, Friess H and Rosenberg R: Effect
of preoperative radio(chemo)therapy on long-term functional outcome
in rectal cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Ann Surg Oncol. 20:1816–1828. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bruheim K, Guren MG, Dahl AA, Skovlund E,
Balteskard L, Carlsen E, Fosså SD and Tveit KM: Sexual function in
males after radiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 76:1012–1017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruheim K, Guren MG, Skovlund E, Hjermstad
MJ, Dahl O, Frykholm G, Carlsen E and Tveit KM: Late side effects
and quality of life after radiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:1005–1011. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilson PM, Ladner RD and Lenz HJ:
Exploring alternative individualized treatment strategies in
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 7 Suppl 1:S28–S36. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cecil TD, Sexton R, Moran BJ and Heald RJ:
Total mesorectal excision results in low local recurrence rates in
lymph node-positive rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 47:1145–1150.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frasson M, Garcia-Granero E, Roda D,
Flor-Lorente B, Roselló S, Esclapez P, Faus C, Navarro S, Campos S
and Cervantes A: Preoperative chemoradiation may not always be
needed for patients with T3 and T2N+ rectal cancer. Cancer.
117:3118–3125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cawthorn SJ, Parums DV, Gibbs NM, A'Hern
RP, Caffarey SM, Broughton CI and Marks CG: Extent of mesorectal
spread and involvement of lateral resection margin as prognostic
factors after surgery for rectal cancer. Lancet. 335:1055–1059.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Willett CG, Badizadegan K, Ancukiewicz M
and Shellito PC: Prognostic factors in stage T3N0 rectal cancer: Do
all patients require postoperative pelvic irradiation and
chemotherapy? Dis Colon Rectum. 42:167–173. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steel MC, Woods R, Mackay JM and Chen F:
Extent of mesorectal invasion is a prognostic indicator in T3
rectal carcinoma. ANZ J Surg. 72:483–487. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyoshi M, Ueno H, Hashiguchi Y, Mochizuki
H and Talbot IC: Extent of mesorectal tumor invasion as a
prognostic factor after curative surgery for T3 rectal cancer
patients. Ann Surg. 243:492–498. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Merkel S, Mansmann U, Siassi M,
Papadopoulos T, Hohenberger W and Hermanek P: The prognostic
inhomogeneity in pT3 rectal carcinomas. Int J Colorectal Dis.
16:298–304. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
MERCURY Study Group: Extramural depth of
tumor invasion at thin-section MR in patients with rectal cancer:
Results of the MERCURY study. Radiology. 243:132–139. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marone P, de Bellis M, D'Angelo V, Delrio
P, Passananti V, Di Girolamo E, Rossi GB, Rega D, Tracey MC and
Tempesta AM: Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the
loco-regional staging of patients with rectal cancer. World J
Gastrointest Endosc. 7:688–701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rafaelsen SR, Vagn-Hansen C, Sørensen T,
Pløen J and Jakobsen A: Transrectal ultrasound and magnetic
resonance imaging measurement of extramural tumor spread in rectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5021–5026. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harewood GC, Kumar KS, Clain JE, Levy MJ
and Nelson H: Clinical implications of quantification of mesorectal
tumor invasion by endoscopic ultrasound: All T3 rectal cancers are
not equal. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:750–755. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muñoz E, Granero-Castro P, Frasson M,
Escartin J, Esclapez P, Campos S, Flor-Lorente B and Garcia-Granero
E: Modified Wong's classification improves the accuracy of rectal
cancer staging by endorectal ultrasound and MRI. Dis Colon Rectum.
56:1332–1338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hildebrandt U and Feifel G: Preoperative
staging of rectal cancer by intrarectal ultrasound. Dis Colon
Rectum. 28:42–46. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho SH, Kim SH, Bae JH, Jang YJ, Kim HJ,
Lee D and Park JS: Society of North America (RSNA): Prognostic
stratification by extramural depth of tumor invasion of primary
rectal cancer based on the Radiological Society of North America
proposal. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 202:1238–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim YW, Cha SW, Pyo J, Kim NK, Min BS, Kim
MJ and Kim H: Factors related to preoperative assessment of the
circumferential resection margin and the extent of mesorectal
invasion by magnetic resonance imaging in rectal cancer: A
prospective comparison study. World J Surg. 33:1952–1960. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Esclapez P, Garcia-Granero E, Flor B,
Garcia-Botello S, Cervantes A, Navarro S and Lledó S: Prognostic
heterogeneity of endosonographic T3 rectal cancer. Dis Colon
Rectum. 52:685–691. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong G, Xiao Y, Zhang J, Dai Q, Li J and
Jiang Y: Value of endorectal ultasound in predicting the
circumferential resection margin and maximum tumor thickness of T3
rectal cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 18:252–256.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Siddiqui AA, Fayiga Y and Huerta S: The
role of endoscopic ultrasound in the evaluation of rectal cancer.
Int Semin Surg Oncol. 3:362006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Assenat E, Thézenas S, Samalin E, Bibeau
F, Portales F, Azria D, Quenet F, Rouanet P, Aubert Saint B and
Senesse P: The value of endoscopic rectal ultrasound in predicting
the lateral clearance and outcome in patients with lower-third
rectal adenocarcinoma. Endoscopy. 39:309–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bipat S, Glas AS, Slors FJ, Zwinderman AH,
Bossuyt PM and Stoker J: Rectal cancer: Local staging and
assessment of lymph node involvement with endoluminal US, CT and MR
imaging-a meta-analysis. Radiology. 232:773–783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fernández-Esparrach G, Ayuso-Colella JR,
Sendino O, Pagés M, Cuatrecasas M, Pellisé M, Maurel J,
Ayuso-Colella C, González-Suárez B, Llach J, et al: EUS and
magnetic resonance imaging in the staging of rectal cancer: A
prospective and comparative study. Gastrointest Endosc. 74:347–354.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burton S, Brown G, Daniels IR, Norman AR,
Mason B and Cunningham D: Royal Marsden Hospital, Colorectal Cancer
Network: MRI directed multidisciplinary team preoperative treatment
strategy: The way to eliminate positive circumferential margins? Br
J Cancer. 94:351–357. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Phang PT, Gollub MJ, Loh BD, Nash GM,
Temple LK, Paty PB, Guillem JG and Weiser MR: Accuracy of
endorectal ultrasound for measurement of the closest predicted
radial mesorectal margin for rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum.
55:59–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Granero-Castro P, Munoz E, Frasson M,
Garcia-Granero A, Esclapez P, Campos S, Flor-Lorente B and
Garcia-Granero E: Evaluation of mesorectal fascia in mid and low
anterior rectal cancer using endorectal ultrasound is feasible and
reliable: A comparison with MRI findings. Dis Colon Rectum.
57:709–714. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|