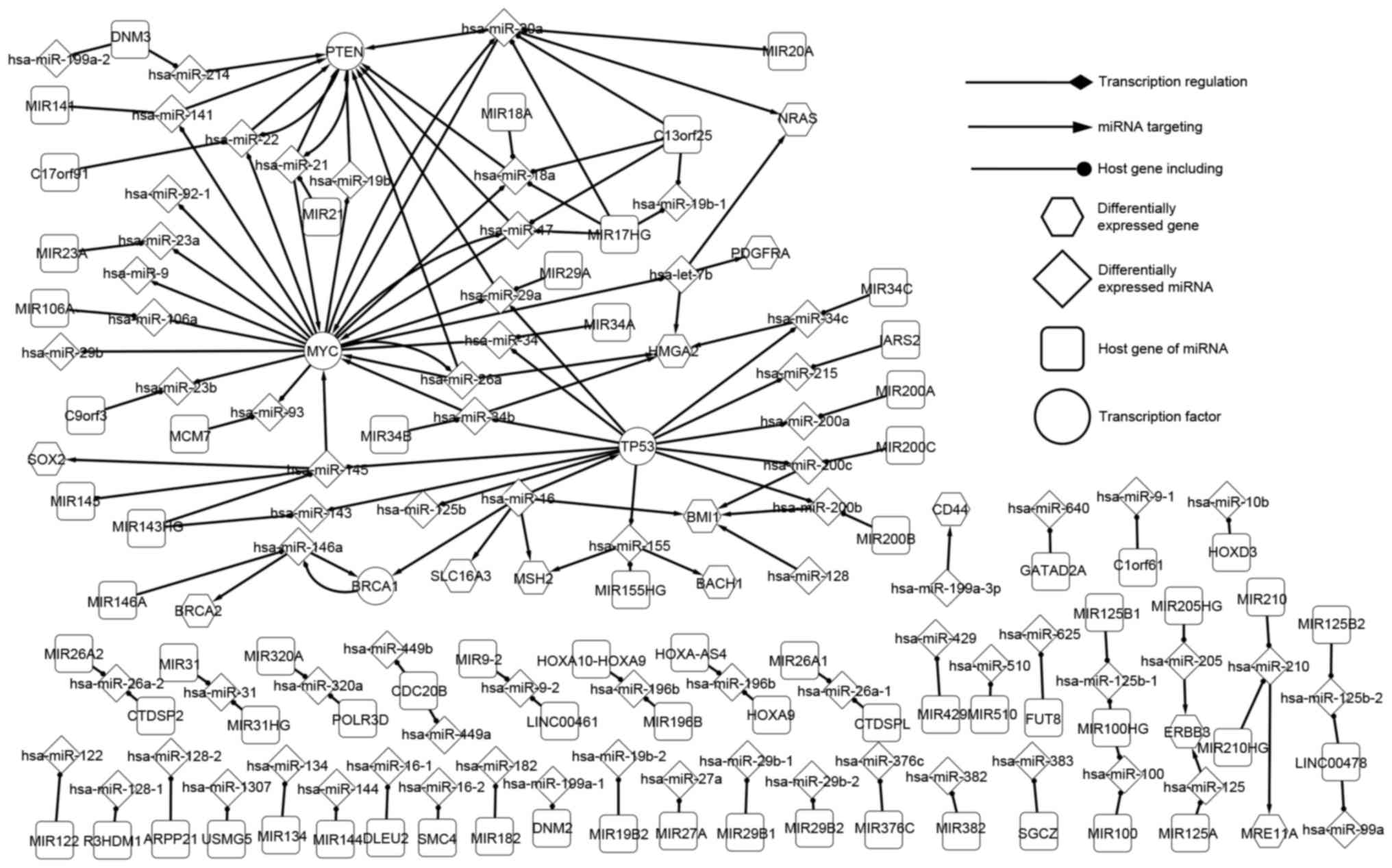
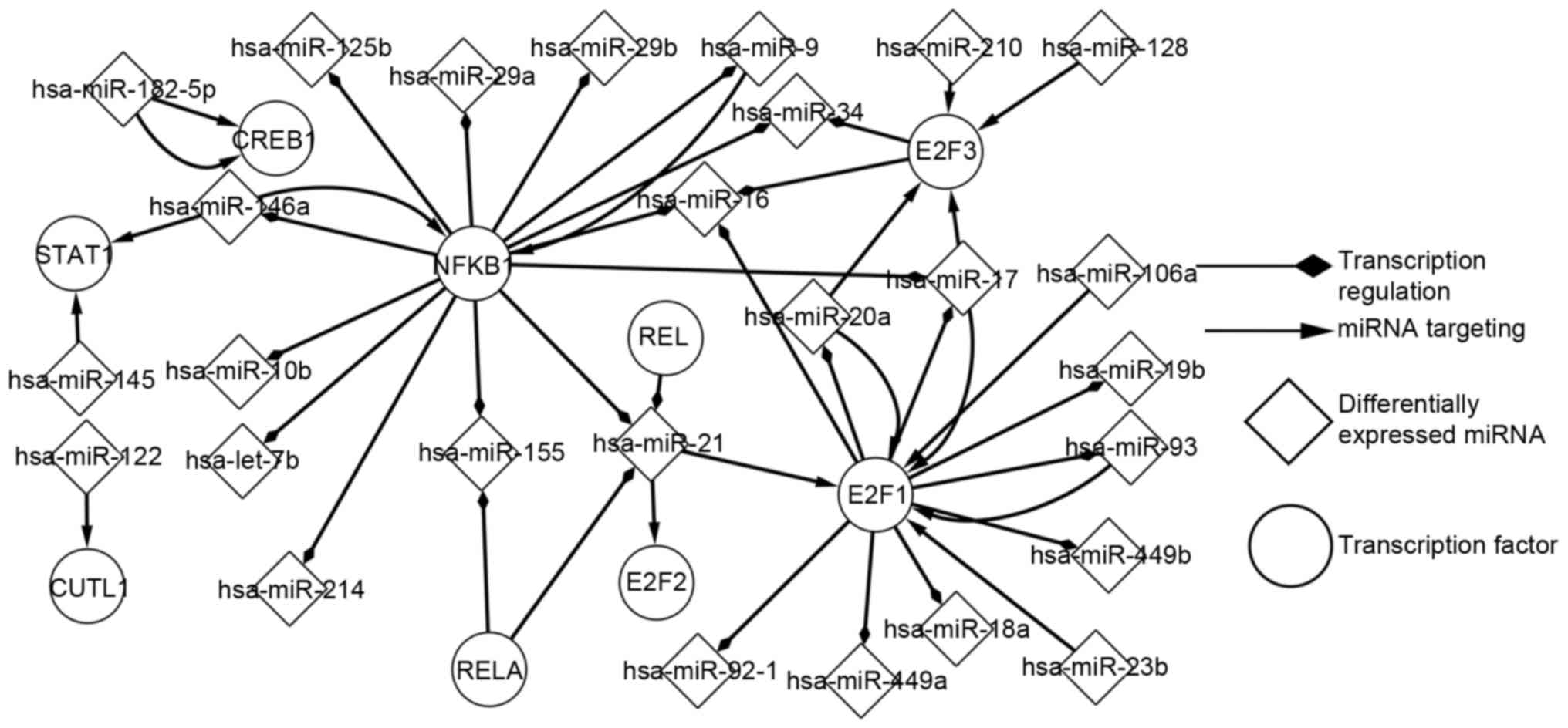
|
1
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: microRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singer G, Kurman RJ, Chang HW, Cho SK and
Shih IeM: Diverse tumorigenic pathways in ovarian serous carcinoma.
Am J Pathol. 160:1223–1228. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Soussi T and Béroud C: Assessing TP53
status in human tumours to evaluate clinical outcome. Nat Rev
Cancer. 1:233–240. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu Z, Kim J, He L, Creighton CJ, Gunaratne
PH, Hawkins SM and Matzuk MM: Functional analysis of miR-34c as a
putative tumor suppressor in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Biol
Reprod. 91:1132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hobert O: Gene regulation by transcription
factors and microRNAs. Science. 319:1785–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes
Dev. 4:1837–1851. 2000.
|
|
7
|
Tran DH, Satou K, Ho TB and Pham TH:
Computational discovery of miR-TF regulatory modules in human
genome. Bioinformation. 4:371–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: microRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ambros V: microRNA pathways in flies and
worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li M, Li J, Ding X, He M and Cheng SY:
microRNA and cancer. AAPS J. 2:309–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gao X, Qiao Y, Han D, Zhang Y and Ma N:
Enemy or partner: Relationship between intronic micrornas and their
host genes. IUBMB Life. 64:835–840. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baskerville S and Bartel DP: Microarray
profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with
neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 11:241–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao G, Huang B, Liu Z, Zhang J, Xu H, Xia
W, Li J, Li S, Chen L, Ding H, et al: Intronic miR-301 feedback
regulates its host gene, ska2, in A549 cells by targeting MEOX2 to
affect ERK/CREB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 396:978–982.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Simossis VA,
Sethupathy P and Hatzigeorgiou AG: The database of experimentally
supported targets: A functional update of TarBase. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:(Database Issue). D155–D158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu SD, Tseng YT, Shrestha S, Lin YL,
Khaleel A, Chou CH, Chu CF, Huang HY, Lin CM, Ho SY, et al:
miRTarBase update 2014: An information resource for experimentally
validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:(Database Issue). D78–D85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:(Database Issue). D105–D110.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:(Database Issue). D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M,
Zhang X, Li M, Wang G and Liu Y: miR2Disease: A manually curated
database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:(Database Issue). D98–D104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ivan C, Hu W, Bottsford-Miller J, Zand B,
Dalton HJ, Liu T, Huang J, Nick AM, Lopez-Berestein G, Coleman RL,
et al: Epigenetic analysis of the Notch superfamily in high-grade
serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 128:506–511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singer G, Kurman RJ, Chang HW, Cho SK and
Shih IeM: Diverse tumorigenic pathways in ovarian serous carcinoma.
Am J Pathol. 160:1223–1228. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmid S, Bieber M, Zhang F, Zhang M, He
B, Jablons D and Teng NN: Wnt and hedgehog gene pathway expression
in serous ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:975–980. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghosh S, Albitar L, LeBaron R, Welch WR,
Samimi G, Birrer MJ, Berkowitz RS and Mok SC: Up-regulation of
stromal versican expression in advanced stage serous ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 119:114–120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ouellet V, Guyot MC, Le Page C,
Filali-Mouhim A, Lussier C, Tonin PN, Provencher DM and Mes-Masson
AM: Tissue array analysis of expression microarray candidates
identifies markers associated with tumor grade and outcome in
serous epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 119:599–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thériault BL, Cybulska P, Shaw PA, Gallie
BL and Bernardini MQ: The role of KIF14 in patient-derived primary
cultures of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells. J Ovarian Res.
7:1232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo LY, Kim E, Cheung HW, Weir BA, Dunn
GP, Shen RR and Hahn WC: The tyrosine kinase adaptor protein FRS2
is oncogenic and amplified in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 13:502–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: Synergetic
regulatory networks mediated by oncogene-driven microRNAs and
transcription factors in serous ovarian cancer. Mol Biosyst.
9:3187–3198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiangjun He, Jing Yang, Qi Zhang, Heng Cui
and Yujun Zhang: Shortening of the 3′untranslated region: An
important mechanism leading to overexpression of HMGA2 in serous
ovarian cancer. Chin Med J. 127:494–499. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ouellet V, Le Page C, Guyot MC, Lussier C,
Tonin PN, Provencher DM and Mes-Masson AM: SET complex in serous
epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 119:2119–2126. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kwon JY, Seo YR and Ahn WS: Recognition of
potential predictive markers for diagnosis in Korean serous ovarian
cancer patients at stage IIIc using array comparative genomic
hybridization with high resolution. Mol Cell Toxicol. 7:772011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bi FF, Li D and Yang Q: Promoter
hypomethylation, especially around the E26 transformation-specific
motif and increased expression of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 in
BRCA-mutated serous ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dai W, Zeller C, Masrour N, Siddiqui N,
Paul J and Brown R: Promoter CpG island methylation of genes in key
cancer pathways associates with clinical outcome in high-grade
serous ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5788–5797. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Montavon C, Gloss BS, Warton K, Barton CA,
Statham AL, Scurry JP, Tabor B, Nguyen TV, Qu W, Samimi G, et al:
Prognostic and diagnostic significance of DNA methylation patterns
in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 124:582–588.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amankwah EK, Wang Q, Schildkraut JM, Tsai
YY, Ramus SJ, Fridley BL, Beesley J, Johnatty SE, Webb PM,
Chenevix-Trench G, et al: Polymorphisms in stromal genes and
susceptibility to serous epithelial ovarian cancer: A report from
the ovarian cancer association consortium. PLoS One. 6:e196422011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kashuba V, Dmitriev AA, Krasnov GS,
Pavlova T, Ignatjev I, Gordiyuk VV, Gerashchenko AV, Braga EA,
Yenamandra SP, Lerman M, et al: NotI microarrays: Novel epigenetic
markers for early detection and prognosis of high grade serous
ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13352–13377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurita T, Izumi H, Kagami S, Kawagoe T,
Toki N, Matsuura Y, Hachisuga T and Kohno K: Mitochondrial
transcription factor A regulates BCL2L1 gene expression and is a
prognostic factor in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci.
103:239–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Berchuck A, Iversen ES, Luo J, Clarke JP,
Horne H, Levine DA, Boyd J, Alonso MA, Secord AA, Bernardini MQ, et
al: Microarray analysis of early stage serous ovarian cancers
demonstrates profiles predictive of favorable outcome. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:2448–2455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hjerpe E, Brage SE, Stolt Frostvik M,
Johansson H, Shoshan M and Avall-Lundqvist E: Metabolic markers and
HSP60 in chemonaive serous solid ovarian cancer versus ascites. Int
J Gynecol Cancer. 24:1389–1394. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cowin PA, George J, Fereday S, Loehrer E,
Van Loo P, Cullinane C, Etemadmoghadam D, Ftouni S, Galletta L,
Anglesio MS, et al: LRP1B deletion in high-grade serous ovarian
cancers is associated with acquired chemotherapy resistance to
liposomal doxorubicin. Cancer Res. 72:4060–4073. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanwar PS, Mohapatra G, Chiang S, Engler
DA, Zhang L, Kaneko-Tarui T, Ohguchi Y, Birrer MJ and Teixeira JM:
Loss of LKB1 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes in the ovarian surface
epithelium induces papillary serous ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:546–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tamir A, Jag U, Sarojini S, Schindewolf C,
Tanaka T, Gharbaran R, Patel H, Sood A, Hu W, Patwa R, et al:
Kallikrein family proteases KLK6 and KLK7 are potential early
detection and diagnostic biomarkers for serous and papillary serous
ovarian cancer subtypes. J Ovarian Res. 7:1092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He QZ, Luo XZ, Wang K, Zhou Q, Ao H, Yang
Y, Li SX, Li Y, Zhu HT and Duan T: Isolation and characterization
of cancer stem cells from high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:173–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Callahan MJ, Nagymanyoki Z, Bonome T,
Johnson ME, Litkouhi B, Sullivan EH, Hirsch MS, Matulonis UA, Liu
J, Birrer MJ, et al: Increased HLA-DMB expression in the tumor
epithelium is associated with increased CTL infiltration and
improved prognosis in advanced-stage serous ovarian cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:7667–7673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li YL, Ye F, Hu Y, Lu WG and Xie X:
Identification of suitable reference genes for gene expression
studies of human serous ovarian cancer by real-time polymerase
chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 394:110–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li YL, Ye F, Cheng XD, Hu Y, Zhou CY, Lü
WG and Xie X: Identification of glia maturation factor beta as an
independent prognostic predictor for serous ovarian cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 46:2104–2118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Borley J, Ghaem-Maghami S, Honeyfield L,
Williamson R and Brown R: Hypomethylation of MSX1 is associated
with decreased gene expression, poor progression free survival and
chemotherapy resistance in serous ovarian cancer. An Int J Obstetr
Gynaecol. 120:2492013.
|
|
48
|
Singh H, Li Y, Fuller PJ, Harrison C, Rao
J, Stephens AN and Nie G: HtrA3 is downregulated in cancer cell
lines and significantly reduced in primary serous and granulosa
cell ovarian tumors. J Cancer. 4:152–164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kumtepe Y, Halici Z, Sengul O, Kunak CS,
Bayir Y, Kilic N, Cadirci E, Pulur A and Bayraktutan Z: High serum
HTATIP2/TIP30 level in serous ovarian cancer as prognostic or
diagnostic marker. Eur J Med Res. 18:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sayer RA, Lancaster JM, Pittman J, Gray J,
Whitaker R, Marks JR and Berchuck A: High insulin-like growth
factor-2 (IGF-2) gene expression is an independent predictor of
poor survival for patients with advanced stage serous epithelial
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 96:355–361. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Emmanuel C, Chiew YE, George J,
Etemadmoghadam D, Anglesio MS, Sharma R, Russell P, Kennedy C,
Fereday S, Hung J, et al: Genomic classification of serous ovarian
cancer with adjacent borderline differentiates RAS pathway and
TP53-mutant tumors and identifies NRAS as an oncogenic driver. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:6618–6630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yoshihara K, Tajima A, Komata D, Yamamoto
T, Kodama S, Fujiwara H, Suzuki M, Onishi Y, Hatae M, Sueyoshi K,
et al: Gene expression profiling of advanced-stage serous ovarian
cancers distinguishes novel subclasses and implicates ZEB2 in tumor
progression and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 100:1421–1428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu Z, Kim J, He L, Creighton CJ, Gunaratne
PH, Hawkins SM and Matzuk MM: Functional analysis of miR-34c as a
putative tumor suppressor in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Biol
Reprod. 91:1132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Merritt MA, Parsons PG, Newton TR, Martyn
AC, Webb PM, Green AC, Papadimos DJ and Boyle GM: Expression
profiling identifies genes involved in neoplastic transformation of
serous ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:3782009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Newton TR, Parsons PG, Lincoln DJ,
Cummings MC, Wyld DK, Webb PM, Green AC and Boyle GM: Expression
profiling correlates with treatment response in women with advanced
serous epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 119:875–883. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bateman NW, Jaworski E, Ao W, Wang G,
Litzi T, Dubil E, Marcus C, Conrads KA, Teng PN, Hood BL, et al:
Elevated AKAP12 in paclitaxel-resistant serous ovarian cancer cells
is prognostic and predictive of poor survival in patients. J
Proteome Res. 14:1900–1910. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bashashati A, Ha G, Tone A, Ding J,
Prentice LM, Roth A, Rosner J, Shumansky K, Kalloger S, Senz J, et
al: Distinct evolutionary trajectories of primary high-grade serous
ovarian cancers revealed through spatial mutational profiling. J
Pathol. 231:21–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jannesari-Ladani F, Hossein G and
Izadi-Mood N: Differential Wnt11 expression related to Wnt5a in
high- and low-grade serous ovarian cancer: Implications for
migration, adhesion and survival. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:1489–1495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ye Q, Chen L, Yin X, Liu YJ, Ji Q and Zhao
E: Development of serous ovarian cancer is associated with the
expression of homologous recombination pathway proteins. Pathol
Oncol Res. 20:931–938. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Karst AM, Jones PM, Vena N, Ligon AH, Liu
JF, Hirsch MS, Etemadmoghadam D, Bowtell DD and Drapkin R: Cyclin
E1 deregulation occurs early in secretory cell transformation to
promote formation of fallopian tube-derived high-grade serous
ovarian cancers. Cancer Res. 74:1141–1152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Martins FC, Santiago Id, Trinh A, Xian J,
Guo A, Sayal K, Jimenez-Linan M, Deen S, Driver K, Mack M, et al:
Combined image and genomic analysis of high-grade serous ovarian
cancer reveals PTEN loss as a common driver event and prognostic
classifier. Genome Biol. 15:5262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tashiro H, Miyazaki K, Okamura H, Iwai A
and Fukumoto M: c-myc over-expression in human primary ovarian
tumours: Its relevance to tumour progression. Int J Cancer.
50:828–833. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kannan K, Coarfa C, Rajapakshe K, Hawkins
SM, Matzuk MM, Milosavljevic A and Yen L: CDKN2D-WDFY2 is a
cancer-specific fusion gene recurrent in high-grade serous ovarian
carcinoma. PLoS Genet. 10:e10042162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Schildkraut JM, Iversen ES, Wilsonv MA,
Clyde MA, Moorman PG, Palmieri RT, Whitaker R, Bentley RC, Marks JR
and Berchuck A: Association between DNA damage response and repair
genes and risk of invasive serous ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
5:e100612010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shah NR, Tancioni I, Ward KK, Lawson C,
Chen XL, Jean C, Sulzmaier FJ, Uryu S, Miller NL, Connolly DC and
Schlaepfer DD: Analyses of merlin/NF2 connection to FAK inhibitor
responsiveness in serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
134:104–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Koti M, Siu A, Clément I, Bidarimath M,
Turashvili G, Edwards A, Rahimi K, Mes-Masson AM and Squire JA: A
distinct pre-existing inflammatory tumour microenvironment is
associated with chemotherapy resistance in high-grade serous
epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1215–1222. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cheon DJ, Tong Y, Sim MS, Dering J, Berel
D, Cui X, Lester J, Beach JA, Tighiouart M, Walts AE, et al: A
collagen-remodeling gene signature regulated by TGF-β signaling is
associated with metastasis and poor survival in serous ovarian
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:711–723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhou J, Gong G, Tan H, Dai F, Zhu X, Chen
Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen P, Wu X and Wen J: Urinary microRNA-30a-5p
is a potential biomarker for ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 33:2915–2923. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li J, Li L, Li Z, Gong G, Chen P, Liu H,
Wang J, Liu Y and Wu X: The role of miR-205 in the VEGF-mediated
promotion of human ovarian cancer cell invasion. Gynecol Oncol.
137:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Swiercz A, Dansonka-Mieszkowska A, Goryca
K, Kulinczak M, Zajdel M, Chechlinska M, Rembiszewska A,
Kupryjańczyk J and Siwicki KJ: 273 MiR-7 Expression depends on TP53
mutational status in primary serous ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer.
48 Suppl 5:S66–S67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Furlong F, Fitzpatrick P, O'Toole S,
Phelan S, McGrogan B, Maguire A, O'Grady A, Gallagher M, Prencipe
M, McGoldrick A, et al: Low MAD2 expression levels associate with
reduced progression-free survival in patients with high-grade
serous epithelial ovarian cancer. J Pathol. 226:746–755. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jang SG, Yoo CW, Park SY, Kang S and Kim
HK: Low expression of miR-449 in gynecologic clear cell carcinoma.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 24:1558–1563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kan CW, Hahn MA, Gard GB, Maidens J, Huh
JY, Marsh DJ and Howell VM: Elevated levels of circulating
microRNA-200 family members correlate with serous epithelial
ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:6272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chong GO, Jeon HS, Han HS, Son JW, Lee YH,
Hong DG, Lee YS and Cho YL: Differential microRNA expression
profiles in primary and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.
Anticancer Res. 35:2611–2617. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang P, Wang M, Jie ZH, Shuang T, Yan XY,
Zhou YY and Wu JL: Detection and significance of miR-210 in
chemotherapy resistant and chemotherapy sensitive ovarian serous
carcinoma. J China Med Univ. 43:487–492. 2014.
|
|
76
|
Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS,
Karolchik D, Cline MS, Goldman M, Barber GP, Clawson H, Coelho A,
et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2011. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:(Database Issue). D876–D882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chekmenev DS, Haid C and Kel AE: P-Match:
Transcription factor binding site search by combining patterns and
weight matrices. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:W432–W437. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wingender E, Dietze P, Karas H and Knüppel
R: TRANSFAC: A database on transcription factors and their DNA
binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 24:238–241. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL,
Hainaut P and Olivier M: TP53 mutations in human cancers:
Functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes.
Oncogene. 26:2157–2165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature.
474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Creighton CJ, Fountain MD, Yu Z, Nagaraja
AK, Zhu H, Khan M, Olokpa E, Zariff A, Gunaratne PH, Matzuk MM and
Anderson ML: Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for
microRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian
carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res. 70:1906–1915. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yang D, Sun Y, Hu L, Zheng H, Ji P, Pecot
CV, Zhao Y, Reynolds S, Cheng H, Rupaimoole R, et al: Integrated
analyses identify a master microRNA regulatory network for the
mesenchymal subtype in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell.
23:186–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ibrahim FF, Jamal R, Syafruddin SE,
Mutalib Ab NS, Saidin S, MdZin RR, Mollah Hossain MM and Mokhtar
NM: microRNA-200c and microRNA-31 regulate proliferation, colony
formation, migration and invasion in serous ovarian cancer. J
Ovarian Res. 8:562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Spizzo R, Nicoloso MS, Lupini L, Lu Y,
Fogarty J, Rossi S, Zagatti B, Fabbri M, Veronese A, Liu X, et al:
miR-145 participates with TP53 in a death-promoting regulatory loop
and targets estrogen receptor-alpha in human breast cancer cells.
Cell Death Differ. 17:246–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|