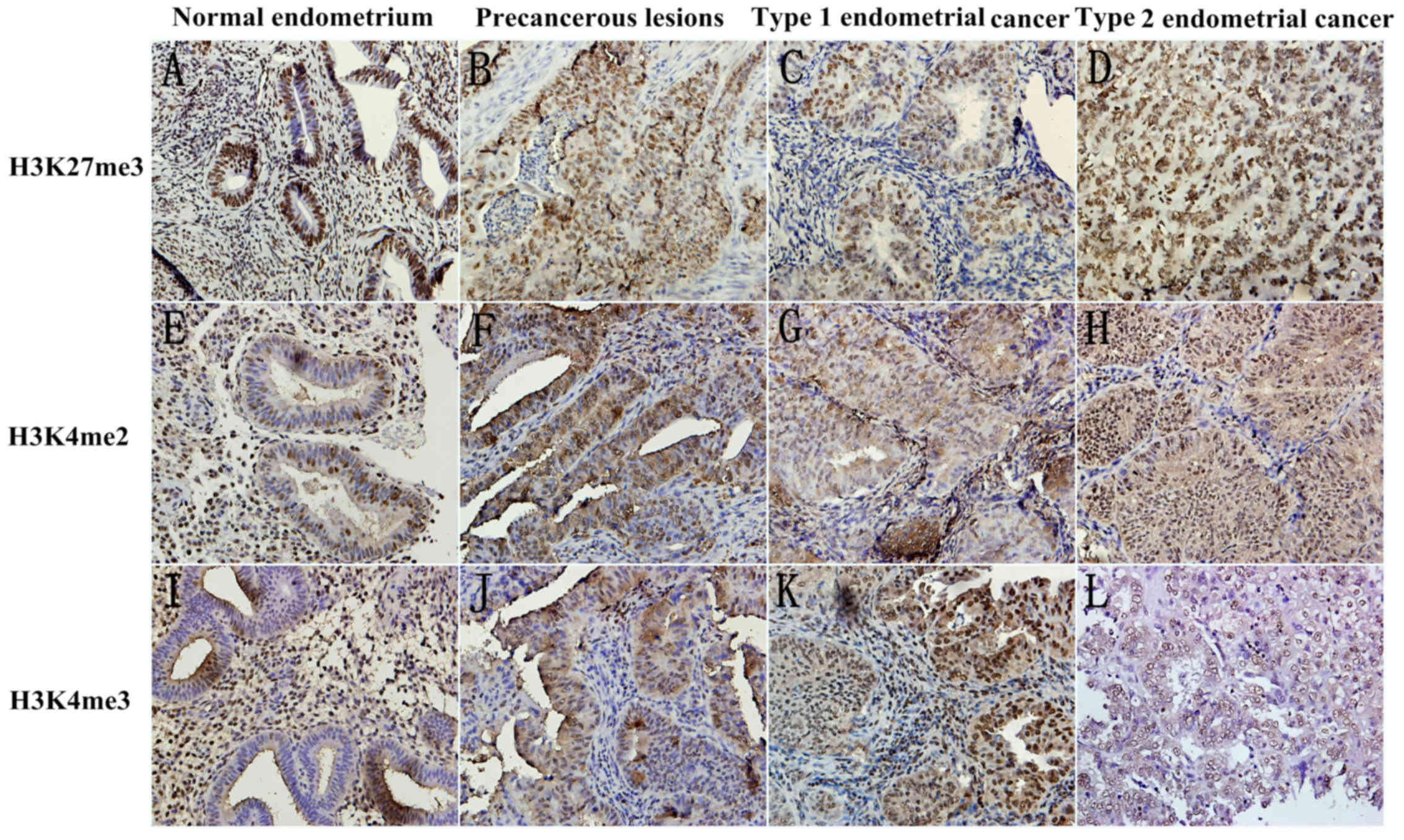
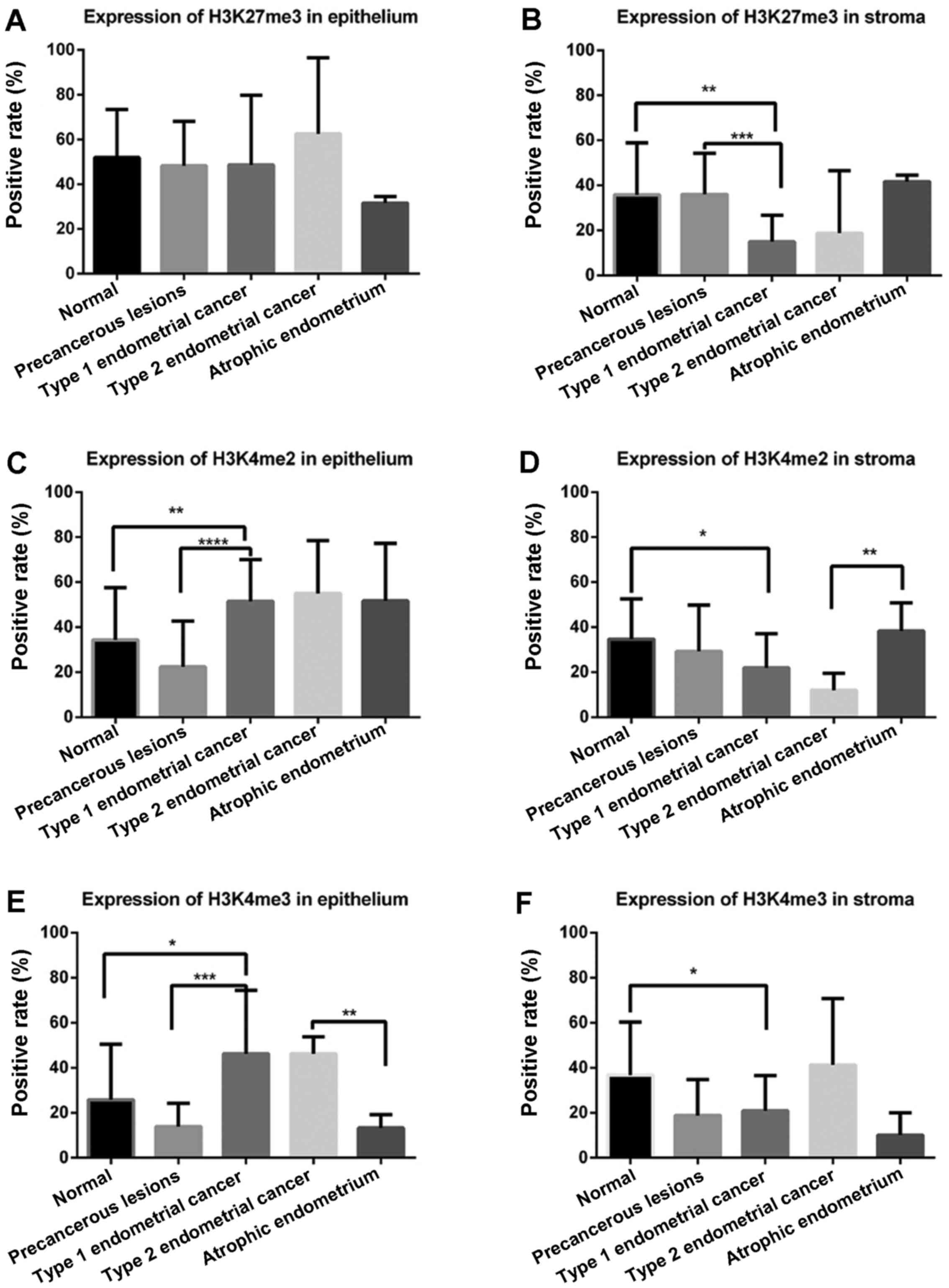
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao Y, Hyttel P and Hall VJ: Regulation of
H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 during early porcine embryonic development.
Mol Reprod Dev. 77:540–549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benard A, Goossens-Beumer IJ, van Hoesel
AQ, de Graaf W, Horati H, Putter H, Zeestraten EC, van de Velde CJ
and Kuppen PJ: Histone trimethylation at H3K4, H3K9 and H4K20
correlates with patient survival and tumor recurrence in
early-stage colon cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:5312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deb M, Kar S, Sengupta D, Shilpi A, Parbin
S, Rath SK, Londhe VA and Patra SK: Chromatin dynamics: H3K4
methylation and H3 variant replacement during development and in
cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:3439–3463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tao H, Li H, Su Y, Feng D, Wang X, Zhang
C, Ma H and Hu Q: Histone methyltransferase G9a and H3K9
dimethylation inhibit the self-renewal of glioma cancer stem cells.
Mol Cell Biochem. 394:23–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ngollo M, Lebert A, Dagdemir A, Judes G,
Karsli-Ceppioglu S, Daures M, Kemeny JL, Penault-Llorca F, Boiteux
JP, Bignon YJ, et al: The association between histone 3 lysine 27
trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: Relationship with
clinicopathological parameters. BMC Cancer. 14:9942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park KC, Heo JH, Jeon JY, Choi HJ, Jo AR,
Kim SW, Kwon HJ, Hong SJ and Han KS: The novel histone deacetylase
inhibitor, N-hydroxy-7-(2-naphthylthio) hepatonomide, exhibits
potent antitumor activity due to cytochrome-c-release-mediated
apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 15:192015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Langevin SM, Kratzke RA and Kelsey KT:
Epigenetics of lung cancer. Transl Res. 165:74–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang WY, Gu JL and Zhen TM: Recent
advances of histone modification in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res
Ther. 10 Suppl:S240–S245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lyu T, Jia N, Wang J, Yan X, Yu Y, Lu Z,
Bast RC Jr, Hua K and Feng W: Expression and epigenetic regulation
of angiogenesis-related factors during dormancy and recurrent
growth of ovarian carcinoma. Epigenetics. 8:1330–1346. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li LL, Xue AM, Li BX, Shen YW, Li YH, Luo
CL, Zhang MC, Jiang JQ, Xu ZD, Xie JH and Zhao ZQ: Erratum to:
JMJD2A contributes to breast cancer progression through
transcriptional repression of the tumor suppressor ARHI. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:1142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stenchever MA, Rizk DE, Falconi G and
Ortiz OC: FIGO task force on standard guidelines for training
residents and fellows in urogynecology, female urolog: FIGO
guidelines for training residents and fellows in urogynecology,
female urology, and female pelvic medicine and reconstructive
surgery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 107:187–190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jia N, Wang J, Li Q, Tao X, Chang K, Hua
K, Yu Y, Wong KK and Feng W: DNA methylation promotes paired box 2
expression via myeloid zinc finger 1 in endometrial cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:84785–84797. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yanokura M, Banno K, Adachi M, Aoki D and
Abe K: Genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing reveals miR-663a is a
novel epimutation candidate in CIMP-high endometrial cancer. Int J
Oncol. 50:1934–1946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones A, Teschendorff AE, Li Q, Hayward
JD, Kannan A, Mould T, West J, Zikan M, Cibula D, Fiegl H, et al:
Role of DNA methylation and epigenetic silencing of HAND2 in
endometrial cancer development. PLoS Med. 10:e10015512013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li K, Chen MK, Situ J, Huang WT, Su ZL, He
D and Gao X: Role of co-expression of c-Myc, EZH2 and p27 in
prognosis of prostate cancer patients after surgery. Chin Med J
(Engl). 126:82–87. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia N, Li Q, Tao X, Wang J, Hua K and Feng
W: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 is involved in the proliferation of
endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 8:2049–2054. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gnani D, Romito I, Artuso S, Chierici M,
De Stefanis C, Panera N, Crudele A, Ceccarelli S, Carcarino E,
D'Oria V, et al: Focal adhesion kinase depletion reduces human
hepatocellular carcinoma growth by repressing enhancer of zeste
homolog 2. Cell Death Differ. 24:889–902. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei Y, Xia W, Zhang Z, Liu J, Wang H,
Adsay NV, Albarracin C, Yu D, Abbruzzese JL, Mills GB, et al: Loss
of trimethylation at lysine 27 of histone H3 is a predictor of poor
outcome in breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. Mol Carcinog.
47:701–706. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rogenhofer S, Kahl P, Mertens C, Hauser S,
Hartmann W, Büttner R, Müller SC, von Ruecker A and Ellinger J:
Global histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27) methylation levels and their
prognostic relevance in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 109:459–465.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen Y, Guo X, Wang Y, Qiu W, Chang Y,
Zhang A and Duan X: Expression and significance of histone H3K27
demethylases in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 12:4702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pellakuru LG, Iwata T, Gurel B, Schultz D,
Hicks J, Bethel C, Yegnasubramanian S and De Marzo AM: Global
levels of H3K27me3 track with differentiation in vivo and are
deregulated by MYC in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 181:560–569.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakazawa T, Kondo T, Ma D, Niu D,
Mochizuki K, Kawasaki T, Yamane T, Iino H, Fujii H and Katoh R:
Global histone modification of histone H3 in colorectal cancer and
its precursor lesions. Hum Pathol. 43:834–842. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He LJ, Cai MY, Xu GL, Li JJ, Weng ZJ, Xu
DZ, Luo GY, Zhu SL and Xie D: Prognostic significance of
overexpression of EZH2 and H3k27me3 proteins in gastric cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3173–3178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Wong CM and Ng IO:
EZH2-mediated H3K27me3 is involved in epigenetic repression of
deleted in liver cancer 1 in human cancers. PLoS One. 8:e682262013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan W, Wang L, Ma Q, Qi M, Lu N, Zhang L
and Han B: Adiponectin as a potential tumor suppressor inhibiting
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition but frequently silenced in
prostate cancer by promoter methylation. Prostate. 75:1197–1205.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng F, Shi J, Long Y, Tian H, Li X, Zhao
AZ, Li RF and Chen T: Adiponectin and endometrial cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1670–1678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mancuso M, Matassa DS, Conte M, Colella G,
Rana G, Fucci L and Piscopo M: H3K4 histone methylation in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim Pol. 56:405–410.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Elsheikh SE, Green AR, Rakha EA, Powe DG,
Ahmed RA, Collins HM, Soria D, Garibaldi JM, Paish CE, Ammar AA, et
al: Global histone modifications in breast cancer correlate with
tumor phenotypes, prognostic factors, and patient outcome. Cancer
Res. 69:3802–3809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Manuyakorn A, Paulus R, Farrell J, Dawson
NA, Tze S, Cheung-Lau G, Hines OJ, Reber H, Seligson DB, Horvath S,
et al: Cellular histone modification patterns predict prognosis and
treatment response in resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: results
from RTOG 9704. J Clin Oncol. 28:1358–1365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seligson DB, Horvath S, McBrian MA, Mah V,
Yu H, Tze S, Wang Q, Chia D, Goodglick L and Kurdistani SK: Global
levels of histone modifications predict prognosis in different
cancers. Am J Pathol. 174:1619–1628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lei Q, Liu X, Fu H, Sun Y, Wang L, Xu G,
Wang W, Yu Z, Liu C, Li P, et al: miR-101 reverses hypomethylation
of the PRDM16 promoter to disrupt mitochondrial function in
astrocytoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:5007–5022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu X, Lei Q, Yu Z, Xu G, Tang H, Wang W,
Wang Z, Li G and Wu M: MiR-101 reverses the hypomethylation of the
LMO3 promoter in glioma cells. Oncotarget. 6:7930–7943. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cannuyer J, Loriot A, Parvizi GK and De
Smet C: Epigenetic hierarchy within the MAGEA1 cancer-germline
gene: Promoter DNA methylation dictates local histone
modifications. PLoS One. 8:e587432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He C, Xu J, Zhang J, Xie D, Ye H, Xiao Z,
Cai M, Xu K, Zeng Y, Li H and Wang J: High expression of
trimethylated histone H3 lysine 4 is associated with poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 43:1425–1435. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ellinger J, Kahl P, Mertens C, Rogenhofer
S, Hauser S, Hartmann W, Bastian PJ, Büttner R, Müller SC and von
Ruecker A: Prognostic relevance of global histone H3 lysine 4
(H3K4) methylation in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
127:2360–2366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Soussi T: Role of the p53 gene in human
malignant tumors. A major discovery in oncology. Rev Prat.
43:2531–2535. 1993.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tang Z, Chen WY, Shimada M, Nguyen UT, Kim
J, Sun XJ, Sengoku T, McGinty RK, Fernandez JP, Muir TW and Roeder
RG: SET1 and p300 act synergistically, through coupled histone
modifications, in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell.
154:297–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mungamuri SK, Wang S, Manfredi JJ, Gu W
and Aaronson SA: Ash2L enables P53-dependent apoptosis by favoring
stable transcription pre-initiation complex formation on its
pro-apoptotic target promoters. Oncogene. 34:2461–2470. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lauberth SM, Nakayama T, Wu X, Ferris AL,
Tang Z, Hughes SH and Roeder RG: H3K4me3 interactions with TAF3
regulate preinitiation complex assembly and selective gene
activation. Cell. 152:1021–1036. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stewart CA, Wang Y, Bonilla-Claudio M,
Martin JF, Gonzalez G, Taketo MM and Behringer RR: CTNNB1 in
mesenchyme regulates epithelial cell differentiation during
Müllerian duct and postnatal uterine development. Mol Endocrinol.
27:1442–1454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ishikawa A, Kudo M, Nakazawa N, Onda M,
Ishiwata T, Takeshita T and Naito Z: Expression of keratinocyte
growth factor and its receptor in human endometrial cancer in
cooperation with steroid hormones. Int J Oncol. 32:565–574.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lessey BA, Albelda S, Buck CA, Castelbaum
AJ, Yeh I, Kohler M and Berchuck A: Distribution of integrin cell
adhesion molecules in endometrial cancer. Am J Pathol. 146:717–726.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|