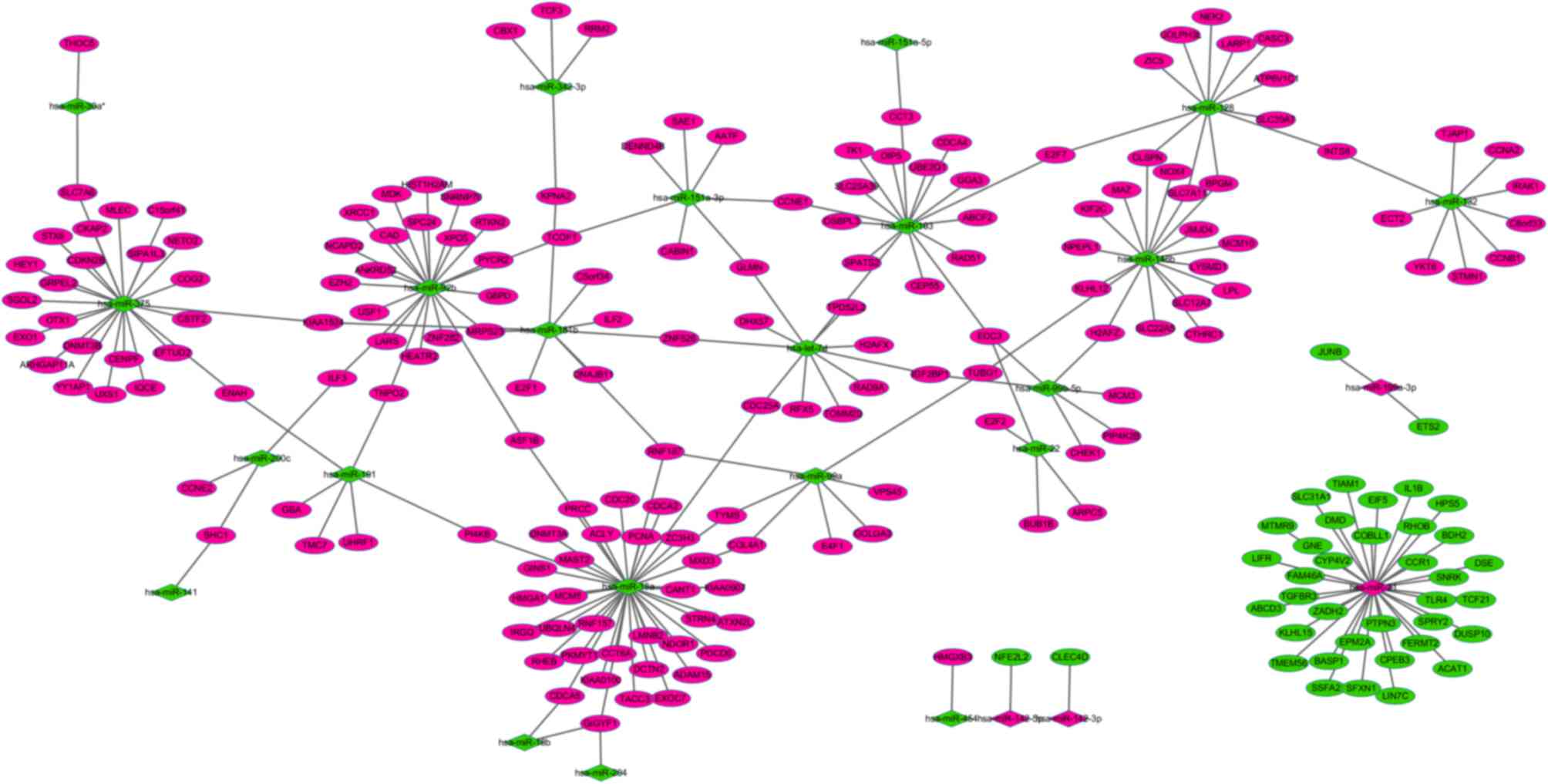
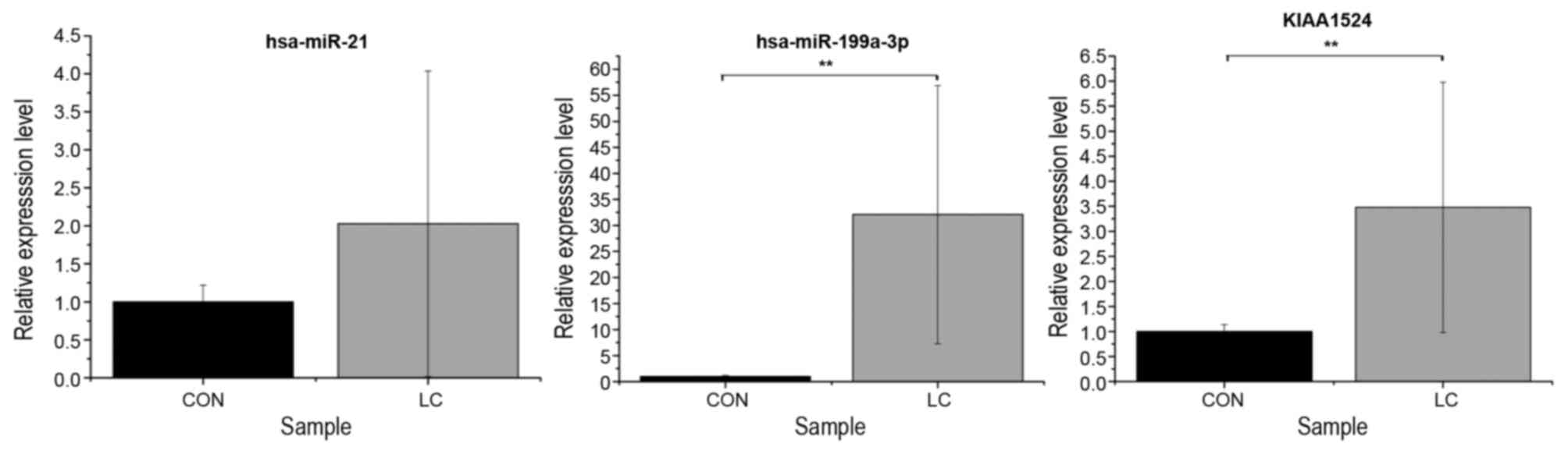
|
1
|
Schuppan D and Afdhal NH: Liver cirrhosis.
Lancet. 371:838–851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siddique I, El-Naga HA, Madda JP, Memon A
and Hasan F: Sampling variability on percutaneous liver biopsy in
patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 38:427–432. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bedossa P, Dargere D and Paradis V:
Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 38:1449–1457. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, Milikowski
C, Molina EG, Pyrsopoulos NT, Feng ZZ, Reddy KR and Schiff ER:
Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in
patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol.
97:2614–2618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, Gombert
S, Giral P, Bruckert E, Grimaldi A, Capron F and Poynard T; LIDO
Study Group, : Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 128:1898–1906. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Povero D, Busletta C, Novo E, di Bonzo LV,
Cannito S, Paternostro C and Parola M: Liver fibrosis: A dynamic
and potentially reversible process. Histol Histopathol.
25:1075–1091. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pinzani M and Vizzutti F: Fibrosis and
cirrhosis reversibility: Clinical features and implications. Clin
Liver Dis. 12:901–913, x. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gieling RG, Burt AD and Mann DA: Fibrosis
and cirrhosis reversibility-molecular mechanisms. Clin Liver Dis.
12:915–937, xi. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
10513–10518. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elfimova N, Schlattjan M, Sowa JP, Dienes
HP, Canbay A and Odenthal M: Circulating microRNAs: Promising
candidates serving as novel biomarkers of acute hepatitis. Front
Physiol. 3:4762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang XW, Heegaard NH and Orum H: MicroRNAs
in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 142:1431–1443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Borel F, Konstantinova P and Jansen PL:
Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of miRNA signatures in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:1371–1383.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: MicroRNAs: New
tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma? Hepatology. 57:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F,
Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP and Odenthal M: MicroRNA gene
expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:1223–1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gupta A, Swaminathan G, Martin-Garcia J
and Navas-Martin S: MicroRNAs, hepatitis C virus and HCV/HIV-1
co-infection: New insights in pathogenesis and therapy. Viruses.
4:2485–2513. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lanford RE, Hildebrandt-Eriksen ES, Petri
A, Persson R, Lindow M, Munk ME, Kauppinen S and Ørum H:
Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic
hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 327:198–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem
S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A,
Zhou Y, et al: Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N
Engl J Med. 368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Noetel A, Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Huang
J and Odenthal M: microRNA are central players in anti- and
profibrotic gene regulation during liver fibrosis. Front Physiol.
3:492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong CM, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Au SL
and Ng IO: Sequential alterations of microRNA expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma development and venous metastasis.
Hepatology. 55:1453–1461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database Issue):
D991–D995. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W and Smyth GK: Voom:
Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq
read counts. Genome Biol. 15:R292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK and
Oshlack A: Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for
selection bias. Genome Biol. 11:R142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Visone R and Croce CM: MiRNAs and cancer.
Am J Pathol. 174:1131–1138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose
JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: Key players in carcinogenesis and
novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ajit SK: Circulating microRNAs as
biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and signaling molecules. Sensors
(Basel). 12:3359–3369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bala S and Szabo G: MicroRNA signature in
alcoholic liver disease. Int J Hepatol. 2012:4982322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li L, Guo Z, Wang J, Mao Y and Gao Q:
Serum miR-18a: A potential marker for hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma screening. Dig Dis Sci. 57:2910–2916.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brockhausen J, Tay SS, Grzelak CA,
Bertolino P, Bowen DG, D'Avigdor WM, Teoh N, Pok S, Shackel N,
Gamble JR, et al: miR-181a mediates TGF-β-induced hepatocyte EMT
and is dysregulated in cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer. Liver
Int. 35:240–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao J, Tang N, Wu K, Dai W, Ye C, Shi J,
Zhang J, Ning B, Zeng X and Lin Y: miR-21 simultaneously regulates
ERK1 signaling in HSC activation and hepatocyte EMT in hepatic
fibrosis. PLoS One. 9:e1080052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang T, Zhang L, Shi C, Sun H, Wang J, Li
R, Zou Z, Ran X and Su Y: TGF-β-induced miR-21 negatively regulates
the antiproliferative activity but has no effect on EMT of TGF-β in
HaCaT cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:366–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL,
Ghosh S, Li T, McKillop IH, Russo MW, Bonkovsky HL and Schrum LW:
Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate
cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 56:300–310. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T,
Kissler S, Bussen M, Galuppo P, Just S, Rottbauer W, Frantz S, et
al: MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating
MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature. 456:980–984. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pandit KV, Milosevic J and Kaminski N:
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Transl Res.
157:191–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Niu J, Shi Y, Tan G, Yang CH, Fan M,
Pfeffer LM and Wu ZH: DNA damage induces NF-κB-dependent
microRNA-21 up-regulation and promotes breast cancer cell invasion.
J Biol Chem. 287:21783–21795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bakirtzi K, Hatziapostolou M,
Karagiannides I, Polytarchou C, Jaeger S, Iliopoulos D and
Pothoulakis C: Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and
−155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice, and is increased in
human colon tumors. Gastroenterology. 141:1749–1761 e1. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Murakami Y, Toyoda H, Tanaka M, Kuroda M,
Harada Y, Matsuda F, Tajima A, Kosaka N, Ochiya T and Shimotohno K:
The progression of liver fibrosis is related with overexpression of
the miR-199 and 200 families. PLoS One. 6:e160812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsang FH, Au SL, Wei L, Fan DN, Lee JM,
Wong CC, Ng IO and Wong CM: MicroRNA-142-3p and microRNA-142-5p are
downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and exhibit synergistic
effects on cell motility. Front Med. 9:331–343. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang B, Li W, Guo K, Xiao Y, Wang Y and
Fan J: miR-181b promotes hepatic stellate cells proliferation by
targeting p27 and is elevated in the serum of cirrhosis patients.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:4–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Znoyko I, Sohara N, Spicer SS, Trojanowska
M and Reuben A: Expression of oncostatin M and its receptors in
normal and cirrhotic human liver. J Hepatol. 43:893–900. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu HC, Chen HJ, Chang YL, Liu CY, Shiau
CW, Cheng AL and Chen KF: Inhibition of CIP2A determines
erlotinib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:356–366. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu HC, Hung MH, Chen YL, Chu PY, Wang CY,
Chao TT, Liu CY, Shiau CW and Chen KF: Erlotinib derivative
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CIP2A to reactivate
protein phosphatase 2A. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Junttila MR, Puustinen P, Niemelä M, Ahola
R, Arnold H, Böttzauw T, Ala-aho R, Nielsen C, Ivaska J, Taya Y, et
al: CIP2A inhibits PP2A in human malignancies. Cell. 130:51–62.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Y, Xu N, Xu J, Kong B, Copple B, Guo
GL and Wang L: E2F1 is a novel fibrogenic gene that regulates
cholestatic liver fibrosis through the Egr-1/SHP/EID1 network.
Hepatology. 60:919–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Swiatkowska A, Zydowicz P, Sroka J and
Ciesiolka J: The role of the 5′ terminal region of p53 mRNA in the
p53 gene expression. Acta Biochim Pol. 63:645–651. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yildiz G, Arslan-Ergul A, Bagislar S, Konu
O, Yuzugullu H, Gursoy-Yuzugullu O, Ozturk N, Ozen C, Ozdag H,
Erdal E, et al: Genome-wide transcriptional reorganization
associated with senescence-to-immortality switch during human
hepatocellular carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e640162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Archer KJ, Mas VR, David K, Maluf DG,
Bornstein K and Fisher RA: Identifying genes for establishing a
multigenic test for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in
hepatitis C virus-positive cirrhotic patients. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 18:2929–2932. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Kong
X, Kulik L, Freise CE, Olthoff KM, Ghobrial RM, McIver P and Fisher
R: Genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor initiation in
hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med.
15:85–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Caillot F, Derambure C, Bioulac-Sage P,
Francois A, Scotte M, Goria O, Hiron M, Daveau M and Salier JP:
Transient and etiology-related transcription regulation in
cirrhosis prior to hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:300–309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wojcicka A, Swierniak M, Kornasiewicz O,
Gierlikowski W, Maciag M, Kolanowska M, Kotlarek M, Gornicka B,
Koperski L, Niewinski G, et al: Next generation sequencing reveals
microRNA isoforms in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 53:208–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vuppalanchi R, Liang T, Goswami CP,
Nalamasu R, Li L, Jones D, Wei R, Liu W, Sarasani V, Janga SC and
Chalasani N: Relationship between differential hepatic microRNA
expression and decreased hepatic cytochrome P450 3A activity in
cirrhosis. PLoS One. 8:e744712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|