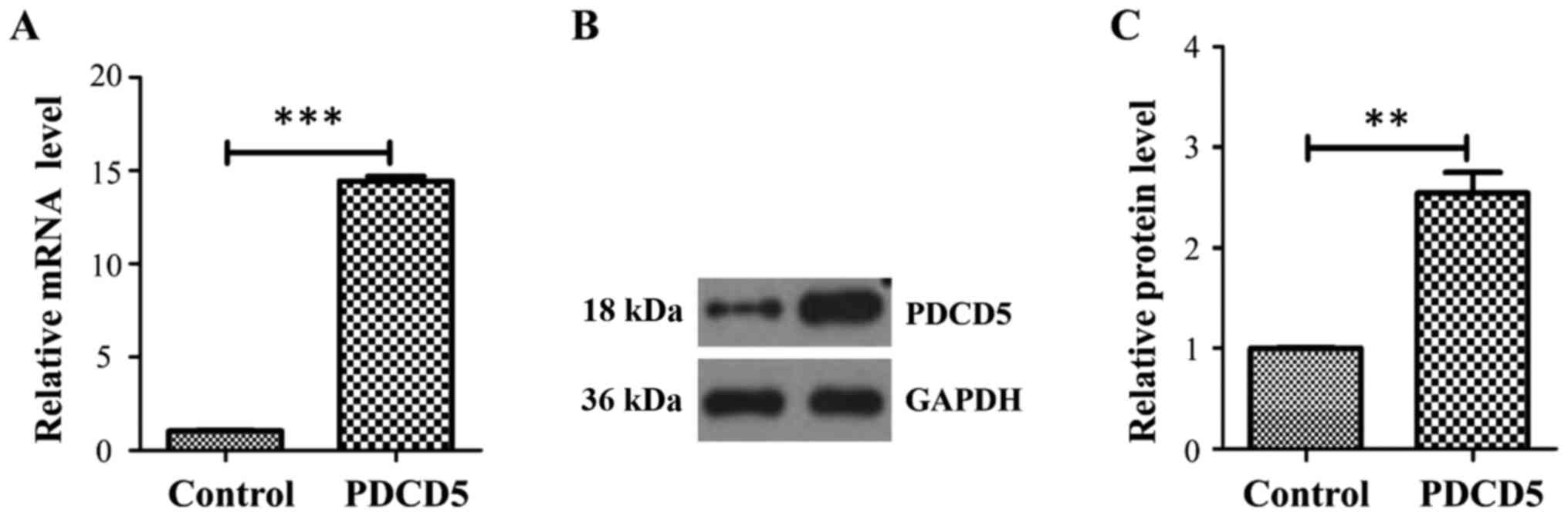
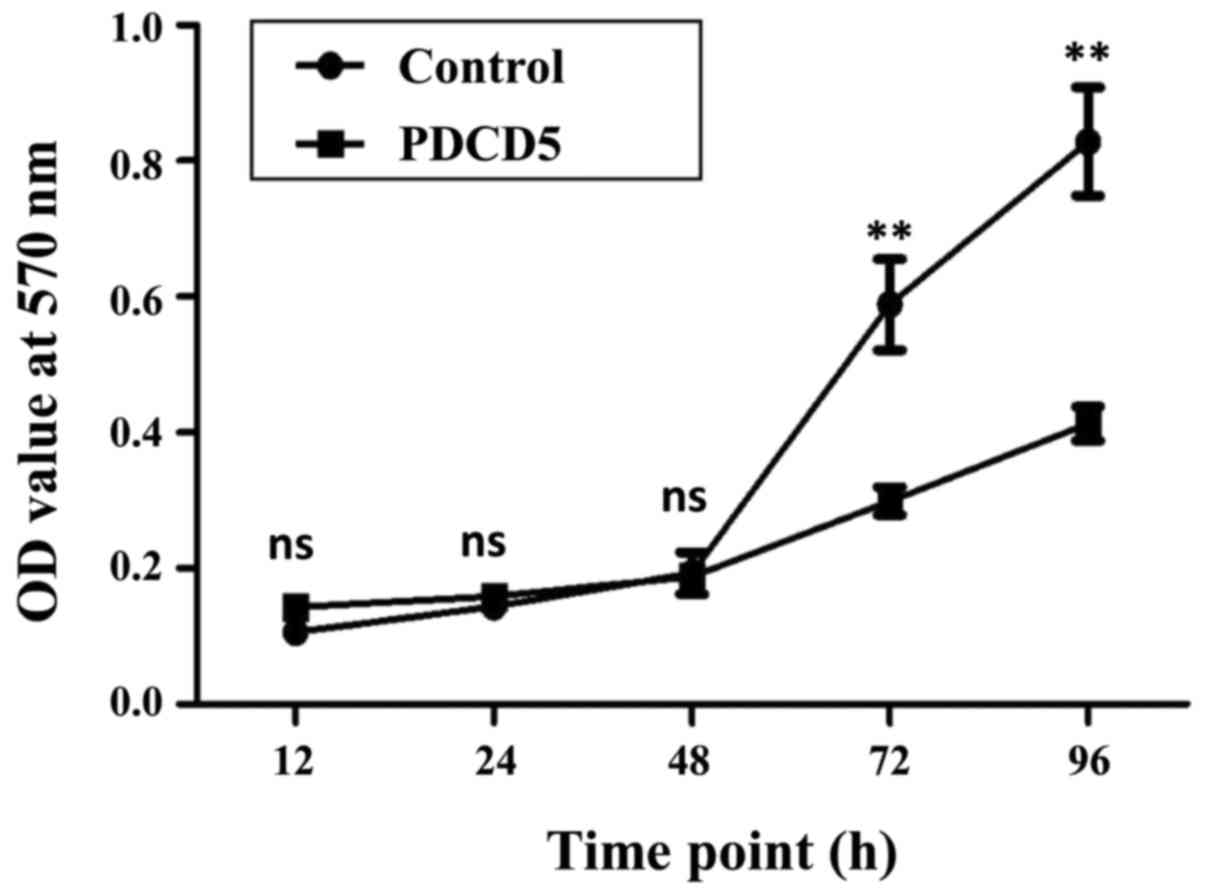
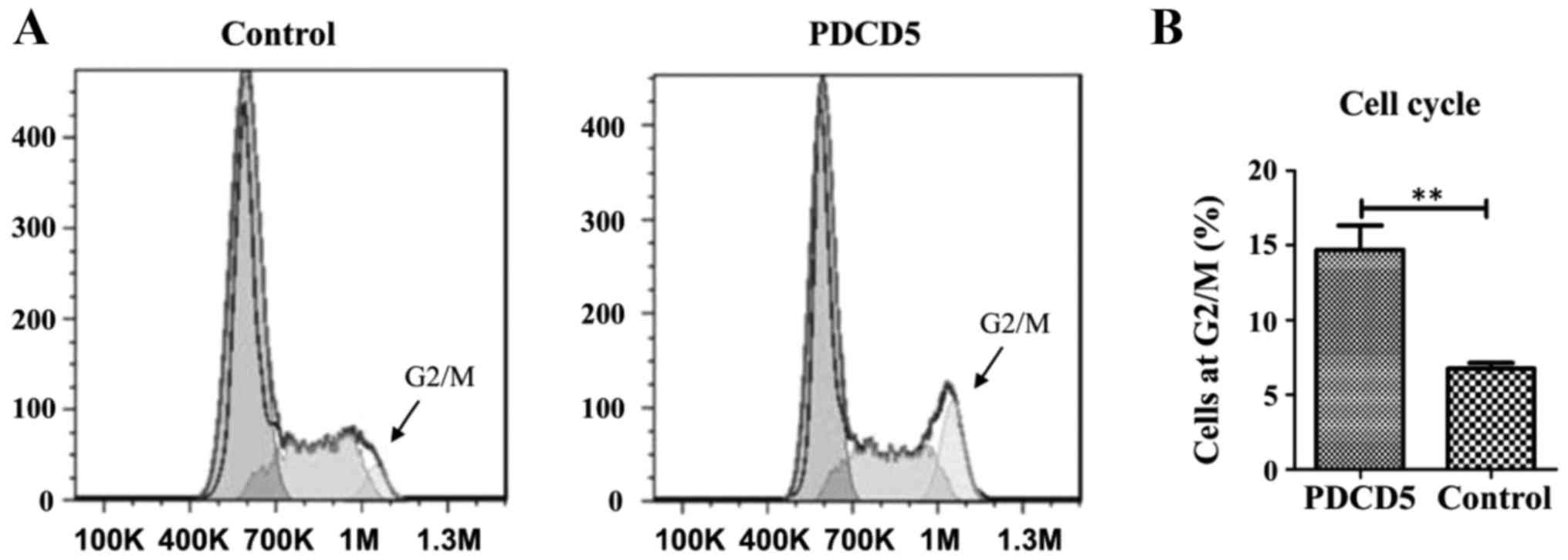
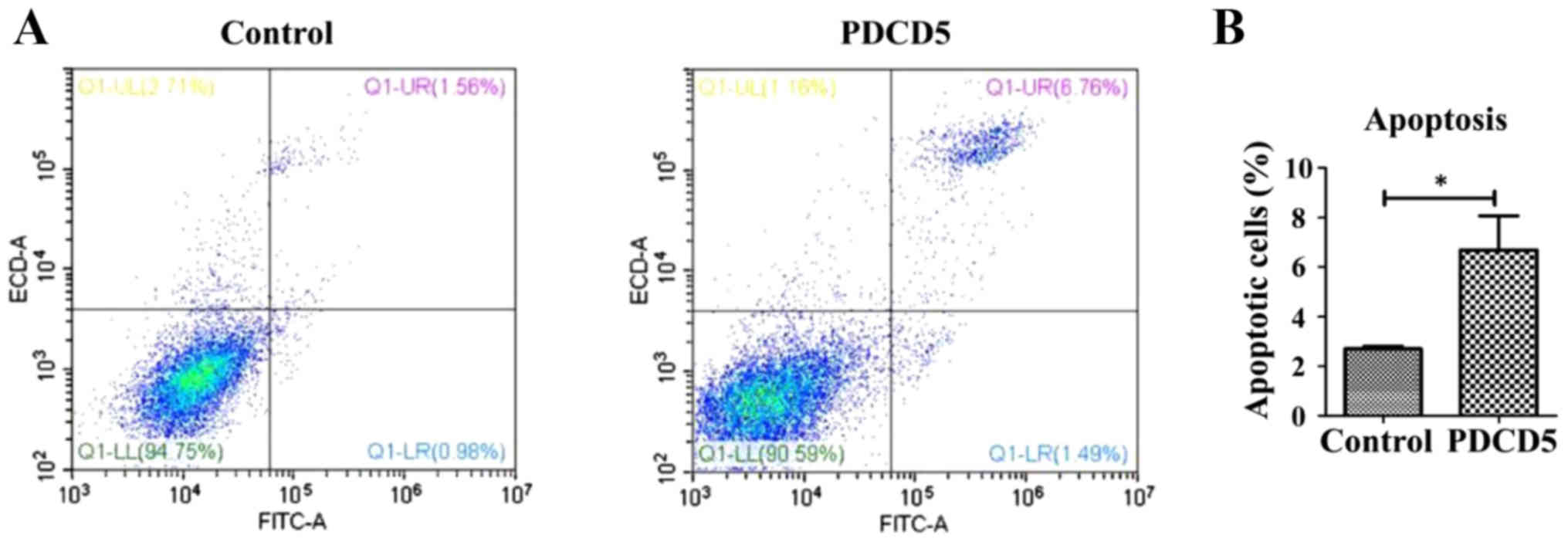
|
1
|
Hipfner DR and Cohen SM: Connecting
proliferation and apoptosis in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 5:805–815. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Löbrich M and Jeggo PA: The impact of a
negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer
induction. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:861–869. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alenzi FQ: Links between apoptosis,
proliferation and the cell cycle. Br J Biomed Sci. 61:99–102. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Song Q, Di C, Chen
G, Tang J and Ma D: TFAR19, a novel apoptosis-related gene cloned
from human leukemia cell line TF-1, could enhance apoptosis of some
tumor cells induced by growth factor withdrawal. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 254:203–210. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang N, Lu HS, Guan ZP, Sun TZ, Chen YY,
Ruan GR, Chen ZK, Jiang J and Bai CJ: Involvement of PDCD5 in the
regulation of apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of
rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis. 12:1433–1441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen LN, Wang Y, Ma DL and Chen YY: Short
interfering RNA against the PDCD5 attenuates cell apoptosis and
caspase-3 activity induced by Bax overexpression. Apoptosis.
11:101–111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang YH, Zhao M, Li WM and Lu YY, Chen YY,
Kang B and Lu YY: Expression of programmed cell death 5 gene
involves in regulation of apoptosis in gastric tumor cells.
Apoptosis. 11:993–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruan GR, Zhao HS, Chang Y, Li JL, Qin YZ,
Liu YR, Chen SS and Huang XJ: Adenovirus-mediated PDCD5 gene
transfer sensitizes K562 cells to apoptosis induced by idarubicin
in vitro and in vivo. Apoptosis. 13:641–648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Salvi M, Xu D, Chen Y, Cabrelle A, Sarno S
and Pinna LA: Programmed cell death protein 5 (PDCD5) is
phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro and in 293T cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 387:606–610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li G, Ma D and Chen Y: Cellular functions
of programmed cell death 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:572–580.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Li X, Wang L, Ding P, Zhang Y, Han
W and Ma D: An alternative form of paraptosis-like cell death,
triggered by TAJ/TROY and enhanced by PDCD5 overexpression. J Cell
Sci. 117:1525–1532. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang S, Li G, Fu X, Qi Y, Li M, Lu G, Hu
J, Wang N, Chen Y, Bai Y and Cui M: PDCD5 protects against cardiac
remodeling by regulating autophagy and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 461:321–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Wang Q, Gao F, Zhu F, Wang X, Zhou
C, Liu C, Chen Y, Ma C, Sun W and Zhang L: Reduced expression of
PDCD5 is associated with high-grade astrocytic gliomas. Oncol Rep.
20:573–579. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du YJ, Xiong L, Lou Y, Tan WL and Zheng
SB: Reduced expression of programmed cell death 5 protein in tissue
of human prostate cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 24:241–245. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Zhou H, Xu L, Liu X, Liu Z, Ma D,
Chen Y and Ma Q: Prognostic significance of downregulated
expression of programmed cell death 5 in chondrosarcoma. J Surg
Oncol. 102:838–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Wang X, Song X, Wei Z, Zhou C,
Zhu F, Wang Q, Ma C and Zhang L: Clinical and prognostic
significance of lost or decreased PDCD5 expression in human
epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 25:353–358. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wang GH and Zhang QY:
Determination of PDCD5 in peripheral blood serum of cancer
patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 23:224–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao M, Gao W, Wang Z, Liu Y, Li Y, Wei C,
Sun Y, Guo C, Zhang L, Wei Z and Wang X: The reduced PDCD5 protein
is correlated with the degree of tumor differentiation in
endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Springerplus. 5:9882016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Zou Z, Xu A, Liu Y, Pan H and Jin
L: Serum programmed cell death protein 5 (PDCD5) levels is
upregulated in liver diseases. J Immunoassay Immunochem.
34:294–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu F, Wu K, Zhao M, Qin Y and Xia M:
Expression and clinical significance of the programmed cell death 5
gene and protein in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Int Med
Res. 41:1838–1847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Wang W, Song CL and Xia P: The
roles of serum PDCD5 in circulating CD133 positive cells of the
patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:11799–11804. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Song XW and Zhao CH: Roles of
programmed cell death protein 5 in inflammation and cancer
(Review). Int J Oncol. 49:1801–1806. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi L, Song Q, Zhang Y, Lou Y and Wang Y,
Tian L, Zheng Y, Ma D, Ke X and Wang Y: Potent antitumor activities
of recombinant human PDCD5 protein in combination with chemotherapy
drugs in K562 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 396:224–230. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yin A, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zhao J and Luo H:
Transfection of PDCD5 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
649:120–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu HY, Chen ZW, Pan YM, Fan L, Guan J and
Lu YY: Transfection of PDCD5 effect on the biological behavior of
tumor cells and sensitized gastric cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Dig Dis Sci. 57:1847–1856. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han XR, Sun Y and Bai XZ: The anti-tumor
role and mechanism of integrated and truncated PDCD5 proteins in
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Signal. 24:1713–1721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Zhou G, La L, Chi X, Cao Y, Liu J,
Zhang Z, Chen Y and Wu B: Transgenic human programmed cell death 5
expression in mice suppresses skin cancer development by enhancing
apoptosis. Life Sci. 92:1208–1214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu W, Li Y and Gao L: Cisplatin in
combination with programmed cell death protein 5 increases
antitumor activity in prostate cancer cells by promoting apoptosis.
Mol Med Rep. 11:4561–4566. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu DZ, Cheng Y, He H, Liu HY and Liu YF:
Recombinant human PDCD5 exhibits an antitumor role in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
Mol Med Rep. 12:8135–8140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao L, Ye X, Ma RQ, Cheng HY, Han HJ, Cui
H, Wei LH and Chang XH: Low programmed cell death 5 expression is a
prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:1084–1090. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xiao J, Li G, Hu J, Qu L, Ma D and Chen Y:
Anti-inflammatory effects of recombinant human PDCD5 (rhPDCD5) in a
rat collagen-induced model of arthritis. Inflammation. 38:70–78.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiao J, Liu W, Chen Y and Deng W:
Recombinant human PDCD5 (rhPDCD5) protein is protective in a mouse
model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation. 12:1172015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu J, Jiang Z, Chen Y, Zhou C and Chen C:
Knockout of programmed cell death 5 (PDCD5) gene attenuates neuron
injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res.
1650:152–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spinola M, Meyer P, Kammerer S, Falvella
FS, Boettger MB, Hoyal CR, Pignatiello C, Fischer R, Roth RB,
Pastorino U, et al: Association of the PDCD5 locus with lung cancer
risk and prognosis in smokers. J Clin Oncol. 24:1672–1678. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nanba K, Toyooka S, Soh J, Tsukuda K,
Yamamoto H, Sakai A, Ouchida M, Kobayashi N, Matsuo K, Koide N, et
al: The allelic distribution of a single nucleotide polymorphism in
the PDCD5 gene locus of Japanese non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Mol Med Rep. 1:667–671. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu L, Chen Y, Song Q, Xu D, Wang Y and Ma
D: PDCD5 interacts with Tip60 and functions as a cooperator in
acetyltransferase activity and DNA damage-induced apoptosis.
Neoplasia. 11:345–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yao H, Feng Y, Zhou T, Wang J and Wang ZX:
NMR studies of the interaction between human programmed cell death
5 and human p53. Biochemistry. 51:2684–2693. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu L, Hu J, Zhao Y, Hu J, Xiao J, Wang Y,
Ma D and Chen Y: PDCD5 interacts with p53 and functions as a
positive regulator in the p53 pathway. Apoptosis. 17:1235–1245.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tracy CM, Gray AJ, Cuéllar J, Shaw TS,
Howlett AC, Taylor RM, Prince JT, Ahn NG, Valpuesta JM and
Willardson BM: Programmed cell death protein 5 interacts with the
cytosolic chaperonin containing tailless complex polypeptide 1
(CCT) to regulate β-tubulin folding. J Biol Chem. 289:4490–4502.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Essers PB, Klasson TD, Pereboom TC, Mans
DA, Nicastro M, Boldt K, Giles RH and MacInnes AW: The von
Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor regulates programmed cell death
5-mediated degradation of Mdm2. Oncogene. 34:771–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Park SY, Choi HK, Jo SH, Seo J, Han EJ,
Choi KC, Jeong JW, Choi Y and Yoon HG: YAF2 promotes TP53-mediated
genotoxic stress response via stabilization of PDCD5. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1853:1060–1072. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Choi HK, Choi Y, Park ES, Park SY, Lee SH,
Seo J, Jeong MH, Jeong JW, Jeong JH, Lee PC, et al: Programmed cell
death 5 mediates HDAC3 decay to promote genotoxic stress response.
Nat Commun. 6:73902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhuge C, Sun X, Chen Y and Lei J: PDCD5
functions as a regulator of p53 dynamics in the DNA damage
response. J Theor Biol. 388:1–10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murshed F, Farhana L, Dawson MI and
Fontana JA: NF-κB p65 recruited SHP regulates PDCD5-mediated
apoptosis in cancer cells. Apoptosis. 19:506–517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park SY, Choi HK, Choi Y, Kwak S, Choi KC
and Yoon HG: Deubiquitinase OTUD5 mediates the sequential
activation of PDCD5 and p53 in response to genotoxic stress. Cancer
Lett. 357:419–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cui X, Choi HK, Choi YS, Park SY, Sung GJ,
Lee YH, Lee J, Jun WJ, Kim K, Choi KC and Yoon HG: DNAJB1
destabilizes PDCD5 to suppress p53-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Lett.
357:307–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pucci B, Kasten M and Giordano A: Cell
cycle and apoptosis. Neoplasia. 2:291–299. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Leng C, Li Y, Qin J, Ma J, Liu X, Cui Y,
Sun H, Wang Z, Hua X, Yu Y, et al: Relationship between expression
of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the
antitumor effects of CD8+T cells. Oncol Rep. 35:699–708. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dong Y, Sun Q and Zhang X: PD-1 and its
ligands are important immune checkpoints in cancer. Oncotarget.
8:2171–2186. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bardhan K, Anagnostou T and Boussiotis VA:
The PD1:PD-L1/2 pathway from discovery to clinical implementation.
Front Immunol. 7:5502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Wei W, Jin HC, Ying RC, Zhu AK
and Zhang FJ: Programmed cell death 2 protein induces gastric
cancer cell growth arrest at the early S phase of the cell cycle
and apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner. Oncol Rep. 33:103–110.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Granier CJ, Wang W, Tsang T, Steward R,
Sabaawy HE, Bhaumik M and Rabson AB: Conditional inactivation of
PDCD2 induces p53 activation and cell cycle arrest. Biol Open.
3:821–831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sun Z, Li S, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE:
miR-21 increases the programmed cell death 4 gene-regulated cell
proliferation in head and neck squamous carcinoma cell lines. Oncol
Rep. 32:2283–2289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xia L, Wen H, Han X, Tang J and Huang Y:
Luteinizing hormone inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human
epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 11:1943–1947.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gao F, Ding L, Zhao M, Qu Z, Huang S and
Zhang L: The clinical significance of reduced programmed cell death
5 expression in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol Rep.
28:2195–2199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
McDermott DF and Atkins MB: PD-1 as a
potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2:662–673.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mo Z, Liu J, Zhang Q, Chen Z, Mei J, Liu
L, Yang S, Li H, Zhou L and You Z: Expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and
PD-L2 is associated with differentiation status and histological
type of endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:944–950. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wen YH, Shi X, Chiriboga L, Matsahashi S,
Yee H and Afonja O: Alterations in the expression of PDCD4 in
ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncol Rep. 18:1387–1393.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fassan M, Cagol M, Pennelli G, Rizzetto C,
Giacomelli L, Battaglia G, Zaninotto G, Ancona E, Ruol A and Rugge
M: Programmed cell death 4 protein in esophageal cancer. Oncol Rep.
24:135–139. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
González-Villasana V, Nieves-Alicea R,
McMurtry V, Gutiérrez-Puente Y and Tari AM: Programmed cell death 4
inhibits leptin-induced breast cancer cell invasion. Oncol Rep.
27:861–866. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Barboza N, Minakhina S, Medina DJ, Balsara
B, Greenwood S, Huzzy L, Rabson AB, Steward R and Schaar DG: PDCD2
functions in cancer cell proliferation and predicts relapsed
leukemia. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:546–555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zidovetzki R, Johnson DA, Arndt-Jovin DJ
and Jovin TM: Rotational mobility of high-affinity epidermal growth
factor receptors on the surface of living A431 cells. Biochemistry.
30:6162–6166. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu SL, Taylor AD, Lu Q, Hanash SM, Im H,
Snyder M and Hancock WS: Identification of potential glycan cancer
markers with sialic acid attached to sialic acid and up-regulated
fucosylated galactose structures in epidermal growth factor
receptor secreted from A431 cell line. Mol Cell Proteomics.
12:1239–1249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang F, Wang S, Yin L, Yang Y, Guan Y,
Wang W, Xu H and Tao N: Quantification of epidermal growth factor
receptor expression level and binding kinetics on cell surfaces by
surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal Chem. 87:9960–9965. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stanton P, Richards S, Reeves J, Nikolic
M, Edington K, Clark L, Robertson G, Souter D, Mitchell R, Hendler
FJ, et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression by human
squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck, cell lines and
xenografts. Br J Cancer. 70:427–433. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ozaki T and Nakagawara A: Role of p53 in
cell death and human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 3:994–1013. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Drosten M, Sum EY, Lechuga CG,
Simón-Carrasco L, Jacob HK, García-Medina R, Huang S, Beijersbergen
RL, Bernards R and Barbacid M: Loss of p53 induces cell
proliferation via Ras-independent activation of the Raf/Mek/Erk
signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:pp. 15155–15160.
2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang HT, Wang YL, Zhang J and Zhang QX:
Artemisinin inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation through
upregulation of p53. Tumour Biol. 35:1403–1409. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ranganathan S, Joseph J and Mehta JL:
Aspirin inhibits human coronary artery endothelial cell
proliferation by upregulation of p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
301:143–146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Taylor WR and Stark GR: Regulation of the
G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene. 20:1803–1815. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L,
Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR: Direct activation of
Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and
apoptosis. Science. 303:1010–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nakazawa K, Dashzeveg N and Yoshida K:
Tumor suppressor p53 induces miR-1915 processing to inhibit Bcl-2
in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. FEBS J. 281:2937–2944.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chui JH, Zhu GY, Li YW, Fong
DW and Yu ZL: Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through MAPK and p53 signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. Oncol Rep.
24:647–651. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ou X, Lu Y, Liao L, Li D, Liu L, Liu H and
Xu H: Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through a pathway involving p53, p21, Bax and
Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 33:1264–1274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhou Y and Ho WS: Combination of
liquiritin, isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin induce apoptotic cell
death through upregulating p53 and p21 in the A549 non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 31:298–304. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|