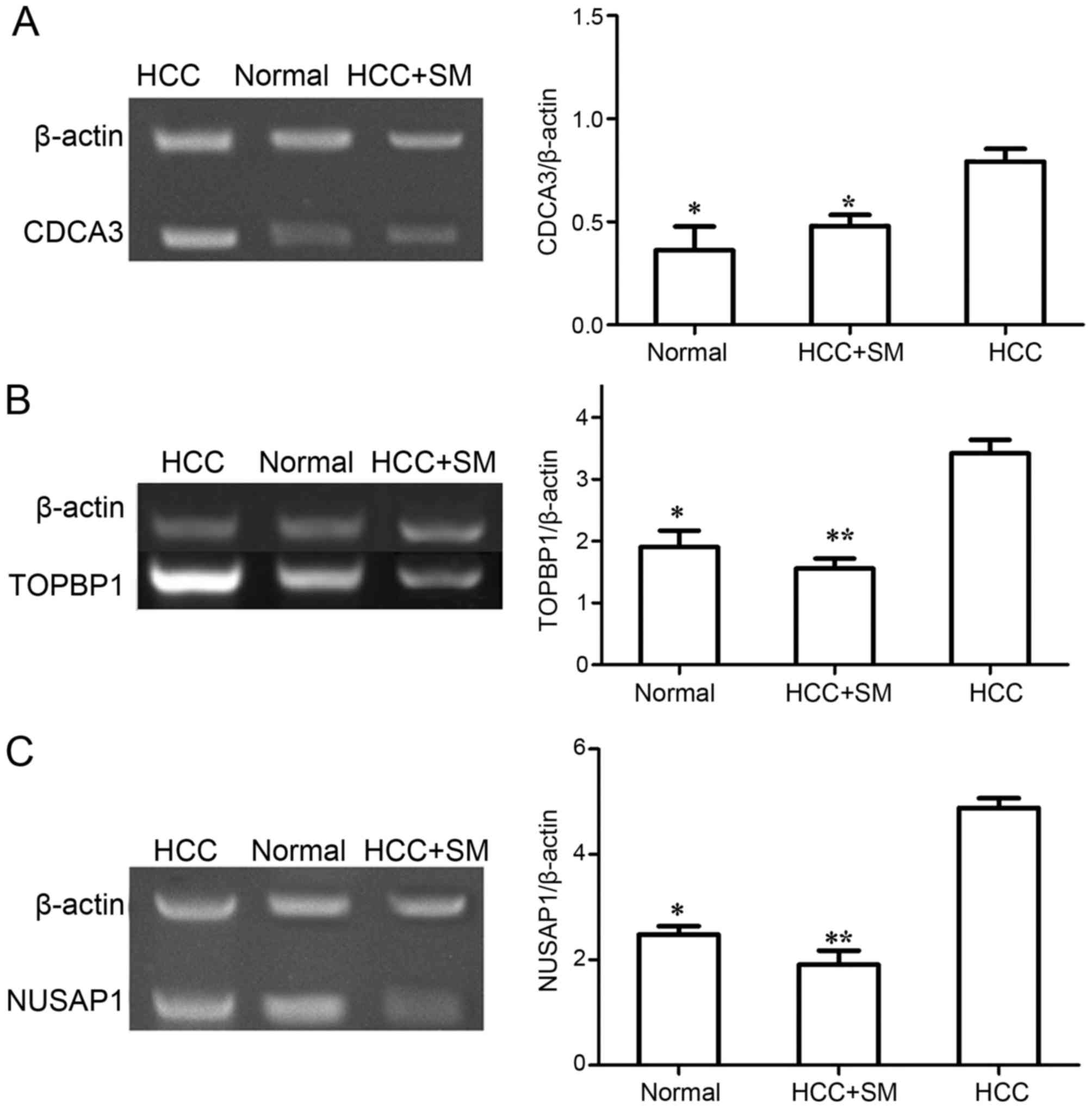
|
1
|
Romaguera D, Vergnaud AC, Peeters PH, van
Gils CH, Chan DS, Ferrari P, Romieu I, Jenab M, Slimani N,
Clavel-Chapelon F, et al: Is concordance with world cancer research
fund/American institute for cancer research guidelines for cancer
prevention related to subsequent risk of cancer? Results from the
EPIC study. Am J Clin Nutr. 96:150–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang YC, Wei LJ, Liu JT, Li SX and Wang
QS: Comparison of cancer incidence between China and the USA.
Cancer Biol Med. 9:128–132. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan M, Li T, Ahmad Khan MK, Rasul A,
Nawaz F, Sun M, Zheng Y and Ma T: Alantolactone induces apoptosis
in HepG2 cells through GSH depletion, inhibition of STAT3
activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed Res Int.
2013:7198582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kojima S, Okuno M, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R,
Friedman SL and Moriwaki H: Acyclic retinoid in the chemoprevention
of hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Int J Oncol. 24:797–805.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deep G, Gangar SC, Rajamanickam S, Raina
K, Gu M, Agarwal C, Oberlies NH and Agarwal R: Angiopreventive
efficacy of pure flavonolignans from milk thistle extract against
prostate cancer: Targeting VEGF-VEGFR signaling. PLoS One.
7:e346302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yurtcu E, Kasapoğlu E and Şahin Fİ:
Protective effects of β-carotene and silymarin on human
lymphocytes. Turk J Biol. 36:47–52. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Ramasamy K and Agarwal R: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett. 269:352–362. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He D, Liu ZP, Honda M, Kaneko S and Chen
L: Coexpression network analysis in chronic hepatitis B and C
hepatic lesions reveals distinct patterns of disease progression to
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Cell Biol. 4:140–152. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu ZP, Wang Y, Zhang XS and Chen L:
Network-based analysis of complex diseases. IET Syst Biol. 6:22–33.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma X, Gao L and Tan K: Modeling disease
progression using dynamics of pathway connectivity. Bioinformatics.
30:2343–2350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma S, Calhoun VD, Phlypo R and Adalı T:
Dynamic changes of spatial functional network connectivity in
healthy individuals and schizophrenia patients using independent
vector analysis. Neuroimage. 90:196–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruan J, Dean AK and Zhang W: A general
co-expression network-based approach to gene expression analysis:
Comparison and applications. BMC Syst Biol. 4:82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mao L, Van Hemert JL, Dash S and Dickerson
JA: Arabidopsis gene co-expression network and its functional
modules. BMC Bioinformatics. 10:3462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Han L, Yuan Y, Li J, Hei N and
Liang H: Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common
system-level properties of prognostic genes across cancer types.
Nat Commun. 5:32312014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma X, Gao L, Karamanlidis G, Gao P, Lee
CF, Garcia-Menendez L, Tian R and Tan K: Revealing pathway dynamics
in heart diseases by analyzing multiple differential networks. PLoS
Comput Biol. 11:e10043322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lovelace ES, Wagoner J, MacDonald J,
Bammler T, Bruckner J, Brownell J, Beyer RP, Zink EM, Kim YM, Kyle
JE, et al: Silymarin suppresses cellular inflammation by inducing
reparative stress signaling. J Nat Prod. 78:1990–2000. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mar JC, Matigian NA, Quackenbush J and
Wells CA: Attract: A method for identifying core pathways that
define cellular phenotypes. PLoS One. 6:e254452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watson-Haigh NS, Kadarmideen HN and
Reverter A: PCIT: An R package for weighted gene co-expression
networks based on partial correlation and information theory
approaches. Bioinformatics. 26:411–413. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N
and Golani I: Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior
genetics research. Behav Brain Res. 125:279–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database issue): D480–D484.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Post-White J, Ladas EJ and Kelly KM:
Advances in the use of milk thistle (Silybum marianum). Integr
Cancer Ther. 6:104–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
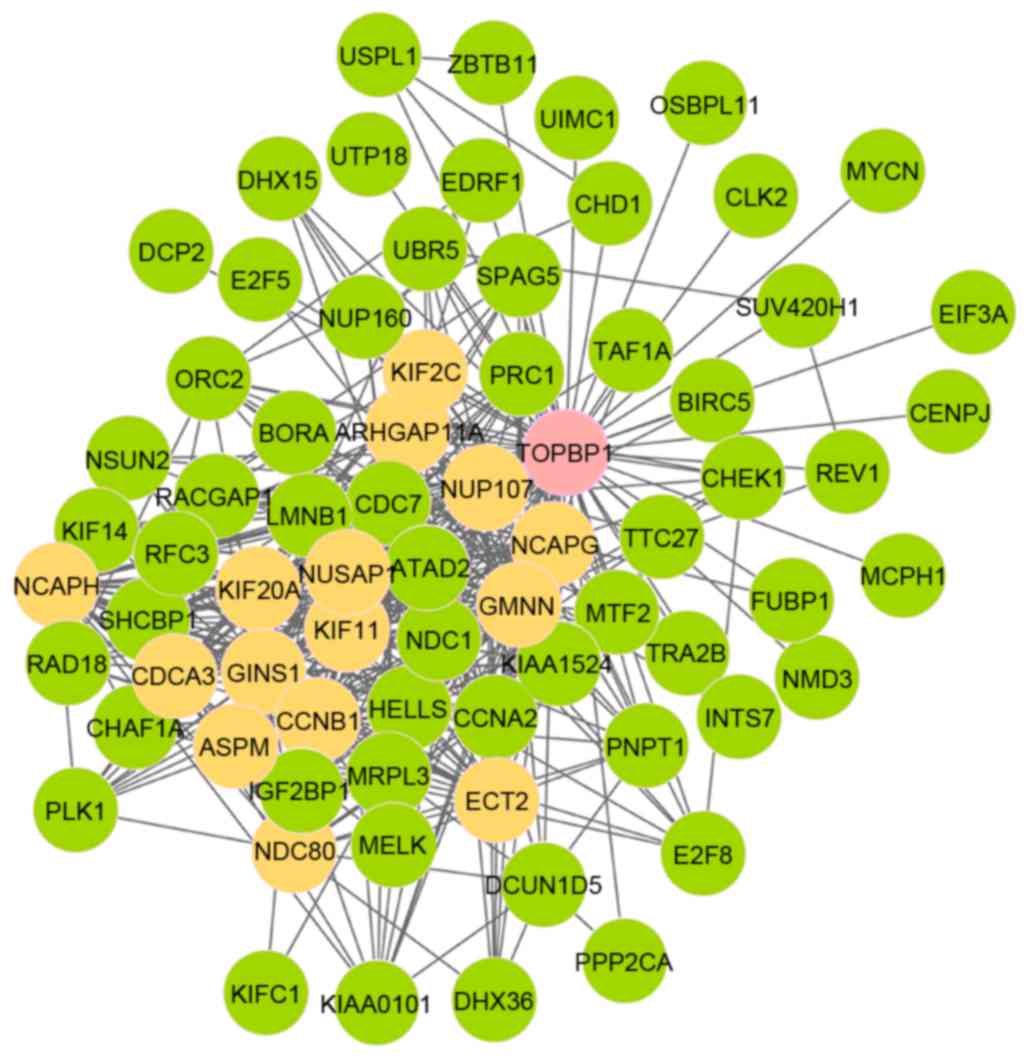
Bang SW, Ko MJ, Kang S, Kim GS, Kang D,
Lee J and Hwang DS: Human TopBP1 localization to the mitotic
centrosome mediates mitotic progression. Exp Cell Res.
317:994–1004. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee Y, Katyal S, Downing SM, Zhao J,
Russell HR and Mckinnon PJ: Neurogenesis requires TopBP1 to prevent
catastrophic replicative DNA damage in early progenitors. Nat
Neurosci. 15:819–826. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Negrini S, Gorgoulis VG and Halazonetis
TD: Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:220–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Katiyar SK, Mantena SK and Meeran SM:
Silymarin protects epidermal keratinocytes from ultraviolet
radiation-induced apoptosis and DNA damage by nucleotide excision
repair mechanism. PLoS One. 6:e214102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
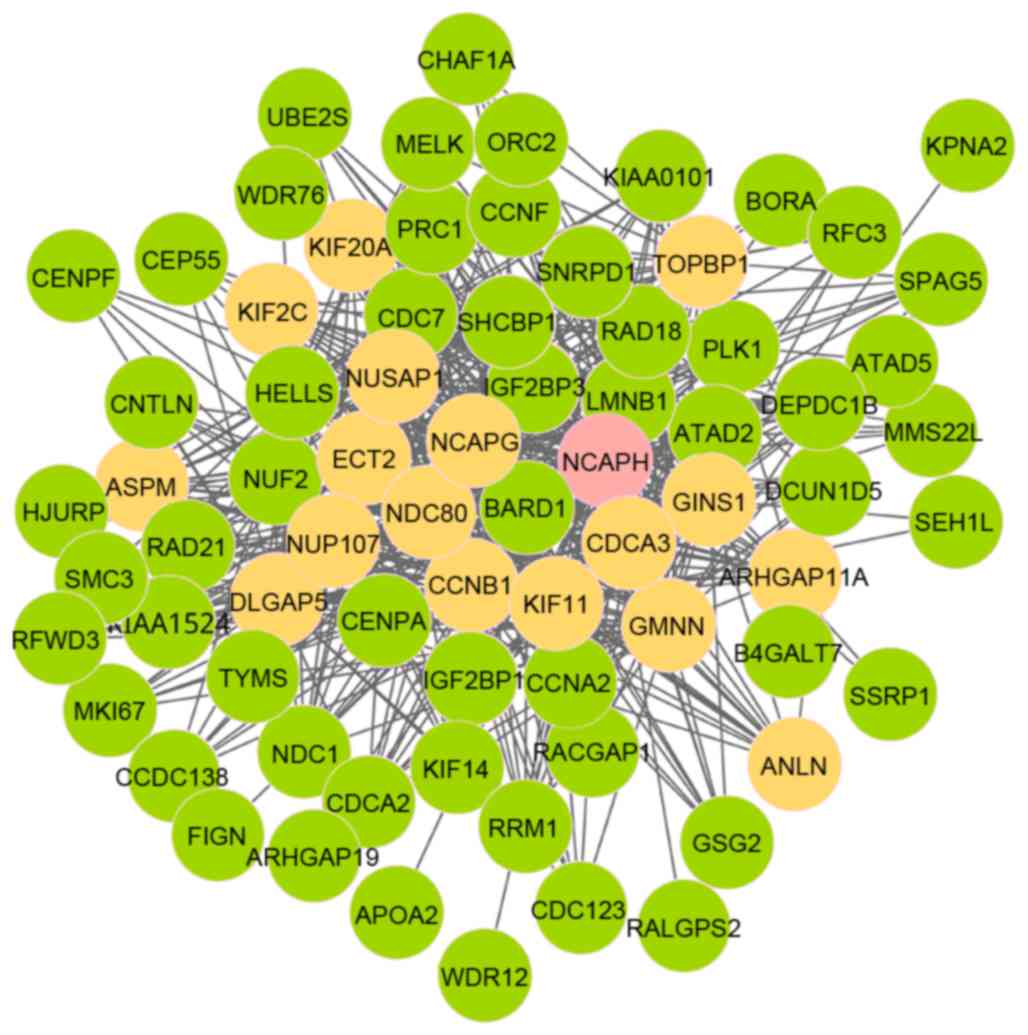
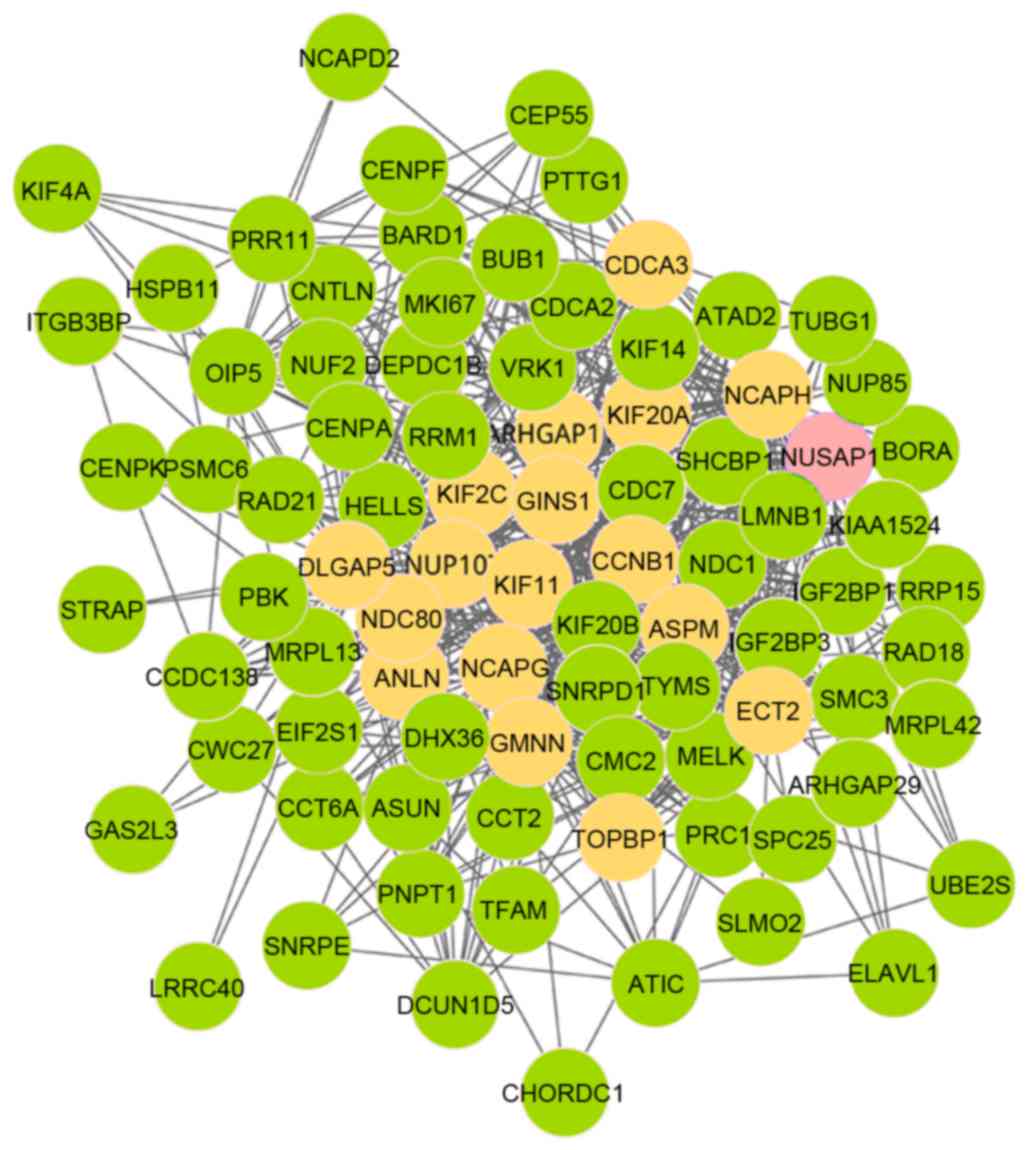
Iyer J, Moghe S, Furukawa M and Tsai MY:
What's Nu (SAP) in mitosis and cancer? Cell Signal. 23:991–998.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu J, Tan M, Huang W C, Li P, Guo H, Tseng
LM, Su XH, Yang WT, Treekitkarnmongkol W, Andreeff M, et al:
Mitotic deregulation by survivin in ErbB2-overexpressing breast
cancer cells contributes to Taxol resistance. Clin Cancer Res.
15:1326–1334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen DT, Nasir A, Culhane A, Venkataramu
C, Fulp W, Rubio R, Wang T, Agrawal D, McCarthy SM, Gruidl M, et
al: Proliferative genes dominate malignancy-risk gene signature in
histologically-normal breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
119:335–346. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Satow R, Shitashige M, Kanai Y, Takeshita
F, Ojima H, Jigami T, Honda K, Kosuge T, Ochiya T, Hirohashi S and
Yamada T: Combined functional genome survey of therapeutic targets
for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2518–2528. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sozmen M, Devrim AK, Tunca R, Bayezit M,
Dag S and Essiz D: Protective effects of silymarin on fumonisin
B1-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Vet Sci. 15:51–60.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Urrego D, Tomczak AP, Zahed F, Stuhmer W
and Pardo LA: Potassium channels in cell cycle and cell
proliferation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
369:201300942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smith A, Simanski S, Fallahi M and Ayad
NG: Redundant ubiquitin ligase activities regulate wee1 degradation
and mitotic entry. Cell Cycle. 6:2795–2799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
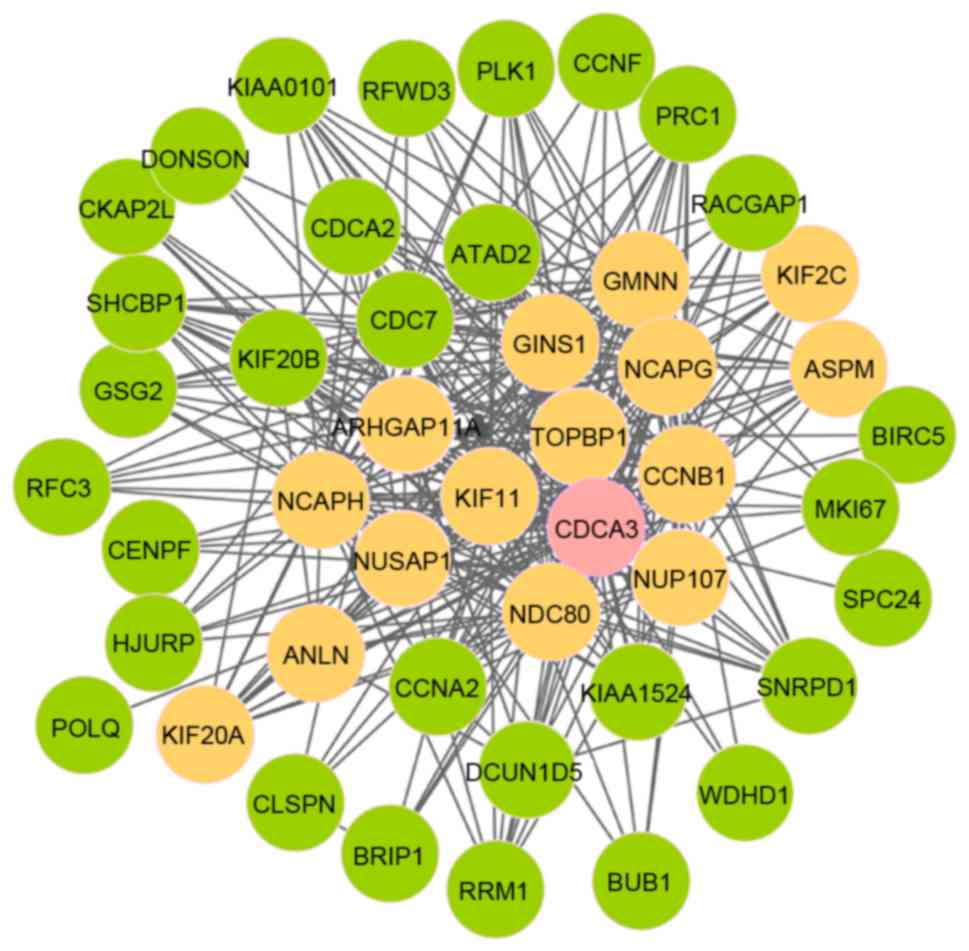
Itzel T, Scholz P, Maass T, et al:
Translating bioinformatics in oncology: Guilt-by-profiling analysis
and identification of KIF18B and CDCA3 as novel driver genes in
carcinogenesis. Bioinformatics. 31:216–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deep G, Singh R, Agarwal C, Kroll D and
Agarwal R: Silymarin and silibinin cause G1 and G2-M cell cycle
arrest via distinct circuitries in human prostate cancer PC3 cells:
A comparison of flavanone silibinin with flavanolignan mixture
silymarin. Oncogene. 25:1053–1069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fan L, Ma Y, Liu Y, Zheng D and Huang G:
Silymarin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ovarian cancer
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 743:79–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|