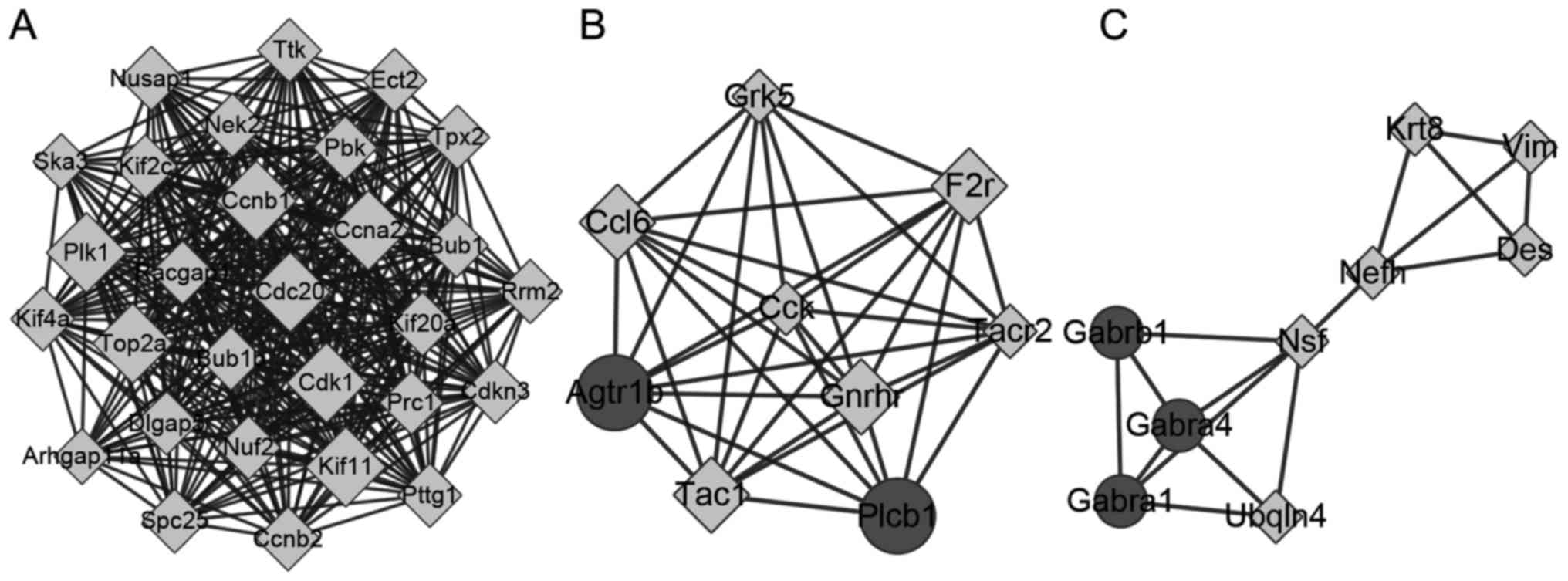
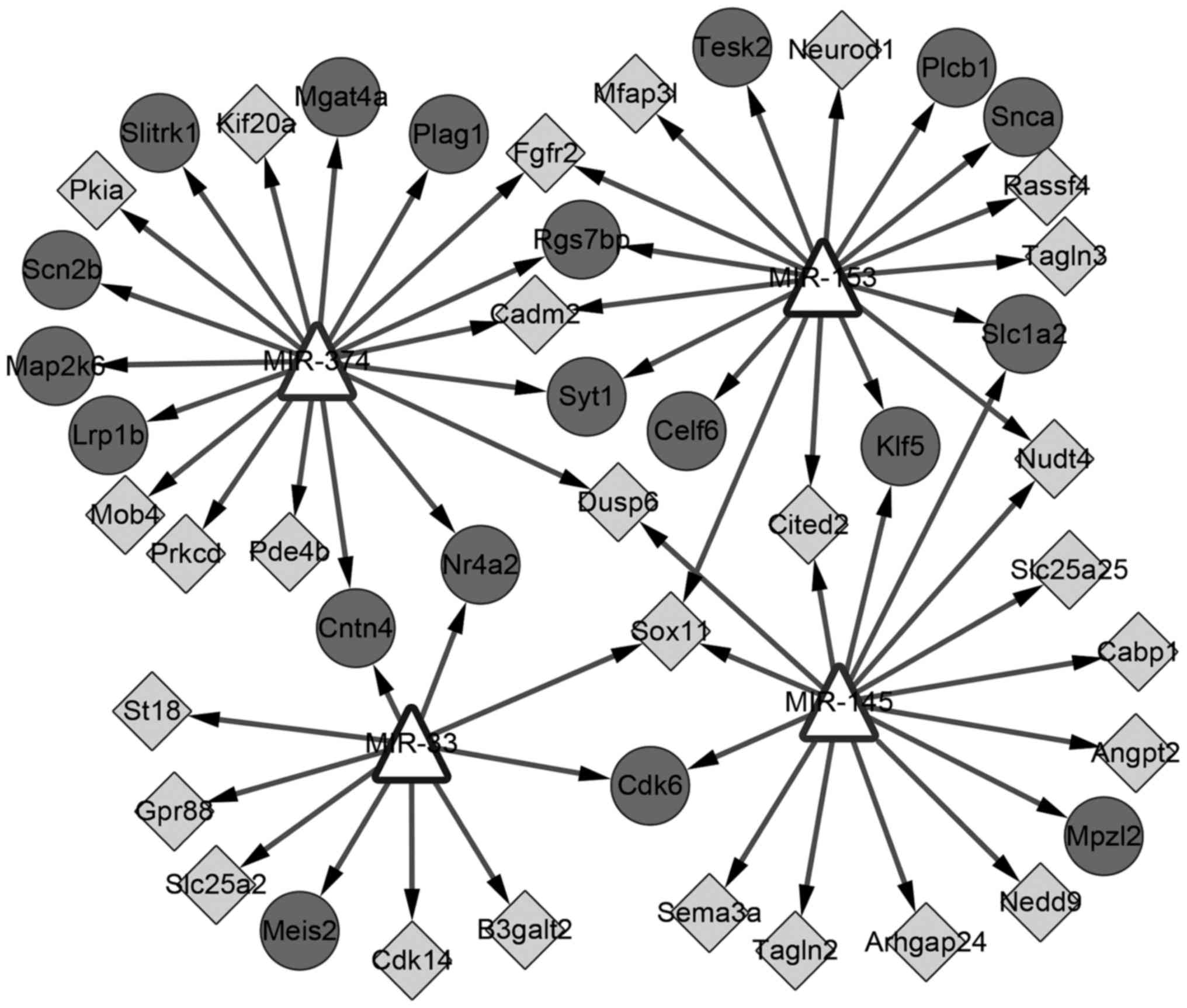
|
1
|
Trouillas J, Roy P, Sturm N, Dantony E,
Cortet-Rudelli C, Viennet G, Bonneville JF, Assaker R, Auger C,
Brue T, et al: A new prognostic clinicopathological classification
of pituitary adenomas: A multicentric case-control study of 410
patients with 8 years post-operative follow-up. Acta Neuropatholo.
126:123–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Daly AF, Rixhon M, Adam C, Dempegioti A,
Tichomirowa MA and Beckers A: High prevalence of pituitary
adenomas: A cross-sectional study in the province of liege,
belgium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:4769–4775. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fernandez A, Karavitaki N and Wass JA:
Prevalence of pituitary adenomas: A community-based,
cross-sectional study in banbury (Oxfordshire, UK). Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 72:377–382. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Müssnich P, Raverot G, Jaffrain-Rea ML,
Fraggetta F, Wierinckx A, Trouillas J, Fusco A and D'Angelo D:
Downregulation of miR-410 targeting the cyclin B1 gene plays a role
in pituitary gonadotroph tumors. Cell Cycle. 14:2590–2597. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heaney AP, Fernando M and Melmed S:
PPAR-gamma receptor ligands: Novel therapy for pituitary adenomas.
J Clin Invest. 111:1381–1388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chesnokova V, Zonis S, Zhou C, Ben-Shlomo
A, Wawrowsky K, Toledano Y, Tong Y, Kovacs K, Scheithauer B and
Melmed S: Lineage-specific restraint of pituitary gonadotroph cell
adenoma growth. PLoS One. 6:e179242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chesnokova V, Zonis S, Wawrowsky K, Tani
Y, Ben-Shlomo A, Ljubimov V, Mamelak A, Bannykh S and Melmed S:
Clusterin and foxl2 act concordantly to regulate pituitary
gonadotroph adenoma growth. Mol Endocrinol. 26:2092–2103. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee M, Lupp A, Mendoza N, Martin N,
Beschorner R, Honegger J, Schlegel J, Shively T, Pulz E, Schulz S,
et al: SSTR3 is a putative target for the medical treatment of
gonadotroph adenomas of the pituitary. Endocr Relat Cancer.
22:111–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
D'Angelo D, Palmieri D, Mussnich P, Roche
M, Wierinckx A, Raverot G, Fedele M, Croce CM, Trouillas J and
Fusco A: Altered microRNA expression profile in human pituitary GH
adenomas: Down-regulation of miRNA targeting HMGA1, HMGA2, and
E2F1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E1128–E1138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leone V, Langella C, D'Angelo D, Mussnich
P, Wierinckx A, Terracciano L, Raverot G, Lachuer J, Rotondi S,
Jaffrain-Rea ML, et al: Mir-23b and miR-130b expression is
downregulated in pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 390:1–7.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee M, Wiedemann T, Gross C, Leinhäuser I,
Roncaroli F, Braren R and Pellegata NS: Targeting PI3K/mTOR
signaling displays potent antitumor efficacy against nonfunctioning
pituitary adenomas. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3204–3215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee M, Marinoni I, Irmler M, Psaras T,
Honegger JB, Beschorner R, Anastasov N, Beckers J, Theodoropoulou
M, Roncaroli F and Pellegata NS: Transcriptome analysis of
MENX-associated rat pituitary adenomas identifies novel molecular
mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of human pituitary
gonadotroph adenomas. Acta Neuropathol. 126:137–150. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Xu C, Sun N, Zhou Y, Yu X, Yan X
and Zhang Q: Gene expression profiling analysis of MENX-associated
rat pituitary adenomas contributes to understand molecular
mechanisms of human pituitary adenomas. Oncol Lett. 11:125–133.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smyth GK: LIMMA: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Statistics for Biology and Health.
397–420. 2005.
|
|
16
|
Ferreira JA: The Benjamini-Hochberg method
in the case of discrete test statistics. Int J Biostat. 3:112007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database Issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based gene set analysis toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Web Server Issue): W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(Web Server Issue): W741–W748. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID bioinformatics resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35(Web Server Issue): W169–W175. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeyaseelan K, Lim KY and Armugam A:
MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to
transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Stroke. 39:959–966. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turczyńska KM, Hellstrand P, Swärd K and
Albinsson S: Regulation of vascular smooth muscle
mechanotransduction by microRNAs and L-type calcium channels.
Commun Integr Biol. 6:e222782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raverot G, Wierinckx A, Dantony E, Auger
C, Chapas G, Villeneuve L, Brue T, Figarella-Branger D, Roy P,
Jouanneau E, et al: Prognostic factors in prolactin pituitary
tumors: clinical, histological, and molecular data from a series of
94 patients with a long postoperative follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 95:1708–1716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kontogeorgos G: Predictive markers of
pituitary adenoma behavior. Neuroendocrinology. 83:179–188. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bahar A, Bicknell JE, Simpson DJ, Clayton
RN and Farrell WE: Loss of expression of the growth inhibitory gene
GADD45 gamma, in human pituitary adenomas, is associated with CpG
island methylation. Oncogene. 23:936–944. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quereda V and Malumbres M: Cell cycle
control of pituitary development and disease. J Mol Endocrinol.
42:75–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chesnokova V and Melmed S: Pituitary
senescence: The evolving role of Pttg. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
326:55–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fedele M, Palmieri D and Fusco A: HMGA2: A
pituitary tumour subtype-specific oncogene? Mol Cell Endocrinol.
326:19–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Butz H, Likó I, Czirják S, Igaz P, Khan
MM, Zivkovic V, Bálint K, Korbonits M, Rácz K and Patócs A:
Down-regulation of Wee1 kinase by a specific subset of microRNA in
human sporadic pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
95:E181–E191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amaral FC, Torres N, Saggioro F, Neder L,
Machado HR, Silva WA Jr, Moreira AC and Castro M: MicroRNAs
differentially expressed in ACTH-secreting pituitary tumors. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 94:320–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Palumbo T, Faucz FR, Azevedo M, Xekouki P,
Iliopoulos D and Stratakis CA: Functional screen analysis reveals
miR-26b and miR-128 as central regulators of pituitary
somatomammotrophic tumor growth through activation of the PTEN-AKT
pathway. Oncogene. 32:1651–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sachdeva M and Mo YY: miR-145-mediated
suppression of cell growth, invasion and metastasis. Am J Transl
Res. 2:170–180. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lauss M, Kriegner A, Vierlinger K and
Noehammer C: Characterization of the drugged human genome.
Pharmacogenomics. 8:1063–1073. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|