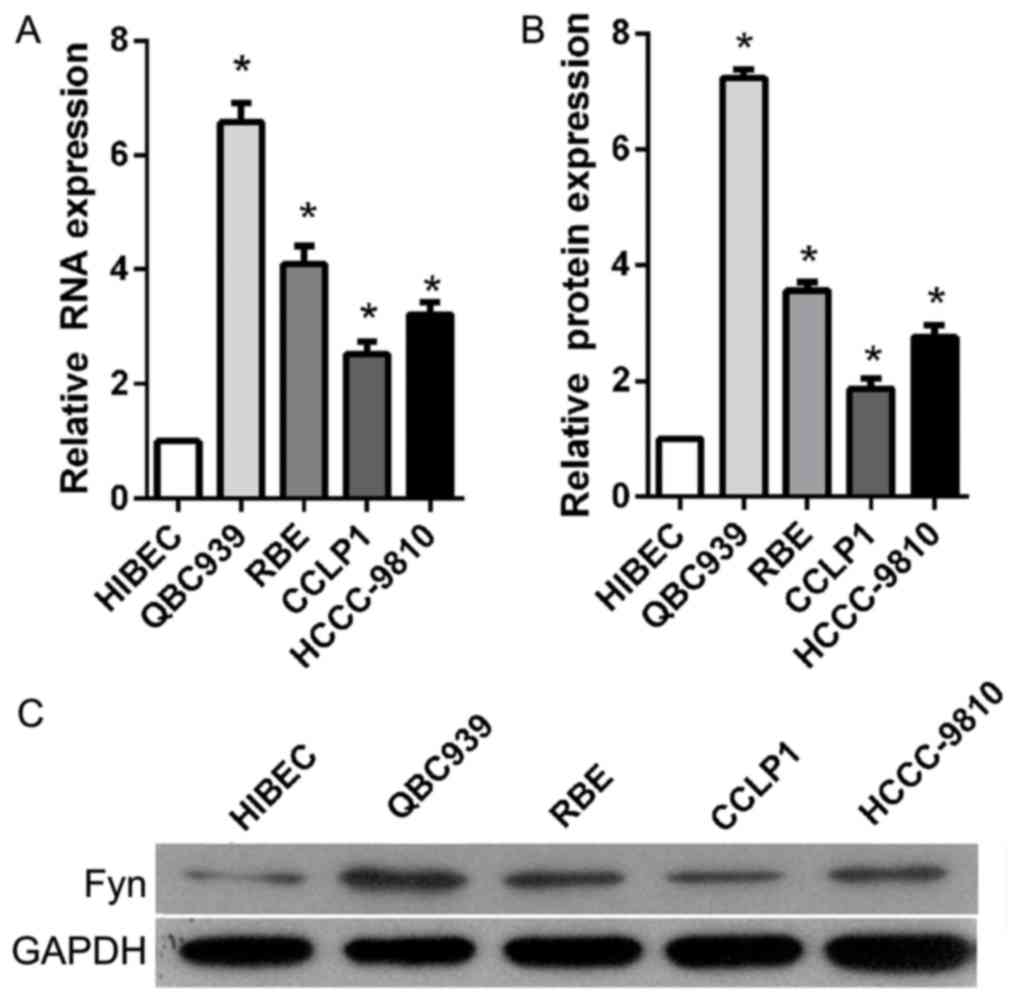
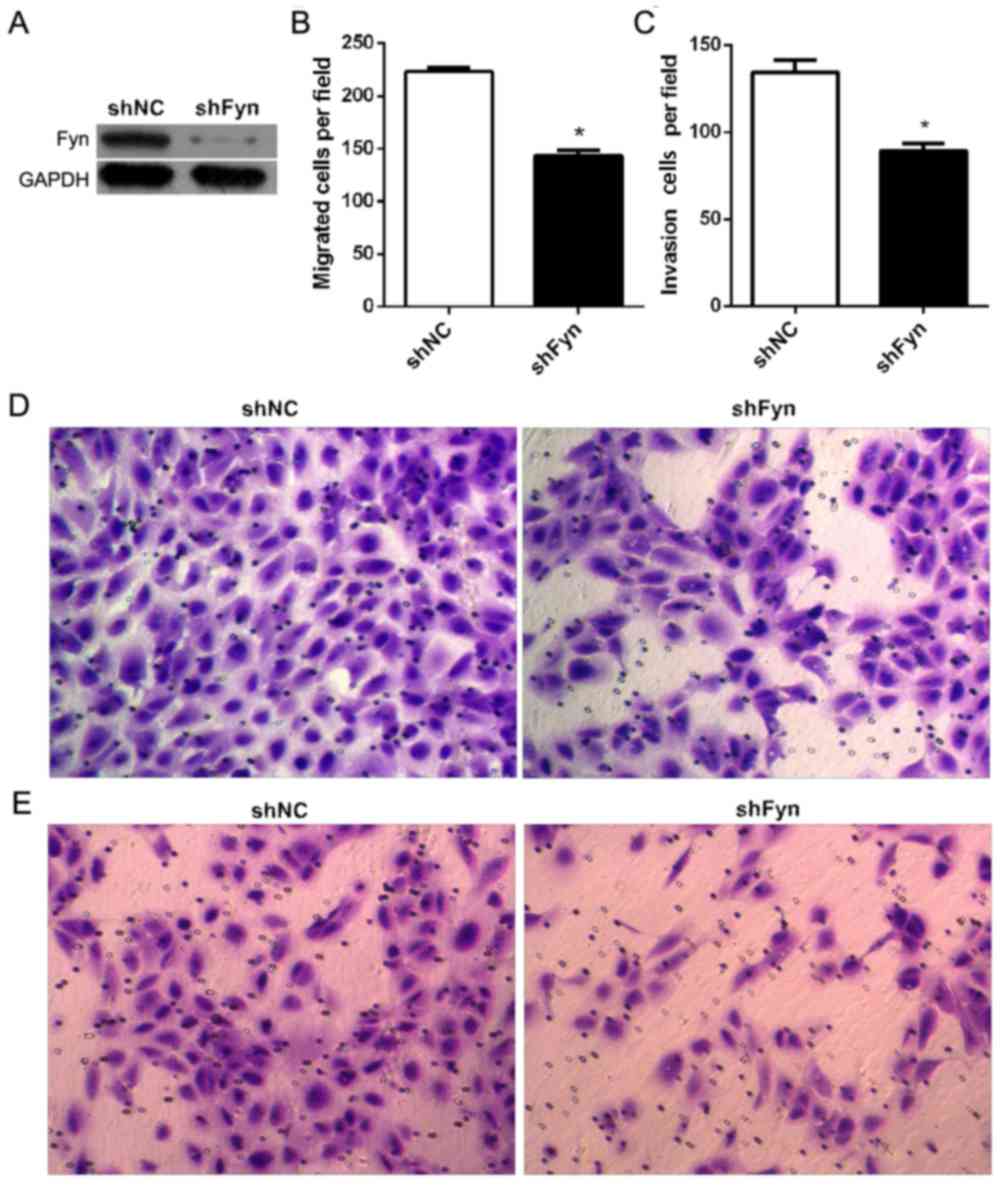
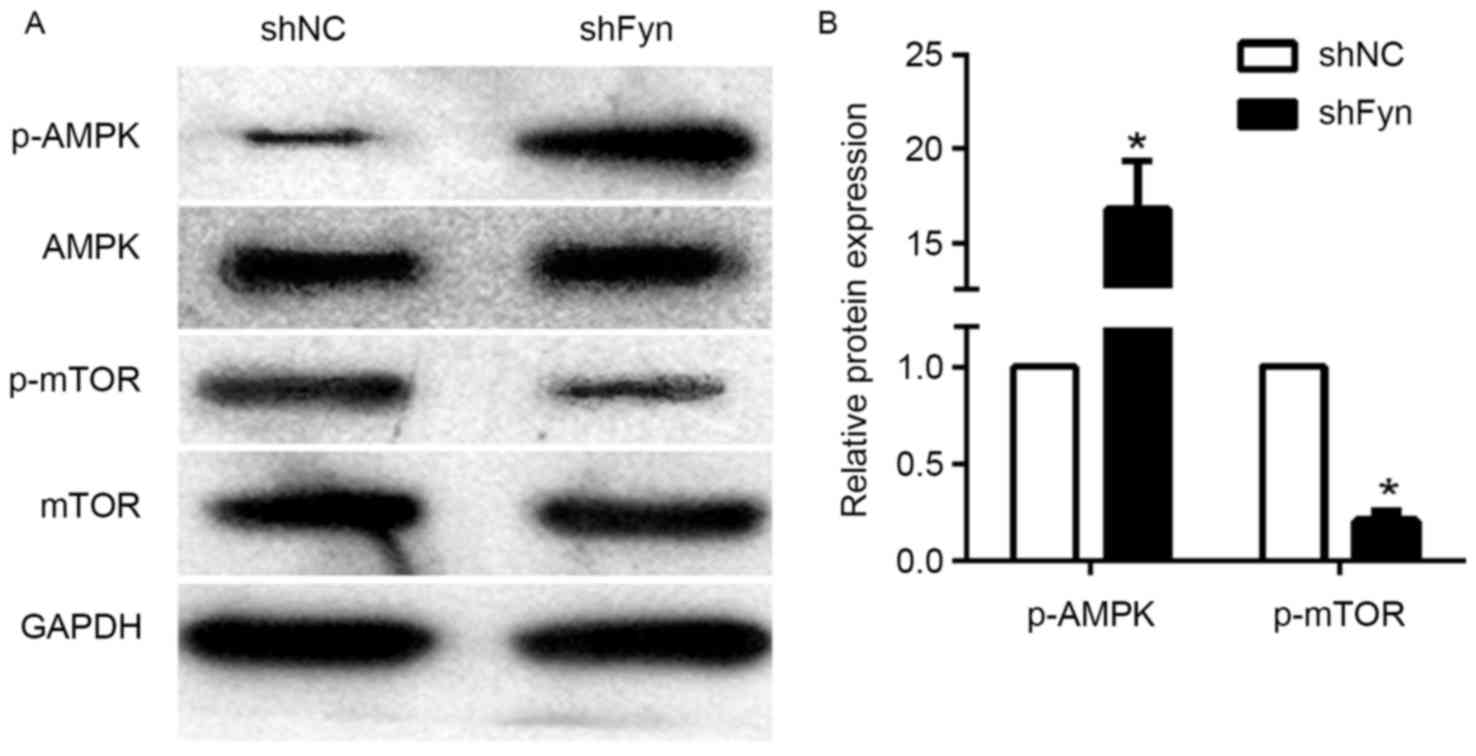
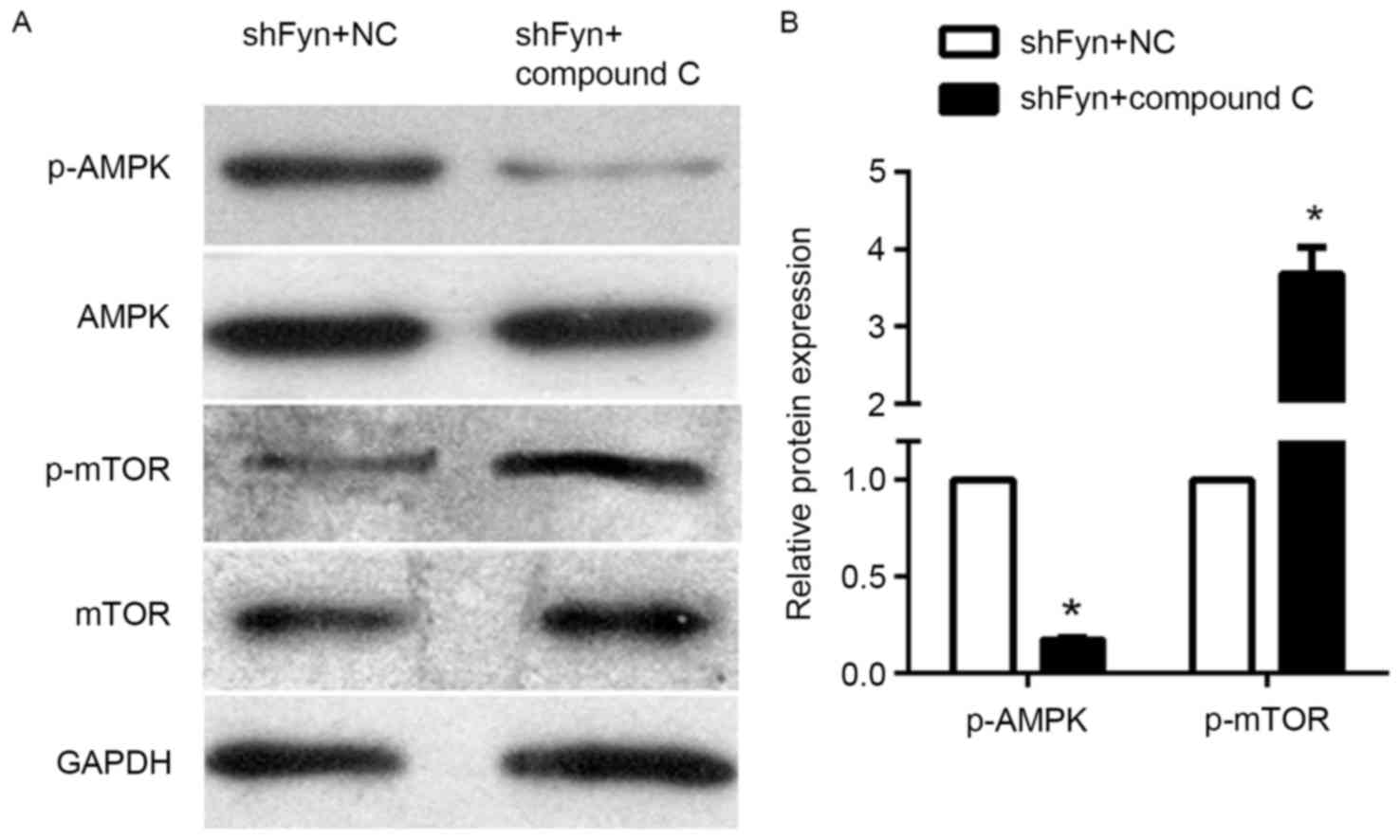
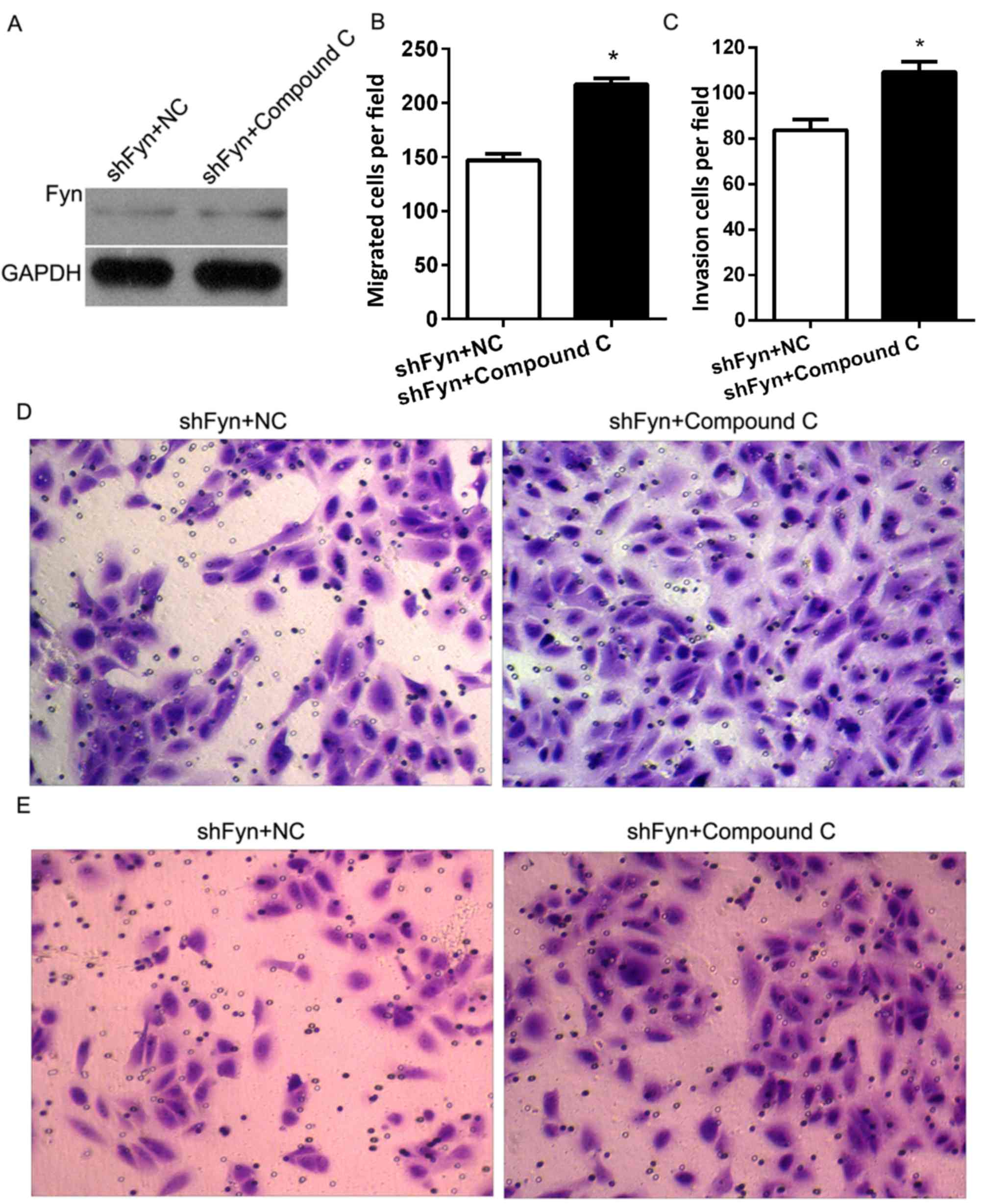
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tyson GL, Ilyas JA, Duan Z, Green LK,
Younes M, El-Serag HB and Davila JA: Secular trends in the
incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in the USA and the impact of
misclassification. Dig Dis Sci. 59:3103–3110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chinese Chapter of International
Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, ; Liver Surgery Group, ;
Surgical Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, ; Cai JQ, Cai
SW, Cong WM, Chen MS, Chen P, Chen XP, Chen YL, Chen YF, Dai CL,
Huang Q, et al: Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: A
consensus from surgical specialists of China. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 34:469–475. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo X, Yuan L, Wang Y, Ge R, Sun Y and Wei
G: Survival outcomes and prognostic factors of surgical therapy for
all potentially resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A large
single-center cohort study. J Gastrointest Surg. 18:562–572. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Yang H, Shen C and Luo J:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Prognostic factors after surgical resection in
China. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:5506–5512. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yubin L, Chihua F, Zhixiang J, Jinrui O,
Zixian L, Jianghua Z, Ye L, Haosheng J and Chaomin L: Surgical
management and prognostic factors of hilar cholangiocarcinoma:
Experience with 115 cases in China. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:2113–2119.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng-Rong L, Hai-Bo Y, Xin C, Chuan-Xin
W, Zuo-Jin L, Bing T, Jian-Ping G and Sheng-Wei L: Resection and
drainage of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: An 11-year experience of a
single center in mainland China. Am Surg. 77:627–633.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Posadas EM, Al-Ahmadie H, Robinson VL,
Jagadeeswaran R, Otto K, Kasza KE, Tretiakov M, Siddiqui J, Pienta
KJ, Stadler WM, et al: FYN is overexpressed in human prostate
cancer. BJU Int. 103:171–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu KV, Zhu S, Cvrljevic A, Huang TT,
Sarkaria S, Ahkavan D, Dang J, Dinca EB, Plaisier SB, Oderberg I,
et al: Fyn and SRC are effectors of oncogenic epidermal growth
factor receptor signaling in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Res.
69:6889–6898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ban K, Gao Y, Amin HM, Howard A, Miller C,
Lin Q, Leng X, Munsell M, Bar-Eli M, Arlinghaus RB and Chandra J:
BCR-ABL1 mediates up-regulation of Fyn in chronic myelogenous
leukemia. Blood. 111:2904–2908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Asawa T, Takato T and Sakai R:
Cooperative roles of Fyn and cortactin in cell migration of
metastatic murine melanoma. J Biol Chem. 278:48367–48376. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JE, Roh E, Lee MH, Yu DH, Kim DJ, Lim
TG, Jung SK, Peng C, Cho YY, Dickinson S, et al: Fyn is a redox
sensor involved in solar ultraviolet light-induced signal
transduction in skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 35:4091–4101. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen ZY, Cai L, Bie P, Wang SG, Jiang Y,
Dong JH and Li XW: Roles of Fyn in pancreatic cancer metastasis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:293–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen ZY, Cai L, Zhu J, Chen M, Chen J, Li
ZH, Liu XD, Wang SG, Bie P, Jiang P, et al: Fyn requires HnRNPA2B1
and Sam68 to synergistically regulate apoptosis in pancreatic
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:1419–1426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gururajan M, Cavassani KA, Sievert M, Duan
P, Lichterman J, Huang JM, Smith B, You S, Nandana S, Chu GC, et
al: SRC family kinase FYN promotes the neuroendocrine phenotype and
visceral metastasis in advanced prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
6:44072–44083. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Q, Qian J, Wang F and Ma Z: Cellular
prion protein accelerates colorectal cancer metastasis via the
Fyn-SP1-SATB1 axis. Oncol Rep. 28:2029–2034. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yadav V and Denning MF: Fyn is induced by
Ras/PI3K/Akt signaling and is required for enhanced
invasion/migration. Mol Carcinog. 50:346–352. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song JL, Zheng W, Chen W, Qian Y, Ouyang
YM and Fan CY: Lentivirus-mediated microRNA-124 gene-modified bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes the repair of
spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Mol Med. 49:e3322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li HX, Gao JM, Liang JQ, Xi JM, Fu M and
Wu YJ: Vitamin D3 potentiates the growth inhibitory effects of
metformin in DU145 human prostate cancer cells mediated by
AMPK/mTOR signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
42:711–717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu T, Wang MC, Jing L, Liu ZY, Guo H, Liu
Y, Bai YY, Cheng YZ, Nan KJ and Liang X: Autophagy facilitates lung
adenocarcinoma resistance to cisplatin treatment by activation of
AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:6421–6431.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kang JI, Hong JY, Lee HJ, Bae SY, Jung C,
Park HJ and Lee SK: Anti-tumor activity of yuanhuacine by
regulating AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway and actin cytoskeleton
organization in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
10:e01443682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|