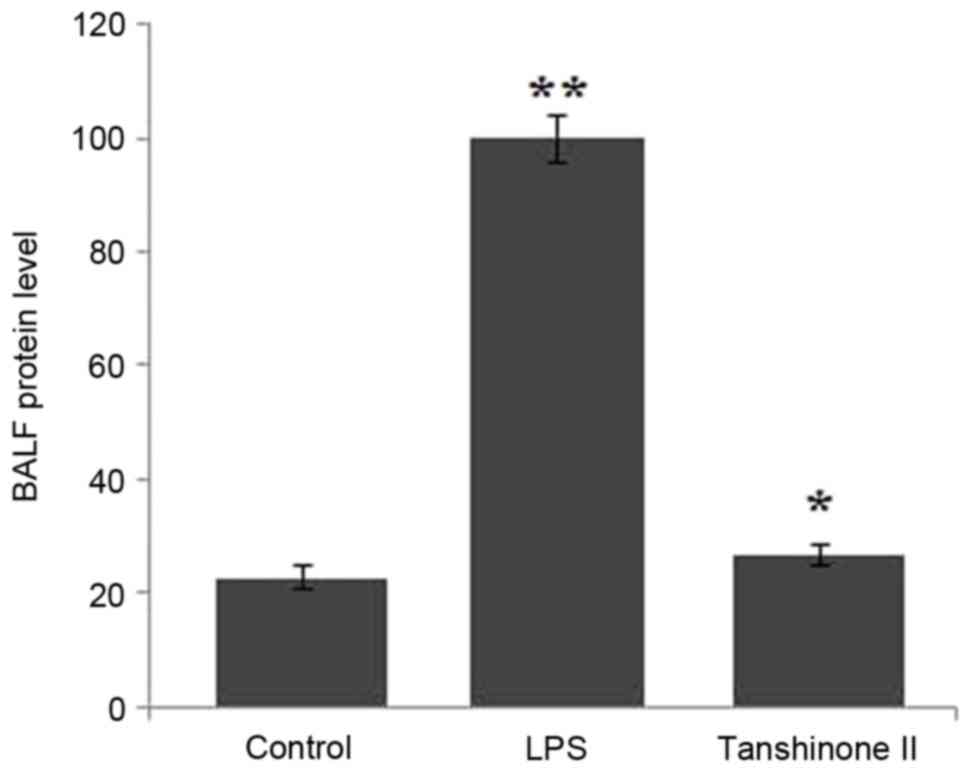
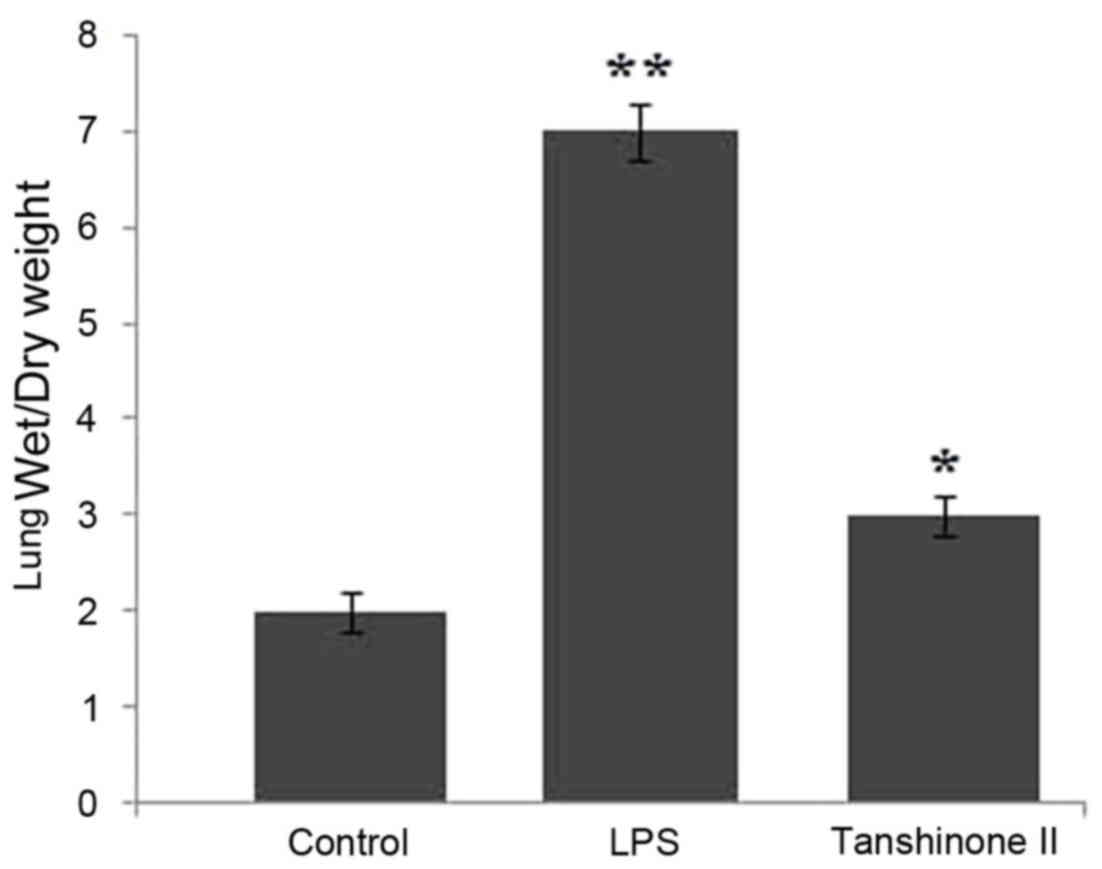
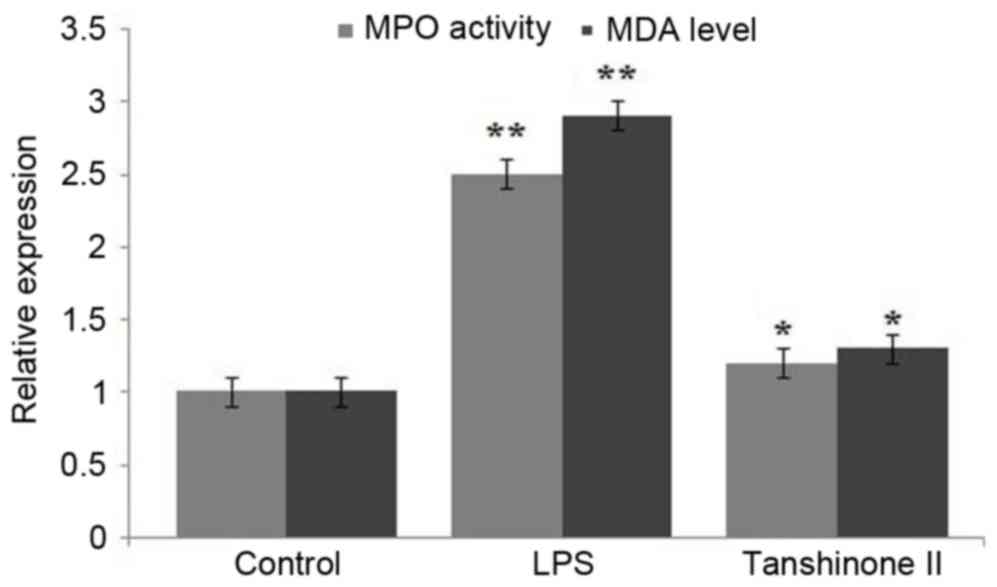
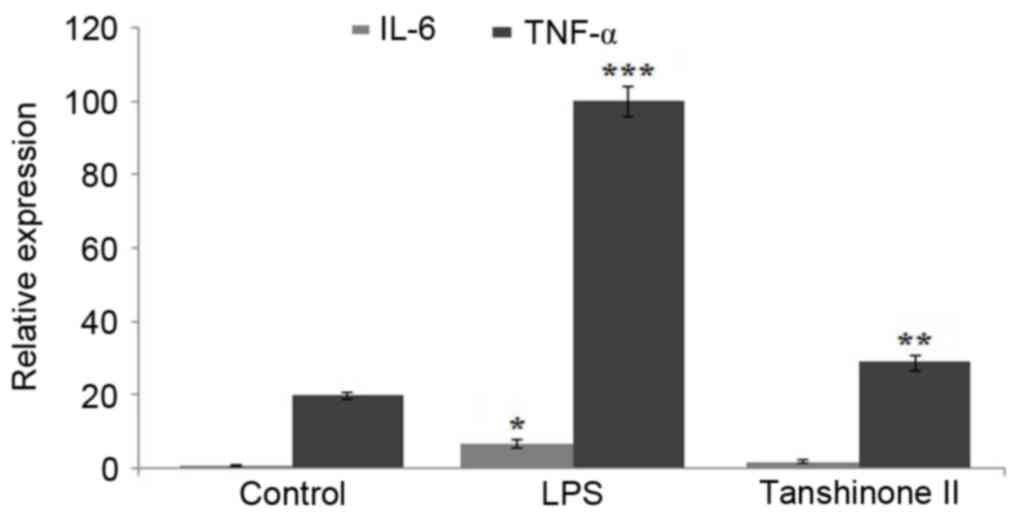
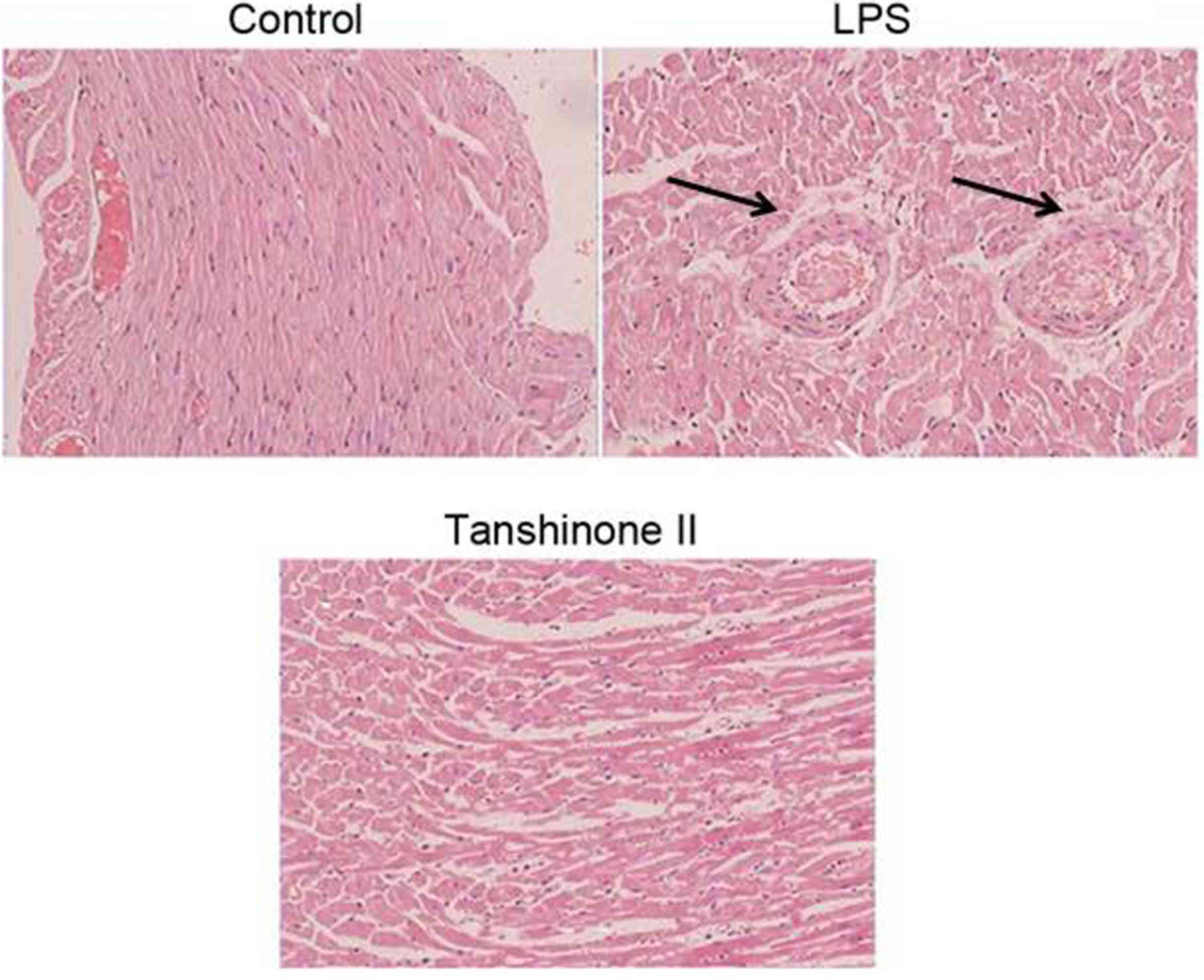
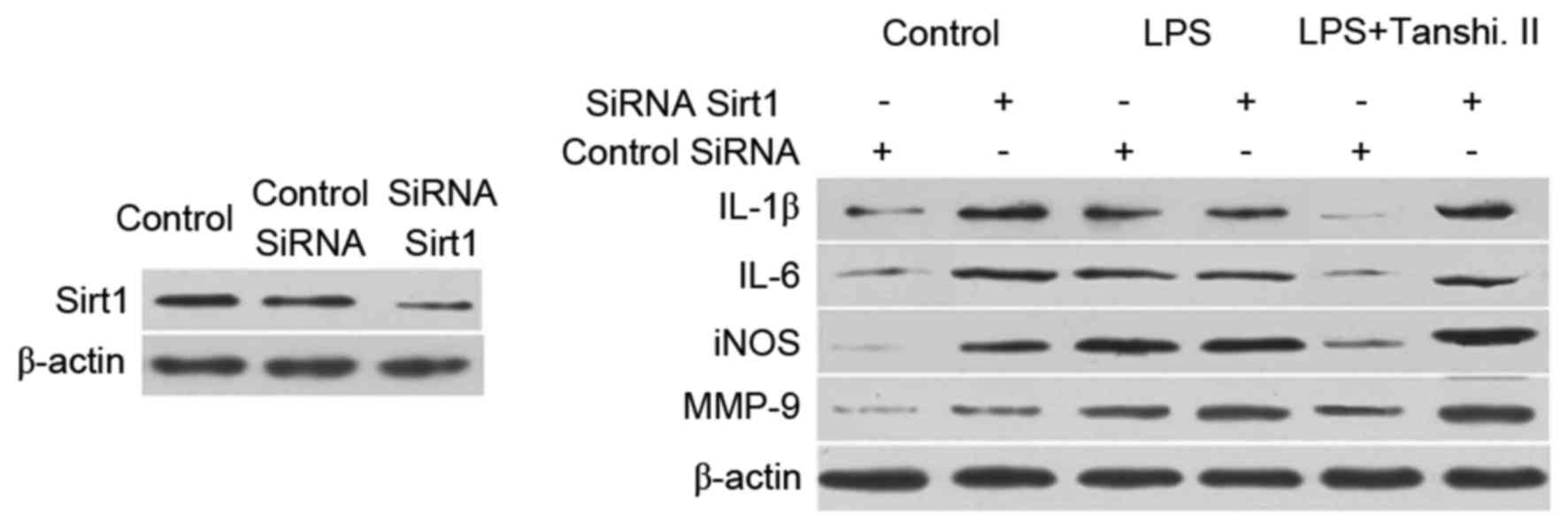
|
1
|
Herridge MS, Cheung AM, Tansey CM,
Matte-Martyn A, Diaz-Granados N, Al-Saidi F, Cooper AB, Guest CB,
Mazer CD, Mehta S, et al: One-year outcomes in survivors of the
acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 348:683–693.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chung YJ, Jarvis B and Pestka J:
Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine
production by satratoxins and other macrocyclic trichothecenes in
the murine macrophage. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 66:379–391.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brandolini L, Asti C, Ruggieri V,
Intilangelo A, Pellegrini L, Chiusaroli R, Caselli GF and Bertini
R: Lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. II. Evaluation
of functional damage in isolated parenchyma strips. Pulm Pharmacol
Ther. 13:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bucher M and Taeger K: Endothelin-receptor
gene-expression in rat endotoxemia. Intensive Care Med. 28:642–647.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Emery DA, Nagaraja KV, Sivanandan V, Lee
BW, Zhang CL and Newman JA: Endotoxin lipopolysaccharide from
Escherichia coli and its effects on the phagocytic function of
systemic and pulmonary macrophages in turkeys. Avian Dis.
35:901–909. 1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Esbenshade AM, Newman JH, Lams PM, Jolles
H and Brigham KL: Respiratory failure after endotoxin infusion in
sheep: Lung mechanics and lung fluid balance. J Appl Physiol Respir
Environ Exerc Physiol. 53:967–976. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J and
Brigham KL: Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: Structural,
functional and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 288:L333–L341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matuschak GM and Lechner AJ: Acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathophysiology
and treatment. Mo Med. 107:252–258. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cross CE, Forte T, Stocker R, Louie S,
Yamamoto Y, Ames BN and Frei B: Oxidative stress and abnormal
cholesterol metabolism in patients with adult respiratory distress
syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 115:396–404. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sabarirajan J, Vijayaraj P and Nachiappan
V: Induction of acute respiratory distress syndrome in rats by
lipopolysaccharide and its effect on oxidative stress and
antioxidant status in lung. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 47:278–284.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Blackwell TS, Blackwell TR, Holden EP,
Christman BW and Christman JW: In vivo antioxidant treatment
suppresses nuclear factor-kappa B activation and neutrophilic lung
inflammation. J Immunol. 157:1630–1637. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sheen WS, Tsai IL, Teng CM and Chen IS:
Nor-neolignan and phenyl propanoid from Zanthoxylum ailanthoides.
Phytochemistry. 36:213–215. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang Z, Hon MH, Chui KY, Xu HM, Lee CM,
Cui YX, Wong HNC, Poon CD and Fung BM: Naturally occurring
benzofuran: Isolation, structure elucidation and total synthesis of
5-(3-hydroxypropyl)-7-methoxy-2-(3′-methoxy-4′hydroxyphenyl)-3-benzo
[b]furancarbaldehyde, a novel adenosine A1 receptor ligand isolated
from salvia miltiorrhiza bunge (danshen). Tetrahedron Lett.
32:2061–2064. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou L, Zuo Z and Chow MS: Danshen: An
overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and
clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. 45:1345–1359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan SL, Wei YQ, Wang XJ, Xiao F, Li SF
and Zhang J: Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of
tanshinone II-A on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:2024–2028. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sung HJ, Choi SM, Yoon Y and An KS:
Tanshinone IIA, an ingredient of Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE, induces
apoptosis in human leukemia cell lines through the activation of
caspase-3. Exp Mol Med. 31:174–178. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hua Y, Li W, Wan-Liang S, Lei W, Zai-Liang
Y, Yuan L, Ke Z, Ying W and Wei-Jing Z: The green tea extract
epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits irradiation-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in adult rats. Int J Mol Med. 34:92–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ford J, Jiang M and Milner J:
Cancer-specific functions of SIRT1 enable human epithelial cancer
cell growth and survival. Cancer Res. 65:10457–10463. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dushianthan A, Grocott MP, Postle AD and
Cusack R: Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung
injury. Postgrad Med J. 87:612–622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gattinoni L, Bombino M, Pelosi P, Lissoni
A, Pesenti A, Fumagalli R and Tagliabue M: Lung structure and
function in different stages of severe adult respiratory distress
syndrome. JAMA. 271:1772–1779. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mu E, Ding R, An X, Li X, Chen S and Ma X:
Heparin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by
inhibiting nitric oxide synthase and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.
Thromb Res. 129:479–485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ni YF, Tian F, Lu ZF, Yang GD, Fu HY, Wang
J, Yan XL, Zhao YC, Wang YJ and Jiang T: Protective effect of
nicotine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice.
Respiration. 81:39–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma Z, Ji W, Fu Q and Ma S: Formononetin
inhibited the inflam-mation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in
mice associated with induction of PPAR gamma expression.
Inflammation. 36:1560–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torun AN, Kulaksizoglu S, Kulaksizoglu M,
Pamuk BO, Isbilen E and Tutuncu NB: Serum total antioxidant status
and lipid peroxidation marker malondialdehyde levels in overt and
subclinical hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 70:469–474.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Lent PL, van de Loo FA, Holthuysen AE,
van den Bersselaar LA and Vermeer H: Major role for interleukin-1
but not tumor necrosis factor in early cartilage damage in immune
complex arthritis in mice. J Rheumatol. 22:2250–2058.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee SJ and Kim MM: Resveratrol with
antioxidant activity inhibits matrix metalloproteinase via
modulation of SIRT1 in human fibrosarcoma cells. Life Sci.
88:465–472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Niederer F, Ospelt C, Brentano F, Hottiger
MO, Gay RE, Gay S, Detmar M and Kyburz D: SIRT1 overexpression in
the rheumatoid arthritis synovium contributes to proinflammatory
cytokine production and apoptosis resistance. Ann Rheum Dis.
70:1866–1873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|