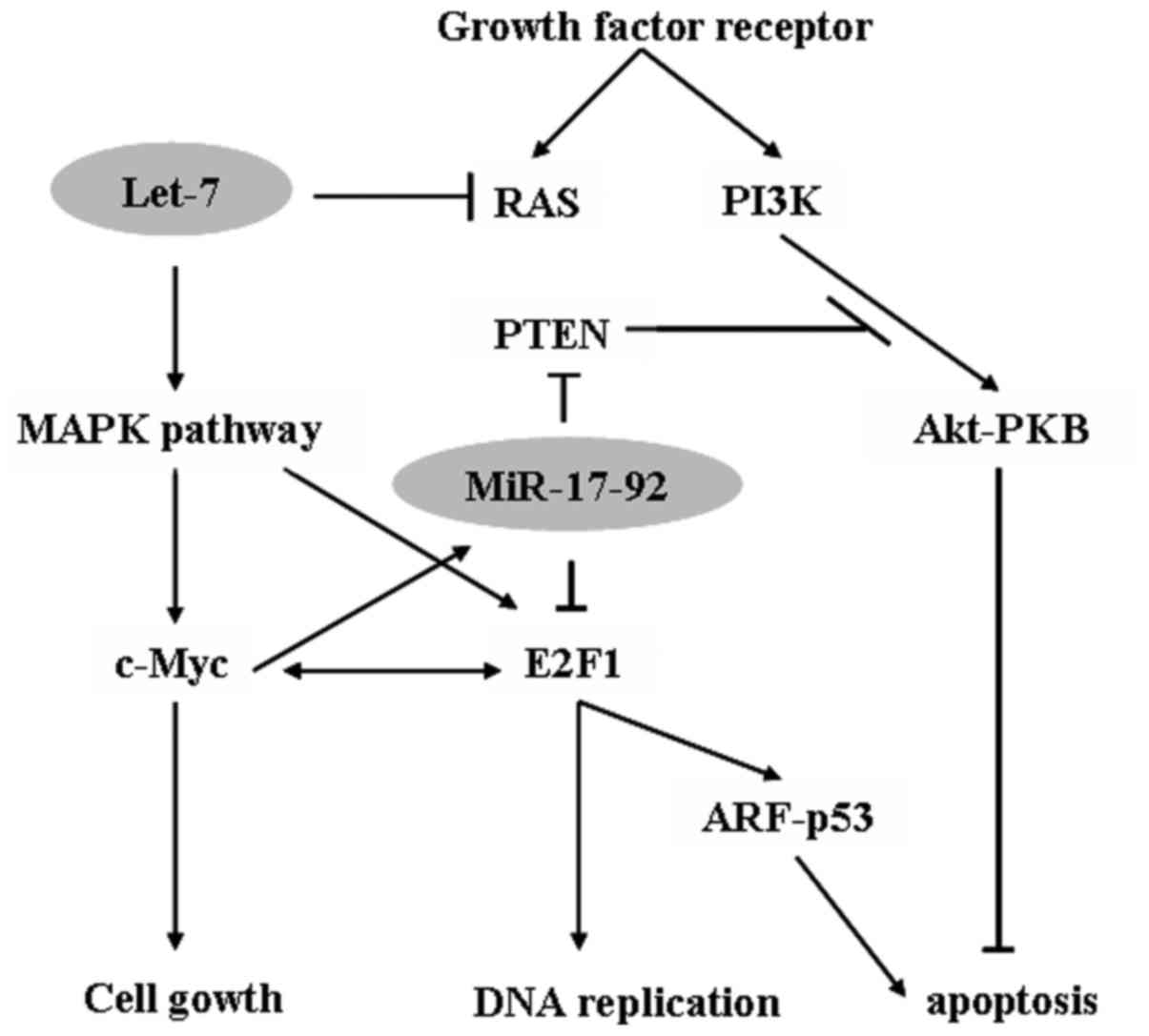
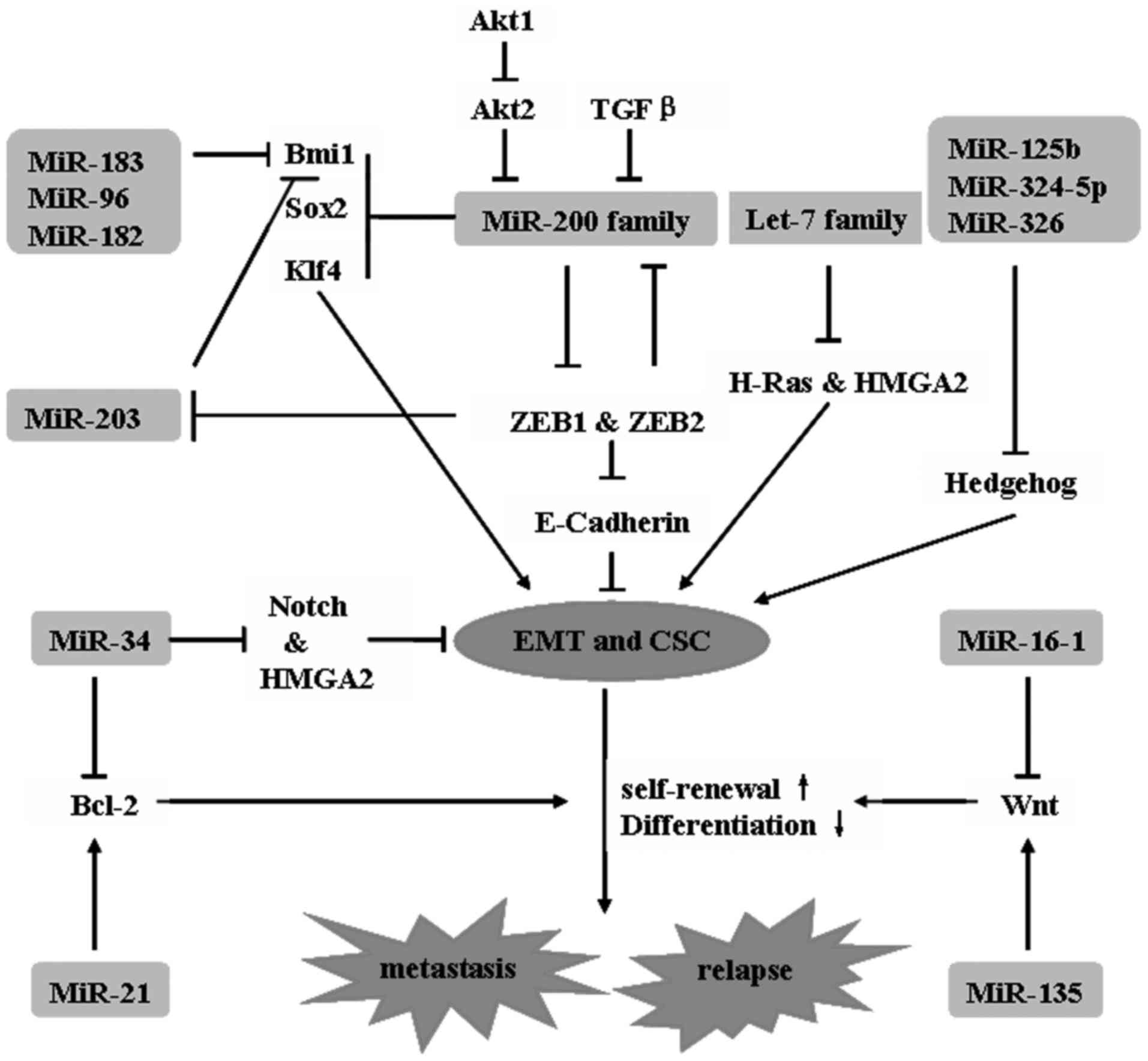
|
1
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The c.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carrington JC and Ambros V: Role of
microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science. 301:336–338.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang JC, Babak T, Corson TW, Chua G, Khan
S, Gallie BL, Hughes TR, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ and Morris QD: Using
expression profiling data to identify human microRNA targets. Nat
Methods. 4:1045–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mattick JS and Gagen MJ: The evolution of
controlled multitasked gene networks: The role of introns and other
noncoding RNAs in the development of complex organisms. Mol Biol
Evol. 18:1611–1630. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Plank M, Maltby S, Mattes J and Foster PS:
Targeting translational control as a novel way to treat
inflammatory disease: The emerging role of MicroRNAs. Clin Exp
Allergy. 43:981–999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fernández-Hernando C, Ramírez CM, Goedeke
L and Suárez Y: MicroRNAs in metabolic disease. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:178–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang W, Kwon EJ and Tsai LH: MicroRNAs in
learning, memory, and neurological diseases. Learn Mem. 19:359–368.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tao G and Martin JF: MicroRNAs get to the
heart of development. Elife. 2:e017102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Menghini R, Stöhr R and Federici M:
MicroRNAs in vascular aging and atherosclerosis. Ageing Res Rev.
17:68–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Timoneda O, Núñez-Hernández F, Balcells I,
Muñoz M, Castelló A, Vera G, Pérez LJ, Egea R, Mir G, Córdoba S, et
al: The role of viral and host microRNAs in the Aujeszky's disease
virus during the infection process. PLoS One. 9:e869652014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:pp. 15524–15529. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leal JA, Feliciano A and Lleonart ME: Stem
cell microRNAs in senescence and immortalization: Novel players in
cancer therapy. Med Res Rev. 33:112–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Anand S: A brief primer on microRNAs and
their roles in angiogenesis. Vasc Cell. 5:22013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding XM: MicroRNAs: Regulators of cancer
metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Chin J
Cancer. 33:140–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raza U, Zhang JD and Sahin O: MicroRNAs:
Master regulators of drug resistance, stemness, and metastasis. J
Mol Med (Berl). 92:321–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Spengler RM, Oakley CK and Davidson BL:
Functional microRNAs and target sites are created by
lineage-specific transposition. Hum Mol Genet. 23:1783–1793. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT and Spillane C:
miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:918–925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang ZW, An Y and Teng CB: The roles of
miR-17-92 cluster in mammal development and tumorigenesis. Yi
Chuan. 31:1094–1100. 2009.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Osada H and Takahashi T: let-7 and
miR-17-92: Small-sized major players in lung cancer development.
Cancer Sci. 102:9–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rinaldi A, Poretti G, Kwee I, Zucca E,
Catapano CV, Tibiletti MG and Bertoni F: Concomitant MYC and
microRNA cluster miR-17-92 (C13orf25) amplification in human mantle
cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:410–412. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shuang T, Shi C, Chang S, Wang M and Bai
CH: Downregulation of miR-17~92 expression increase
paclitaxel sensitivity in human ovarian carcinoma SKOV3-TR30 cells
via BIM instead of PTEN. Int J Mol Sci. 14:3802–3816. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shuang T, Shi C, Chang S, Wang M and Bai
CH: miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte differentiation by
negatively regulating tumor-suppressor Rb2/p130. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:pp. 2889–2894. 2008; PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cho WJ, Shin JM, Kim JS, Lee MR, Hong KS,
Lee JH, Koo KH, Park JW and Kim KS: miR-372 regulates cell cycle
and apoptosis of ags human gastric cancer cell line through direct
regulation of LATS2. Mol Cells. 28:521–527. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE
and Peter ME: The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F19–F36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He XY, Chen JX, Ou-Yang X, Zhang Z and
Peng HM: Construction of let-7a expression plasmid and its
inhibitory effect on k-Ras protein in A549 lung cancer cells. Nan
Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 30:2427–2431. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang YY, Ren T, Cai YY and He XY: MicroRNA
let-7a inhibits the proliferation and invasion of nonsmall cell
lung cancer cell line 95D by regulating K-Ras and HMGA2 gene
expression. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 28:131–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia XM, Jin WY, Shi RZ, Zhang YF and Chen
J: Clinical significance and the correlation of expression between
Let-7 and K-ras in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett.
1:1045–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okada N, Lin CP, Ribeiro MC, Biton A, Lai
G, He X, Bu P, Vogel H, Jablons DM, Keller AC, et al: A positive
feedback between p53 and miR-34 miRNAs mediates tumor suppression.
Genes Dev. 28:438–450. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheng CY, Hwang CI, Corney DC,
Flesken-Nikitin A, Jiang L, Oner GM, Munroe RJ, Schimenti JC,
Hermeking H and Nikitin AY: miR-34 cooperates with p53 in
suppression of prostate cancer by joint regulation of stem cell
compartment. Cell Rep. 6:1000–1007. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li
L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, et al: MicroRNA miR-34
inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One.
4:e68162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cannell IG and Bushell M: Regulation of
Myc by miR-34c: A mechanism to prevent genomic instability? Cell
Cycle. 9:2726–2730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shah M and Allegrucci C: Stem cell
plasticity in development and cancer: Epigenetic origin of cancer
stem cells. Subcell Biochem. 61:545–565. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lerner RG and Petritsch C: A
microRNA-operated switch of asymmetric-to-symmetric cancer stem
cell divisions. Nat Cell Biol. 16:212–214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun X, Fan C, Hu LJ, Du N, Xu CW and Ren
H: Role of let-7 in maintaining characteristics of breast cancer
stem cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:789–792.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen KJ, Hou Y, Wang K, Li J, Xia Y, Yang
XY, Lv G, Xing XL and Shen F: Reexpression of Let-7 g microRNA
inhibits the proliferation and migration via K-Ras/HMGA2/snail axis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int.
2014:7424172014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lim YY, Wright JA, Attema JL, Gregory PA,
Bert AG, Smith E, Thomas D, Lopez AF, Drew PA, Khew-Goodall Y and
Goodall GJ: Epigenetic modulation of the miR-200 family is
associated with transition to a breast cancer stem-cell-like state.
J Cell Sci. 126:2256–2266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH,
Gregory PA, Goodall GJ, Thilaganathan N, Du L, Zhang Y,
Pertsemlidis A and Kurie JM: Contextual extracellular cues promote
tumor cell EMT and metastasis by regulating miR-200 family
expression. Genes Dev. 23:2140–2151. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Truong HH, Xiong J, Ghotra VP, Nirmala E,
Haazen L, Le Dévédec SE, Balcioğlu HE, He S, Snaar-Jagalska BE,
Vreugdenhil E, et al: β1 integrin inhibition elicits a
prometastatic switch through the TGFβ-miR-200-ZEB network in
E-cadherin-positive triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Signal.
7:ra152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou
C, Hirsch HA, Tsichlis PN and Struhl K: Loss of miR-200 inhibition
of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the
formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell.
39:761–772. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ouzounova M, Vuong T, Ancey PB, Ferrand M,
Durand G, Le-Calvez Kelm F, Croce C, Matar C, Herceg Z and
Hernandez-Vargas H: MicroRNA miR-30 family regulates non-attachment
growth of breast cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 14:1392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Samples J, Willis M and Klauber-Demore N:
Targeting angiogenesis and the tumor microenvironment. Surg Oncol
Clin N Am. 22:629–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pasquier E, Andre N, Trahair T and
Kavallaris M: Reply: Comment on ‘Beta-blockers increase response to
chemotherapy via direct anti-tumour and anti-angiogenic mechanisms
in neuroblastoma’-β-blockers are potent anti-angiogenic and
chemo-sensitising agents, rather than cytotoxic drugs. Br J Cancer.
109:2024–2025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kuhnert F and Kuo CJ: miR-17-92
angiogenesis micromanagement. Blood. 115:4631–4633. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chan JK, Kiet TK, Blansit K, Ramasubbaiah
R, Hilton JF, Kapp DS and Matei D: MiR-378 as a biomarker for
response to anti-angiogenic treatment in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 133:568–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Melo SA and Kalluri R: Angiogenesis is
controlled by miR-27b associated with endothelial tip cells. Blood.
119:2439–2440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Santhekadur PK, Das SK, Gredler R, Chen D,
Srivastava J, Robertson C, Baldwin AS Jr, Fisher PB and Sarkar D:
Multifunction protein staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1
(SND1) promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma through novel pathway that involves nuclear factor κB and
miR-221. J Biol Chem. 287:13952–13958. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xue G, Yan HL, Zhang Y, Hao LQ, Zhu XT,
Mei Q and Sun SH: c-Myc-mediated repression of miR-15-16 in hypoxia
is induced by increased HIF-2α and promotes tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis by upregulating FGF2. Oncogene. 34:1393–1406. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu YY, Han JY, Lin SC, Liu ZY and Jiang
WT: Effect of CDH1 gene methylation on transforming growth factor
(TGF-β)-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar
epithelial cell line A549. Genet Mol Res. 13:8568–8576. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Garg M: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- activating transcription factors - multifunctional regulators in
cancer. World J Stem Cells. 5:188–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Young JA, Ting KK, Li J, Moller T, Dunn L,
Lu Y, Moses J, Prado-Lourenço L, Khachigian LM, Ng M, et al:
Regulation of vascular leak and recovery from ischemic injury by
general and VE-cadherin-restricted miRNA antagonists of miR-27.
Blood. 122:2911–2919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tellez CS, Juri DE, Do K, Bernauer AM,
Thomas CL, Damiani LA, Tessema M, Leng S and Belinsky SA: EMT and
stem cell-like properties associated with miR-205 and miR-200
epigenetic silencing are early manifestations during
carcinogen-induced transformation of human lung epithelial cells.
Cancer Res. 71:3087–3097. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Tu X, Zang Y, Zhu
J, Chen J, Dong L and Zhang J: miR-30 inhibits TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting
Snail1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:1100–1105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen J, Wang L, Matyunina LV, Hill CG and
McDonald JF: Overexpression of miR-429 induces
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) in metastatic ovarian
cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 121:200–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stahlhut C and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs and the
cancer phenotype: Profiling, signatures and clinical implications.
Genome Med. 5:1112013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
de Leeuw DC, van den Ancker W, Denkers F,
de Menezes RX, Westers TM, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA
and Smit L: MicroRNA profiling can classify acute leukemias of
ambiguous lineage as either acute myeloid leukemia or acute
lymphoid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2187–2196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sun YF, Leu JD, Chen SM, Lin IF and Lee
YJ: Results based on 124 cases of breast cancer and 97 controls
from Taiwan suggest that the single nucleotide polymorphism
(SNP309) in the MDM2 gene promoter is associated with earlier onset
and increased risk of breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:132009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bolmeson C, Esguerra JL, Salehi A, Speidel
D, Eliasson L and Cilio CM: Differences in islet-enriched miRNAs in
healthy and glucose intolerant human subjects. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 404:16–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wee EJ, Peters K, Nair SS, Hulf T, Stein
S, Wagner S, Bailey P, Lee SY, Qu WJ, Brewster B, et al: Mapping
the regulatory sequences controlling 93 breast cancer-associated
miRNA genes leads to the identification of two functional promoters
of the Hsa-mir-200b cluster, methylation of which is associated
with metastasis or hormone receptor status in advanced breast
cancer. Oncogene. 31:4182–4195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rothé F, Ignatiadis M, Chaboteaux C,
Haibe-Kains B, Kheddoumi N, Majjaj S, Badran B, Fayyad-Kazan H,
Desmedt C, Harris AL, et al: Global microRNA expression profiling
identifies MiR-210 associated with tumor proliferation, invasion
and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. PLoS One. 6:e209802011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang M, Shen H, Qiu C, Ni Y, Wang L, Dong
W, Liao Y and Du J: High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts
recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer.
Eur J Cancer. 49:604–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z,
Gomez MF, Lund E and Dahlberg JE: Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC
RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp.
3627–3632. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhu J, Feng Y, Ke Z, Yang Z, Zhou J, Huang
X and Wang L: Down-regulation of miR-183 promotes migration and
invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting Ezrin. Am J Pathol.
180:2440–2451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Toiyama Y, Hur K, Tanaka K, Inoue Y,
Kusunoki M, Boland CR and Goel A: Serum miR-200c is a novel
prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with
colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 259:735–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Viré E, Curtis C, Davalos V, Git A, Robson
S, Villanueva A, Vidal A, Barbieri I, Aparicio S, Esteller M, et
al: The breast cancer oncogene EMSY represses transcription of
antimetastatic microRNA miR-31. Mol Cell. 53:806–818. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Deng ZQ, Yin JY, Tang Q, Liu FQ, Qian J,
Lin J, Shao R, Zhang M and He L: Over-expression of miR-98 in FFPE
tissues might serve as a valuable source for biomarker discovery in
breast cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:1166–1171.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu H and Mo YY: Targeting miR-205 in
breast cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:1439–1448. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li X, Xie W, Xie C, Huang C, Zhu J, Liang
Z, Deng F, Zhu M, Zhu W, Wu R, et al: Curcumin modulates
miR-19/PTEN/AKT/p53 Axis to suppress bisphenol a-induced MCF-7
breast cancer cell proliferation. Phytother Res. 28:1553–1560.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hong S, Noh H, Teng Y, Shao J, Rehmani H,
Ding HF, Dong Z, Su SB, Shi H, Kim J and Huang S: SHOX2 Is a direct
miR-375 target and a novel epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
inducer in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 16:279–290. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhao H, Wang Y, Yang L, Jiang R and Li W:
MiR-25 promotes gastric cancer cells growth and motility by
targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem. 385:207–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, Magnus JF,
Kibukawa M, Schelter JM, Kobayashi SV, Lim L, Burchard J, Jackson
AL, et al: MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and
promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2167–2174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Choi OR and Lim IK: Loss of p21(Sdi1)
expression in senescent cells after DNA damage accompanied with
increase of miR-93 expression and reduced p53 interaction with p21
(Sdi1) gene promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 407:406–411.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sarkar S, Dubaybo H, Ali S, Goncalves P,
Kollepara SL, Sethi S, Philip PA and Li Y: Down-regulation of
miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through
up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2) and PUMA. Am J Cancer
Res. 3:465–477. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kurashina R, Kikuchi K, Iwaki J, Yoshitake
H, Takeshita T and Takizawa T: Placenta-specific miRNA (miR-512-3p)
targets PPP3R1 encoding the calcineurin B regulatory subunit in
BeWo cells. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 40:650–660. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu Z, Zhu J, Cao H, Ren H and Fang X:
miR-10b promotes cell invasion through RhoC-AKT signaling pathway
by targeting HOXD10 in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:1553–1560.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Papagiannakopoulos T, Friedmann-Morvinski
D, Neveu P, Dugas JC, Gill RM, Huillard E, Liu C, Zong H, Rowitch
DH, Barres BA, et al: Pro-neural miR-128 is a glioma tumor
suppressor that targets mitogenic kinases. Oncogene. 31:1884–1895.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xie Q, Huang Z, Yan Y, Li F and Zhong X:
miR-221 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related gene
expressions via regulation of PTEN/Akt signaling in drug-resistant
glioma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 34:218–222. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu HS, Zong HL, Shang M, Ming X, Zhao JP,
Ma C and Cao L: MiR-324-5p inhibits proliferation of glioma by
target regulation of GLI1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:828–832.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yang X, Yu J, Yin J, Xiang Q, Tang H and
Lei X: MiR-195 regulates cell apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by targeting LATS2. Pharmazie. 67:645–651.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tsang TY, Tang WY, Chan JY, Co NN, Au
Yeung CL, Yau PL, Kong SK, Fung KP and Kwok TT: P-glycoprotein
enhances radiation-induced apoptotic cell death through the
regulation of miR-16 and Bcl-2 expressions in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Apoptosis. 16:524–535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li L, Guo Z, Wang J, Mao Y and Gao Q:
Serum miR-18a: A potential marker for hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma screening. Dig Dis Sci. 57:2910–2916.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Zhang A, Li X, Liu J,
Zhao J, Zhao Y, Gao J, Fang D and Rao Z: IL-6 upregulation
contributes to the reduction of miR-26a expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:32–38.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Sheng Y, Li J, Zou C, Wang S, Cao Y, Zhang
J, Huang A and Tang H: Downregulation of miR-101-3p by hepatitis B
virus promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by targeting Rab5a. Arch Virol. 159:2397–2410.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yang XW, Zhang LJ, Huang XH, Chen LZ, Su
Q, Zeng WT, Li W and Wang Q: miR-145 suppresses cell invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: MiR-145 targets ADAM17. Hepatol
Res. 44:551–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Law PT, Ching AK, Chan AW, Wong QW, Wong
CK, To KF and Wong N: MiR-145 modulates multiple components of the
insulin-like growth factor pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 33:1134–41. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Epis MR, Giles KM, Barker A, Kendrick TS
and Leedman PJ: miR-331-3p regulates ERBB-2 expression and androgen
receptor signaling in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem.
284:24696–24704. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, Hynes PG,
Casey OM, Fang L, Yi M, Stephens RM, Seng V, Sheppard-Tillman H, et
al: MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and
tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene.
32:296–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Weiler J, Hunziker J and Hall J:
Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): Ammunition to target miRNAs
implicated in human disease? Gene Ther. 13:496–502. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Baigude H and Rana TM: Strategies to
antagonize miRNA functions in vitro and in vivo. Nanomedicine
(Lond). 9:2545–2555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lennox KA and Behlke MA: Chemical
modification and design of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides. Gene Ther.
18:1111–1120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gaglione M, Milano G, Chambery A, Moggio
L, Romanelli A and Messere A: PNA-based artificial nucleases as
antisense and anti-miRNA oligonucleotide agents. Mol Biosyst.
7:2490–2499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kim JH, Yeom JH, Ko JJ, Han MS, Lee K, Na
SY and Bae J: Effective delivery of anti-miRNA DNA oligonucleotides
by functionalized gold nanoparticles. J Biotechnol. 155:287–292.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Rayner KJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, McDaniel
AL, Marshall SM, van Gils JM, Ray TD, Sheedy FJ, Goedeke L, Liu X,
et al: Inhibition of miR-33a/b in non-human primates raises plasma
HDL and lowers VLDL triglycerides. Nature. 478:404–407. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ziegler S, Eberle ME, Wölfle SJ, Heeg K
and Bekeredjian-Ding I: Bifunctional oligodeoxynucleotide/antagomiR
constructs: Evaluation of a new tool for microRNA silencing.
Nucleic Acid Ther. 23:427–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Velu CS and Grimes HL: Utilizing antagomiR
(antisense microRNA) to knock down microRNA in murine bone marrow
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 928:185–195. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chabot S, Orio J, Castanier R, Bellard E,
Nielsen SJ, Golzio M and Teissié J: LNA-based oligonucleotide
electrotransfer for miRNA inhibition. Mol Ther. 20:1590–1598. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kluiver J, Slezak-Prochazka I,
Smigielska-Czepiel K, Halsema N, Kroesen BJ and van den Berg A:
Generation of miRNA sponge constructs. Methods. 58:113–117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Niu WY, Wu SQ, Xu ZZ, Lin J and Zhan R:
Anti-leukemia mechanism of miR-17 and miR-20a silencing mediated by
miRNA sponge. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 22:932–937.
2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wu SQ, Xu ZZ, Lin J and Zhan R:
Construction of miRNA sponge targeting miR-20a and stable
expression in Jurkat leukemia cell line. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye
Xue Za Zhi. 20:1056–1062. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
de Melo Maia B, Ling H, Monroig P, Ciccone
M, Soares FA, Calin GA and Rocha RM: Design of a miRNA sponge for
the miR-17 miRNA family as a therapeutic strategy against vulvar
carcinoma. Mol Cell Probes. 29:420–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Qureshi AT, Monroe WT, Dasa V, Gimble JM
and Hayes DJ: miR-148b-nanoparticle conjugates for light mediated
osteogenesis of human adipose stromal/stem cells. Biomaterials.
34:7799–7810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Babar IA, Cheng CJ, Booth CJ, Liang X,
Weidhaas JB, Saltzman WM and Slack FJ: Nanoparticle-based therapy
in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model of
lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp. E1695–E1704. 2012;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chen Y, Zhu X, Zhang X, Liu B and Huang L:
Nanoparticles modified with tumor-targeting scFv deliver siRNA and
miRNA for cancer therapy. Mol Ther. 18:1650–1656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
de Campos VE, Teixeira CA, da Veiga VF,
Ricci E Jr and Holandino C: L-tyrosine-loaded nanoparticles
increase the antitumoral activity of direct electric current in a
metastatic melanoma cell model. Int J Nanomedicine. 5:961–971.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gu J, Chen X, Xin H, Fang X and Sha X:
Serum-resistant complex nanoparticles functionalized with
imidazole-rich polypeptide for gene delivery to pulmonary
metastatic melanoma. Int J Pharm. 461:559–569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|