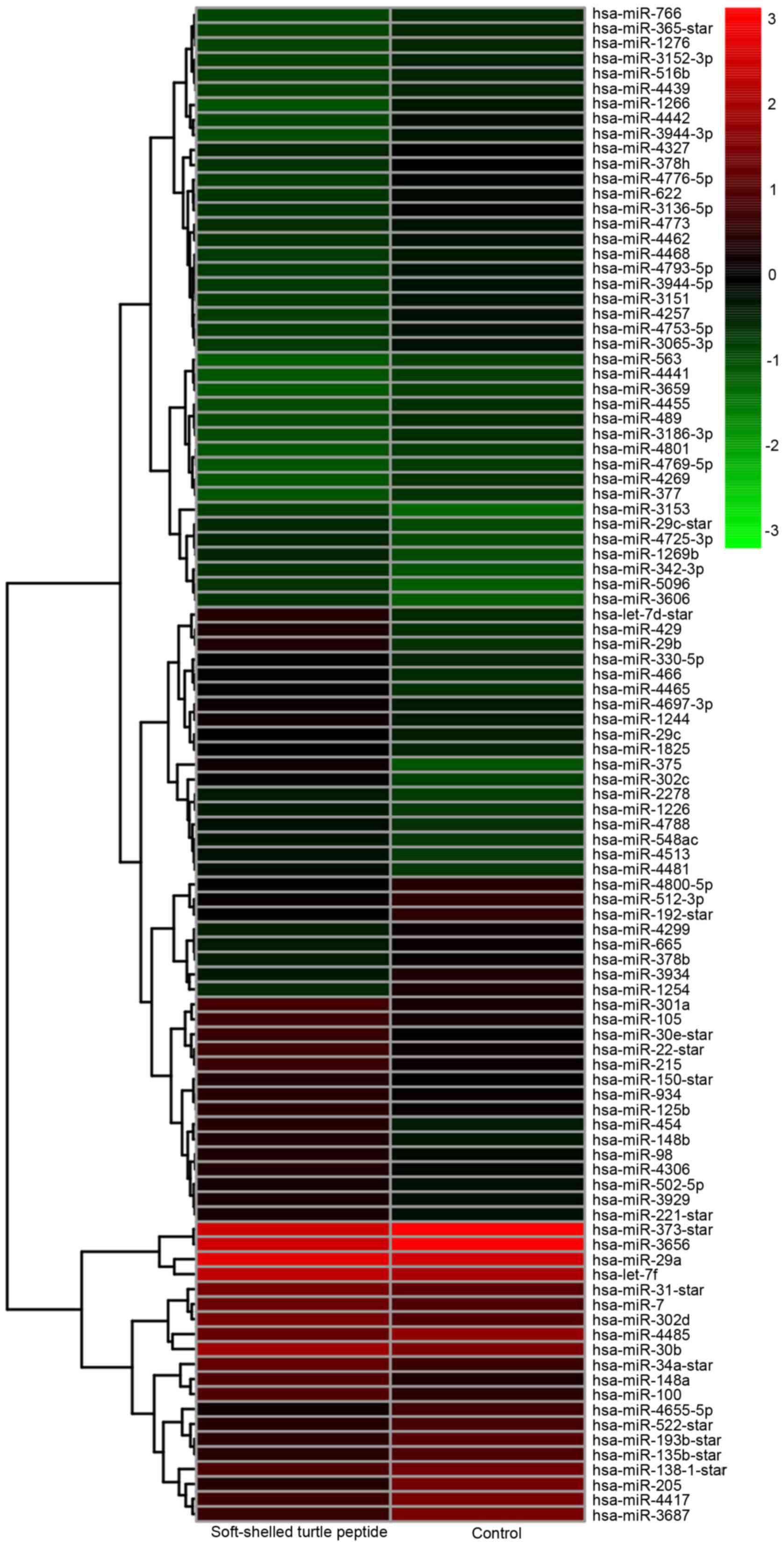
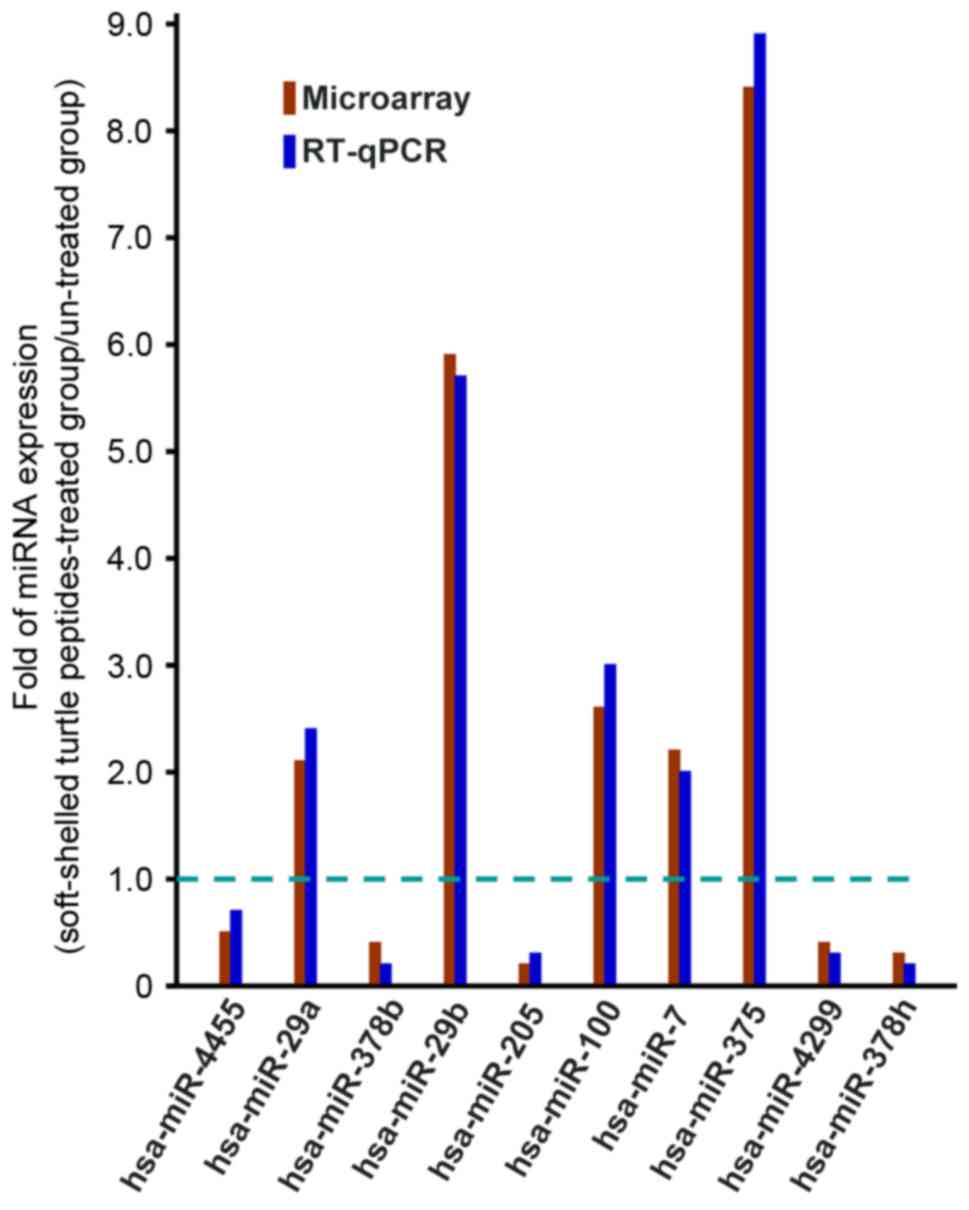
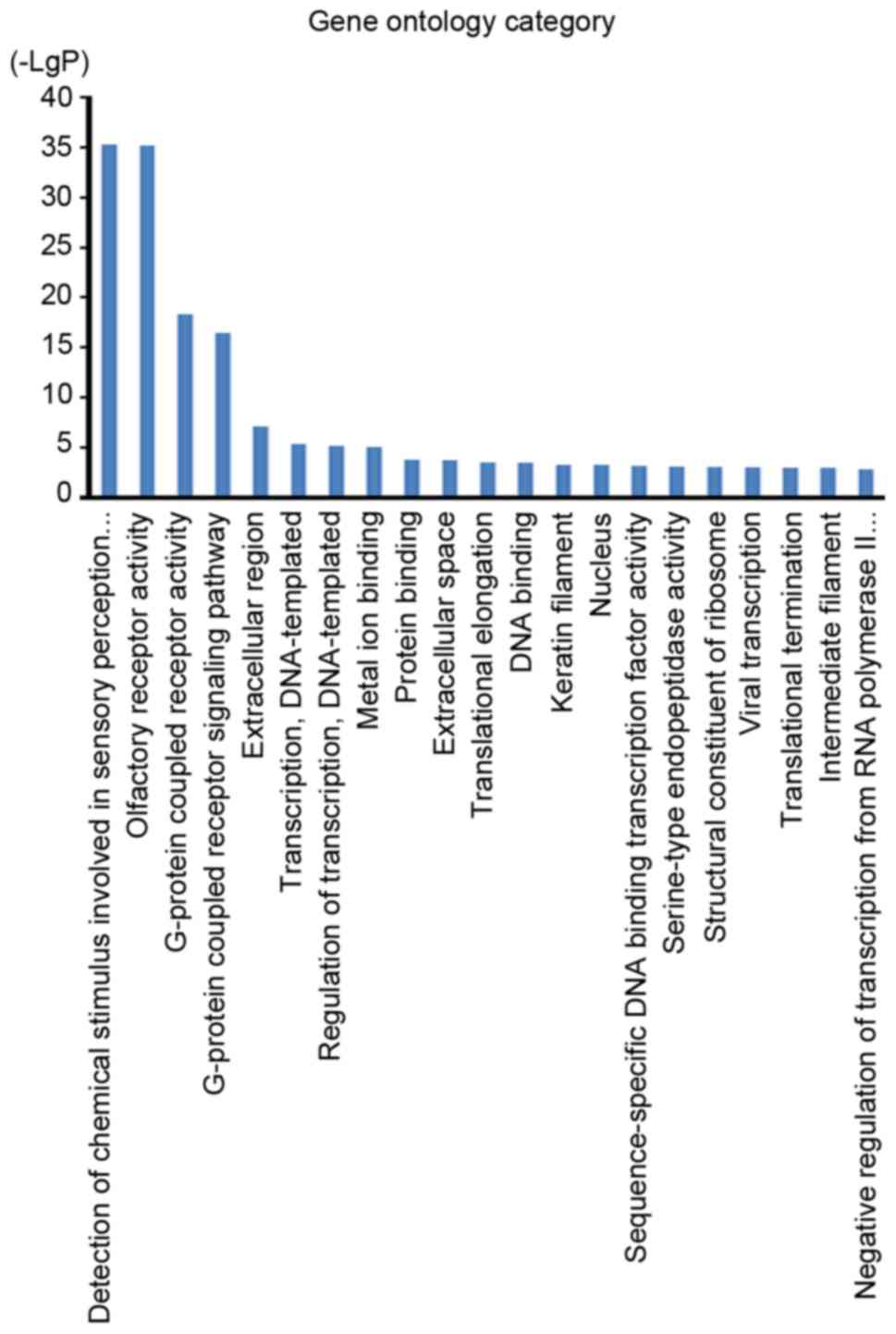
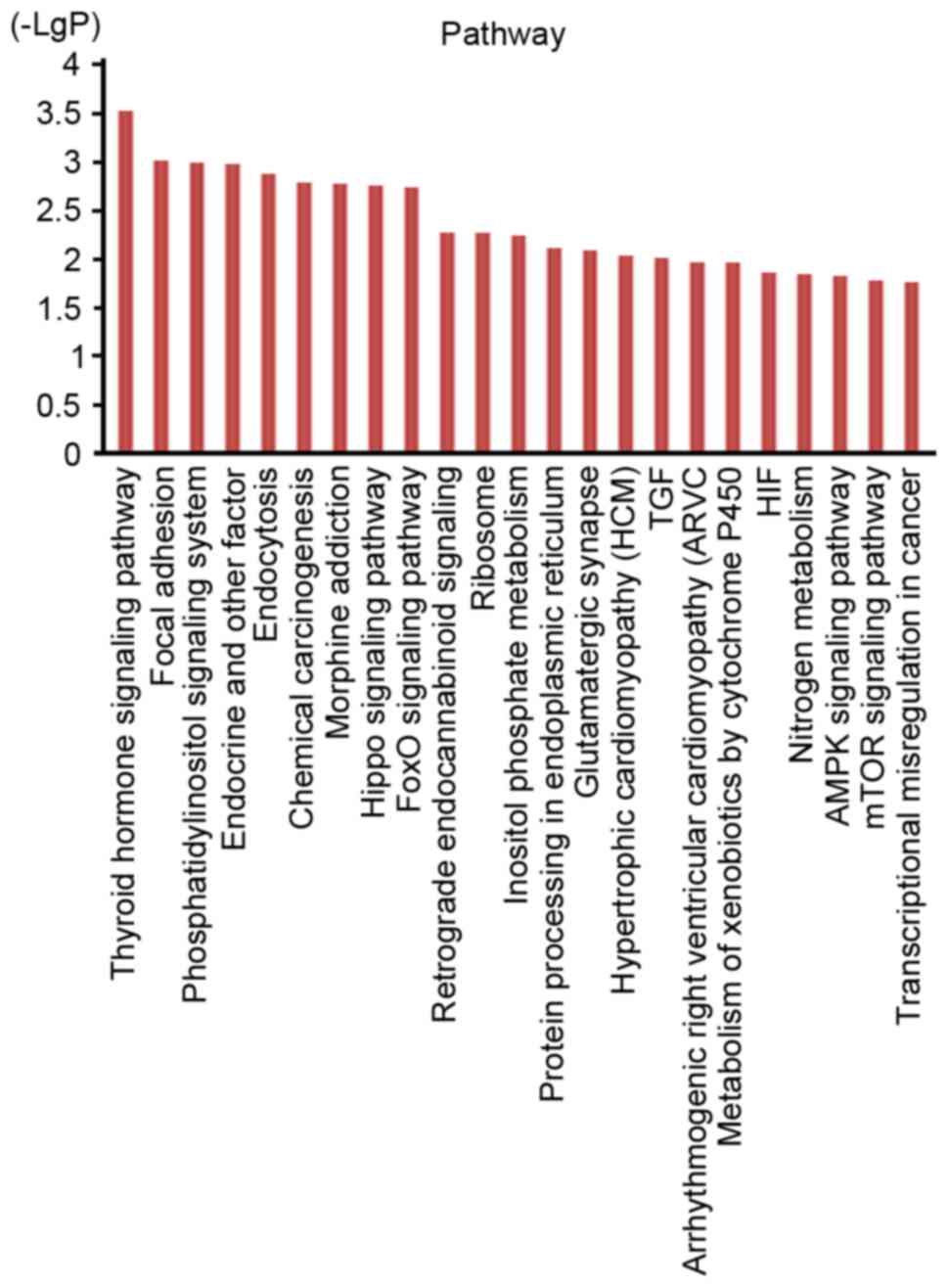
|
1
|
Toyota M, Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Yamano H,
Imai K and Shinomura Y: Integrated analysis of genetic and
epigenetic alterations in cancer. Epigenomics. 1:291–299. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gerhauser C: Cancer chemoprevention and
nutriepigenetics: State of the art and future challenges. Top Curr
Chem. 329:73–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu XX, Yu JL, Ying LS, Han J, Wang S, Yu
QM, Wang XB, Fang XH and Ling ZQ: Stepwise cumulation of RUNX3
methylation mediated by Helicobacter pylori infection contributes
to gastric carcinoma progression. Cancer. 118:5507–5517. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fang MZ, Wang Y, Ai N, Hou Z, Sun Y, Lu H,
Welsh W and Yang CS: Tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced
genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 63:7563–7570.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nandakumar V, Vaid M and Katiyar SK:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reactivates silenced tumor
suppressor genes, Cip1/p21 and p16INK4a, by reducing DNA
methylation and increasing histones acetylation in human skin
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:537–544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan H, Zhu Y, Liu B, Wu H, Li Y, Wu X,
Zhou Q and Xu K: Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates the
apoptosis of highly metastatic human non-small cell lung cancer
cells induced by isothiocyanates. Br J Nutr. 106:1779–1791. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lawson AP, Long MJ, Coffey RT, Qian Y,
Weerapana E, El Oualid F and Hedstrom L: Naturally occurring
isothiocyanates exert anticancer effects by inhibiting
deubiquitinating enzymes. Cancer Res. 75:5130–5142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guan F, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Li M and
Wang C: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and migration of
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through autophagy-dependent Akt
degradation. PLoS One. 11:e01465532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chhabria SV, Akbarsha MA, Li AP, Kharkar
PS and Desai KB: In situ allicin generation using targeted
alliinase delivery for inhibition of MIA PaCa-2 cells via
epigenetic changes, oxidative stress and cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor (CDKI) expression. Apoptosis. 20:1388–1409. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sinha D, Sarkar N, Biswas J and Bishayee
A: Resveratrol for breast cancer prevention and therapy:
Preclinical evidence and molecular mechanisms. Semin Cancer Biol.
40-41:1–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park JS, Khoi PN, Joo YE, Lee YH, Lang SA,
Stoeltzing O and Jung YD: EGCG inhibits recepteur dorigine nantais
expression by suppressing Egr-1 in gastric cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 42:1120–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Iwasaki M, Haiman CA, Kono S,
Wilkens LR, Keku TO, Berndt SI, Tsugane S and Le Marchand L:
Interaction between red meat intake and NAT2 genotype in increasing
the risk of colorectal cancer in Japanese and African Americans.
PLoS One. 10:e01449552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taunk P, Hecht E and Stolzenberg-Solomon
R: Are meat and heme iron intake associated with pancreatic cancer?
Results from the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Cohort. Int J Cancer.
138:2172–2189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C and Cervellin G: Meat
consumption and cancer risk: A critical review of published
meta-analyses. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 97:1–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao CG and Shen YM: Anti-cancer effect
and edible methods of soft-shelled turtle. China Agricultural
Publishing House; Beijing: 2008
|
|
16
|
Fu JJ, Tan SL, Li YG, Lv H, Zhu WF and Liu
HN: Adjuvant effects of snapping turtle co-peptide (STCP) on
radiotherapy for cancer. J Jiangxi Uni Trad Chin Med. 27:68–71.
2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Juzėnas S, Saltenienė V, Kupcinskas J,
Link A, Kiudelis G, Jonaitis L, Jarmalaite S, Kupcinskas L,
Malfertheiner P and Skieceviciene J: Analysis of deregulated
microRNAs and their target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01323272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding L, Xu Y, Zhang W, Deng Y, Si M, Du Y,
Yao H, Liu X, Ke Y, Si J and Zhou T: miR-375 frequently
downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting JAK2. Cell Res. 20:784–793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Xing R, Zhang X, Dong W, Zhang J,
Yan Z, Li W, Cui J and Lu Y: miR-375 targets the p53 gene to
regulate cellular response to ionizing radiation and etoposide in
gastric cancer cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 12:741–750. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shiotani A, Murao T, Kimura Y, Matsumoto
H, Kamada T, Kusunoki H, Inoue K, Uedo N, Iishi H and Haruma K:
Identification of serum miRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for
detection of high risk for early gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
109:2323–2330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui H, Wang L, Gong P, Zhao C, Zhang S,
Zhang K, Zhou R, Zhao Z and Fan H: Deregulation between miR-29b/c
and DNMT3A is associated with epigenetic silencing of the CDH1
gene, affecting cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01239262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lang N, Liu M, Tang QL, Chen X, Liu Z and
Bi F: Effects of microRNA-29 family members on proliferation and
invasion of gastric cancer cell lines. Chin J Cancer. 29:603–610.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun T, Wang C, Xing J and Wu D: miR-429
modulates the expression of c-myc in human gastric carcinoma cells.
Eur J Cancer. 47:2552–2559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu D, Xia P, Diao D, Cheng Y, Zhang H,
Yuan D, Huang C and Dang C: miRNA-429 suppresses the growth of
gastric cancer cells in vitro. J Biomed Res. 26:389–393. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ning X, Shi Z, Liu X, Zhang A, Han L,
Jiang K, Kang C and Zhang Q: DNMT1 and EZH2 mediated methylation
silences the microRNA-200b/a/429 gene and promotes tumor
progression. Cancer Lett. 359:198–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu P, Zhang J, Zhu J, Shi J, Zhu Q and
Gao Y: MiR-429 induces gastric carcinoma cell apoptosis through
Bcl-2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1572–1580. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sakamoto N, Naito Y, Oue N, Sentani K,
Uraoka N, Zarni Oo H, Yanagihara K, Aoyagi K, Sasaki H and Yasui W:
MicroRNA-148a is downregulated in gastric cancer, targets MMP7, and
indicates tumor invasiveness and poor prognosis. Cancer Sci.
105:236–243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zuo J, Xia J, Ju F, Yan J, Zhu A, Jin S,
Shan T and Zhou H: MicroRNA-148a can regulate runt-related
transcription factor 3 gene expression via modulation of DNA
methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Mol Cells. 35:313–319. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim SY, Jeon TY, Choi CI, Kim DH, Kim DH,
Kim GH, Ryu DY, Lee BE and Kim HH: Validation of circulating miRNA
biomarkers for predicting lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer.
J Mol Diagn. 15:661–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zuo QF, Cao LY, Yu T, Gong L, Wang LN,
Zhao YL, Xiao B and Zou QM: MicroRNA-22 inhibits tumor growth and
metastasis in gastric cancer by directly targeting MMP14 and Snail.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e20002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang Y, Liu X, Su B, Zhang Z, Zeng X, Lei
Y, Shan J, Wu Y, Tang H and Su Q: microRNA-22 acts as a metastasis
suppressor by targeting metadherin in gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep.
11:454–460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Yu H, Lu X, Zhang P, Wang M and Hu
Y: miR-22 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric
cancer cells by inhibiting CD151. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
445:175–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sugihara H, Ishimoto T, Watanabe M,
Sawayama H, Iwatsuki M, Baba Y, Komohara Y, Takeya M and Baba H:
Identification of miR-30e* regulation of Bmi1 expression mediated
by tumor-associated macrophages in gastrointestinal cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e818392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song YX, Yue ZY, Wang ZN, Xu YY, Luo Y, Xu
HM, Zhang X, Jiang L, Xing CZ and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-148b is
frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and acts as a tumor
suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 10:12011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang B, Huang J, Liu H, Guo W and Li G:
miR-335 directly, while miR-34a indirectly modulate survivin
expression and regulate growth, apoptosis, and invasion of gastric
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:1771–1779. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peng Y, Guo JJ, Liu YM and Wu XL:
MicroRNA-34A inhibits the growth, invasion and metastasis of
gastric cancer by targeting PDGFR and MET expression. Biosci Rep.
34:e001122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cao W, Fan R, Wang L, Cheng S, Li H, Jiang
J, Geng M, Jin Y and Wu Y: Expression and regulatory function of
miRNA-34a in targeting survivin in gastric cancer cells. Tumour
Biol. 34:963–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He M, Gao L, Zhang S, Tao L, Wang J, Yang
J and Zhu M: Prognostic significance of miR-34a and its target
proteins of FOXP1, p53, and BCL2 in gastric MALT lymphoma and
DLBCL. Gastric Cancer. 17:431–441. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yin WZ, Li F, Zhang L, Ren XP, Zhang N and
Wen JF: Down-regulation of microRNA-205 promotes gastric cancer
cell proliferation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:1027–1032.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen L, Lü MH, Zhang D, Hao NB, Fan YH, Wu
YY, Wang SM, Xie R, Fang DC, Zhang H, et al: miR-1207-5p and
miR-1266 suppress gastric cancer growth and invasion by targeting
telomerase reverse transcriptase. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10342014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu YJ and Fan Y: miR-215/192 participates
in gastric cancer progression. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:34–40. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jin Z, Selaru FM, Cheng Y, Kan T, Agarwal
R, Mori Y, Olaru AV, Yang J, David S, Hamilton JP, et al:
MicroRNA-192 and −215 are upregulated in human gastric cancer in
vivo and suppress ALCAM expression in vitro. Oncogene.
30:1577–1585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Q, Ge X, Zhang Y, Xia H, Yuan D, Tang
Q, Chen L, Pang X, Leng W and Bi F: Plasma miR-122 and miR-192 as
potential novel biomarkers for the early detection of distant
metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1863–1870. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wen X, Wu JQ, Peng W, Feng JF and Tang JH:
MicroRNA-377 predicts poor clinical outcome of gastric cancer and
induces tumorigenesis by targeting multiple tumor-suppressor genes.
Oncol Rep. 34:203–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen J, Sun D, Chu H, Gong Z, Zhang C,
Gong B, Li Y, Li N and Jiang L: Screening of differential microRNA
expression in gastric signet ring cell carcinoma and gastric
adenocarcinoma and target gene prediction. Oncol Rep. 33:2963–2971.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Link A, Balaguer F and Goel A: Cancer
chemoprevention by dietary polyphenols: Promising role for
epigenetics. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1771–1792. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Avissar M, Christensen BC, Kelsey KT and
Marsit CJ: MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2850–2855. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y,
Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, Kumamoto K, Hughes D, et
al: MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: Associations with survival. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6192–6200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bhatti I, Lee A, James V, Hall RI, Lund
JN, Tufarelli C, Lobo DN and Larvin M: Knockdown of microRNA-21
inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting
programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 15:199–208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C,
Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S and Zucman-Rossi J:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu Y, Jin J, Liu Y, Huang Z, Deng Y, You
T, Zhou T, Si J and Zhuo W: Snail-regulated MiR-375 inhibits
migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting JAK2.
PLoS One. 9:e995162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chang H, Kim N, Park JH, Nam RH, Choi YJ,
Lee HS, Yoon H, Shin CM, Park YS, Kim JM and Lee DH: Different
microRNA expression levels in gastric cancer depending on
Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut Liver. 9:188–196. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen D, Li Y, Li Y, Jin L, Su Z, Yu Z,
Yang S, Mao X and Lai Y: Tumor suppressive microRNA429 regulates
cellular function by targeting VEGF in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:1361–1366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Z, Zhou Q, Miao Y, Tian H, Li Y,
Feng X and Song X: MiR-429 induces apoptosis of glioblastoma cell
through Bcl-2. Tumour Biol. Oct 28–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
58
|
Liu W, An J, Li K and Hou H: miR-429
regulates gastric cancer cell invasiveness through ZEB proteins.
Tumour Biol. Oct 15–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
59
|
Zheng B, Liang L, Wang C, Huang S, Cao X,
Zha R, Liu L, Jia D, Tian Q, Wu J, et al: MicroRNA-148a suppresses
tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in
gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7574–7583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Patel M, Verma A, Aslam I, Pringle H and
Singh B: Novel plasma microRNA biomarkers for the identification of
colitis-associated carcinoma. Lancet. 385 Suppl 1:S782015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Touhara K, Sengoku S, Inaki K, Tsuboi A,
Hirono J, Sato T, Sakano H and Haga T: Functional identification
and reconstitution of an odorant receptor in single olfactory
neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:pp. 4040–4045. 1999; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Feldmesser E, Olender T, Khen M, Yanai I,
Ophir R and Lancet D: Widespread ectopic expression of olfactory
receptor genes. BMC Genomics. 7:1212006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kang N, Kim H, Jae Y, Lee N, Ku CR,
Margolis F, Lee EJ, Bahk YY, Kim MS and Koo J: Olfactory marker
protein expression is an indicator of olfactory receptor-associated
events in non-olfactory tissues. PLoS One. 10:e01160972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sanz G, Leray I, Dewaele A, Sobilo J,
Lerondel S, Bouet S, Grébert D, Monnerie R, Pajot-Augy E and Mir
LM: Promotion of cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis emergence
caused by olfactory receptor stimulation. PLoS One. 9:e851102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gelis L, Jovancevic N, Bechara FG, Neuhaus
EM and Hatt H: Functional expression of olfactory receptors in
human primary melanoma and melanoma metastasis. Exp Dermatol.
26:569–576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zeng Q and Hong W: The emerging role of
the Hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control,
and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell. 13:188–192. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Meng Z, Moroishi T and Guan KL: Mechanisms
of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 30:1–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhao Y and Yang X: The Hippo pathway in
chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 137:2767–2773.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xie D, Cui J, Xia T, Jia Z, Wang L, Wei W,
Zhu A, Gao Y, Xie K and Quan M: Hippo transducer TAZ promotes
epithelial mesenchymal transition and supports pancreatic cancer
progression. Oncotarget. 6:35949–35963. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Yuan C, Wang D, Zhang
W, Qi B, Qiu J, Song X, Ye J, et al: The Hippo transducer TAZ
promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell
maintenance in oral cancer. Mol Oncol. 9:1091–1105. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yagi H, Asanoma K, Ohgami T, Ichinoe A,
Sonoda K and Kato K: GEP oncogene promotes cell proliferation
through YAP activation in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 35:4471–4480.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lamar JM, Stern P, Liu H, Schindler JW,
Jiang ZG and Hynes RO: The Hippo pathway target, YAP, promotes
metastasis through its TEAD-interaction domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:pp. E2441–E2450. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang G, Lu X, Dey P, Deng P, Wu CC, Jiang
S, Fang Z, Zhao K, Konaparthi R, Hua S, et al: Targeting
YAP-dependent MDSC infiltration impairs tumor progression. Cancer
Dis. 6:80–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhou GX, Li XY, Zhang Q, Zhao K, Zhang CP,
Xue CH, Yang K and Tian ZB: Effects of the hippo signaling pathway
in human gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5199–5205.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Perra A, Kowalik MA, Ghiso E,
Ledda-Columbano GM, Di Tommaso L, Angioni MM, Raschioni C, Testore
E, Roncalli M, Giordano S and Columbano A: YAP activation is an
early event and a potential therapeutic target in liver cancer
development. J Hepatol. 61:1088–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Santucci M, Vignudelli T, Ferrari S, Mor
M, Scalvini L, Bolognesi ML, Uliassi E and Costi MP: The Hippo
pathway and YAP/TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interaction as targets for
regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. J Med Chem.
58:4857–4873. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu AM, Poon RT and Luk JM: MicroRNA-375
targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits
tumor properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:623–627. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Guan H, Tan P, Xie L, Mi B, Fang Z, Li J,
Yue J, Liao H and Li F: FOXO1 inhibits osteosarcoma oncogenesis via
Wnt/β-catenin pathway suppression. Oncogenesis. 4:e1662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bullock M: FOXO factors and breast cancer:
Outfoxing endocrine resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer. 23:R113–R130.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Martins R, Lithgow GJ and Link W: Long
live FOXO: Unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and
longevity. Aging Cell. 15:196–207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bar N and Dikstein R: miR-22 forms a
regulatory loop in PTEN/AKT pathway and modulates signaling
kinetics. PloS One. 5:e108592010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu C, Jin B, Chen L, Zhuo D, Zhang Z, Gong
K and Mao Z: MiR-30d induces apoptosis and is regulated by the
Akt/FOXO pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Signal.
25:1212–1221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|