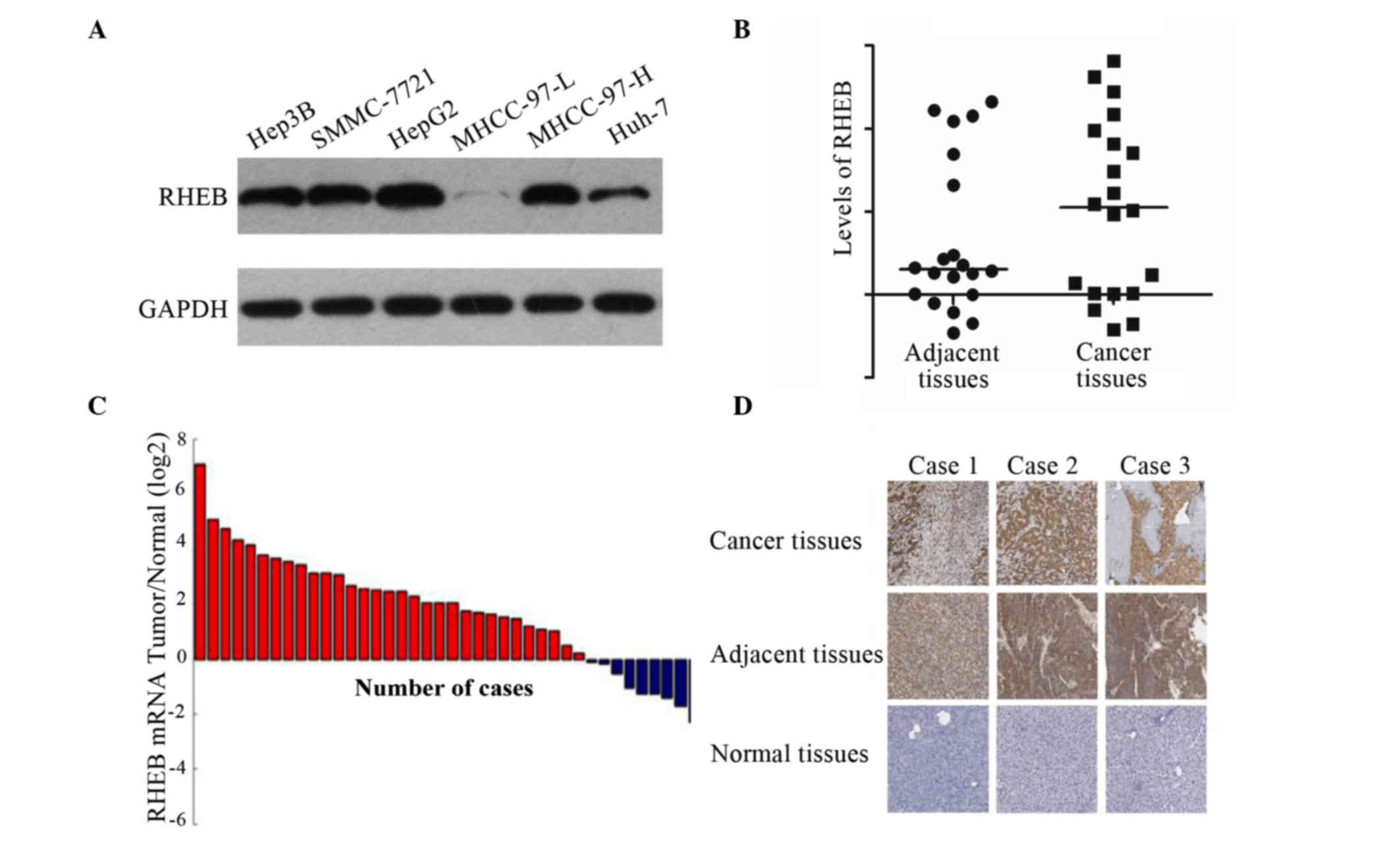
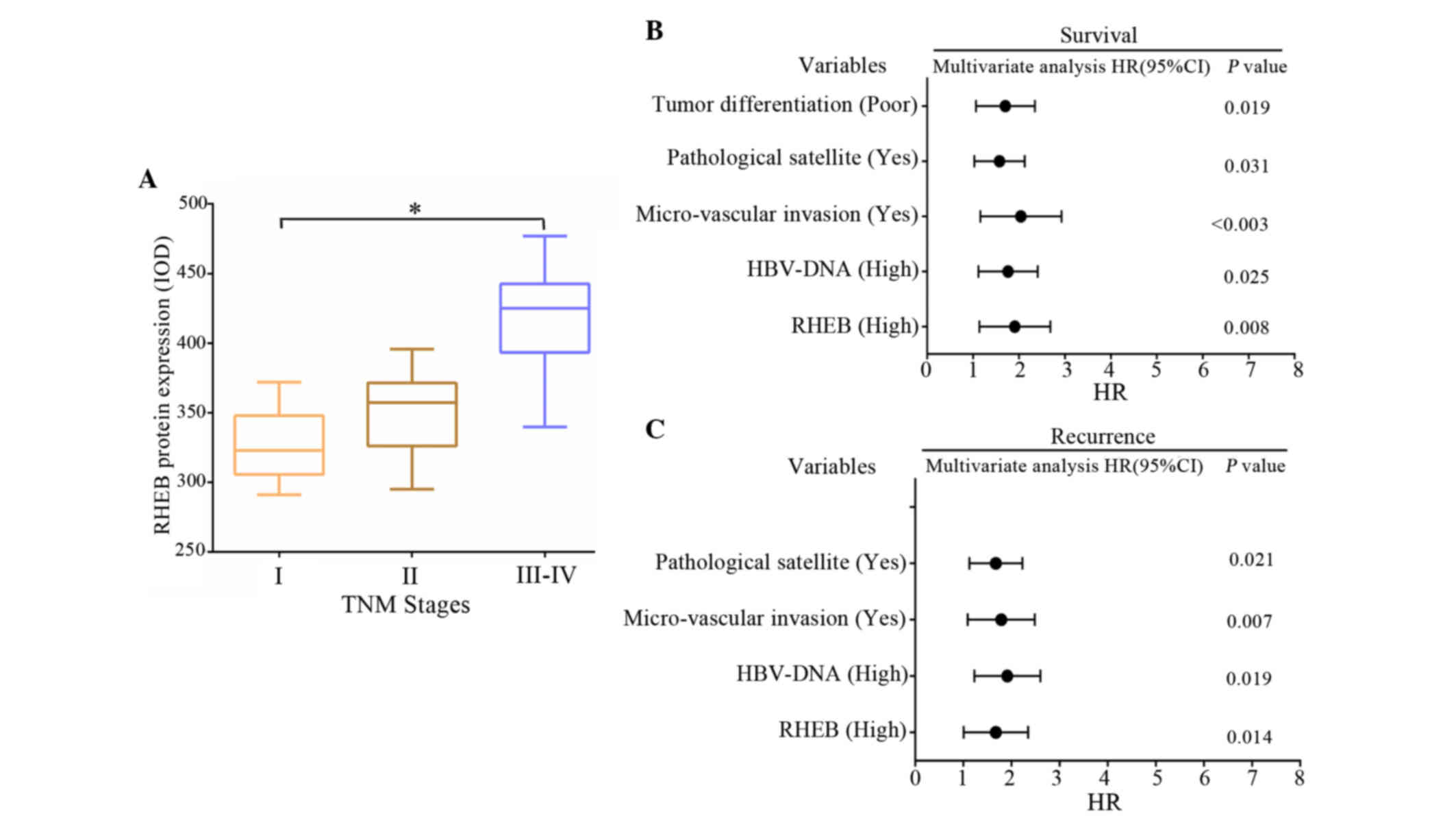
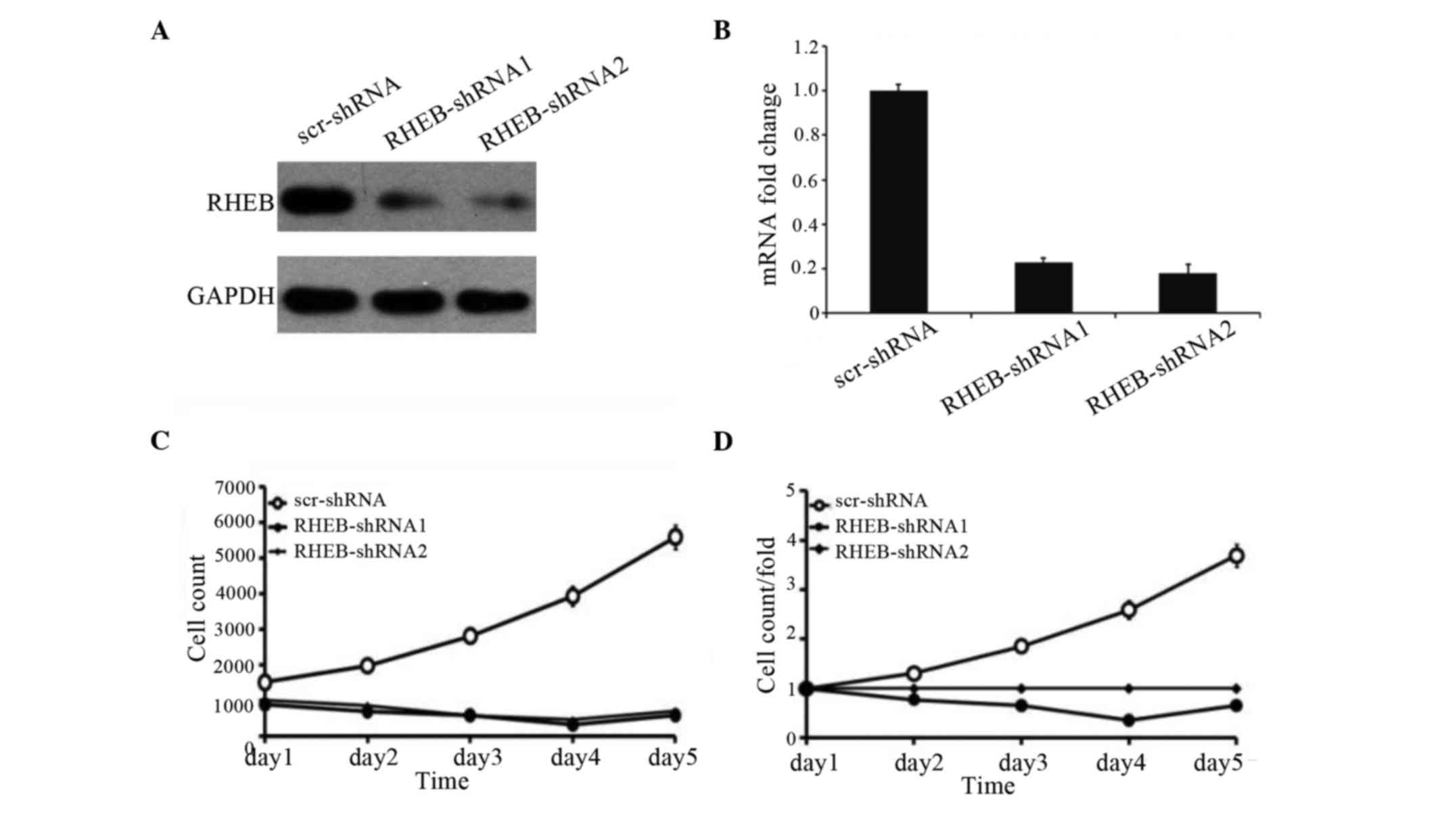
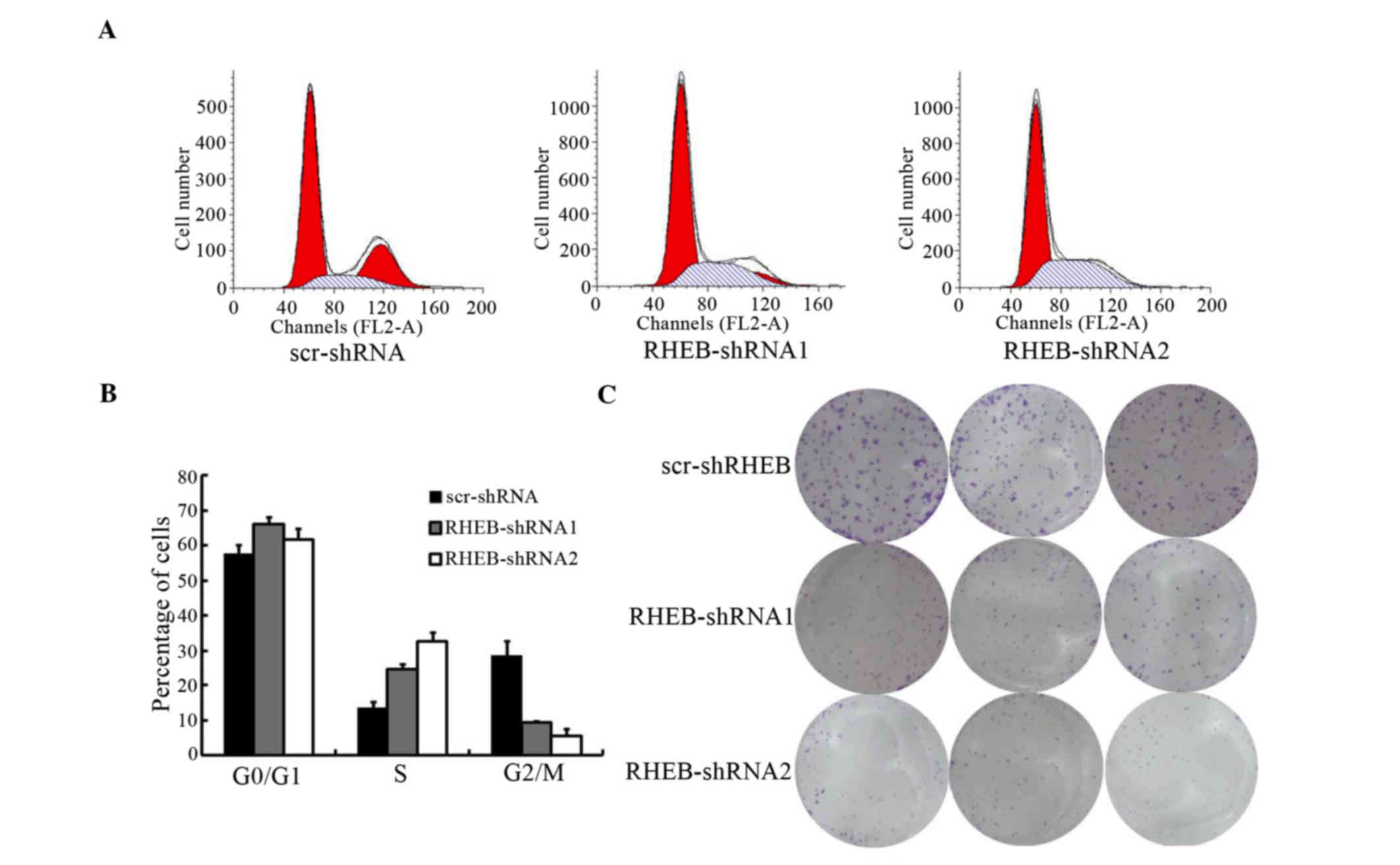
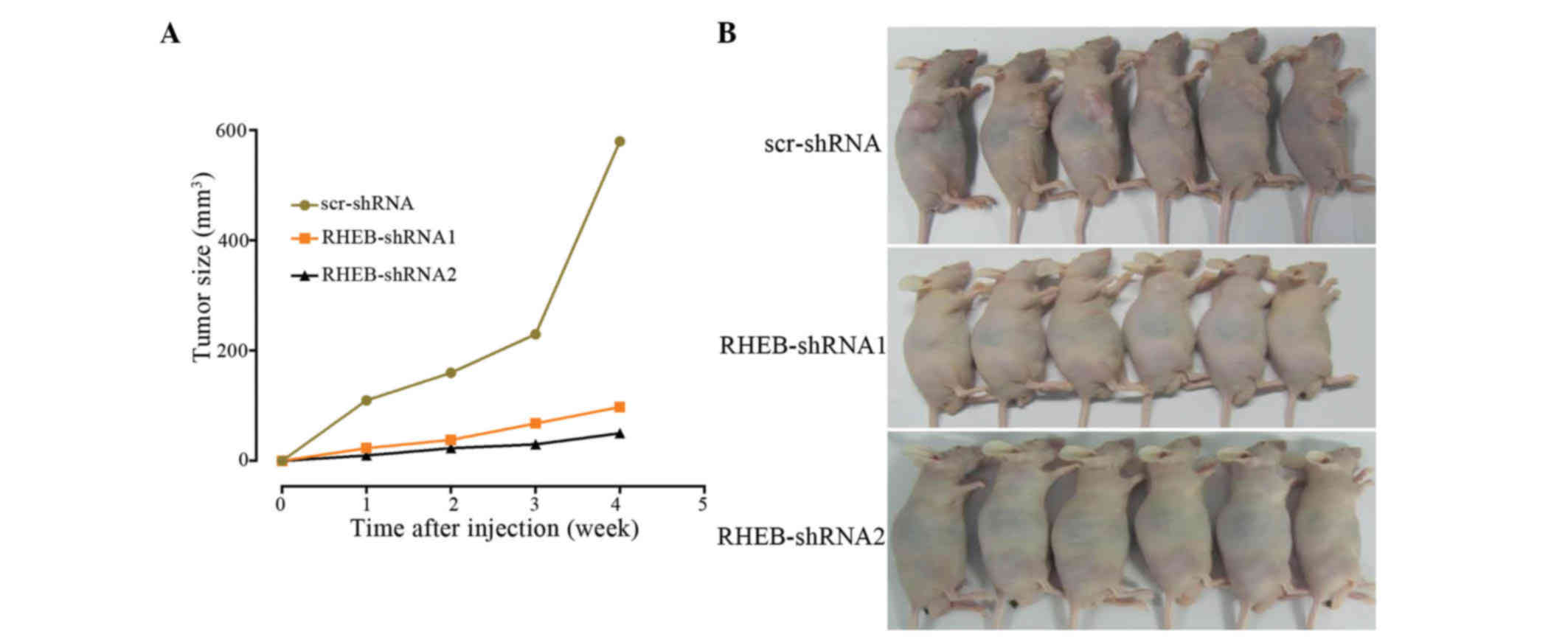
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song P, Feng X, Zhang K, et al: Screening
for and surveillance of high-risk patients with HBV-related chronic
liver disease: Promoting the early detection of hepatocellular
carcinoma in China. Biosci Trends. 7:1–6. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye
QH, Wang L, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Li Y, et al: A decade's studies on
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
130:187–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka M, Katayama F, Kato H, Tanaka H,
Wang J, Qiao YL and Inoue M: Hepatitis B and C virus infection and
hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A review of epidemiology and
control measures. J Epidemiol. 21:401–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singhal A, Jayaraman M, Dhanasekaran DN
and Kohli V: Molecular and serum markers in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Predictive tools for prognosis and recurrence. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 82:116–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feng YX, Wang T, Deng YZ, Yang P, Li JJ,
Guan DX, Yao F, Zhu YQ, Qin Y, Wang H, et al: Sorafenib suppresses
postsurgical recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
in an orthotopic mouse model. Hepatology. 53:483–492. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu KT, Wang CC, Lu LG, Zhang WD, Zhang FJ,
Shi F and Li CX: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical study of
long-term survival and choice of treatment modalities. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:3649–3657. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Im E, von Lintig FC, Chen J, Zhuang S, Qui
W, Chowdhury S, Worley PF, Boss GR and Pilz RB: Rheb is in a high
activation state and inhibits B-Raf kinase in mammalian cells.
Oncogene. 21:6356–6365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aspuria PJ and Tamanoi F: The Rheb family
of GTP-binding proteins. Cell Signal. 16:1105–1112. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inoki K, Li Y, Xu T and Guan KL: Rheb
GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR
signaling. Genes Dev. 17:1829–1834. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu ZH, Shvartsman MB, Lee AY, Shao JM,
Murray MM, Kladney RD, Fan D, Krajewski S, Chiang GG, Mills GB and
Arbeit JM: Mammalian target of rapamycin activator RHEB is
frequently overexpressed in human carcinomas and is critical and
sufficient for skin epithelial carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
70:3287–3298. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kobayashi T, Shimizu Y, Terada N, Yamasaki
T, Nakamura E, Toda Y, Nishiyama H, Kamoto T, Ogawa O and Inoue T:
Regulation of androgen receptor transactivity and mTOR-S6 kinase
pathway by Rheb in prostate cancer cell proliferation. Prostate.
70:866–874. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wazir U, Newbold RF, Jiang WG, Sharma AK
and Mokbel K: Prognostic and therapeutic implications of mTORC1 and
Rictor expression in human breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 29:1969–1974.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Avruch J, Hara K, Lin Y, Liu M, Long X,
Ortiz-Vega S and Yonezawa K: Insulin and amino-acid regulation of
mTOR signaling and kinase activity through the Rheb GTPase.
Oncogene. 25:6361–6372. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: Defining the
role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 12:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saucedo LJ, Gao X, Chiarelli DA, Li L, Pan
D and Edgar BA: Rheb promotes cell growth as a component of the
insulin/TOR signalling network. Nat Cell Biol. 5:566–571. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inoue T, Yoshida T, Shimizu Y, Kobayashi
T, Yamasaki T, Toda Y, Segawa T, Kamoto T, Nakamura E and Ogawa O:
Requirement of androgen-dependent activation of protein kinase
Czeta for androgen-dependent cell proliferation in LNCaP Cells and
its roles in transition to androgen-independent cells. Mol
Endocrinol. 20:3053–3069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stocker H, Radimerski T, Schindelholz B,
Wittwer F, Belawat P, Daram P, Breuer S, Thomas G and Hafen E: Rheb
is an essential regulator of S6K in controlling cell growth in
Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol. 5:559–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mavrakis KJ, Zhu H, Silva RL, Mills JR,
Teruya-Feldstein J, Lowe SW, Tam W, Pelletier J and Wendel HG:
Tumorigenic activity and therapeutic inhibition of Rheb GTPase.
Genes Dev. 22:2178–2188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wen ZH, Su YC, Lai PL, Zhang Y, Xu YF,
Zhao A, Yao GY, Jia CH, Lin J, Xu S, et al: Critical role of
arachidonic acid-activated mTOR signaling in breast carcinogenesis
and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 32:160–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng H, Liu A, Liu B, Li M, Yu H and Luo
X: Ras homologue enriched in brain is a critical target of
farnesyltransferase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 297:117–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mazhab-Jafari MT, Marshall CB, Ho J,
Ishiyama N, Stambolic V and Ikura M: Structure-guided mutation of
the conserved G3-box glycine in Rheb generates a constitutively
activated regulator of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). J Biol
Chem. 289:12195–12201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|