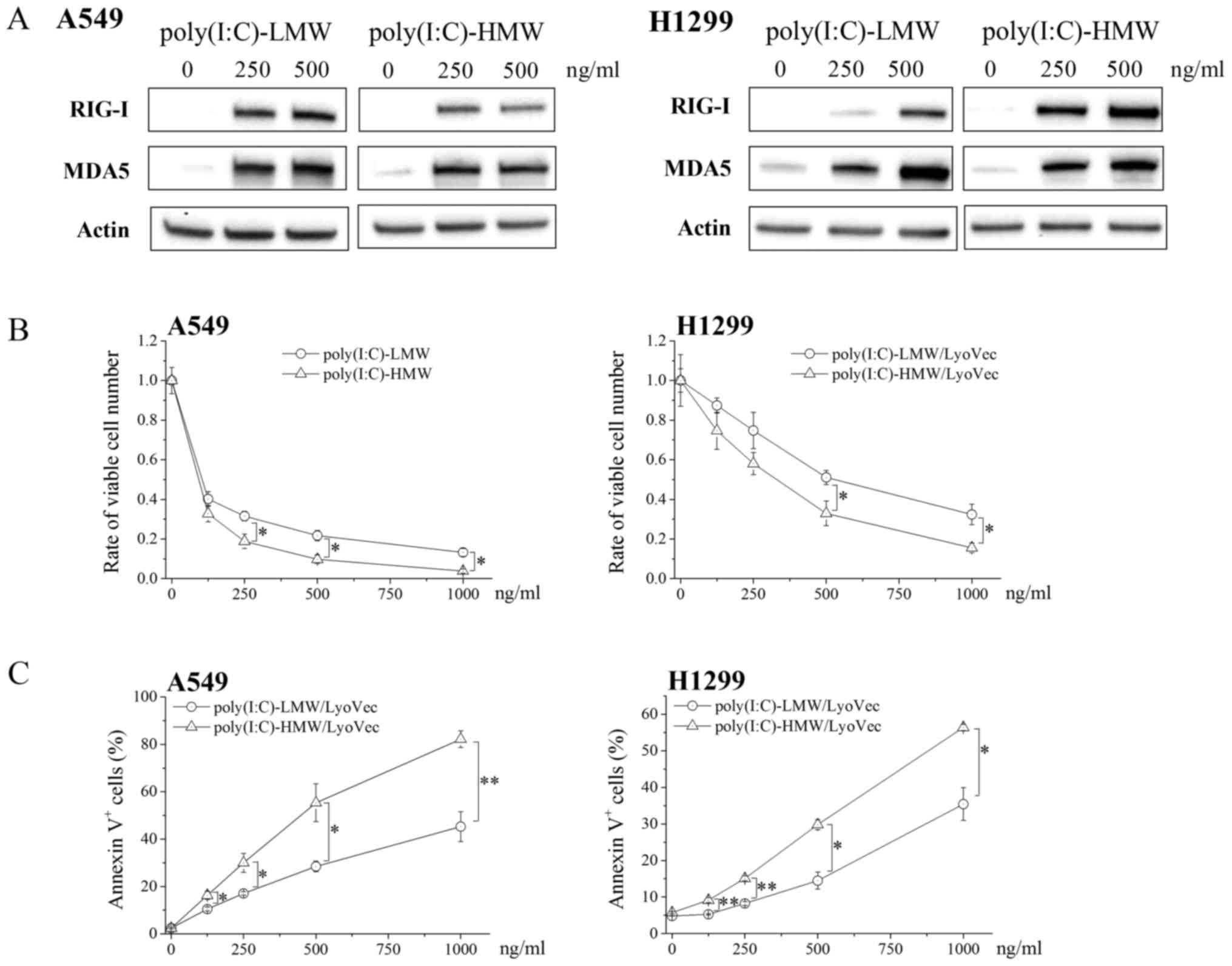
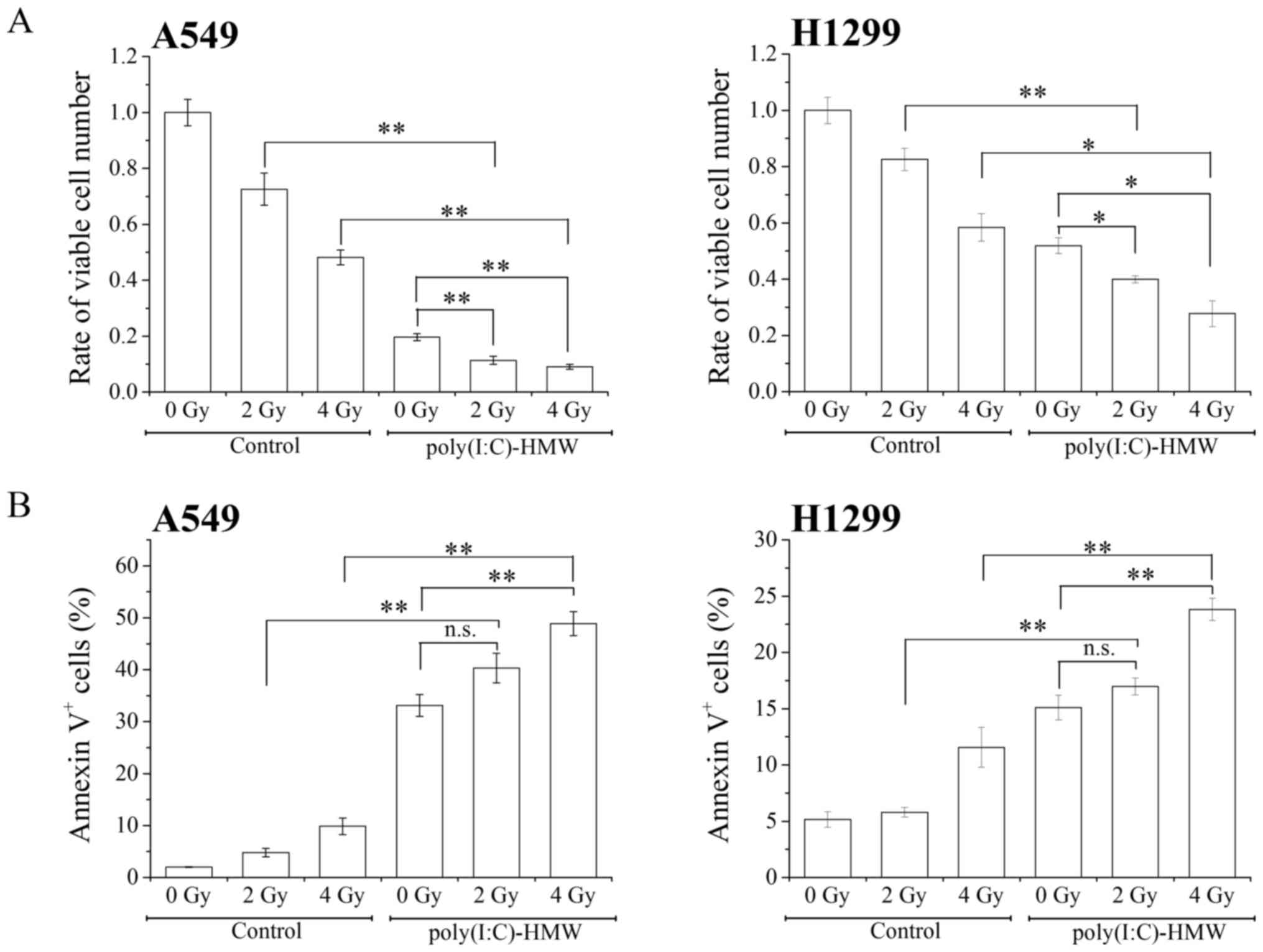
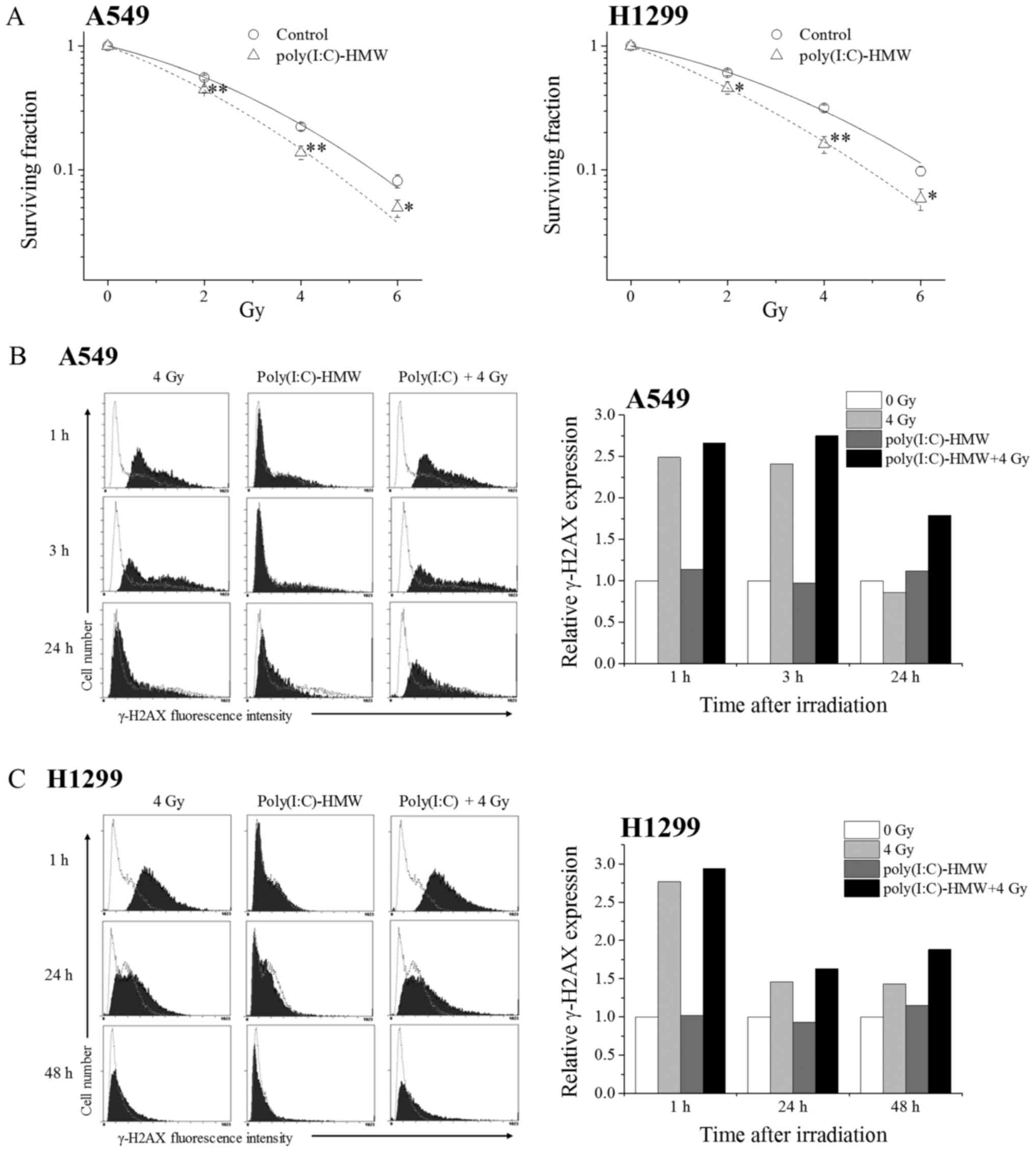
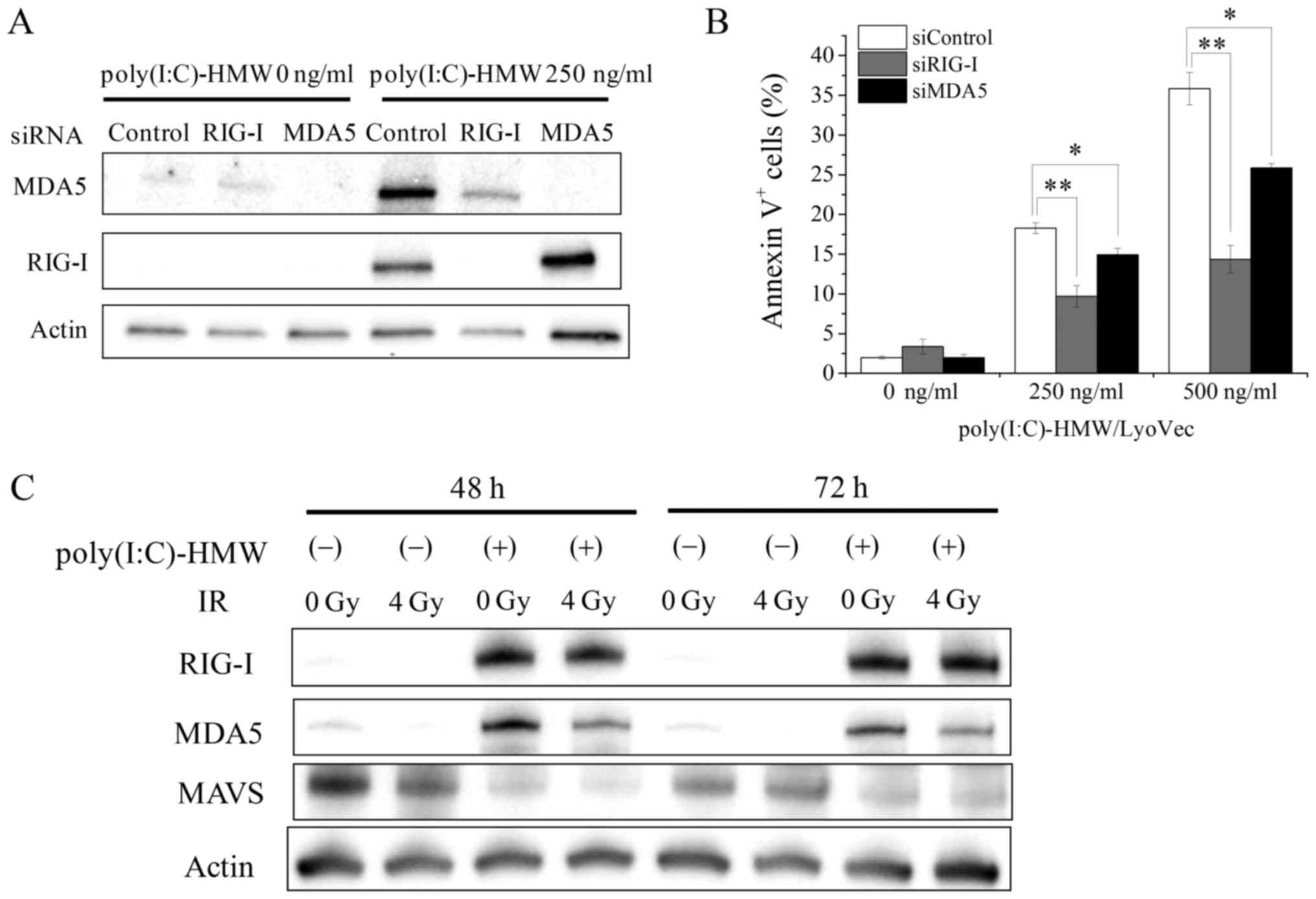
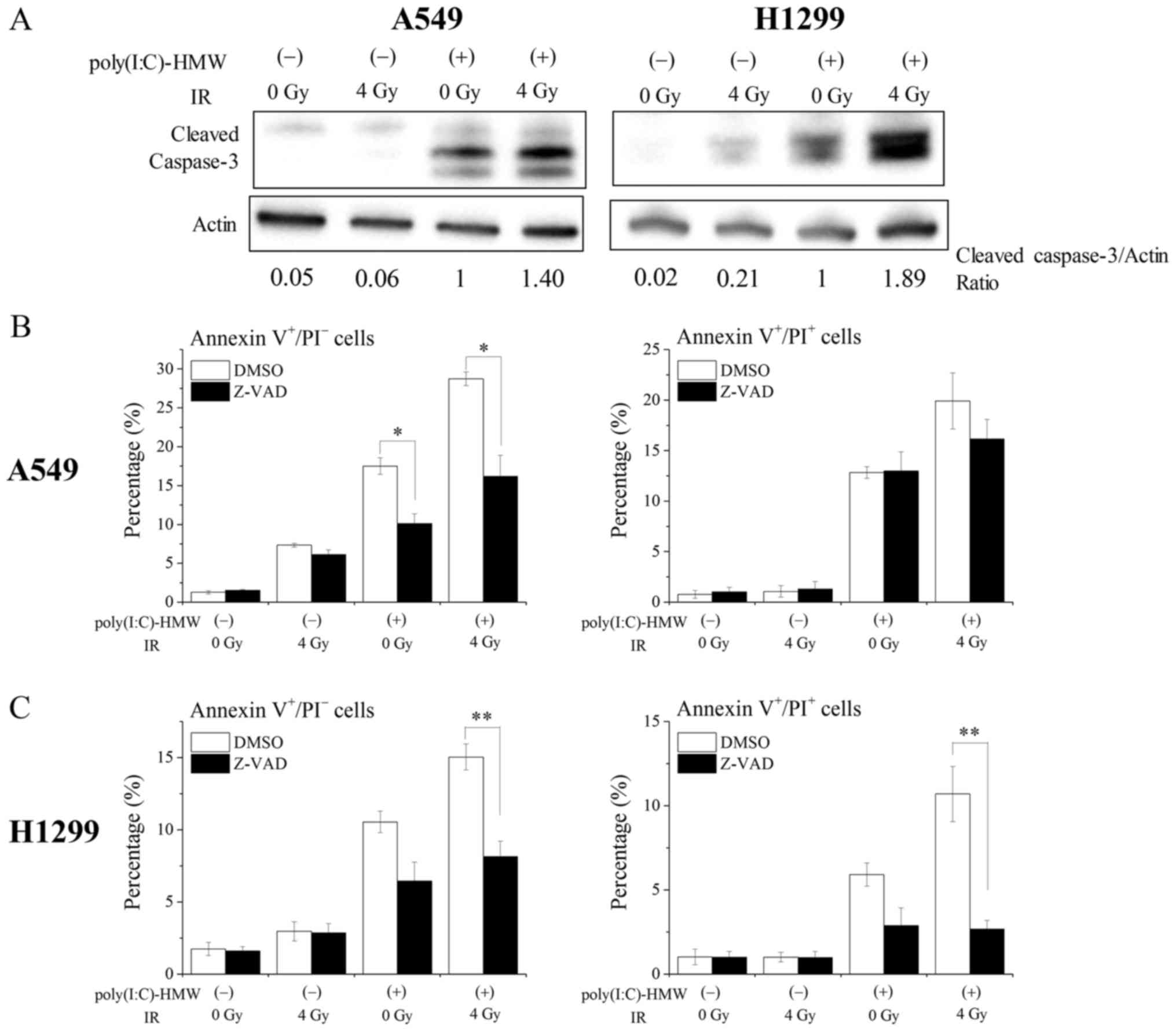
|
1
|
Duchen MR: Mitochondria in health and
disease: Perspectives on a new mitochondrial biology. Mol Aspects
Med. 25:365–451. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pourcelot M and Arnoult D: Mitochondrial
dynamics and the innate antiviral immune response. FEBS J.
281:3791–3802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsumiya T and Stafforini DM: Function
and regulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I. Crit Rev Immunol.
30:489–513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kato H, Takeuchi O, Mikamo-Satoh E, Hirai
R, Kawai T, Matsushita K, Hiiragi A, Dermody TS, Fujita T and Akira
S: Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic
acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma
differentiation-associated gene 5. J Exp Med. 205:1601–1610. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Yoneyama M,
Yamamoto M, Matsui K, Uematsu S, Jung A, Kawai T, Ishii KJ, et al:
Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition
of RNA viruses. Nature. 441:101–105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li K, Qu S, Chen X, Wu Q and Shi M:
Promising targets for cancer immunotherapy: TLRs, RLRs, and
STING-mediated innate immune pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 18:pii:
E4042017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Besch R, Poeck H, Hohenauer T, Senft D,
Häcker G, Berking C, Hornung V, Endres S, Ruzicka T, Rothenfusser S
and Hartmann G: Proapoptotic signaling induced by RIG-I and MDA-5
results in type I interferon-independent apoptosis in human
melanoma cells. J Clin Invest. 119:2399–2411. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan D, Xia M, Meng G, Xu C, Song Y and
Wei J: Anti-angiogenic efficacy of 5′-triphosphate siRNA combining
VEGF silencing and RIG-I activation in NSCLCs. Oncotarget.
6:29664–29674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoshino H, Chiba K, Saitoh T and
Kashiwakura I: Ionizing radiation affects the expression of
Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in human monocytic cells through c-Jun
N-terminal kinase activation. J Radiat Res. 55:876–884. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshino H, Saitoh T, Kozakai M and
Kashiwakura I: Effects of ionizing radiation on retinoic
acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors. Biomed Rep. 3:59–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsai MF, Wang CC and Chen JJ: Tumour
suppressor HLJ1: A potential diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic
target in non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol.
5:865–873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoshino H, Kumai Y and Kashiwakura I:
Effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress on apoptosis induction in
radioresistant macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 15:2867–2872. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fukushi S, Yoshino H, Yoshizawa A and
Kashiwakura I: p53-independent structure-activity relationships of
3-ring mesogenic compounds' activity as cytotoxic effects against
human non-small cell lung cancer lines. BMC Cancer. 16:5212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS
and Bonner WM: DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX
phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 273:5858–5868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jacobs JL and Coyne CB: Mechanisms of MAVS
regulation at the mitochondrial membrane. J Mol Biol.
425:5009–5019. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Castanier C, Zemirli N, Portier A, Garcin
D, Bidère N, Vazquez A and Arnoult D: MAVS ubiquitination by the E3
ligase TRIM25 and degradation by the proteasome is involved in type
I interferon production after activation of the antiviral
RIG-I-like receptors. BMC Biol. 10:442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imaizumi T, Aizawa-Yashiro T, Tsuruga K,
Tanaka H, Matsumiya T, Yoshida H, Tatsuta T, Xing F, Hayakari R and
Satoh K: Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 regulates the
expression of a chemokine CXCL10 in human mesangial cells:
Implications for chronic inflammatory renal diseases. Tohoku J Exp
Med. 228:17–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poeck H, Besch R, Maihoefer C, Renn M,
Tormo D, Morskaya SS, Kirschnek S, Gaffal E, Landsberg J, Hellmuth
J, et al: 5′-Triphosphate-siRNA: Turning gene silencing and
Rig-Iactivation against melanoma. Nat Med. 14:1256–1263. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li D, Gale RP, Liu Y, Lei B, Wang Y, Diao
D and Zhang M: 5′-Triphosphate siRNA targeting MDR1 reverses
multi-drug resistance and activates RIG-I-induced
immune-stimulatory and apoptotic effects against human myeloid
leukaemia cells. Leuk Res. 58:23–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duewell P, Steger A, Lohr H, Bourhis H,
Hoelz H, Kirchleitner SV, Stieg MR, Grassmann S, Kobold S, Siveke
JT, et al: RIG-I-like helicases induce immunogenic cell death of
pancreatic cancer cells and sensitize tumors toward killing by
CD8(+) T cells. Cell Death Differ. 21:1825–1837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ranoa DR, Parekh AD, Pitroda SP, Huang X,
Darga T, Wong AC, Huang L, Andrade J, Staley JP, Satoh T, et al:
Cancer therapies activate RIG-I-like receptor pathway through
endogenous non-coding RNAs. Oncotarget. 7:26496–26515. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Widau RC, Parekh AD, Ranck MC, Golden DW,
Kumar KA, Sood RF, Pitroda SP, Liao Z, Huang X, Darga TE, et al:
RIG-I-like receptor LGP2 protects tumor cells from ionizing
radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:pp. E484–E491. 2014;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burnette BC, Liang H, Lee Y, Chlewicki L,
Khodarev NN, Weichselbaum RR, Fu YX and Auh SL: The efficacy of
radiotherapy relies upon induction of type i interferon-dependent
innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Res. 71:2488–2496. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmidberger H, Rave-Fränk M, Lehmann J,
Schweinfurth S, Rehring E, Henckel K and Hess CF: The combined
effect of interferon beta and radiation on five human tumor cell
lines and embryonal lung fibroblasts. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
43:405–412. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lei Y, Moore CB, Liesman RM, O'Connor BP,
Bergstralh DT, Chen ZJ, Pickles RJ and Ting JP: MAVS-mediated
apoptosis and its inhibition by viral proteins. PLoS One.
4:e54662009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu CY, Chiang RL, Chang TH, Liao CL and
Lin YL: The interferon stimulator mitochondrial antiviral signaling
protein facilitates cell death by disrupting the mitochondrial
membrane potential and by activating caspases. J Virol.
84:2421–2431. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
El Maadidi S, Faletti L, Berg B, Wenzl C,
Wieland K, Chen ZJ, Maurer U and Borner C: A novel mitochondrial
MAVS/Caspase-8 platform links RNA virus-induced innate antiviral
signaling to Bax/Bak-independent apoptosis. J Immunol.
192:1171–1183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Verbrugge I, de Vries E, Tait SW, Wissink
EH, Walczak H, Verheij M and Borst J: Ionizing radiation modulates
the TRAIL death-inducing signaling complex, allowing bypass of the
mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Oncogene. 27:574–584. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim MJ, Lee KH and Lee SJ: Ionizing
radiation utilizes c-Jun N-terminal kinase for amplification of
mitochondrial apoptotic cell death in human cervical cancer cells.
FEBS J. 275:2096–2108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maier P, Hartmann L, Wenz F and Herskind
C: Cellular pathways in response to ionizing radiation and their
targetability for tumor radiosensitization. Int J Mol Sci. 17:pii:
E1022016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim JY, An YM, Choi WH, Kim JM, Cho S, Yoo
BR, Kang JW, Lee YS, Lee YJ and Cho J: Pro-apoptotic Noxa is
involved in ablative focal irradiation-induced lung injury. J Cell
Mol Med. 21:711–719. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Guo YM, Hirokawa M, Iwamoto K,
Ubukawa K, Michishita Y, Fujishima N, Tagawa H, Takahashi N, Xiao
W, et al: A synthetic double-stranded RNA, poly I:C, induces a
rapid apoptosis of human CD34(+) cells. Exp Hematol. 40:330–341.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|