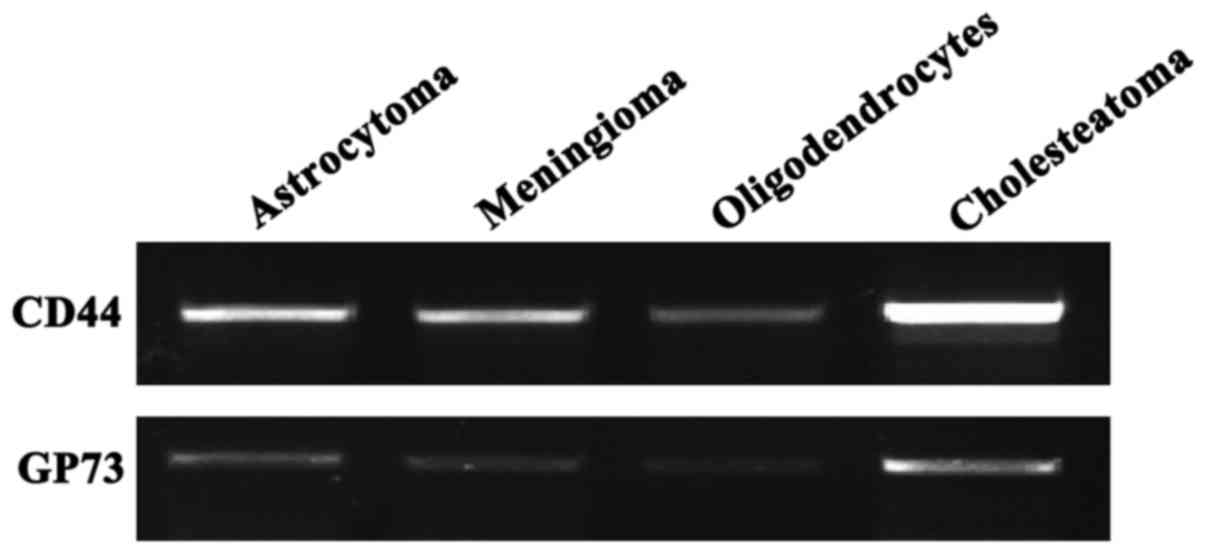
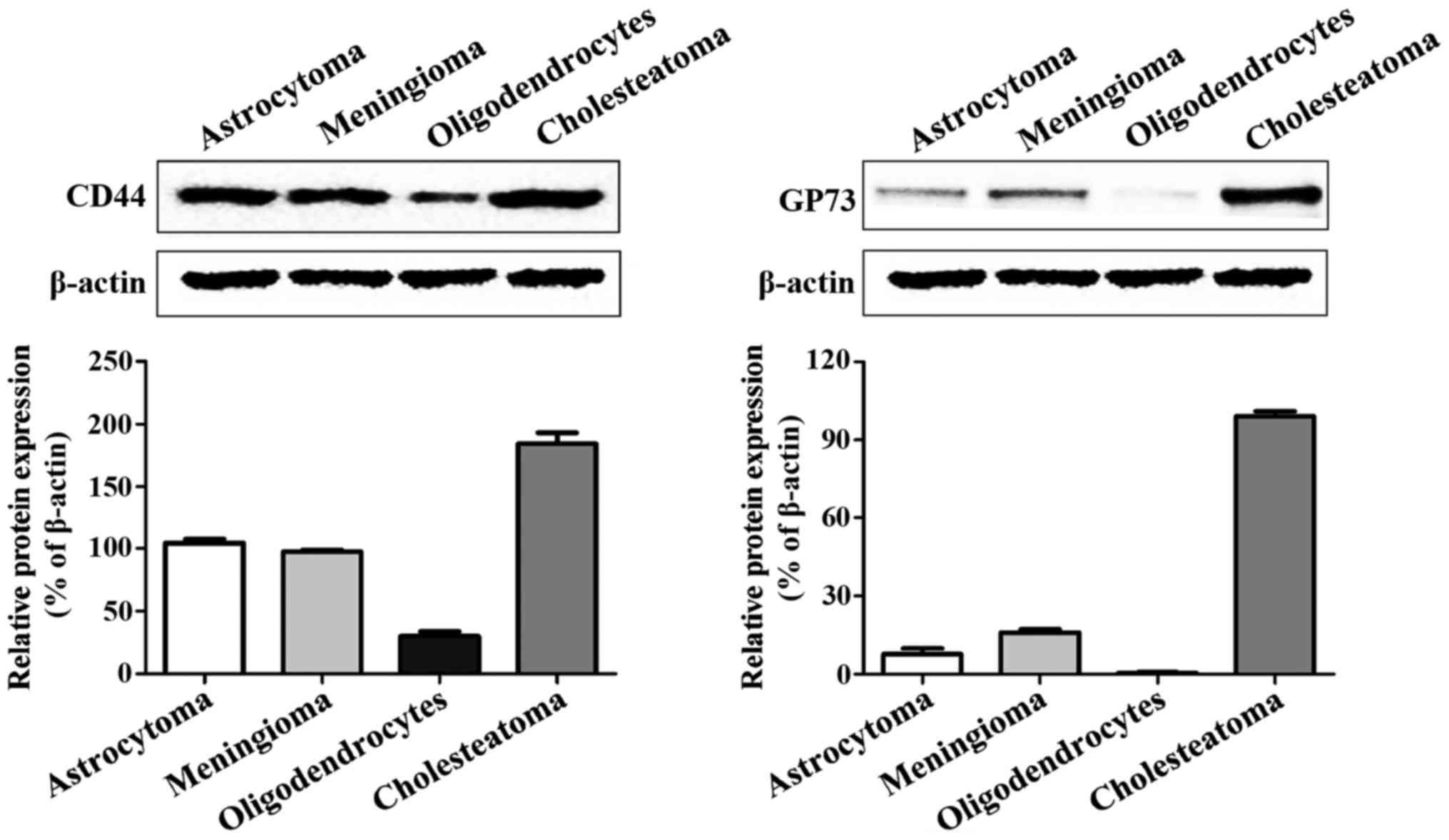
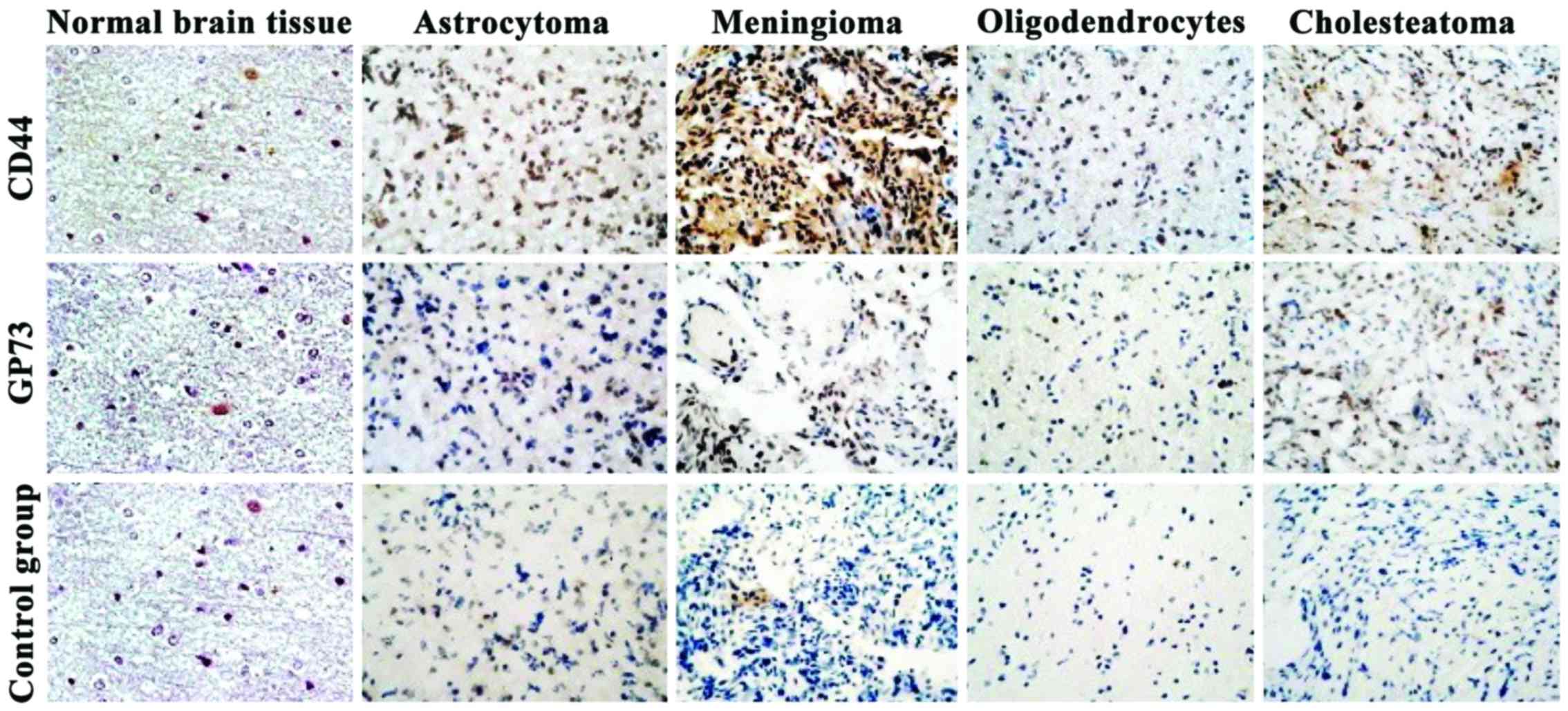
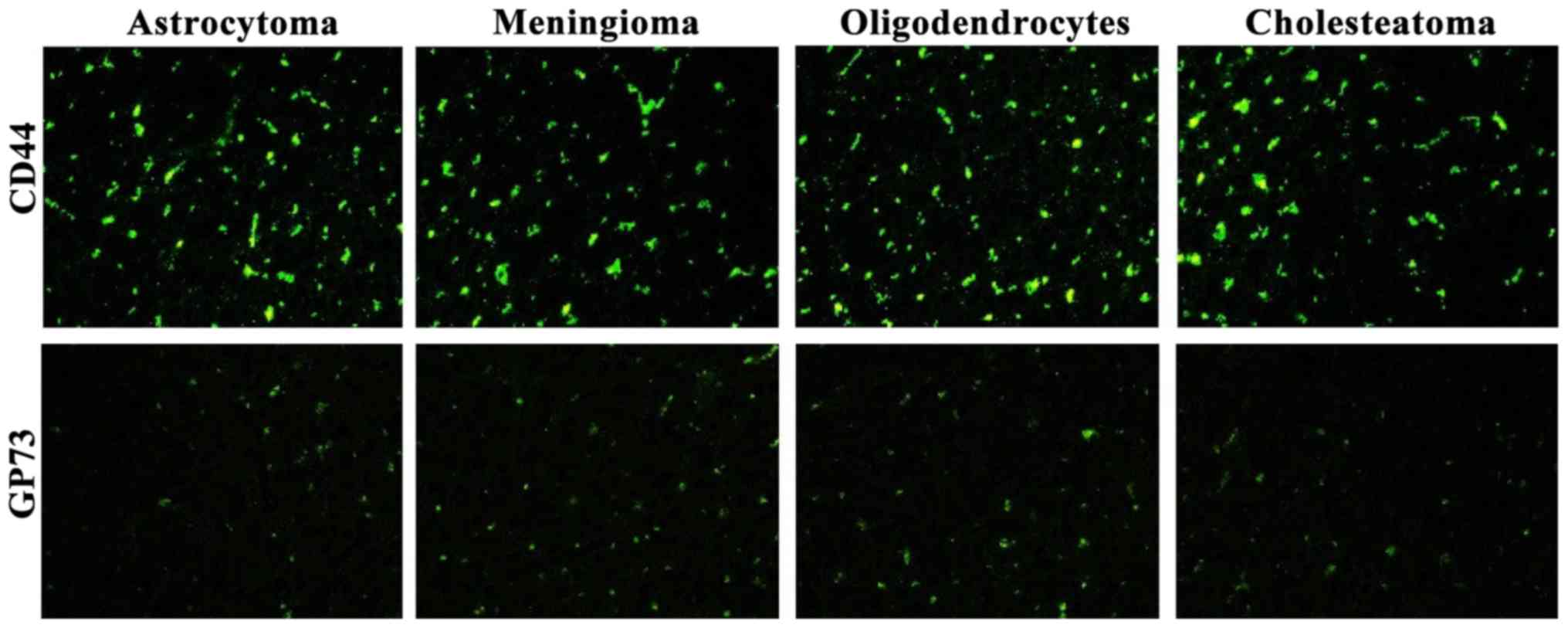
|
1
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti
B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F and Vescovi
A: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Orian-Rousseau V and Ponta H: Perspectives
of CD44 targeting therapies. Arch Toxicol. 89:3–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goodison S, Urquidi V and Tarin D: CD44
cell adhesion molecules. Mol Pathol. 52:189–196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bachert C, Fimmel C and Linstedt AD:
Endosomal trafficking and proprotein convertase cleavage of cis
Golgi protein GP73 produces marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Traffic. 8:1415–1423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N,
Radovanovic I and Ruiz i Altaba A: HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling
regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and
tumorigenicity. Curr Biol. 17:165–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gladson CL: The extracellular matrix of
gliomas: Modulation of cell function. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
58:1029–1040. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Diamandis P, Wildenhain J, Clarke ID,
Sacher AG, Graham J, Bellows DS, Ling EK, Ward RJ, Jamieson LG,
Tyers M, et al: Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional
ground state of neural stem cells. Nat Chem Biol. 3:268–273. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sonoda Y, Ozawa T, Aldape KD, Deen DF,
Berger MS and Pieper RO: Akt pathway activation converts anaplastic
astrocytoma to glioblastoma multiforme in a human astrocyte model
of glioma. Cancer Res. 61:6674–6678. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lagadec C, Vlashi E, Della Donna L, Meng
Y, Dekmezian C, Kim K and Pajonk F: Survival and self-renewing
capacity of breast cancer initiating cells during fractionated
radiation treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marhaba R and Zöller M: CD44 in cancer
progression: Adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J Mol
Histol. 35:211–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Stamenkovic I and Yu Q: CD44
attenuates activation of the hippo signaling pathway and is a prime
therapeutic target for glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 70:2455–2464.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anido J, Sáez-Borderías A, Gonzàlez-Juncà
A, Rodón L, Folch G, Carmona MA, Prieto-Sánchez RM, Barba I,
Martínez-Sáez E, Prudkin L, et al: TGF-β receptor inhibitors target
the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human
glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 18:655–668. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Naor D, Sionov RV and Ish-Shalom D: CD44:
Structure, function, and association with the malignant process.
Adv Cancer Res. 71:241–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iczkowski KA, Bai S and Pantazis CG:
Prostate cancer overexpresses CD44 variants 7–9 at the messenger
RNA and protein level. Anticancer Res. 23:3129–3140.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Georgolios A, Batistatou A,
Charalabopoulos A, Manolopoulos L and Charalabopoulos K: The role
of CD44 adhesion molecule in oral cavity cancer. Exp Oncol.
28:94–98. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kladney RD, Cui X, Bulla GA, Brunt EM and
Fimmel CJ: Expression of GP73, a resident Golgi membrane protein,
in viral and nonviral liver disease. Hepatology. 35:1431–1440.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kladney RD, Tollefson AE, Wold WS and
Fimmel CJ: Upregulation of the Golgi protein GP73 by adenovirus
infection requires the E1A CtBP interaction domain. Virology.
301:236–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu JS, Wu DW, Liang S and Miao XY: GP73, a
resident Golgi glycoprotein, is sensibility and specificity for
hepatocellular carcinoma of diagnosis in a hepatitis B-endemic
Asian population. Med Oncol. 27:339–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun Y, Yang H, Mao Y, Xu H, Zhang J, Li G,
Lu X, Sang X, Zhao H, Zhong S, et al: Increased Golgi protein 73
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue correlates with tumor
aggression but not survival. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1207–1212.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|