|
1
|
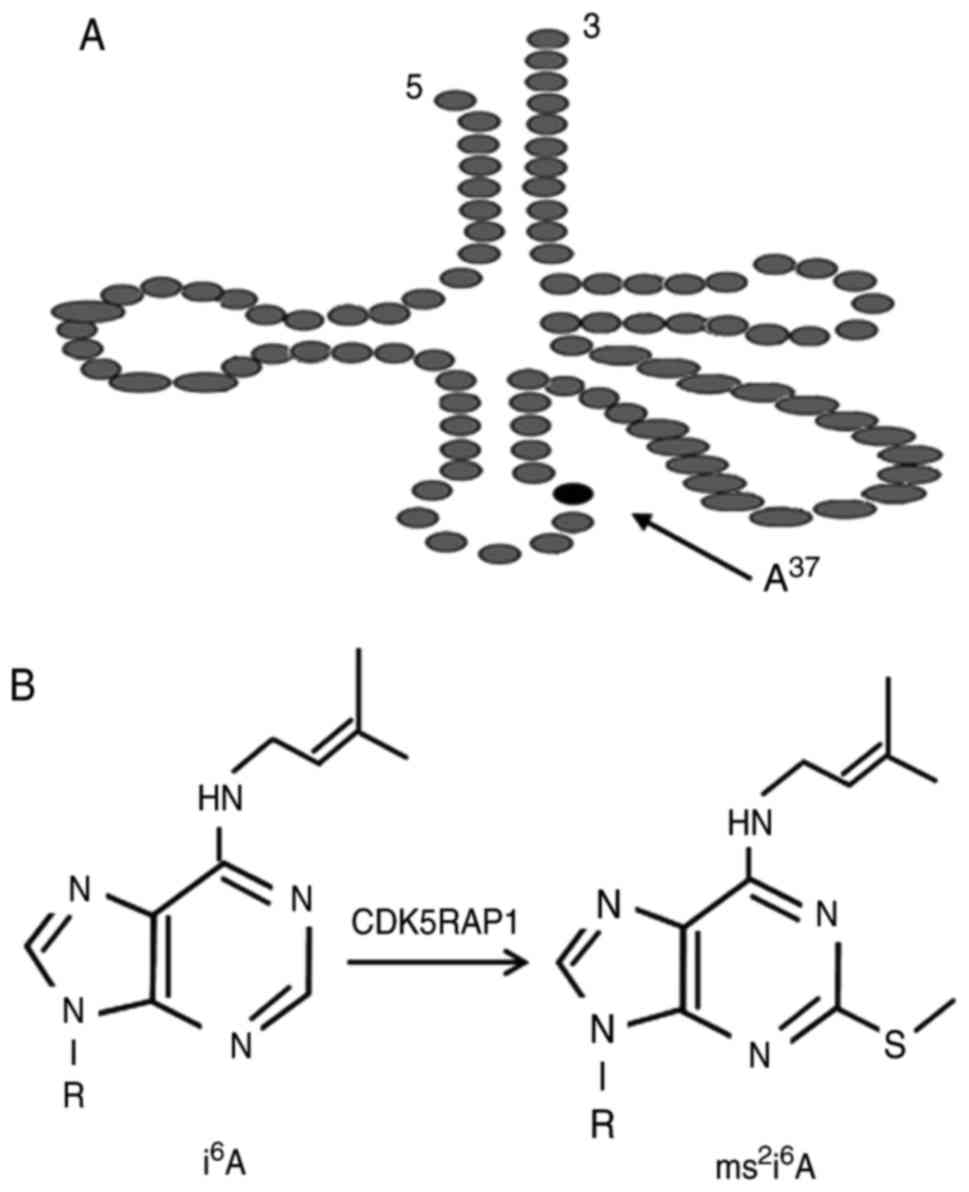
Hatanaka M, Higashi Y, Kawai K, Su J, Zeng
W, Chen X and Kanekura T: CD147-targeted siRNA in A375 malignant
melanoma cells induces the phosphorylation of EGFR and
downregulates cdc25C and MEK phosphorylation. Oncol Lett.
11:2424–2428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ostheimer C, Bormann C, Fiedler E, Marsch
W and Vordermark D: Malignant melanoma brain metastases: Treatment
results and prognostic factors-a single-center retrospective study.
Int J Oncol. 46:2439–2448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reiter V, Matschkal DM, Wagner M, Globisch
D, Kneuttinger AC, Müller M and Carell T: The CDK5 repressor
CDK5RAP1 is a methylthiotransferase acting on nuclear and
mitochondrial RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:6235–6240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zou X, Ji C, Jin F, Liu J, Wu M, Zheng H,
Wang Y, Li X, Xu J, Gu S, et al: Cloning, characterization and
expression of CDK5RAP1_v3 and CDK5RAP1_v4, two novel splice
variants of human CDK5RAP1. Genes Genet Syst. 79:177–182. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pierrel F, Douki T, Fontecave M and Atta
M: MiaB protein is a bifunctional radical-S-adenosylmethionine
enzyme involved in thiolation and methylation of tRNA. J Biol Chem.
279:47555–47563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei FY, Zhou B, Suzuki T, Miyata K,
Ujihara Y, Horiguchi H, Takahashi N, Xie P, Michiue H, Fujimura A,
et al: Cdk5rap1-mediated 2-methylthio modification of mitochondrial
tRNAs governs protein translation and contributes to myopathy in
mice and humans. Cell Metab. 21:428–442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang H, Wei L, Li C, Zhou J and Li Z:
CDK5RAP1 deficiency induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human breast cancer cell line by the ROS/JNK signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 33:1089–1096. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brody JG, Rudel RA, Michels KB, Moysich
KB, Bernstein L, Attfield KR and Gray S: Environmental pollutants,
diet, physical activity, body size, and breast cancer: Where do we
stand in research to identify opportunities for prevention? Cancer.
109 12 Suppl:S2627–S2634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li X, Zhao H, Wang Q, Liang H and Jiang X:
Fucoidan protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress via
normalization of reactive oxygen species generation through the
Ca2+-dependent ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
11:3746–3752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Myatt SS, Brosens JJ and Lam EW: Sense and
sensitivity: FOXO and ROS in cancer development and treatment.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:675–687. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Zhang T, Sun W, Wang Z, Zuo D,
Zhou Z, Li S, Xu J, Yin F, Hua Y and Cai Z: Erianin induces
G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via the ROS/JNK
signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e22472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurihara Y and Furue M: Interferon-γ
enhances phorbol myristate acetate-induced cell attachment and
tumor necrosis factor production via the NF-κB pathway in THP-1
human monocytic cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:1739–1744. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chandel NS, Trzyna WC, McClintock DS and
Schumacker PT: Role of oxidants in NF-κB activation and TNF-alpha
gene transcription induced by hypoxia and endotoxin. J Immunol.
165:1013–1021. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Turillazzi E, Neri M, Cerretani D,
Cantatore S, Frati P, Moltoni L, Busardò FP, Pomara C, Riezzo I and
Fineschi V: Lipid peroxidation and apoptotic response in rat brain
areas induced by long-term administration of nandrolone: The mutual
crosstalk between ROS and NF-kB. J Cell Mol Med. 20:601–612. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lou L, Zhou J, Liu Y, Wei YI, Zhao J, Deng
J, Dong B, Zhu L, Wu A, Yang Y and Chai L: Chlorogenic acid induces
apoptosis to inhibit inflammatory proliferation of IL-6-induced
fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating the activation of
JAK/STAT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:2054–2060.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishiura H, Tokita K, Li Y, Harada K,
Woodruff TM, Taylor SM, Nsiama TK, Nishino N and Yamamoto T: The
role of the ribosomal protein S19 C-terminus in Gi
protein-dependent alternative activation of p38 MAP kinase via the
C5a receptor in HMC-1 cells. Apoptosis. 15:966–981. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Shu T, Liang Y, Gu W, Wang C, Song
X, Fan C and Wang W: GDC-0152 attenuates the malignant progression
of osteosarcoma promoted by ANGPTL2 via PI3K/AKT but not p38MAPK
signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:1651–1658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Zhao H, Wang Q, Liang H and Jiang X:
Fucoidan protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress via
normalization of reactive oxygen species generation through the
Ca2+-dependent ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
11:3746–3752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Tian Z and Xie P: Targeting
complement anaphylatoxin C5a receptor in hyperoxic lung injury in
mice. Mol Med Rep. 10:1786–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang X, Yu J, Ma Z, Zhang H and Xie F:
Effects of fucoidan on insulin stimulation and pancreatic
protection via the cAMP signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Mol
Med Rep. 12:4501–4507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moncini S, Bevilacqua A, Venturin M,
Fallini C, Ratti A, Nicolin A and Riva P: The 3′untranslated region
of human Cyclin-Dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit 1 contains
regulatory elements affecting transcript stability. BMC Mol Biol.
8:1112007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jenner LB, Demeshkina N, Yusupova G and
Yusupov M: Structural aspects of messenger RNA reading frame
maintenance by the ribosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17:555–560. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin MK, Uhm YK, Lee JH, Kim SK, Chung JH
and Lee MH: Association between CDK5RAP1 polymorphisms and
susceptibility to vitiligo in the Korean population. Eur J
Dermatol. 22:495–499. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsumoto T, Jimi S, Migita K, Takamatsu Y
and Hara S: Inhibition of glucose transporter 1 induces apoptosis
and sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to conventional
chemotherapeutic agents. Leuk Res. 41:103–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dewaele M, Maes H and Agostinis P:
ROS-mediated mechanisms of autophagy stimulation and their
relevance in cancer therapy. Autophagy. 6:838–854. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zou P, Zhang J, Xia Y, Kanchana K, Guo G,
Chen W, Huang Y, Wang Z, Yang S and Liang G: ROS generation
mediates the anti-cancer effects of WZ35 via activating JNK and ER
stress apoptotic pathways in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
6:5860–5876. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Padua MB and Hansen PJ: Changes in
expression of cell-cycle-related genes in PC-3 prostate cancer
cells caused by ovine uterine serpin. J Cell Biochem.
107:1182–1188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chu H, Yu H, Ren D, Zhu K and Huang H:
Plumbagin exerts protective effects in nucleus pulposus cells by
attenuating hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress,
inflammation and apoptosis through NF-κB and Nrf-2. Int J Mol Med.
37:1669–1676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J
Clin Invest. 107:241–246. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang G, Xiao X, Rosen DG, Cheng X, Wu X,
Chang B, Liu G, Xue F, Mercado-Uribe I, Chiao P, et al: The
biphasic role of NF-kappaB in progression and chemoresistance of
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2181–2194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|