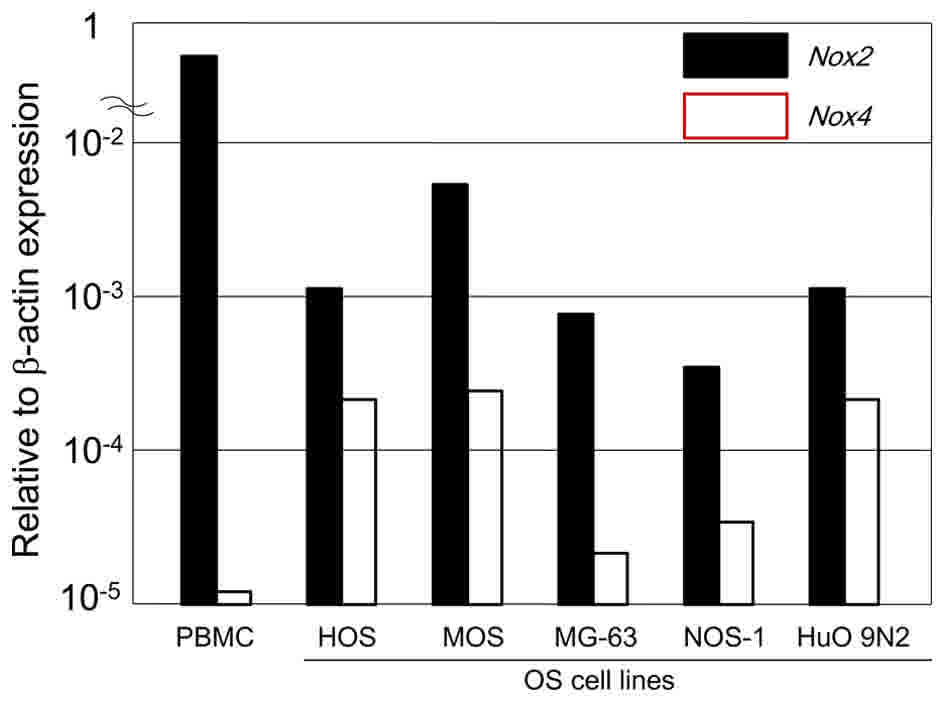
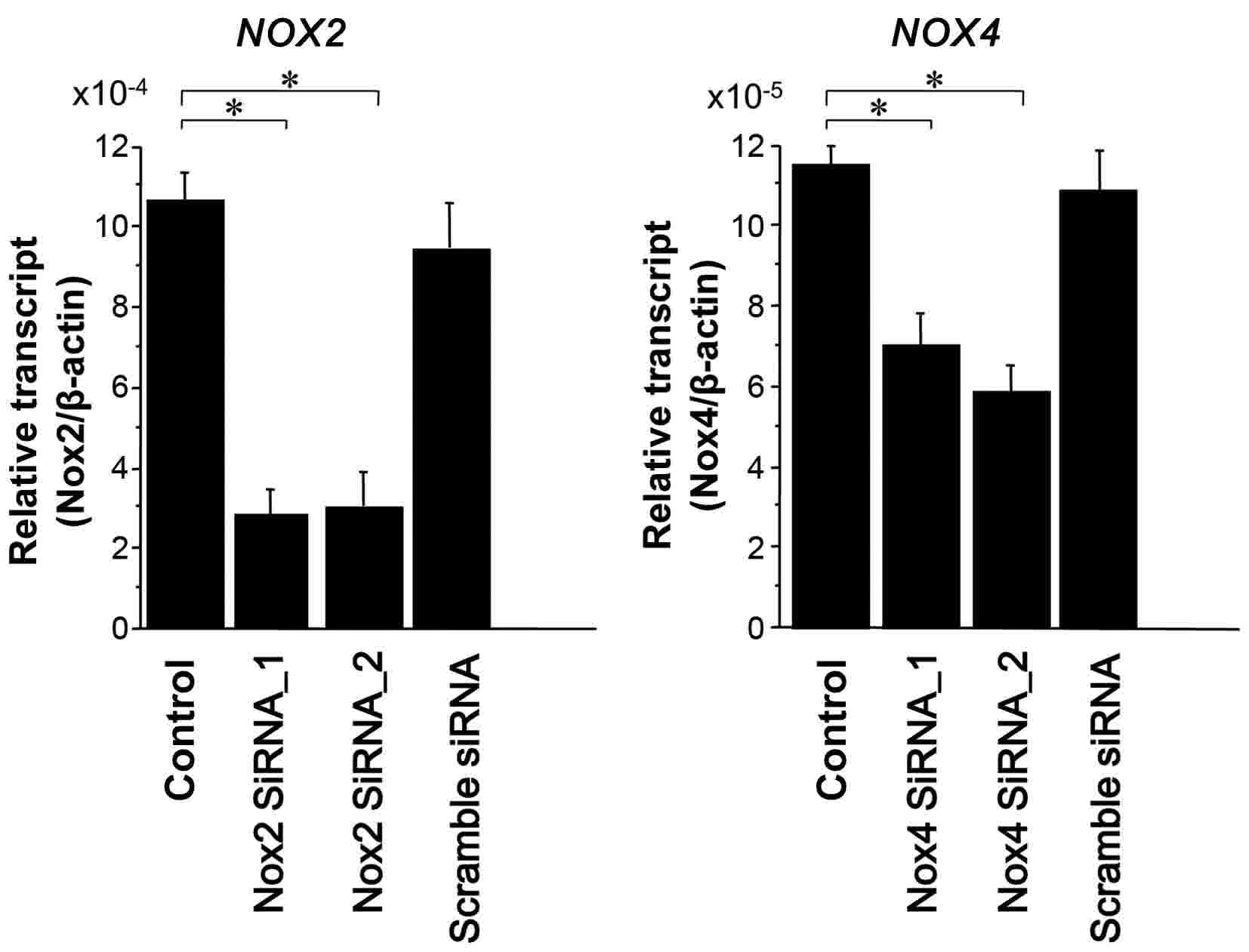
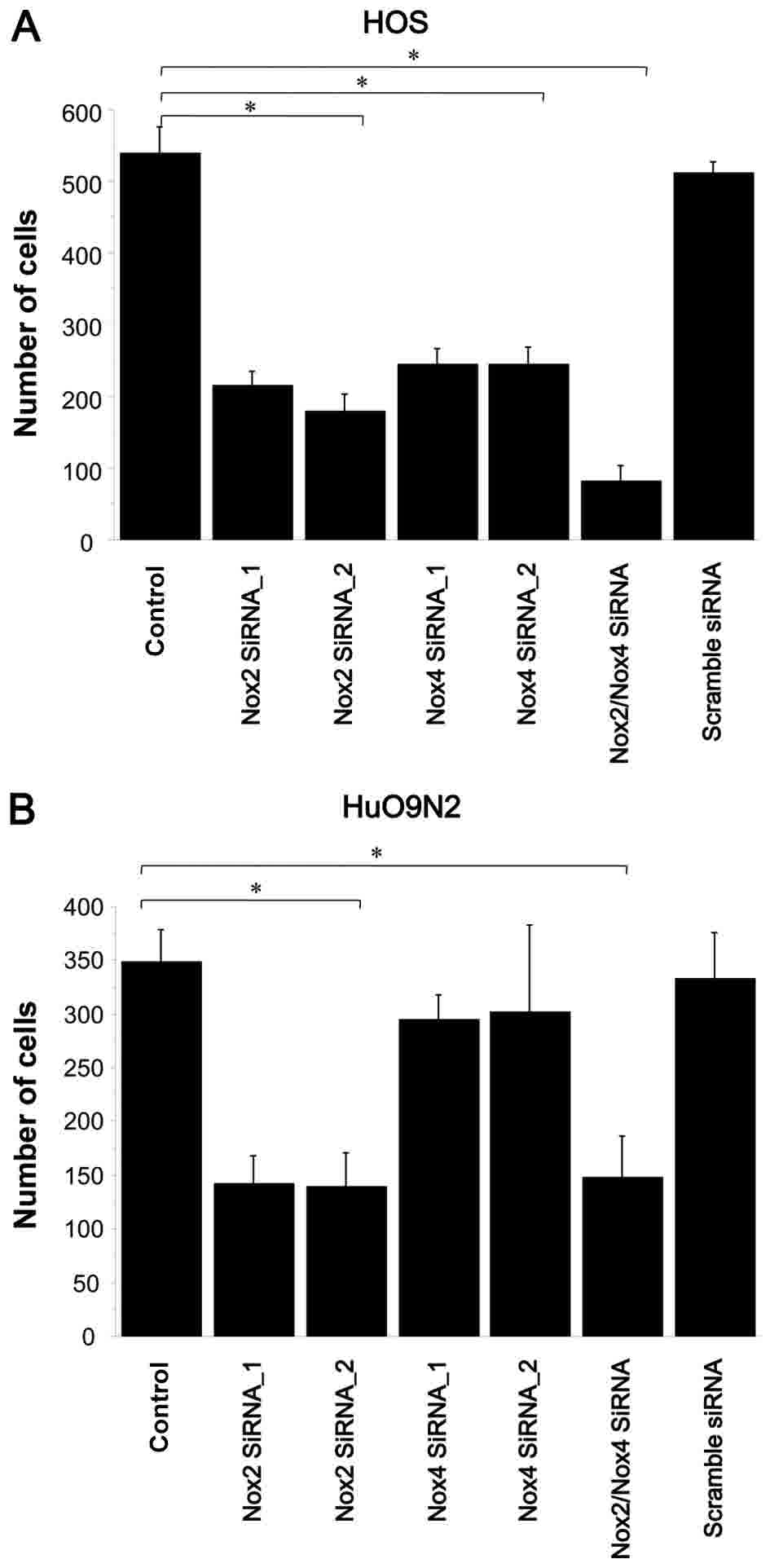
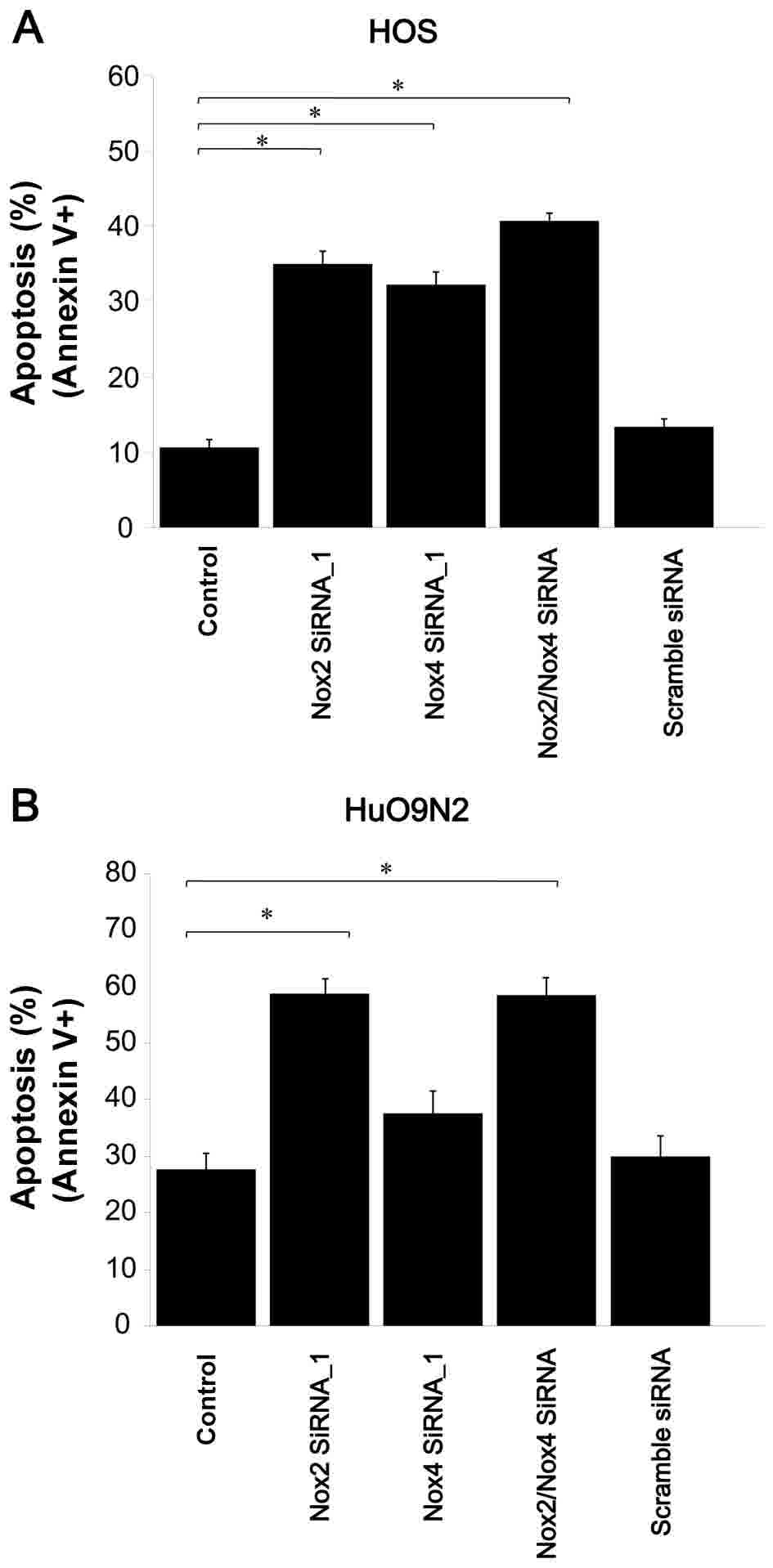
|
1
|
Raymond AK, Ayala AG and Knuutila K:
Conventional osteosarcomaFletcher CDM, Unni KK and Mertens F: World
Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and
Genetics of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Lyon: IARC Press; pp.
264–270. 2002
|
|
2
|
Arndt CA and Crist WM: Common
musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. N Engl J Med.
341:342–352. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
International osteosarcoma incidence patterns in children and
adolescents, middle ages and elderly persons. Int J Cancer.
125:229–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anninga JK, Gelderblom H, Fiocco M, Kroep
JR, Taminiau AH, Hogendoorn PC and Egeler RM: Chemotherapeutic
adjuvant treatment for osteosarcoma: Where do we stand? Eur J
Cancer. 47:2431–2445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uribe-Botero G, Russell WO, Sutow WW and
Martin RG: Primary osteosarcoma of bone. Clinicopathologic
investigation of 243 cases, with necropsy studies in 54. Am J Clin
Pathol. 67:427–435. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW, Green AA,
Pratt CB, Belasco JB, Pritchard J, Malpas JS, Baker AR, Kirkpatrick
JA, et al: The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free
survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J
Med. 314:1600–1606. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anderson P: Chemotherapy for osteosarcoma
with high-dose methotrexate is effective and outpatient therapy is
now possible. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 4:624–625. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ritter J and Bielack SS: Osteosarcoma. Ann
Oncol. 21 Suppl 7:vii320–vii325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ellegast J, Barth TF, Schulte M, Bielack
SS, Schmid M and Mayer-Steinacker R: Metastasis of osteosarcoma
after 16 years. J Clin Oncol. 29:e62–e66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Andreou D, Bielack SS, Carrle D, Kevric M,
Kotz R, Winkelmann W, Jundt G, Werner M, Fehlberg S, Kager L, et
al: The influence of tumor- and treatment-related factors on the
development of local recurrence in osteosarcoma after adequate
surgery. An analysis of 1355 patients treated on neoadjuvant
cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. Ann Oncol.
22:1228–1235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bielack SS: Osteosarcoma: Time to move on?
Eur J Cancer. 46:1942–1945. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Federman N, Bernthal N, Eilber FC and Tap
WD: The multidisciplinary management of osteosarcoma. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 10:82–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ito M, Barys L, O'Reilly T, Young S,
Gorbatcheva B, Monahan J, Zumstein-Mecker S, Choong PF, Dickinson
I, Crowe P, et al: Comprehensive mapping of p53 pathway alterations
reveals an apparent role for both SNP309 and MDM2 amplification in
sarcomagenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 17:416–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Savage SA, Stewart BJ, Liao JS, Helman LJ
and Chanock SJ: Telomere stability genes are not mutated in
osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 160:79–81. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Savage SA, Mirabello L, Wang Z,
Gastier-Foster JM, Gorlick R, Khanna C, Flanagan AM, Tirabosco R,
Andrulis IL, Wunder JS, et al: Genome-wide association study
identifies two susceptibility loci for osteosarcoma. Nat Genet.
45:799–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mirabello L, Koster R, Moriarity BS,
Spector LG, Meltzer PS, Gary J, Machiela MJ, Pankratz N, Panagiotou
OA, Largaespada D, et al: A genome-wide scan identifies variants in
NFIB associated with metastasis in patients with osteosarcoma.
Cancer Discov. 5:920–931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brar SS, Kennedy TP, Sturrock AB,
Huecksteadt TP, Quinn MT, Whorton AR and Hoidal JR: An NAD(P)H
oxidase regulates growth and transcription in melanoma cells. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 282:C1212–C1224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M
and Mazur M: Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative
stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 160:1–40. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rhee SG: Cell signaling.
H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling.
Science. 312:1882–1883. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Storz P: Reactive oxygen species in tumor
progression. Front Biosci. 10:1881–1896. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szatrowski TP and Nathan CF: Production of
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 51:794–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lambeth JD: NOX enzymes and the biology of
reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:181–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bedard K and Krause KH: The NOX family of
ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology.
Physiol Rev. 87:245–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng G, Cao Z, Xu X, Meir EG and Lambeth
JD: Homologs of gp91phox: Cloning and tissue expression of Nox3,
Nox4, and Nox5. Gene. 269:131–140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Donkó A, Péterfi Z, Sum A, Leto T and
Geiszt M: Dual oxidases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
360:2301–2308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geiszt M, Witta J, Baffi J, Lekstrom K and
Leto TL: Dual oxidases represent novel hydrogen peroxide sources
supporting mucosal surface host defense. FASEB J. 17:1502–1504.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Juhasz A, Ge Y, Markel S, Chiu A,
Matsumoto L, van Balgooy J, Roy K and Doroshow JH: Expression of
NADPH oxidase homologues and accessory genes in human cancer cell
lines, tumours and adjacent normal tissues. Free Radic Res.
43:523–532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu Y, Antony S, Juhasz A, Lu J, Ge Y,
Jiang G, Roy K and Doroshow JH: Up-regulation and sustained
activation of Stat1 are essential for interferon-gamma
(IFN-gamma)-induced dual oxidase 2 (Duox2) and dual oxidase A2
(DuoxA2) expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. J Biol
Chem. 286:12245–12256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kanamori M, Ohmori K, Yasuda T and Yudoh
K: Effects of hyperthermia and differentiation on cultured Dunn
osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Detect Prev. 27:76–81. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yasuda T, Kanamori M, Nogami S, Hori T,
Oya T, Suzuki K and Kimura T: Establishment of a new human
osteosarcoma cell line, UTOS-1: Cytogenetic characterization by
array comparative genomic hybridization. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
28:262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hori T, Kondo T, Kanamori M, Tabuchi Y,
Ogawa R, Zhao QL, Ahmed K, Yasuda T, Seki S, Suzuki K and Kimura T:
Ionizing radiation enhances tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis through
up-regulations of death receptor 4 (DR4) and death receptor 5 (DR5)
in human osteosarcoma cells. J Orthop Res. 28:739–745.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kanamori M, Sano A, Yasuda T, Hori T and
Suzuki K: Array-based comparative genomic hybridization for
genomic-wide screening of DNA copy number alterations in aggressive
bone tumors. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:1002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miura Y, Thoburn CJ, Bright EC, Phelps ML,
Shin T, Matsui EC, Matsui WH, Arai S, Fuchs EJ, Vogelsang GB, et
al: Association of Foxp3 regulatory gene expression with
graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 104:2187–2193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kumar S, Kain V and Sitasawad SL:
Cardiotoxicity of calmidazolium chloride is attributed to calcium
aggravation, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and apoptosis. Free
Radic Biol Med. 47:699–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, Kalisky T, Dorie
MJ, Kulp AN, Qian D, Lam JS, Ailles LE, Wong M, et al: Association
of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer
stem cells. Nature. 458:780–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mochizuki T, Furuta S, Mitsushita J, Shang
WH, Ito M, Yokoo Y, Yamaura M, Ishizone S, Nakayama J, Konagai A,
et al: Inhibition of NADPH oxidase 4 activates apoptosis via the
AKT/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 pathway in pancreatic
cancer PANC-1 cells. Oncogene. 25:3699–3707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ushio-Fukai M and Nakamura Y: Reactive
oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 266:37–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shono T, Yokoyama N, Uesaka T, Kuroda J,
Takeya R, Yamasaki T, Amano T, Mizoguchi M, Suzuki SO, Niiro H, et
al: Enhanced expression of NADPH oxidase Nox4 in human gliomas and
its roles in cell proliferation and survival. Int J Cancer.
123:787–792. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yamaura M, Mitsushita J, Furuta S, Kiniwa
Y, Ashida A, Goto Y, Shang WH, Kubodera M, Kato M, Takata M, et al:
NADPH oxidase 4 contributes to transformation phenotype of melanoma
cells by regulating G2-M cell cycle progression. Cancer Res.
69:2647–2654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Graham KA, Kulawiec M, Owens KM, Li X,
Desouki MM, Chandra D and Singh KK: NADPH oxidase 4 is an
oncoprotein localized to mitochondria. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:223–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McCann SK, Dusting GJ and Roulston CL:
Nox2 knockout delays infarct progression and increases vascular
recovery through angiogenesis in mice following ischaemic stroke
with reperfusion. PLoS One. 9:e1106022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li ZY, Jiang WY and Cui ZJ: An essential
role of NAD(P)H oxidase 2 in UVA-induced calcium oscillations in
mast cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 14:414–428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sorce S, Nuvolone M, Keller A, Falsig J,
Varol A, Schwarz P, Bieri M, Budka H and Aguzzi A: The role of the
NADPH oxidase NOX2 in prion pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog.
10:e10045312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Menden H, Welak S, Cossette S, Ramchandran
R and Sampath V: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated
angiopoietin-2-dependent autocrine angiogenesis is regulated by
NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 290:5449–5461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maraldi T, Prata C, Dalla Sega Vieceli F,
Caliceti C, Zambonin L, Fiorentini D and Hakim G: NAD(P)H oxidase
isoform Nox2 plays a prosurvival role in human leukaemia cells.
Free Radic Res. 43:1111–1121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jones KJ, Chetram MA, Bethea DA, Bryant
LK, Odero-Marah V and Hinton CV: Cysteine (C)-X-C Receptor 4
Regulates NADPH Oxidase-2 during oxidative stress in prostate
cancer cells. Cancer Microenviron. Sep 28–2013.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li SZ, Hu YY, Zhao J, Zhao YB, Sun JD,
Yang YF, Ji CC, Liu ZB, Cao WD, Qu Y, et al: MicroRNA-34a induces
apoptosis in the human glioma cell line, A172, through enhanced ROS
production and NOX2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
444:6–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|