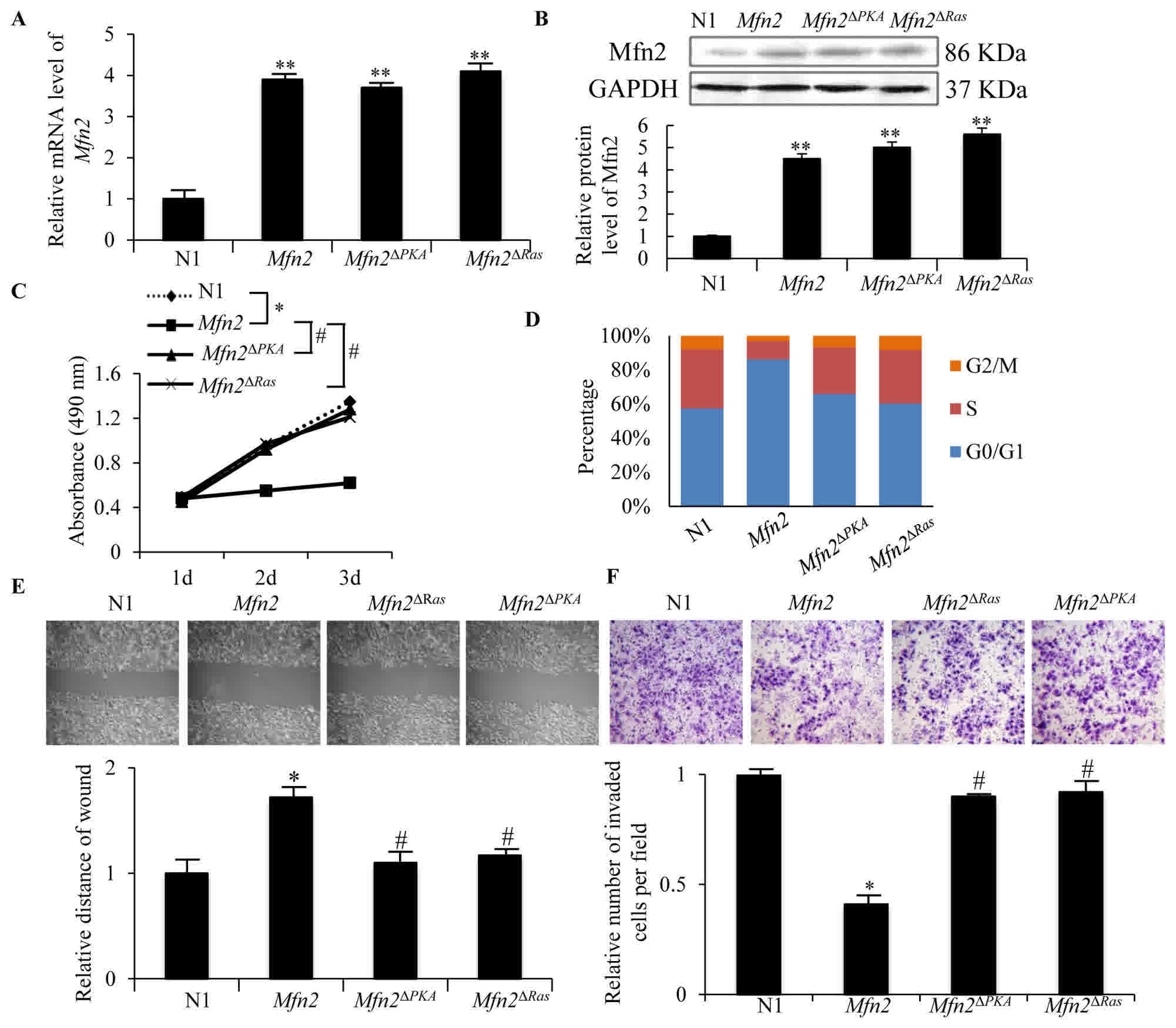
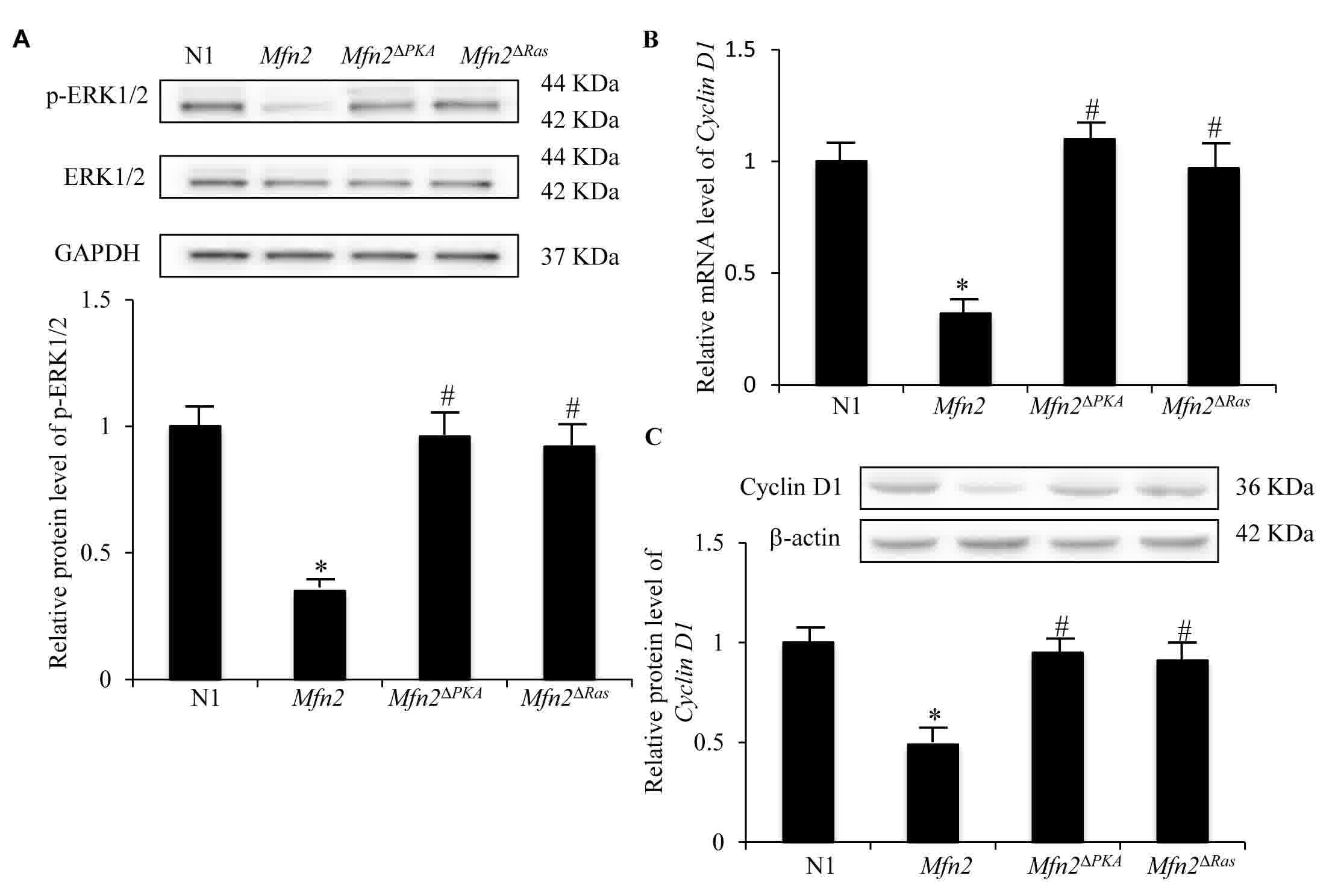
|
1
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fojo T: Multiple paths to a drug
resistance phenotype: Mutations, translocations, deletions and
amplification of coding genes or promoter regions, epigenetic
changes and microRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 10:59–67. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen KH, Guo X, Ma D, Guo Y, Li Q, Yang D,
Li P, Qiu X, Wen S, Xiao RP and Tang J: Dysregulation of HSG
triggers vascular proliferative disorders. Nat Cell Biol.
6:872–883. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang D, Ma C, Li S, Ran Y, Chen J, Lu P,
Shi S and Zhu D: Effect of Mitofusin 2 on smooth muscle cells
proliferation in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Microvasc Res.
84:286–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang GE, Jin HL, Lin XK, Chen C, Liu XS,
Zhang Q and Yu JR: Anti-tumor effects of Mfn2 in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:13005–13021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Sun Q, Wu Z, Zhou D, Wei J, Xie H,
Zhou L and Zheng S: Mitochondrial dysfunction-related genes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:1141–1149.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin B, Fu G, Pan H, Cheng X, Zhou L, Lv J,
Chen G and Zheng S: Anti-tumour efficacy of mitofusin-2 in urinary
bladder carcinoma. Med Oncol. 28 Suppl 1:S373–S380. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma L, Liu Y, Geng C, Qi X and Jiang J:
Estrogen receptor β inhibits estradiol-induced proliferation and
migration of MCF-7 cells through regulation of mitofusin 2. Int J
Oncol. 42:1993–2000. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia Y, Wu YQ, Zhang L, Li XL, Yuan HL, He
XJ, Tao DD, Gong JP and Qiu FZ: Effects of mitofusin-2 gene on
proliferation and chemosensitivity of human breast carcinoma cell
line MCF-7. Ai Zheng. 26:815–819. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chik F and Szyf M: Effects of specific
DNMT gene depletion on cancer cell transformation and breast cancer
cell invasion; toward selective DNMT inhibitors. Carcinogenesis.
32:224–232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Antequera F and Bird A: Number of CpG
islands and genes in human and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:11995–11999. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bergman Y and Cedar H: DNA methylation
dynamics in health and disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:274–281.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Akhavan-Niaki H and Samadani AA: DNA
methylation and cancer development: Molecular mechanism. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 67:501–513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanwal R and Gupta S: Epigenetic
modifications in cancer. Clin Genet. 81:303–311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou W, Cao WJ, Chen LL, Xiaomei G and
Guanghui CH: Effect of mitofusin 2 gene with protein kinase A
phosphorylation site deletion on the proliferation of vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Clin Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Res.
14:1322–1325. 2010.
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gnyszka A, Jastrzebski Z and Flis S: DNA
methyltransferase inhibitors and their emerging role in epigenetic
therapy of cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:2989–2996. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoo CB and Jones PA: Epigenetic therapy of
cancer: Past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:37–50.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee S, Kim HS, Roh KH, Lee BC, Shin TH,
Yoo JM, Kim YL, Yu KR, Kang KS and Seo KW: DNA methyltransferase
inhibition accelerates the immunomodulation and migration of human
mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 5:80202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Huo D, Chen Y, Nwachukwu C, Collins
C, Rowell J, Slamon DJ and Olopade OI: CpG island methylation
affects accessibility of the proximal BRCA1 promoter to
transcription factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:593–601. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo Y, Stacey DW and Hitomi M:
Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1 expression during G2
phase. Oncogene. 21:7545–7556. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sorianello E, Soriano FX,
Fernandez-Pascual S, Sancho A, Naon D, Vila-Caballer M,
Gonzalez-Navarro H, Portugal J, Andres V, Palacin M and Zorzano A:
The promoter activity of human Mfn2 depends on Sp1 in vascular
smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 94:38–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vucic EA, Brown CJ and Lam WL: Epigenetics
of cancer progression. Pharmacogenomics. 9:215–234. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tada M, Kanai F, Tanaka Y, Tateishi K,
Ohta M, Asaoka Y, Seto M, Muroyama R, Fukai K, Imazeki F, et al:
Down-regulation of hedgehog-interacting protein through genetic and
epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:3768–3776. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duffy MJ, Napieralski R, Martens JW, Span
PN, Spyratos F, Sweep FC, Brunner N, Foekens JA and Schmitt M:
EORTC PathoBiology Group: Methylated genes as new cancer
biomarkers. Eur J Cancer. 45:335–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tost J, Hamzaoui H, Busato F, Neyret A,
Mourah S, Dupont JM and Bouizar Z: Methylation of specific CpG
sites in the P2 promoter of parathyroid hormone-related protein
determines the invasive potential of breast cancer cell lines.
Epigenetics. 6:1035–1046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caffarelli E and Filetici P: Epigenetic
regulation in cancer development. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
16:2682–2694. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coppedè F: The role of epigenetics in
colorectal cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:935–948.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Milavetz BI and Balakrishnan L: Viral
epigenetics. Methods Mol Biol. 1238:569–596. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu Y, Sarkissyan M and Vadgama JV:
Epigenetics in breast and prostate cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
1238:425–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou X, Zhang L, Zheng B, Yan Y, Zhang Y,
Xie H, Zhou L, Zheng S and Wang W: MicroRNA-761 is upregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates tumorigenesis by targeting
Mitofusin-2. Cancer Sci. 107:424–432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Santel A and Fuller MT: Control of
mitochondrial morphology by a human mitofusin. J Cell Sci.
114:867–874. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rojo M, Legros F, Chateau D and Lombès A:
Membrane topology and mitochondrial targeting of mitofusins,
ubiquitous mammalian homologs of the transmembrane GTPase Fzo. J
Cell Sci. 115:1663–1674. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karbowski M, Lee YJ, Gaume B, Jeong SY,
Frank S, Nechushtan A, Santel A, Fuller M, Smith CL and Youle RJ:
Spatial and temporal association of Bax with mitochondrial fission
sites, Drp1, and Mfn2 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 159:931–938.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen H, Detmer SA, Ewald AJ, Griffin EE,
Fraser SE and Chan DC: Mitofusins Mfn1 and Mfn2 coordinately
regulate mitochondrial fusion and are essential for embryonic
development. J Cell Biol. 160:189–200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stefansson OA, Jonasson JG, Olafsdottir K,
Hilmarsdottir H, Olafsdottir G, Esteller M, Johannsson OT and
Eyfjord JE: CpG island hypermethylation of BRCA1 and loss of pRb as
co-occurring events in basal/triple-negative breast cancer.
Epigenetics. 6:638–649. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang W, Zhu F, Wang S, Wei J, Jia C, Zhang
Y, Zhou L, Xie H and Zheng S: HSG provides antitumor efficacy on
hepatocellular carcinoma both in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
24:183–188. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia Y, Wu Y, He X, Gong J and Qiu F:
Effects of mitofusin-2 gene on cell proliferation and chemotherapy
sensitivity of MCF-7. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
28:185–189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang W, Zhou D, Wei J, Wu Z, Cheng X, Sun
Q, Xie H, Zhou L and Zheng S: Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits
p53-mediated upregulation of mitofusin-2 in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:355–360. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rehman J, Zhang HJ, Toth PT, Zhang Y,
Marsboom G, Hong Z, Salgia R, Husain AN, Wietholt C and Archer SL:
Inhibition of mitochondrial fission prevents cell cycle progression
in lung cancer. FASEB J. 26:2175–2186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lou Y, Li R, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Jin
B, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhong H, Wen S and Han B: Mitofusin-2
over-expresses and leads to dysregulation of cell cycle and cell
invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Med Oncol. 32:1322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lou Y, Zhang Y, Li R, Gu P, Xiong L, Zhong
H, Zhang W and Han B: Transcriptional profiling revealed the
anti-proliferative effect of MFN2 deficiency and identified risk
factors in lung adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:8643–8655. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ansurudeen I, Willenberg HS, Kopprasch S,
Krug AW, Ehrhart-Bornstein M and Bornstein SR: Endothelial factors
mediate aldosterone release via PKA-independent pathways. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 300:66–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Martini CN, Plaza MV and Vila Mdel C:
PKA-dependent and independent cAMP signaling in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts
differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 298:42–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Omar B, Zmuda-Trzebiatowska E, Manganiello
V, Göransson O and Degerman E: Regulation of AMP-activated protein
kinase by cAMP in adipocytes: Roles for phosphodiesterases, protein
kinase B protein kinase A, Epac and lipolysis. Cell Signal.
21:760–766. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
McConnachie G, Langeberg LK and Scott JD:
AKAP signaling complexes: Getting to the heart of the matter.
Trends Mol Med. 12:317–323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lorenowicz MJ, Fernandez-Borja M, Kooistra
MR, Bos JL and Hordijk PL: PKA and Epac1 regulate endothelial
integrity and migration through parallel and independent pathways.
Eur J Cell Biol. 87:779–792. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kannan A, Wells RB, Sivakumar S, Komatsu
S, Singh KP, Samten B, Philley JV, Sauter ER, Ikebe M, Idell S, et
al: Mitochondrial reprogramming regulates breast cancer
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3348–3360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|