|
1
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127:S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong C, Zhao B, Long F, Liu Y, Liu Z, Li
S, Yang X, Sun D, Wang H, Liu Q, et al: Nogo-B receptor promotes
the chemoresistance of human liver cancer via the ubiquitination of
p53 protein. Oncotarget. 7:8850–8865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng Z, Liu J, Yang Z, Wu L, Xie H, Jiang
C, Lin B, Chen T, Xing C, Liu Z, et al: MicroRNA-452 promotes
stem-like cells of liver cancer by inhibiting Sox7 involving
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:28000–28012. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qin Y, Zhao D, Zhou HG, Wang XH, Zhong WL,
Chen S, Gu WG, Wang W, Zhang CH, Liu YR, et al: Apigenin inhibits
NF-κB and snail signaling, EMT and metastasis in human liver
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:41421–41431. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in liver cancer patients following liver
transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gibb EA, Brown CJ and Lam WL: The
functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol
Cancer. 10:382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang TH, Liang LZ, Liu XL, Wu JN, Su K,
Chen JY, Zheng QY, Huang HZ and Liao GQ: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1
interacts with miR-124 and modulates tongue cancer growth by
targeting JAG1. Oncol Rep. 37:2087–2094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Wu Z, Yuan J, Sun L, Lin L, Huang N,
Bin J, Liao Y and Liao W: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes
gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating
vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 395:31–44.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin Y, Cui Z, Li X, Jin X and Peng J:
Upregulation of long non-coding RNA PlncRNA-1 promotes
proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 8:26090–26099. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei W, Liu Y, Lu Y, Yang B and Tang L:
LncRNA XIST promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation through
miR-133a/EGFR. J Cell Biochem. 118:3349–3358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xue X, Yang YA, Zhang A, Fong KW, Kim J,
Song B, Li S, Zhao JC and Yu J: LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling
and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene.
35:2746–2755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson
G, Frank J, Burghardt R, Kim S and Safe S: HOTAIR is a negative
prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Liu Z, Sun M, Liu J, Wang Z and Wei
D: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen FJ, Sun M, Li SQ, Wu QQ, Ji L, Liu
ZL, Zhou GZ, Cao G, Jin L, Xie HW, et al: Upregulation of the long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
metastasis and poor prognosis. Mol Carcinog. 52:908–915. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao J, Jia LI, Jingli DU and Xiaolei LI:
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a marker for liver cancer progression
and tumor recurrence. Oncol Lett. 11:1791–1798. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geng YJ, Xie SL, Li Q, Ma J and Wang GY:
Large Intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with liver
cancer progression. J Int Med Res. 39:2119–2128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNA target recognition and
regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su DN, Wu SP, Chen HT and He JH: HOTAIR, a
long non-coding RNA driver of malignancy whose expression is
activated by FOXC1, negatively regulates miRNA-1 in liver cancer.
Oncol Lett. 12:4061–4067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
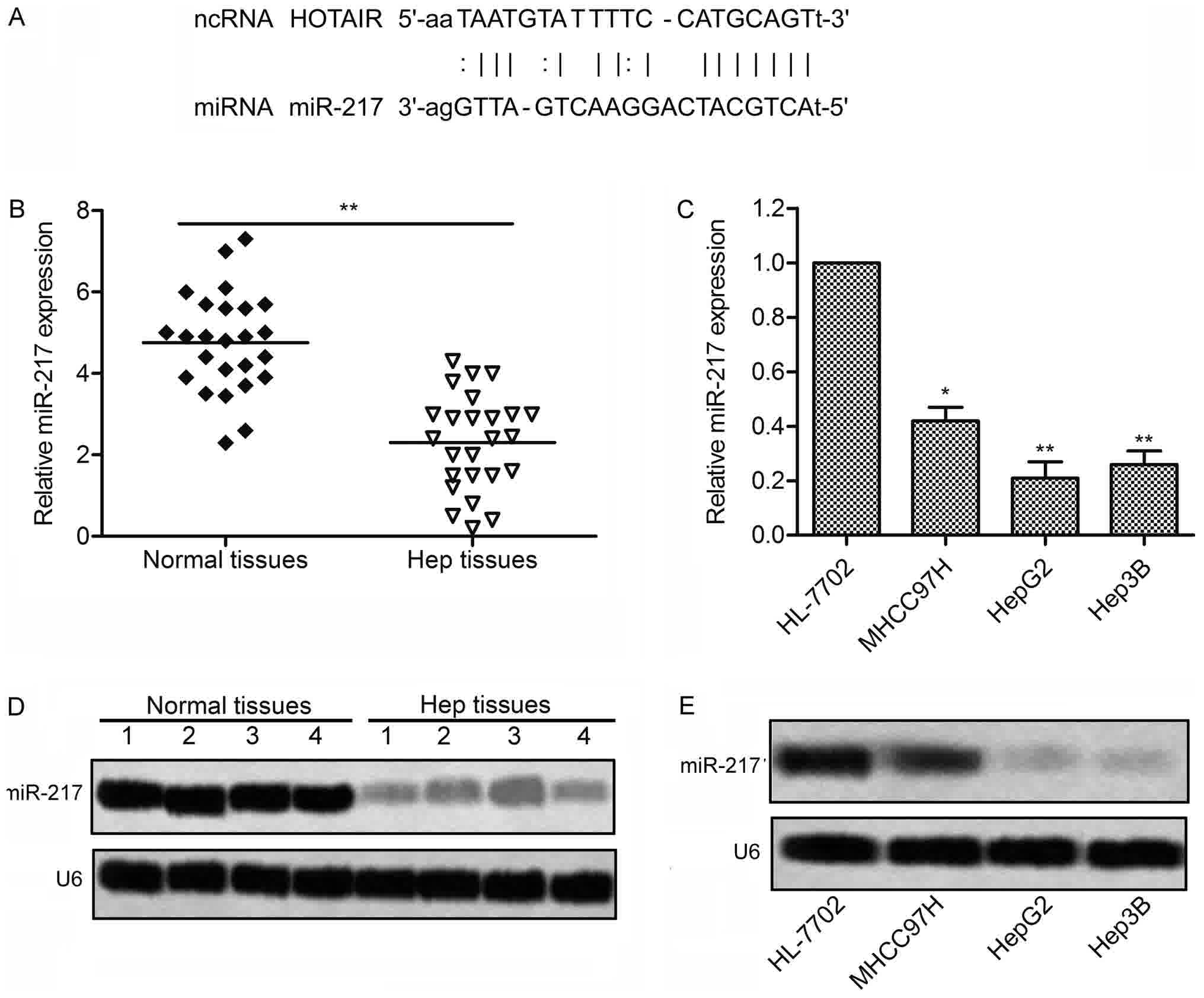
Su J, Wang Q, Liu Y and Zhong M: miR-217
inhibits invasion of liver cancer cells through direct suppression
of E2F3. Mol Cell Biochem. 392:289–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: HepG2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Fukuda T, Hang Q, Hou S, Isaji T,
Kameyama A and Gu J: Inhibition of fucosylation by 2-fluorofucose
suppresses human liver cancer HepG2 cell proliferation and
migration as well as tumor formation. Sci Rep. 7:115632017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shao LW, Huang LH, Yan S, Jin JD and Ren
SY: Cordycepin induces apoptosis in human liver cancer HepG2 cells
through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways. Oncol Lett.
12:995–1000. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li H, An J, Wu M, Zheng Q, Gui X, Li T, Pu
H and Lu D: LncRNA HOTAIR promotes human liver cancer stem cell
malignant growth through downregulation of SETD2. Oncotarget.
6:27847–27864. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao JZ, Li J, Jl DU and Li XL: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a marker for liver cancer progression and
tumor recurrence. Oncol Lett. 11:1791–1798. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun X, Du P, Yuan W, Du Z, Yu M, Yu X and
Hu T: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates cyclin J via inhibition
of microRNA-205 expression in bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis.
6:e19072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ke J, Yao Y, Zheng J, Wang P, Liu YH, Ma
J, Li Z, Liu XB, Li ZQ, Wang ZH and Xue YX: Knockdown of long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits malignant biological behaviors of
human glioma cells via modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget.
6:21934–21949. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma MZ, Li CX, Zhang Y, Weng MZ, Zhang MD,
Qin YY, Gong W and Quan ZW: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a c-Myc
activated driver of malignancy, negatively regulates miRNA-130a in
gallbladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:1562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo J, Feng Z, Huang Z, Wang H and Lu W:
MicroRNA-217 functions as a tumour suppressor gene and correlates
with cell resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer. Mol Cells.
37:664–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang B, Shen ZL, Jiang KW, Zhao G, Wang
CY, Yan YC, Yang Y, Zhang JZ, Shen C, Gao ZD, et al: MicroRNA-217
functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer
cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism.
BMC Cancer. 15:4372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li J, Li D and Zhang W: Tumor suppressor
role of miR-217 in human epithelial ovarian cancer by targeting
IGF1R. Oncol Rep. 35:1671–1679. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng S, Zhu S, Wang B, Li X, Liu Y, Qin Q,
Gong Q, Niu Y, Xiang C, Chen J, et al: Chronic pancreatitis and
pancreatic cancer demonstrate active epithelial-mesenchymal
transition profile, regulated by miR-217-SIRT1 pathway. Cancer
Lett. 355:184–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|