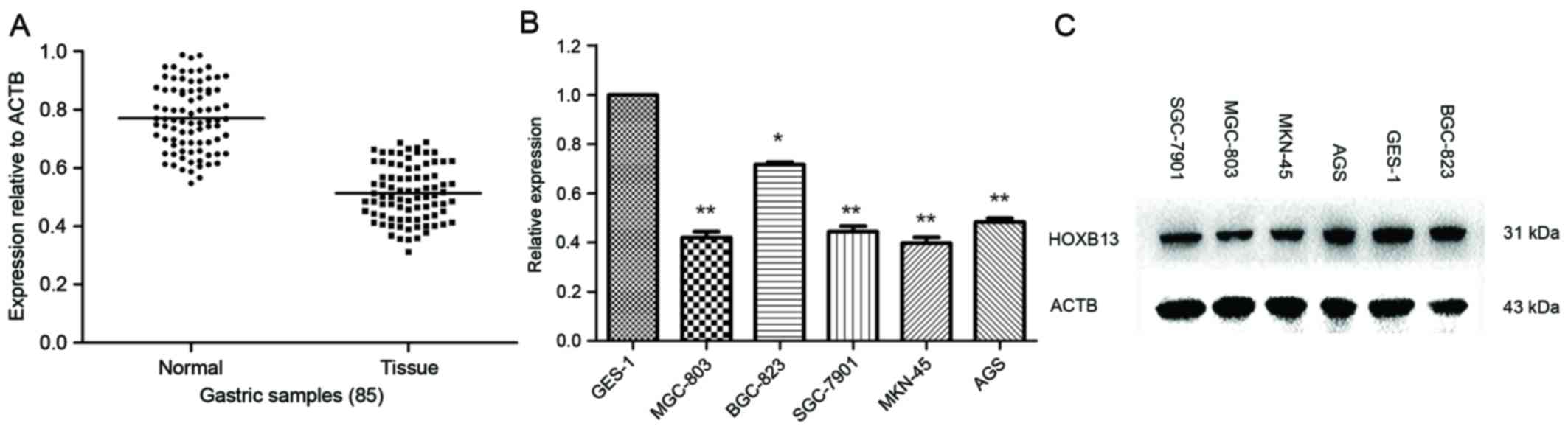
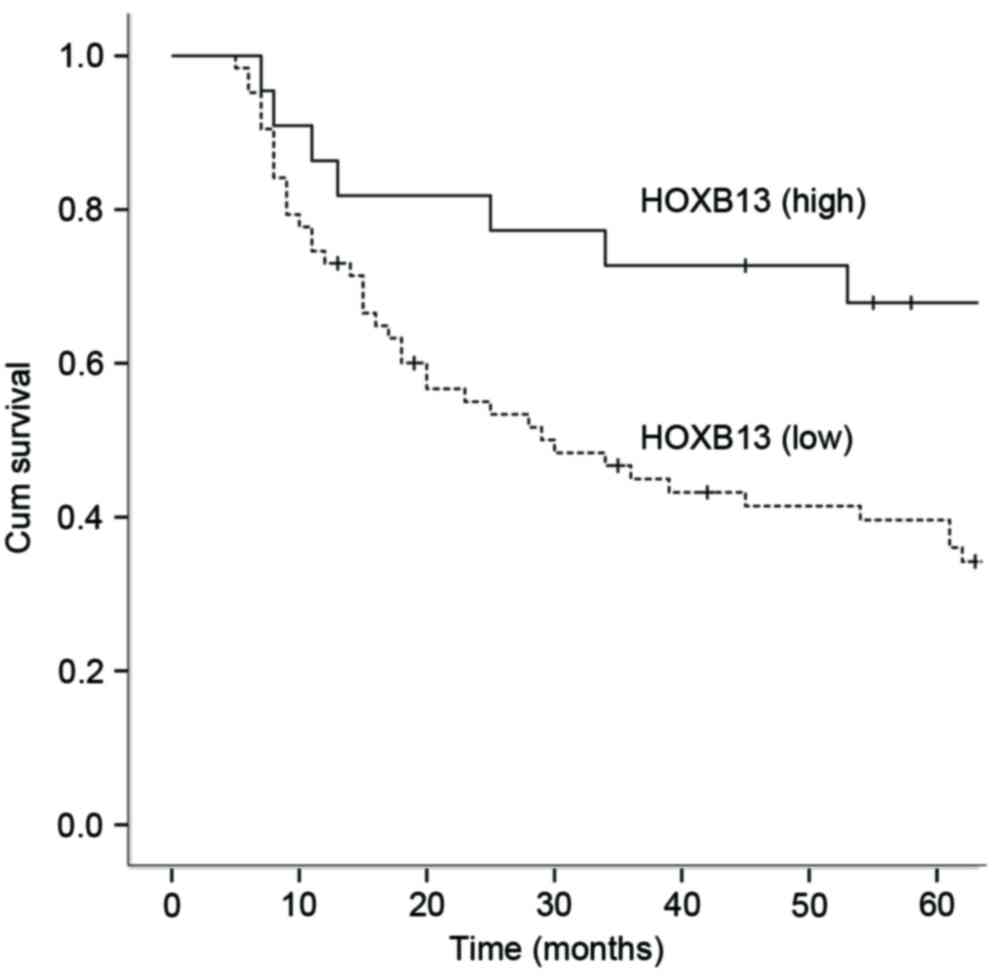
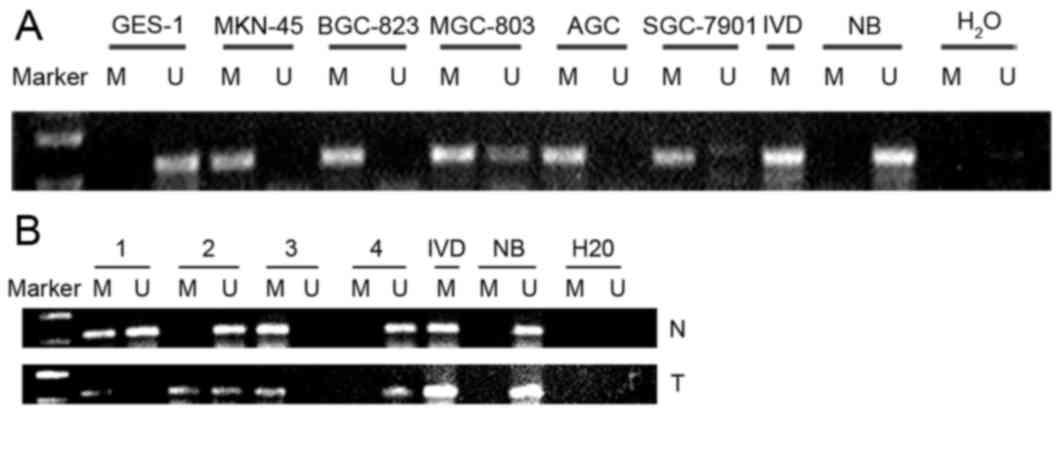
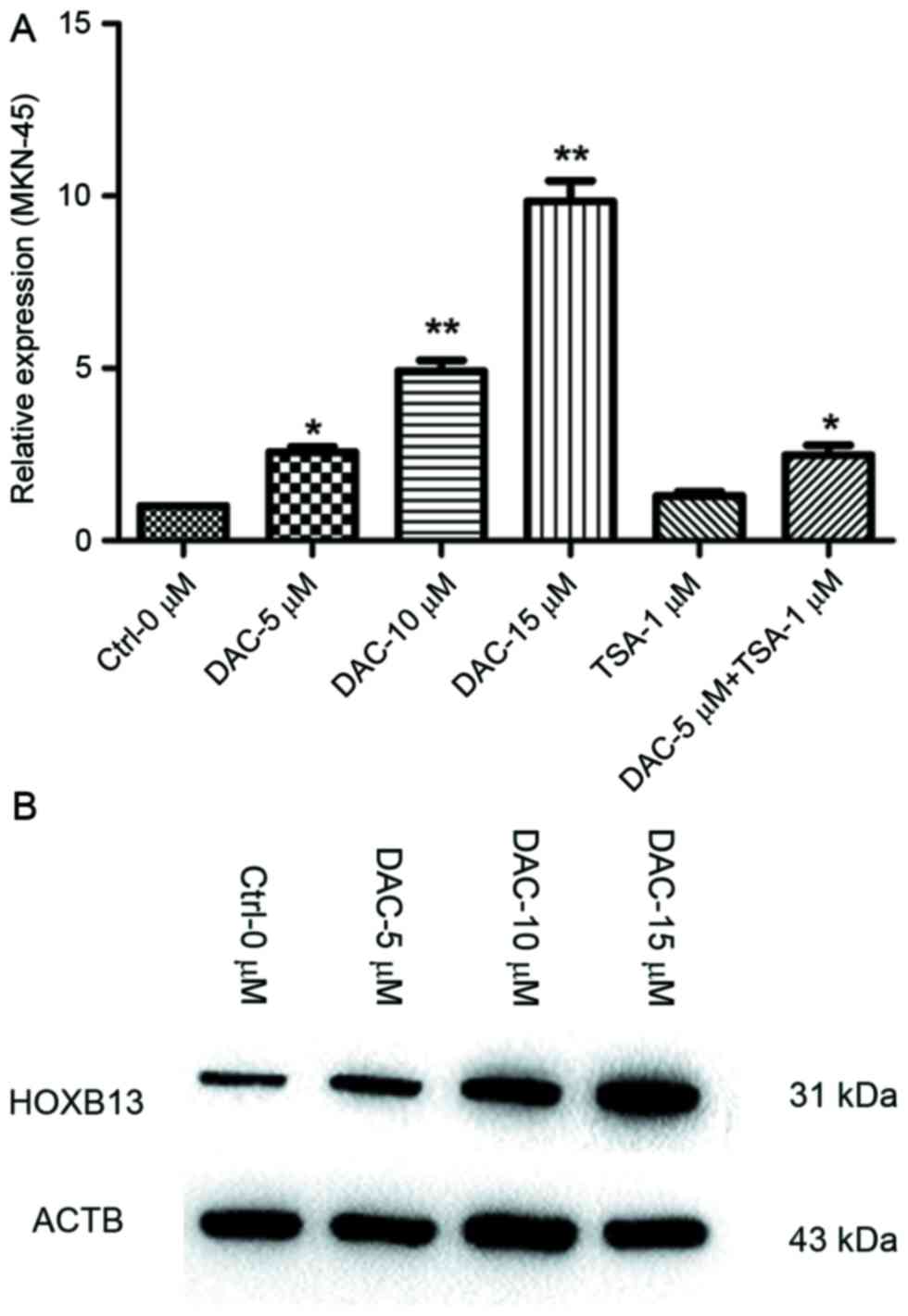
|
1
|
Shen L, Shan YS, Hu HM, Price TJ, Sirohi
B, Yeh KH, Yang YH, Sano T, Yang HK, Zhang X, et al: Management of
gastric cancer in Asia: Resource-stratified guidelines. Lancet
Oncol. 14:e535–e547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, Harewood
R, Spika D, Wang XS, Bannon F, Ahn JV, Johnson CJ, Bonaventure A,
et al: Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis
of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279
population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet.
385:977–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Soubeyran P, Haglund K, Garcia S, Barth
BU, Iovanna J and Dikic I: Homeobox gene cdx1 regulates ras, rho
and pi3 kinase pathways leading to transformation and tumorigenesis
of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 20:4180–4187. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu JY, Sun QK, Wang W and Jia WD:
High-level expression of HOXB13 is closely associated with tumor
angiogenesis and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 7:2925–2933. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghoshal K, Motiwala T, Claus R, Yan P,
Kutay H, Datta J, Majumder S, Bai S, Majumder A, Huang T, et al:
HOXB13, a target of DNMT3B, is methylated at an upstream CpG
island, and functions as a tumor suppressor in primary colorectal
tumors. PLoS One. 5:e103382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Economides KD, Zeltser L and Capecchi MR:
Hoxb13 mutations cause overgrowth of caudal spinal cord and tail
vertebrae. Dev Biol. 256:317–330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jung C, Kim RS, Lee SJ, Wang C and Jeng
MH: HOXB13 homeodomain protein suppresses the growth of prostate
cancer cells by the negative regulation of T-cell factor 4. Cancer
Res. 64:3046–3051. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jung C, Kim RS, Zhang H, Lee SJ, Sheng H,
Loehrer PJ, Gardner TA, Jeng MH and Kao C: HOXB13 is downregulated
in colorectal cancer to confer TCF4-mediated transactivation. Br J
Cancer. 92:2233–2239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Decker B and Ostrander EA: Dysregulation
of the homeobox transcription factor gene HOXB13: Role in prostate
cancer. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 7:193–201. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chung N, Jee BK, Chae SW, Jeon YW, Lee KH
and Rha HK: HOX gene analysis of endothelial cell differentiation
in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biol Rep.
36:227–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Jin J and Tao Q: Aberrant
methylation of tumor suppressor genes in renal cell carcinoma. Ai
Zheng. 26:1276–1280. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Muthusamy V, Duraisamy S, Bradbury CM,
Hobbs C, Curley DP, Nelson B and Bosenberg M: Epigenetic silencing
of novel tumor suppressors in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res.
66:11187–11193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tommasi S, Karm DL, Wu X, Yen Y and
Pfeifer GP: Methylation of homeobox genes is a frequent and early
epigenetic event in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R142009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okuda H, Toyota M, Ishida W, Furihata M,
Tsuchiya M, Kamada M, Tokino T and Shuin T: Epigenetic inactivation
of the candidate tumor suppressor gene HOXB13 in human renal cell
carcinoma. Oncogene. 25:1733–1742. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rauch T, Li H, Wu X and Pfeifer GP:
MIRA-assisted microarray analysis, a new technology for the
determination of DNA methylation patterns, identifies frequent
methylation of homeodomain-containing genes in lung cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:7939–7947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ewing CM, Ray AM, Lange EM, Zuhlke KA,
Robbins CM, Tembe WD, Wiley KE, Isaacs SD, Johnq D, Wang Y, et al:
Germline mutations in HOXB13 and prostate-cancer risk. N Engl J
Med. 366:141–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ang MK, Ooi AS, Thike AA, Tan P, Zhang Z,
Dykema K, Furge K, Teh BT and Tan PH: Molecular classification of
breast phyllodes tumors: Validation of the histologic grading
scheme and insights into malignant progression. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 129:319–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Miao J, Wang Z, Provencher H, Muir B,
Dahiya S, Carney E, Leong CO, Sgroi DC and Orsulic S: HOXB13
promotes ovarian cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:17093–17098. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan H, Kajiyama H, Ito S, Chen D, Shibata
K, Hamaguchi M, Kikkawa F and Senga T: HOXB13 and ALX4 induce SLUG
expression for the promotion of EMT and cell invasion in ovarian
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:13359–13370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lopez R, Garrido E, Piña P, Hidalgo A,
Lazos M, Ochoa R and Salcedo M: HOXB homeobox gene expression in
cervical carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 16:329–335. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Souza Setubal Destro MF, Bitu CC,
Zecchin KG, Graner E, Lopes MA, Kowalski LP and Coletta RD:
Overexpression of HOXB7 homeobox gene in oral cancer induces
cellular proliferation and is associated with poor prognosis. Int J
Oncol. 8:141–149. 2010.
|
|
22
|
Maia S, Cardoso M, Pinto P, Pinheiro M,
Santos C, Peixoto A, Bento MJ, Oliveira J, Henrique R, Jeronimo C
and Teixeira MR: Identification of two novel HOXB13 germline
mutations in portuguese prostate cancer patients. PLoS One.
10:e01327282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beebe-Dimmer J, Hathcock M, Yee C, Okoth
LA, Ewing CM, Isaacs WB, Cooney KA and Thibodeau SN: The HOXB13
G84E mutation is associated with an increased risk for prostate
cancer and other malignancies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
24:1366–1372. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C: TNM classification of malignant tumours.
Wiley-Blackwell. 80:1803–1804. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Dahiya S, Provencher H, Muir B,
Carney E, Coser K, Shioda T, Ma XJ and Sgroi DC: The prognostic
biomarkers HOXB13, IL17BR, and CHDH are regulated by estrogen in
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6327–6334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang F, Yang Y, Fu Z, Xu N, Chen F, Yin H,
Lu X, Shen R and Lu C: Differential DNA methylation status between
breast carcinomatous and normal tissues. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:699–707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association:
Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma-2nd English edition.
Gastric Cancer. 1:10–24. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gopalakrishnan S, Van Emburgh BO and
Robertson KD: DNA methylation in development and human disease.
Mutat Res. 647:30–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanwal R and Gupta S: Epigenetics and
cancer. J Appl Physiol (1985). 109:598–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang X, Zhang S, Ma J, Li Z, Zhi Y, Chen
J, Lu Y and Dai D: Association of NDRG1 gene promoter methylation
with reduced NDRG1 expression in gastric cancer cells and tissue
specimens. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:93–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu X, Chang X, Li Z, Wang J, Deng P, Zhu
X, Liu J, Zhang C, Chen S and Dai D: Aberrant SOX11, promoter
methylation is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 38:183–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Li Y, Liu J, Zhang C and Dai D:
Epigenetic regulation of microrna-335 and its clinical significance
in gastric cancer. J Modern Oncol. 2016.
|
|
34
|
Zeltser L, Desplan C and Heintz N:
Hoxb-13: A new Hox gene in a distant region of the HOXB cluster
maintains colinearity. Development. 122:2475–2484. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marra L, Cantile M, Scognamiglio G,
Perdonà S, La Mantia E, Cerrone M, Giqantino V, Cillo C, Caraqlia
M, Piqnata S, et al: Deregulation of HOX B13 expression in urinary
bladder cancer progression. Curr Med Chem. 20:833–839. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Varinot J, Cussenot O, Roupret M, Conort
P, Bitker MO, Chartier-kastler E, Cheng L and Compérat E: HOXB13 is
a sensitive and specific marker of prostate cells, useful in
distinguishing between carcinomas of prostatic and urothelial
origin. Virchows Arch. 463:803–809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|