Introduction
H2S, a signalling molecule in mammals and
other taxa, is synthesized from L-cysteine by cystathionine
β-synthase (CBS), cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) and
3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MPST) through one-carbon
metabolism and the transsulfuration pathway (1,2).
Endogenous H2S and/or the associated enzymes have been
observed to participate in a range of physiological and
pathological processes, including vasodilation, smooth muscle
relaxation, inflammation and tumorigenesis (3–7). The
expression and activity levels of these enzymes in human urothelial
cell carcinoma of the bladder (UCB) tissues and cell lines were
determined in our previous study (8).
H2S may exert various effects in disease
through the activation or inhibition of ion channels, particularly
through thiol groups, including metallothionein, thioredoxin,
disulfide and, most importantly, glutathione (GSH) (9). GSH maintains a redox balance in cells by
directly scavenging free radicals, including reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and by
functioning as a cofactor for protective enzymes to decrease
oxidative stress (10,11). Accordingly, there are a substantial
number of studies regarding the association between UCB
carcinogenesis and the aberrant activation of cellular signals or
redox status, as reviewed by Wallerand et al (12). Previous studies have revealed that
H2S is able to interact directly with free radicals and
modulate oxidative stress to induce the activation of a range of
tumorigenic pathways (13,14).
A number of studies have identified one-carbon
metabolism and transsulfuration pathways, as well as variations of
these pathways that may increase the risk of UCB (15,16). These
results have indicated H2S as a target for the
development of modulating agents for treatment, diagnosis and
prognosis for urology oncologists (2). The aim of the present study was to
assess CBS, CSE and MPST expression levels, and H2S
production, in human UCB tissue and cells, and to examine their
functions in carcinogenesis. Owing to the lack of MPST-specific
inhibitors, and as the homocysteine metabolism is affected by the
CBS-specific inhibitors aminooxyacetic acid and hydroxylamine
(1,2,15,16), a CSE-specific inhibitor was used to
modulate H2S biosynthesis in the present study.
Materials and methods
Tissue samples
Human UCB tumour specimens were obtained from 27
male patients that had received transurethral resection or radical
cystectomy for UBC (mean age, 58.6 years; range, 51–70 years), and
normal bladder tissue samples from 7 male patients that had
received ureteral reimplantation or cystoscopic biopsy (mean age,
56.4 years; range, 47–68 years) at Chao Yang Hospital (Beijing,
China), between August 2014 and March 2016. The present study was
approved by Beijing Chao Yang Hospital's institutional research
ethics board, including the use of human samples and animal
experiments (approval no. AN-1405-002-100). Written informed
consent was obtained from all patients enrolled in the present
study.
All samples were confirmed and staged by two
independent experienced pathologists according to the
tumor-node-metastasis system (17).
Table I lists the clinical and
pathological characteristics of the enrolled patients with UCB. A
total of 27 UCB tumour samples were used for western blot analysis,
and 23 UCB tumor samples were used for determination of
H2S production; the normal bladder tissue samples were
used as controls and examined for protein levels and H2S
production. Specimens analysed by western blotting were divided
into three groups: ‘Norm’ group for the 7 normal bladder samples;
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) group for 15 samples
(stage Ta/T1); and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) group for
12 samples (≥T2). Specimens analysed for the determination of
H2S production were also divided into the three groups
as above, but with 11 samples in the NMIBC group.
 | Table I.Clinical and pathological
characteristics of the patients with urothelial cell carcinoma of
the bladder. |
Table I.
Clinical and pathological
characteristics of the patients with urothelial cell carcinoma of
the bladder.
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|
| Sex, n |
|
|
Male | 27 |
|
Female | 0 |
| Age, years (mean ±
standard deviation) | 58.6±9.8 |
| Grade, n |
|
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 9 |
| 3 | 7 |
| Pathological stage,
n |
|
| Ta | 4 |
| T1 | 11 |
| T2 | 7 |
| T3 | 4 |
| T4 | 1 |
Cell culture and reagents
The human high-grade UCB cell lines 5637, EJ and
UM-UC-3 were purchased from the Type Culture Collection of the
Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing, China) and were maintained in
a 37°C humidified incubator with 5% CO2 and 95%
O2. The immortalized human normal bladder urothelium
cell line SV-HUC-1 was cultured in a 1:1 mixture of Dulbecco's
modified Eagle's medium and Ham's F12 medium (HyClone; GE
Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, UT, USA). The 5637, UM-UC-3 and EJ
cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal
bovine serum (both HyClone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences), 100 U
penicillin G and 100 µg streptomycin (Lonza Group, Ltd., Basel,
Switzerland).
Although the EJ cell line is reported to be
contaminated, it is a derivative of T24 cells, which were also
extracted from a bladder carcinoma. Therefore, this contamination
issue was considered unlikely to affect the outcomes of the present
study (18,19).
PBS, diaminobenzidine (DAB), EDTA, DAPI, L-cysteine,
NaOH, cisplatin (CDDP), DL-propargylglycine (PAG) and NaHS were
purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany).
Immunofluorescence
Immunohistochemical staining for CBS, CSE and MPST
was performed with paraffin-embedded MIBC tissue sections, and
SV-HUC-1 or EJ cell slides. PBS containing 0.2% Triton X-100 and
0.1% goat serum albumin (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, Inc., Dallas,
TX, USA) was used to preincubate 5-µm-thick sections for 30 min at
room temperature, and the samples were boiled in 0.01% (w/v) EDTA
(cat. no. sc-29092; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) for 10 min in
the microwave. Cells grown on coverslips were rinsed with PBS and
fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min, followed by a 30-min
pre-incubation with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Nanjing Keygen Biotech Co.,
Ltd., Nanjing, China) in PBS buffer at 4°C. Primary antibodies
against CBS (cat. no. H00000875-M02), CSE (cat. no. H00054414-M;
diluted 1:200; Abnova, Taipei, Taiwan) and MPST (cat. no.
sc-376168; dilution, 1:100; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) were
incubated with the tissue sections and cells on slides overnight at
4°C. The samples were rinsed twice with PBS containing 0.1% Triton
X-100 (PBST; Nanjing Keygen Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China)
followed by incubation for 1 h with a horseradish peroxidase
(HRP)-conjugated goat IgG secondary antibody (cat. no. sc-2354;
dilution, 1:100; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) at room
temperature. The cells on slides were washed twice with PBS,
followed by incubation with a goat-anti-mouse secondary antibody
conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (cat. no. sc-2356;
dilution, 1:50; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) for 1 h at 37°C.
Finally, the samples were stained with ≥98% (HPLC and TLC) DAPI
(cat. no. D9542; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 5 min at room
temperature. Images were captured using a confocal microscope
(Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan; magnification ×100).
Western blot assay
Human bladder tissue and cells were lysed in lysis
buffer (Nanjing Keygen Biotech Co. Ltd.), and protein
concentrations were determined with Bradford's method. A total of
50 µg protein from each sample was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Hercules, CA, USA) and transferred onto
nitrocellulose membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Fat-free milk powder (5%) was used to block the
membranes in PBS for 60 min at room temperature, which were then
incubated with the following antibodies: Monoclonal mouse
anti-human CBS and CSE (both diluted 1:1,000; Abnova); polyclonal
rabbit anti-human MPST (dilution, 1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc.), extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2; cat. no.
V114A), phosphorylated (p)-Erk1/2 (cat. no. 9101S), cleaved
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) p85 (cat. no. G734A) (all
diluted 1:1,000; Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA), B-cell
lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2; cat. no. 3498S), Bcl-2-like 1 (Bcl-xL; cat. no.
2762S), Bcl-2-associated X (Bax; cat. no. 2774S), Bcl-2-associated
agonist of cell death (Bad; cat. no. 9292S) and GAPDH (cat. no.
8884S) (all diluted 1:1,000; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers,
MA, USA).
Following primary antibody incubation, the membranes
were incubated with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat IgG
secondary antibody (cat. no. sc-2354; dilution, 1:2,000; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc.). Enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Pharmacia
Biotech; GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) was used to detect
signals, and a Kodak Image Station (Kodak, Rochester, NY, USA) was
used for analysis and recording.
Determination of H2S
production
Determination of H2S production was
performed using a previously described method (20). Briefly, a 10-fold volume (w/v) of
ice-cold potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) was used to homogenize
tissues and cells. Reactions were performed in custom-made glass
chambers 1 cm in diameter and 2 cm in height in a Pyrex Erlenmeyer
flask. Cryovial test tubes (size, 2 ml) containing 0.5 ml 1 M
sodium hydroxide were inserted into the chambers. A mixture of 500
µl cell homogenate with 500 µl 50 mmol/l (pH 6.8) PBS and 1 ml
reaction system solution [100 mmol/l (pH 7.4) PBS, 10 mmol/l
L-cysteine and 2 mmol/l phosphate pyridoxine aldehyde] was
prepared. The protein concentration of the sample was determined,
and 2 ml mixed solution was transferred to the outer area of the
flask. NaOH (1 mol/l) was added to the chamber of the flask, which
was incubated for 90 min at 37°C in a water bath. At the end of the
reaction, 1 ml 50% trichloroacetic acid was added. The flask was
incubated at 37°C for 60 min, and the contents of the central
chambers were transferred to a 12-well cell culture plate (Corning
Incorporated, Corning, NY, USA) containing 1 ml antioxidant
solution. A sulfide-sensitive electrode (PXS-270; Shanghai INESA
Auto Lecetronics System Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was employed to
determine the H2S concentration of the solution using a
standard curve. The H2S activities are expressed in
nmol/(min × mg), adjusted to the protein concentration of the
corresponding samples.
Cell viability test
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates (10,000
cells/well) and incubated at 37°C for 24 h to reach 50–60%
confluence. The cells were treated with CDDP (5 µg/l), CDDP + PAG
(10 or 100 µM) or CDDP + NaHS (10 or 100 µM), incubated for 72 h,
and then harvested for further analysis. Cell viability was
assessed using the CellTiter 96 Aqueous Assay kit (Promega
Corporation), according to the manufacturer's protocol, at
different time intervals using a multiwell spectrophotometer
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Tumorigenesis assay
EJ cells (1×107 cells/mouse) were
injected subcutaneously into the axillar area of 6-week-old male
BALB/c-nu mice (10 mice per treatment), which were purchased from
the Experimental Animal Center of Peking University Health Science
(Haidian, China); the average weight of mice was 20.0±0.9 g. Mice
had access to food and water ad libitum, and were kept at a
temperature of 20–26°C, a humidity of 30–70% and in a 12 h light/12
h dark cycle. CDDP (5 mg/kg), CDDP (5 mg/kg) + PAG (100 µM) or CDDP
(5 mg/kg) + NaHS (100 µM) were injected into the abdominal cavity.
Following sacrifice at intervals of 4 days, the tumour volumes were
determined using the equation: Length × width2 ×0.5. The
study was performed in strict accordance with the recommendations
in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the
National Institutes of Health.
Statistical analysis
A Student's t-test was performed to compare
differences 2 groups. One-way analysis of variance followed by and
Dunnett's test was used to evaluate the statistical significance
between ≥3 groups. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard
deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (version
17.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P<0.05 was considered to
represent a statistically significant difference.
Results
Immunofluorescence and western blot
analyses of CBS, CSE and MPST in tissue and cells
As determined by western blotting, the bladder
tissue samples exhibited increasing CBS, CSE and MPST protein
expression from normal tissue to NMIBC to MIBC (Fig. 1A-C). The protein levels for all three
H2S-associated enzymes in UCB tissue were increased
compared with those in normal controls. However, between the NMIBC
and the MIBC groups, the only significant difference was in the CSE
level (P=0.023; Fig. 1B). The UCB
sections (Fig. 1D) exhibited moderate
to strong immunoreactivity for CBS, CSE and MPST. The highest
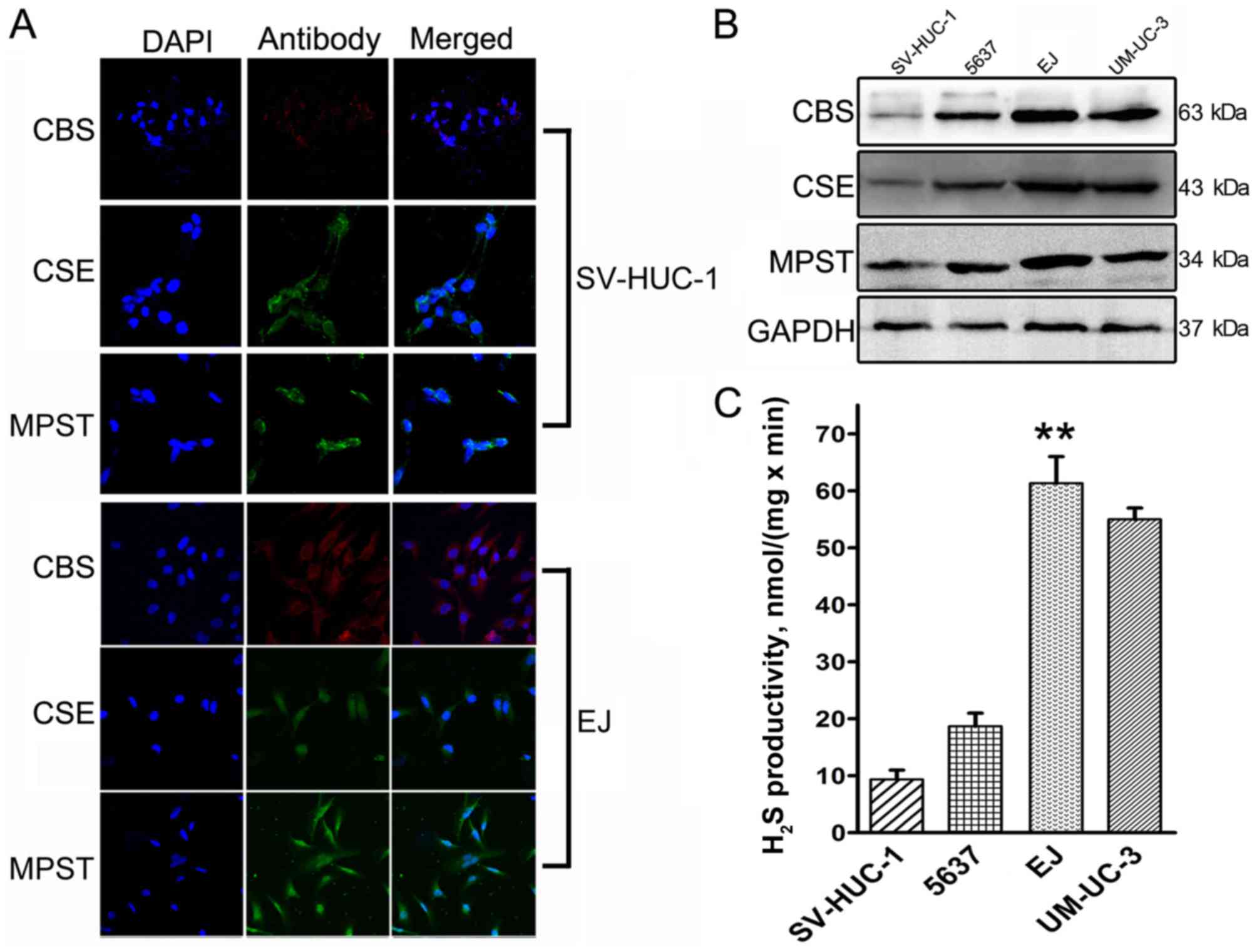
expression among the cells was observed in EJ cells (Fig. 2). SV-HUC-1 normal bladder urothelium
cells exhibited low to moderate immunoreactivity for CBS, CSE and
MPST (Fig. 2A), whereas our previous
study demonstrated moderate to strong immunoreactivity in EJ cells
(Fig. 2A) (8).
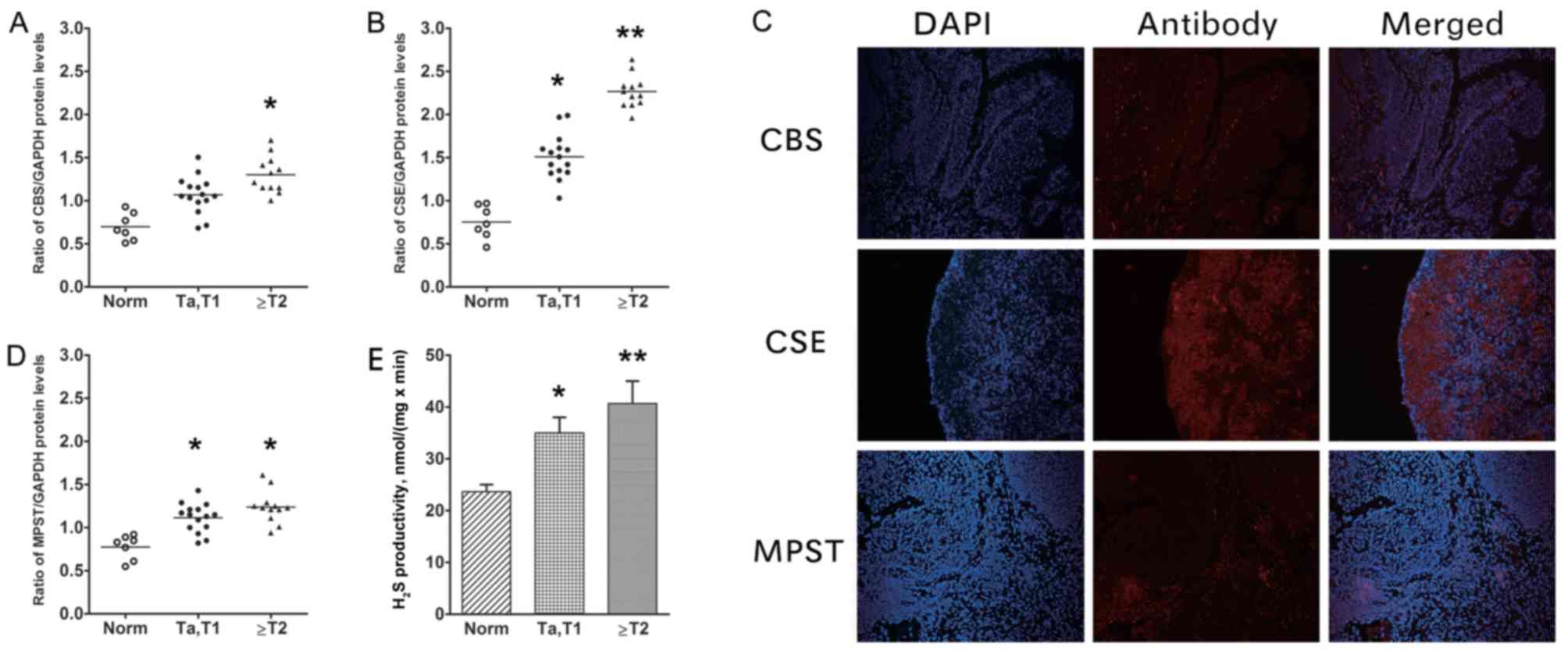 | Figure 1.CBS, CSE and MPST protein levels, and
H2S productivity in human UCB tumour and adjacent tissue
samples. Protein expression levels of (A) CBS and (B) CSE and
compared with GAPDH in samples from patients. (C) Representative
images of MIBC UCB sections, demonstrating moderate to strong
immunoreactivity for CBS, CSE and MPST (×10, magnification). (D)
MPST compared with GAPDH in samples from patients, as determined by
western blotting. (E) Determination of H2S productivity
rate. The rate of H2S productivity was higher in bladder
tumour samples compared with in adjacent controls (vs. NMIBC,
P=0.035; vs. MIBC, P=0.007), with statistical significance also
identified between the UCB groups (P=0.021). Thus, the levels of
CBS, CSE and MPST expression, and H2S productivity, were
higher in bladder tumours compared with in normal bladder tissue.
*P<0.05; **P<0.01 vs. Norm. CBS, cystathionine β-synthase;
CSE, cystathionine γ-lyase; MPST, 3-mercaptopyruvate
sulfurtransferase; UCB, urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder;
NMIBC, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer; MIBC, muscle-invasive
bladder cancer; Norm, normal; T, tumor. |
H2S productivity rate in
bladder tissue and cells
The H2S productivity rate was determined
for bladder tissue samples and cells. UCB tissues exhibited
increased H2S productivity compared with in the normal
control samples (normal samples vs. NMIBC, P=0.035; normal samples
vs. MIBC, P=0.007); the different UCB groups also differed
significantly (NMIBC vs. MIBC, P=0.021; Fig. 1E). In addition, decreased
H2S productivity was detected in the normal human
urinary tract epithelial cell line SV-HUC-1 compared with the
bladder cancer cell lines derived from low-grade (5637) and
invasive transitional (UM-UC-3 and EJ) cell carcinoma lines. To
investigate the mechanism by which H2S contributes to
bladder cancer malignancy, EJ cells were employed as a model, as
the rate of H2S production was the highest in these
cells (P=0.003; Fig. 2C).
H2S levels affect CDDP
cytotoxicity in EJ cells
The effects of altered H2S levels on the
cell viability following treatment with CDDP in EJ cells are
presented in Fig. 3. Although an
endogenous H2S synthase CSE inhibitor (PAG) and
exogenous H2S donor (NaHS) alone did not induce any
alteration in the viability of the EJ cells, treatment with PAG or
NaHS affected the CDDP cytotoxicity (Fig.
3A and B). Increased H2S levels using NaHS activated
p-Erk1/2, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression in CDDP-treated EJ cells, and
down-regulated levels of Bax, Bad and cleaved PARP (Fig. 3C). By contrast, the endogenous
H2S synthase CSE inhibitor PAG up-regulated the
expression of Bax, Bad and cleaved PARP, and decreased the levels
of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and p-Erk1/2 (Fig.
3C). The Erk1/2 expression level was unaffected by all
treatments.
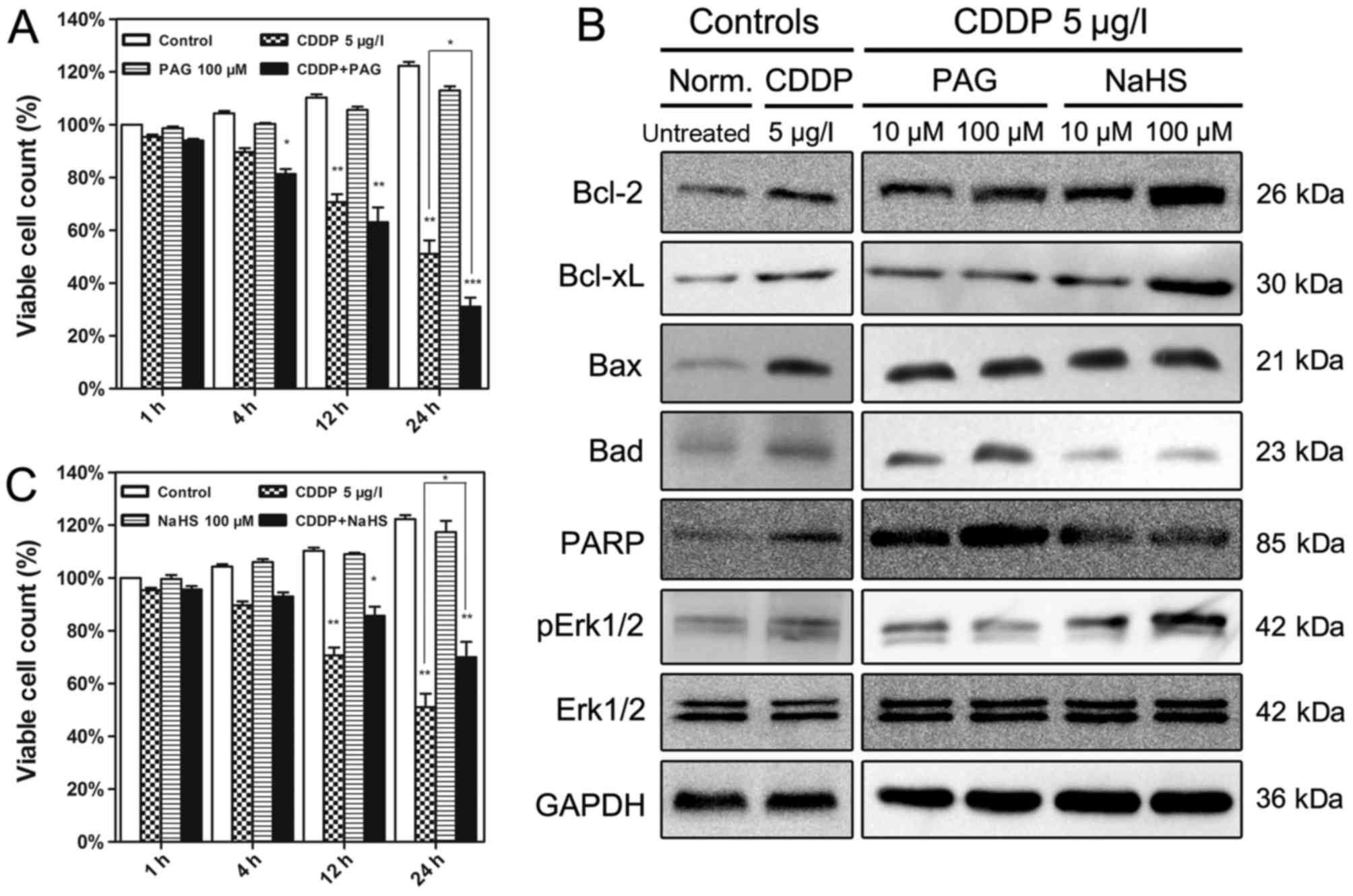 | Figure 3.Effects of PAG and NaHS on cell
viability and the expression of H2S-associated proteins
in EJ cells. (A) EJ cells received different treatments for
different time periods. The cells treated with 100 µM PAG were the
most affected by treatment with CDDP. (B) Western blotting was
employed to verify the modulation of apoptosis-associated protein
expression at 12 h. (C) NaHS (100 µM) significantly alleviated the
cytotoxicity of CDDP in EJ cells at different time periods. Data
are presented as the means ± standard deviation of three
experimental repeats. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs.
Control. PAG, propargylglycine; CDDP, cisplatin; Bcl-2, B-cell
lymphoma 2; Bcl-xL, Bcl-2-like 1; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X; Bad,
Bcl-2-associated agonist of cell death; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase; Erk1/2, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2;
pErk1/2, phosphorylated Erk1/2; Norm., normal. |
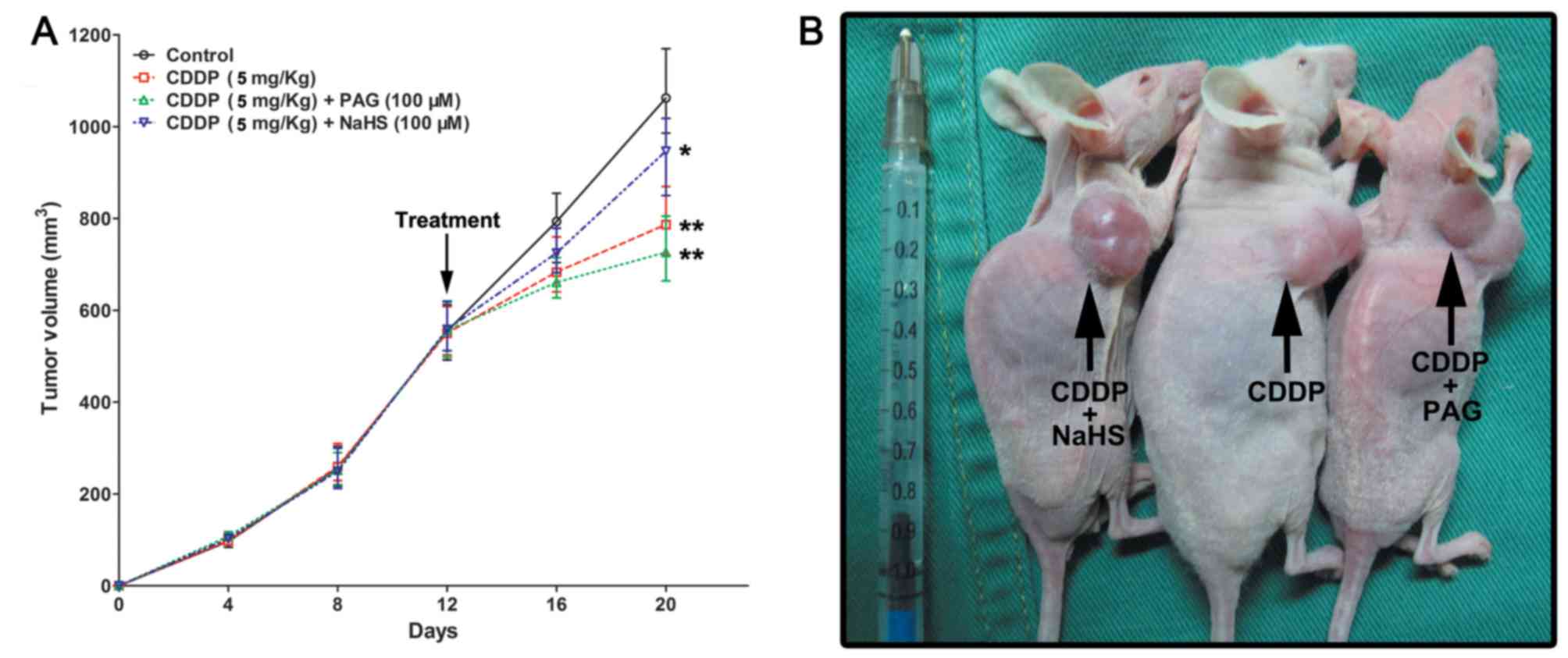
Combining CDDP with PAG inhibits UCB
growth
CDDP + PAG treatment (tumor volume, 721.13±21.41
mm3; P=0.0019) and CDDP alone treatment (tumor volume,
768.64±29.06 mm3; P=0.0086) were associated with the
significant suppression of EJ cell tumorigenesis compared with
those derived from the control group (tumor volume, 1,112.02±52.13
mm3). CDDP + NaHS (tumor volume, 952.46±59.87
mm3; P=0.021) led to a moderate inhibition of EJ cell
(Fig. 4A and B).
Discussion
Our previous study identified that endogenous
H2S, and the associated enzymes CBS, CSE and MPST, are
highly expressed in human UCB tissues and cell lines (8), which is consistent with a number of
other studies (1,2,7,9,21). To the
best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to
demonstrate that increased levels of H2S exert
cytoprotective effects on UCB cells treated with CDDP. Furthermore,
these results demonstrate that the H2S production and
CSE expression levels were significantly different between the
NMIBC and MIBC groups. This result suggests that H2S
production and CSE expression may serve as biomarkers for
urologists to determine a prognosis. Although addition of the
H2S donor NaHS or the H2S synthase inhibitor
PAG did not result in changes to EJ cell viability, altered
H2S levels affected the viability of CDDP-treated EJ
cells. The cytotoxicity of CDDP in EJ cells was mitigated by high
levels of H2S or its biosynthetic enzymes, which
appeared to involve the activation of the Erk1/2 signalling pathway
and interruption of the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
We hypothesize that H2S participates in additional
cellular events in the carcinogenesis of the urothelium, which
warrants further studies.
H2S counteracted the cytotoxicity of CDDP
in UCB cells, which is of considerable interest as altering the
H2S level alone did not elicit any effect on cell
viability in the present study. GSH, the most important scavenger
of ROS and RNS in the human body, and a widely studied molecule, is
a product of the H2S biosynthesis pathway (1,10,11,22). The
catenation and interchalcogen bond formation between H2S
and thiol-containing substances may facilitate the metabolism and
recycling of thiol compounds, including those containing disulfide
bridges in cellular redox signalling, and GSH (9,22); GSH is
up-regulated to serve complex, although controversial, functions in
UCB (23,24). Previous studies have identified that
H2S is able to stimulate GSH synthesis (9) and that the anomalous expression of
GSH-associated enzymes, including glutathione synthetases and
γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, is involved in tumorigenesis and
chemoresistance in UCB (10,11,23–26).
Therefore, up-regulated H2S biosynthesis in UCB may
serve functions similar to those of GSH in UCB. Another previous
study indicated that PAG enhanced the effect of CDDP on bladder
tumours in a murine model (27).
The increased expression of CBS, CSE and MPST in
human UCB raises questions regarding the function of the level of
H2S in urothelial carcinogenesis. H2S
interacts with nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO), which
together create a complex network that contributes to inflammation
and carcinogenesis (2,14). NO and CO have been demonstrated to
participate in oxidation-reduction processes, and to promote
angiogenesis via cGMP-mediated or non-cGMP-mediated pathways,
similar to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), in UCB (28,29). These
results suggest a potential function for H2S in
angiogenesis through cross-talk between these gaseous molecules in
UCB. Accumulating evidence indicates that H2S acts on
ion channels, including ATP-sensitive potassium channels (9,14).
Additionally, H2S functions in signal transduction,
including in the mitogen-activated protein kinase, VEGF,
insulin-like growth factor, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein
kinase B, nuclear factor-κB, signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3, nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-related factor
2 and HIF-1α signalling pathways (2,29–31). Given that disrupted cell signalling
contributes to the initiation of UCB (12,32), the
possible interaction between an increase in H2S and the
activation of aberrant cellular signals in UCB is plausible and
warrants further research.
Genetic analysis of the function of one-carbon
metabolism and transsulfuration pathways in bladder cancer has
produced notable results. For example, several CSE
single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) may be associated with an
increased risk of bladder cancer (15,16). SNPs
may lead to abnormal transcription and translation, affecting the
expression or function of the encoded protein (33). Although SNPs in the CSE gene in
patients with bladder cancer have been identified, analysis of the
CSE mRNA and protein expression levels and catalytic activity has
not been reported. Therefore, it is not possible to compare between
these previous studies and the present study. Nevertheless, the
present study may provide a clue regarding how alterations in
H2S-associated enzymes may contribute to UCB
tumorigenesis.
The endogenous signalling molecule H2S
and its associated biosynthetic enzymes CBS, CSE and MPST are
expressed at increased levels in human UCB, including in bladder
tumour tissue and cell lines. However, clinical trials of the
approach reported in the present study are not possible at present,
as the drugs that inhibit H2S production are not
suitable for use in the clinic. Regardless, the inhibition of
H2S levels enhanced CDDP-induced apoptosis in UCB cells
in vitro, and this may represent a new therapeutic target or
diagnostic marker for UCB.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81302231), the
Beijing Outstanding Talent Training (grant no. 2014000021469G0104),
the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals' Youth Programme
(grant no. QML20160303) and from Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital 1351
Talents Project Funding (grant no. CYXX-2017-11).
Availability of data and materials
The analysed datasets generated during the study are
available from the corresponding author, on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
NX had full access to all the data in the study and
is responsible for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of
the data analysis. WW and JG were major contributors in writing the
manuscript and statistical analysis. LS, HP, and YN performed data
acquisition. MW and FY analysed and interpreted data. All authors
have read and approved the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Beijing Chao
Yang Hospital's institutional research ethics board, including the
use of human samples and animal experiments (protocol no.
AN-1405-002-100). Informed consent was obtained from all patients
enrolled in the study.
Consent for publication
The study was performed with the patients' informed
consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
CBS
|
cystathionine β-synthase
|
|
CDDP
|
cisplatin
|
|
CSE
|
cystathionine γ-lyase
|
|
HIF-1α
|
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
|
|
MIBC
|
muscle-invasive bladder cancer
|
|
MPST
|
3-mercaptopyruvate
sulfurtransferase
|
|
NMIBC
|
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
|
|
PAG
|
propargylglycine
|
|
RNS
|
reactive nitrogen species
|
|
ROS
|
reactive oxygen species
|
|
SNP
|
single-nucleotide polymorphism
|
|
UCB
|
urothelial cell carcinoma of the
bladder
|
|
VEGF
|
vascular endothelial growth factor
|
References
|
1
|
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide: Its
production, release and functions. Amino Acids. 41:113–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L, Rose P and Moore PK: Hydrogen
sulfide and cell signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 51:169–187.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang G, Wu L, Jiang B, Yang W, Qi J, Cao
K, Meng Q, Mustafa AK, Mu W, Zhang S, et al: H2S as a physiologic
vasorelaxant: Hypertension in mice with deletion of cystathionine
gamma-lyase. Science. 322:587–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whiteman M, Le Trionnaire S, Chopra M, Fox
B and Whatmore J: Emerging role of hydrogen sulfide in health and
disease: Critical appraisal of biomarkers and pharmacological
tools. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:459–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hegde A and Bhatia M: Hydrogen sulfide in
inflammation: Friend or foe? Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets.
10:118–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargyl-cysteine, increases CSE in
SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a novel anti-cancer
effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One. 6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chattopadhyay M, Kodela R, Nath N,
Barsegian A, Boring D and Kashfi K: Hydrogen sulfide-releasing
aspirin suppresses NF-κβ signaling in estrogen receptor negative
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:723–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gai JW, Qin W, Liu M, Wang HF, Zhang M, Li
M, Zhou WH, Ma QT, Liu GM and Song WH: Expression profile of
hydrogen sulfide and its synthases correlates with tumor stage and
grade in urothelial cell carcinoma of bladder. Urol Oncol.
34:1662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kimura Y, Goto Y and Kimura H: Hydrogen
sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative
stress in mitochondria. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1–13. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahn H, Lee E, Kim K and Lee C: Effect of
glutathione and its related enzymes on chemosensitivity of renal
cell carcinoma and bladder carcinoma cell lines. J Urol.
151:263–267. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simic T, Savic-Radojevic A,
Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Matic M and Mimic-Oka J: Glutathione
S-transferases in kidney and urinary bladder tumors. Nat Rev Urol.
6:281–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wallerand H, Reiter RR and Ravaud A:
Molecular targeting in the treatment of either advanced or
metastatic bladder cancer or both according to the signalling
pathways. Curr Opin Urol. 18:524–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szabó C: Hydrogen sulphide and its
therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:917–935. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kajimura M, Fukuda R, Bateman RM, Yamamoto
T and Suematsu M: Interactions of multiple gas-transducing systems:
Hallmarks and uncertainties of CO, NO, and H2S gas biology.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 13:157–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moore LE, Malats N, Rothman N, Real FX,
Kogevinas M, Karami S, García-Closas R, Silverman D, Chanock S,
Welch R, et al: Polymorphisms in one-carbon metabolism and
trans-sulfuration pathway genes and susceptibility to bladder
cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:2452–2458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chung CJ, Pu YS, Su CT, Chen HW, Huang YK,
Shiue HS and Hsueh YM: Polymorphisms in one-carbon metabolism
pathway genes, urinary arsenic profile, and urothelial carcinoma.
Cancer Causes Control. 21:1605–1613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edge S, Byrd D, Compton C, Fritz A, Greene
F and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. Springer;
New York, NY: 2010
|
|
18
|
Masters JR, Hepburn PJ, Walker L, Highman
WJ, Trejdosiewicz LK, Povey S, Parkar M, Hill BT, Riddle PR and
Franks LM: Tissue culture model of transitional cell carcinoma:
Characterization of twenty-two human urothelial cell lines. Cancer
Res. 46:3630–3636. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Capes-Davis A, Theodosopoulos G, Atkin I,
Drexler HG, Kohara A, MacLeod RA, Masters JR, Nakamura Y, Reid YA,
Reddel RR and Freshney RI: Check your cultures! A list of
cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int J Cancer.
127:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Tang C, Jin H and Du J: Regulatory
effects of sulfur dioxide on the development of atherosclerotic
lesions and vascular hydrogen sulfide in atherosclerotic rats.
Atherosclerosis. 215:323–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo H, Gai JW, Wang Y, Jin HF, Du JB and
Jin J: Characterization of hydrogen sulfide and its synthases,
cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase, in human
prostatic tissue and cells. Urology. 79:4832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moran LK, Gutteridge JM and Quinlan GJ:
Thiols in cellular redox signalling and control. Curr Med Chem.
8:763–772. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pendyala L, Velagapudi S, Toth K,
Zdanowicz J, Glaves D, Slocum H, Perez R, Huben R, Creaven PJ and
Raghavan D: Translational studies of glutathione in bladder cancer
cell lines and human specimens. Clin Cancer Res. 3:793–798.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Singh SV, Xu BH, Tkalcevic GT, Gupta V,
Roberts B and Ruiz P: Glutathione-linked detoxification pathway in
normal and malignant human bladder tissue. Cancer Lett. 77:15–24.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Savic-Radojevic A, Mimic-Oka J,
Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Opacic M, Dragicevic D, Kravic T, Djokic M,
Micic S and Simic T: Glutathione S-transferase-P1 expression
correlates with increased antioxidant capacity in transitional cell
carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol. 52:470–477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Byun SS, Kim SW, Choi H, Lee C and Lee E:
Augmentation of cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant human
bladder cancer cells by modulating glutathione concentrations and
glutathione-related enzyme activities. BJU Int. 95:1086–1090. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Satoh M, Kloth DM, Kadhim SA, Chin JL,
Naganuma A, Imura N and Cherian MG: Modulation of both cisplatin
nephrotoxicity and drug resistance in murine bladder tumor by
controlling metallothionein synthesis. Cancer Res. 53:1829–1832.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ehsan A, Sommer F, Schmidt A, Klotz T,
Koslowski J, Niggemann S, Jacobs G, Engelmann U, Addicks K and
Bloch W: Nitric oxide pathways in human bladder carcinoma. The
distribution of nitric oxide synthases, soluble guanylyl cyclase,
cyclic guanosine monophosphate, and nitrotyrosine. Cancer.
95:2293–2301. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyake M, Fujimoto K, Anai S, Ohnishi S,
Kuwada M, Nakai Y, Inoue T, Matsumura Y, Tomioka A, Ikeda T, et al:
Heme oxygenase-1 promotes angiogenesis in urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Oncol Rep. 25:653–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang GD and Wang H: H(2)S and cellular
proliferation and apoptosis. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 59:133–140.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baskar R and Bian J: Hydrogen sulfide gas
has cell growth regulatory role. Eur J Pharmacol. 656:5–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitra AP, Bartsch CC and Cote RJ:
Strategies for molecular expression profiling in bladder cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:317–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Teng S, Michonova-Alexova E and Alexov E:
Approaches and resources for prediction of the effects of
non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism on protein function
and interactions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 9:123–133. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|