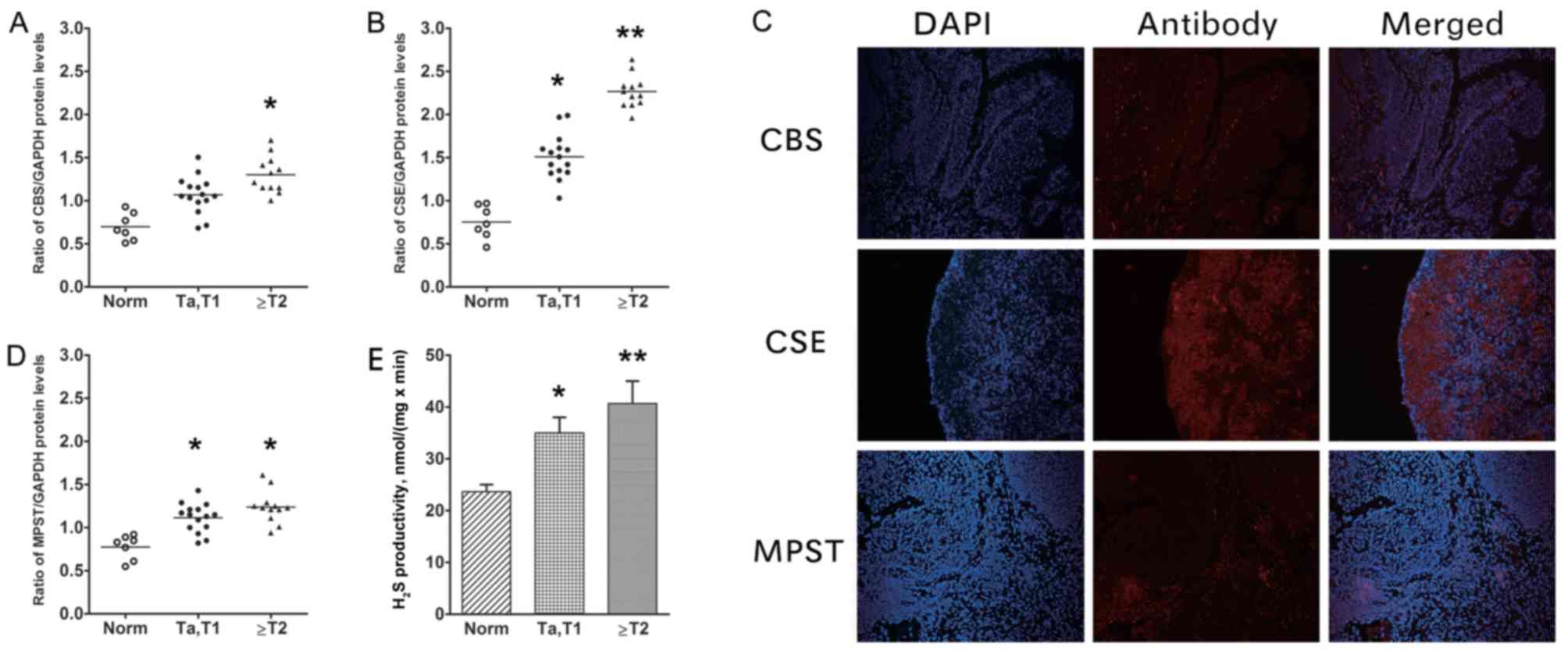
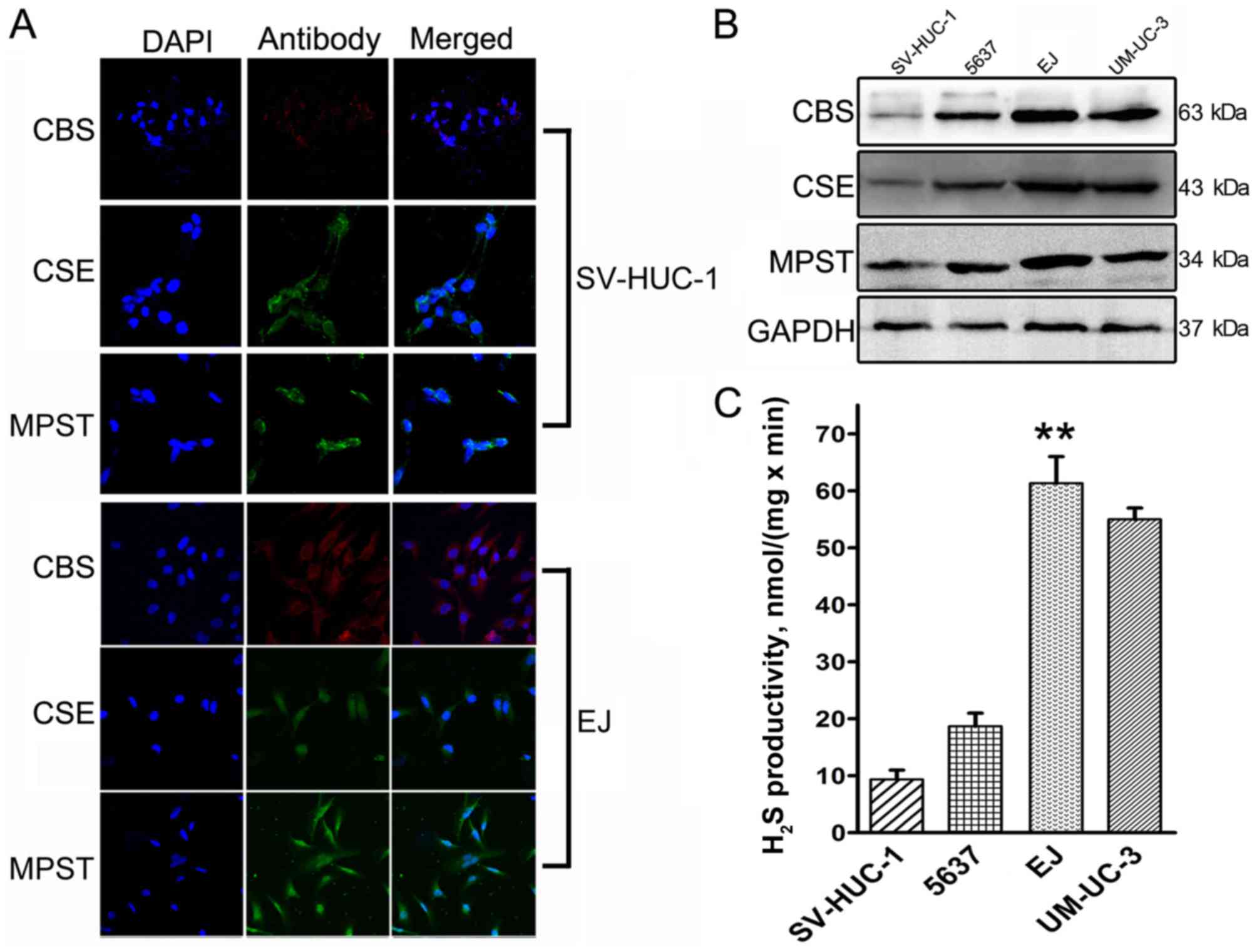
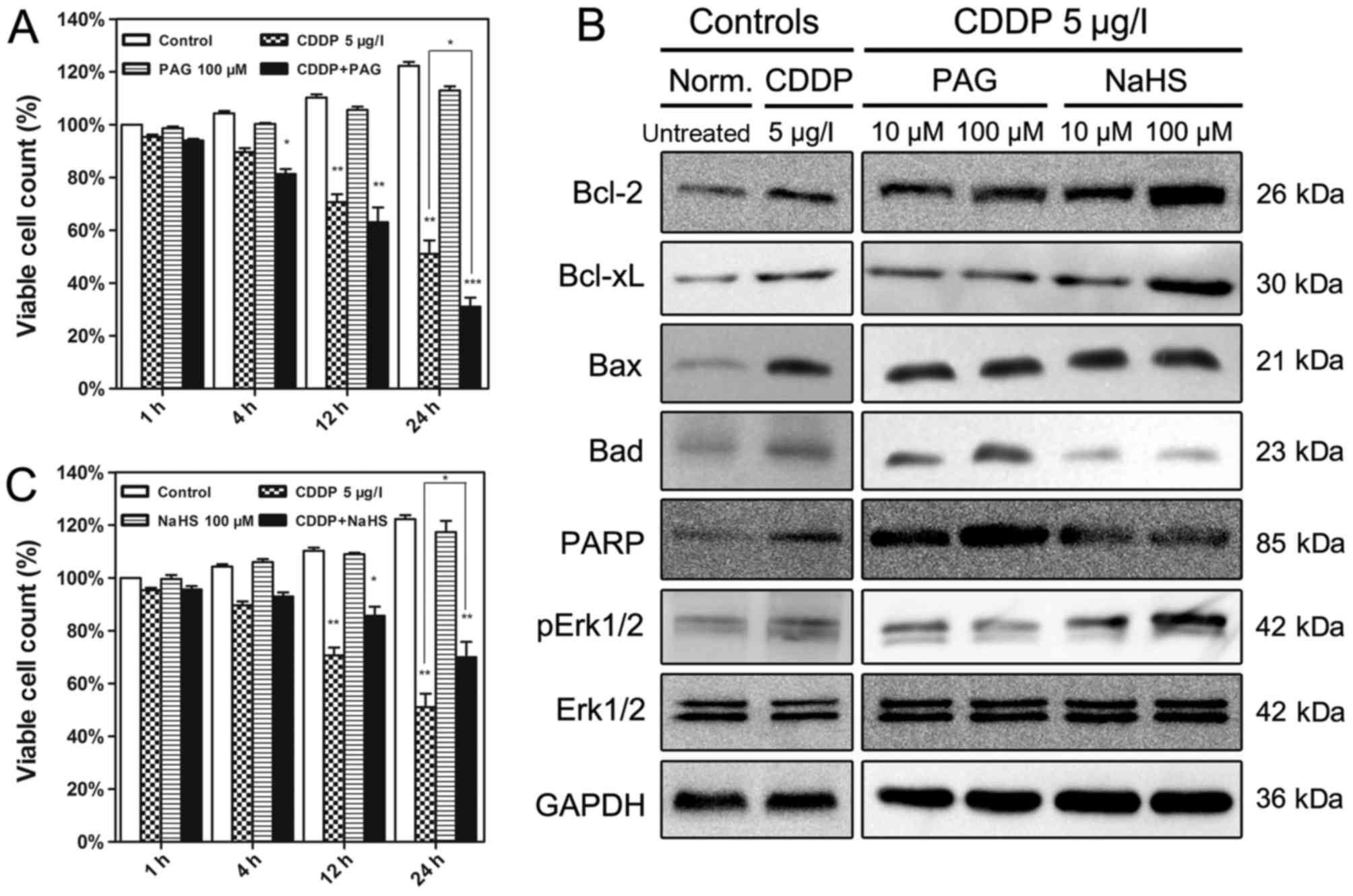
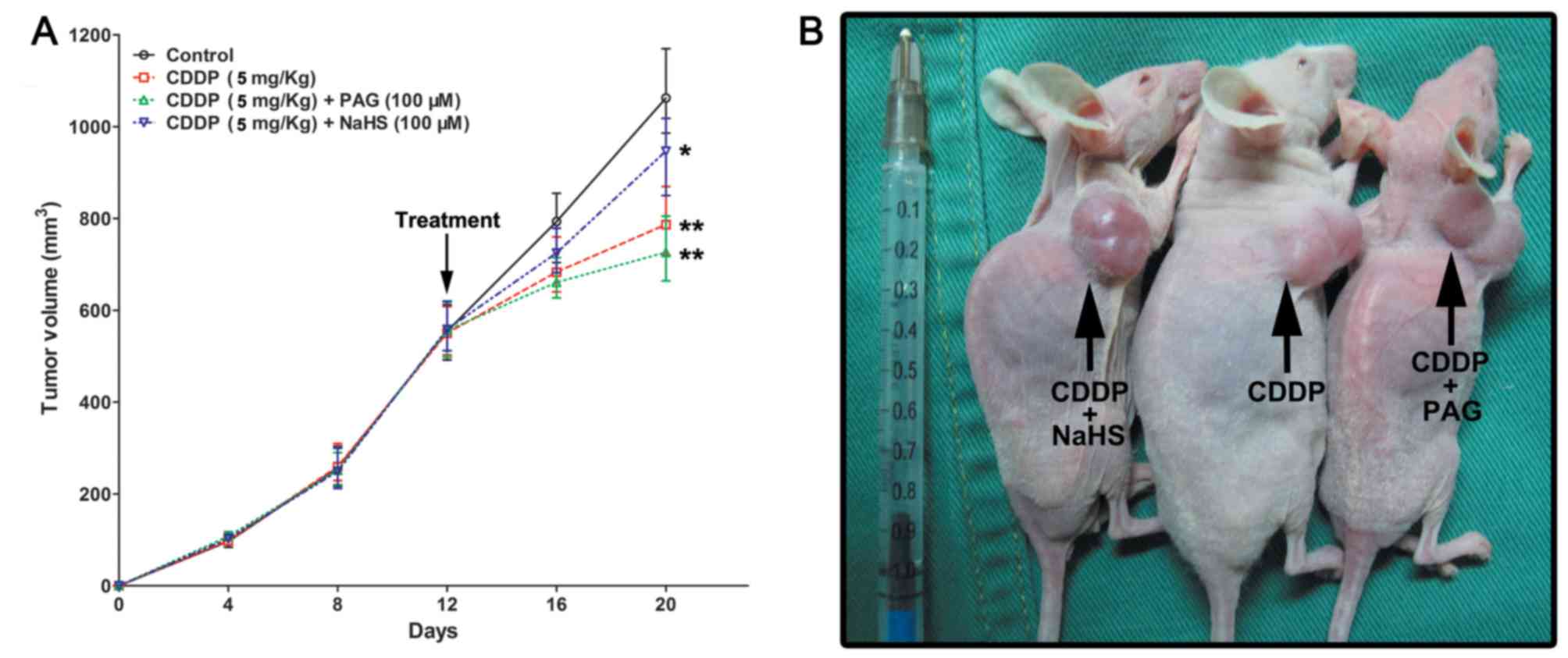
|
1
|
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide: Its
production, release and functions. Amino Acids. 41:113–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L, Rose P and Moore PK: Hydrogen
sulfide and cell signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 51:169–187.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang G, Wu L, Jiang B, Yang W, Qi J, Cao
K, Meng Q, Mustafa AK, Mu W, Zhang S, et al: H2S as a physiologic
vasorelaxant: Hypertension in mice with deletion of cystathionine
gamma-lyase. Science. 322:587–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whiteman M, Le Trionnaire S, Chopra M, Fox
B and Whatmore J: Emerging role of hydrogen sulfide in health and
disease: Critical appraisal of biomarkers and pharmacological
tools. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:459–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hegde A and Bhatia M: Hydrogen sulfide in
inflammation: Friend or foe? Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets.
10:118–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargyl-cysteine, increases CSE in
SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a novel anti-cancer
effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One. 6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chattopadhyay M, Kodela R, Nath N,
Barsegian A, Boring D and Kashfi K: Hydrogen sulfide-releasing
aspirin suppresses NF-κβ signaling in estrogen receptor negative
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:723–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gai JW, Qin W, Liu M, Wang HF, Zhang M, Li
M, Zhou WH, Ma QT, Liu GM and Song WH: Expression profile of
hydrogen sulfide and its synthases correlates with tumor stage and
grade in urothelial cell carcinoma of bladder. Urol Oncol.
34:1662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kimura Y, Goto Y and Kimura H: Hydrogen
sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative
stress in mitochondria. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1–13. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahn H, Lee E, Kim K and Lee C: Effect of
glutathione and its related enzymes on chemosensitivity of renal
cell carcinoma and bladder carcinoma cell lines. J Urol.
151:263–267. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simic T, Savic-Radojevic A,
Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Matic M and Mimic-Oka J: Glutathione
S-transferases in kidney and urinary bladder tumors. Nat Rev Urol.
6:281–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wallerand H, Reiter RR and Ravaud A:
Molecular targeting in the treatment of either advanced or
metastatic bladder cancer or both according to the signalling
pathways. Curr Opin Urol. 18:524–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szabó C: Hydrogen sulphide and its
therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:917–935. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kajimura M, Fukuda R, Bateman RM, Yamamoto
T and Suematsu M: Interactions of multiple gas-transducing systems:
Hallmarks and uncertainties of CO, NO, and H2S gas biology.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 13:157–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moore LE, Malats N, Rothman N, Real FX,
Kogevinas M, Karami S, García-Closas R, Silverman D, Chanock S,
Welch R, et al: Polymorphisms in one-carbon metabolism and
trans-sulfuration pathway genes and susceptibility to bladder
cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:2452–2458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chung CJ, Pu YS, Su CT, Chen HW, Huang YK,
Shiue HS and Hsueh YM: Polymorphisms in one-carbon metabolism
pathway genes, urinary arsenic profile, and urothelial carcinoma.
Cancer Causes Control. 21:1605–1613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edge S, Byrd D, Compton C, Fritz A, Greene
F and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. Springer;
New York, NY: 2010
|
|
18
|
Masters JR, Hepburn PJ, Walker L, Highman
WJ, Trejdosiewicz LK, Povey S, Parkar M, Hill BT, Riddle PR and
Franks LM: Tissue culture model of transitional cell carcinoma:
Characterization of twenty-two human urothelial cell lines. Cancer
Res. 46:3630–3636. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Capes-Davis A, Theodosopoulos G, Atkin I,
Drexler HG, Kohara A, MacLeod RA, Masters JR, Nakamura Y, Reid YA,
Reddel RR and Freshney RI: Check your cultures! A list of
cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int J Cancer.
127:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Tang C, Jin H and Du J: Regulatory
effects of sulfur dioxide on the development of atherosclerotic
lesions and vascular hydrogen sulfide in atherosclerotic rats.
Atherosclerosis. 215:323–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo H, Gai JW, Wang Y, Jin HF, Du JB and
Jin J: Characterization of hydrogen sulfide and its synthases,
cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase, in human
prostatic tissue and cells. Urology. 79:4832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moran LK, Gutteridge JM and Quinlan GJ:
Thiols in cellular redox signalling and control. Curr Med Chem.
8:763–772. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pendyala L, Velagapudi S, Toth K,
Zdanowicz J, Glaves D, Slocum H, Perez R, Huben R, Creaven PJ and
Raghavan D: Translational studies of glutathione in bladder cancer
cell lines and human specimens. Clin Cancer Res. 3:793–798.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Singh SV, Xu BH, Tkalcevic GT, Gupta V,
Roberts B and Ruiz P: Glutathione-linked detoxification pathway in
normal and malignant human bladder tissue. Cancer Lett. 77:15–24.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Savic-Radojevic A, Mimic-Oka J,
Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Opacic M, Dragicevic D, Kravic T, Djokic M,
Micic S and Simic T: Glutathione S-transferase-P1 expression
correlates with increased antioxidant capacity in transitional cell
carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol. 52:470–477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Byun SS, Kim SW, Choi H, Lee C and Lee E:
Augmentation of cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant human
bladder cancer cells by modulating glutathione concentrations and
glutathione-related enzyme activities. BJU Int. 95:1086–1090. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Satoh M, Kloth DM, Kadhim SA, Chin JL,
Naganuma A, Imura N and Cherian MG: Modulation of both cisplatin
nephrotoxicity and drug resistance in murine bladder tumor by
controlling metallothionein synthesis. Cancer Res. 53:1829–1832.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ehsan A, Sommer F, Schmidt A, Klotz T,
Koslowski J, Niggemann S, Jacobs G, Engelmann U, Addicks K and
Bloch W: Nitric oxide pathways in human bladder carcinoma. The
distribution of nitric oxide synthases, soluble guanylyl cyclase,
cyclic guanosine monophosphate, and nitrotyrosine. Cancer.
95:2293–2301. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyake M, Fujimoto K, Anai S, Ohnishi S,
Kuwada M, Nakai Y, Inoue T, Matsumura Y, Tomioka A, Ikeda T, et al:
Heme oxygenase-1 promotes angiogenesis in urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Oncol Rep. 25:653–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang GD and Wang H: H(2)S and cellular
proliferation and apoptosis. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 59:133–140.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baskar R and Bian J: Hydrogen sulfide gas
has cell growth regulatory role. Eur J Pharmacol. 656:5–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitra AP, Bartsch CC and Cote RJ:
Strategies for molecular expression profiling in bladder cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:317–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Teng S, Michonova-Alexova E and Alexov E:
Approaches and resources for prediction of the effects of
non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism on protein function
and interactions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 9:123–133. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|