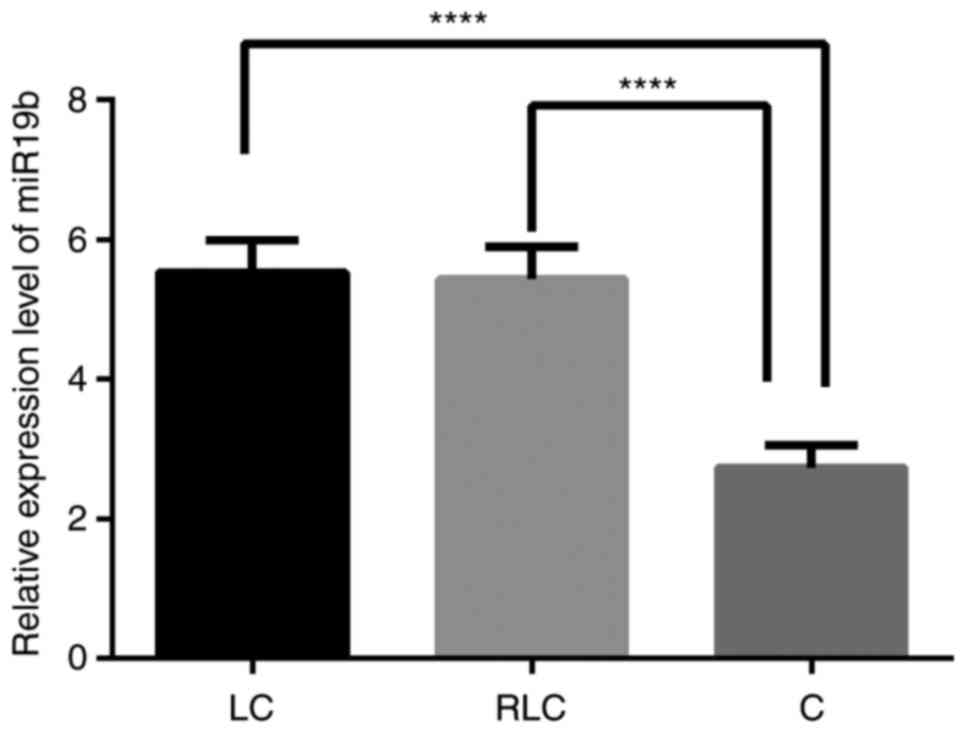
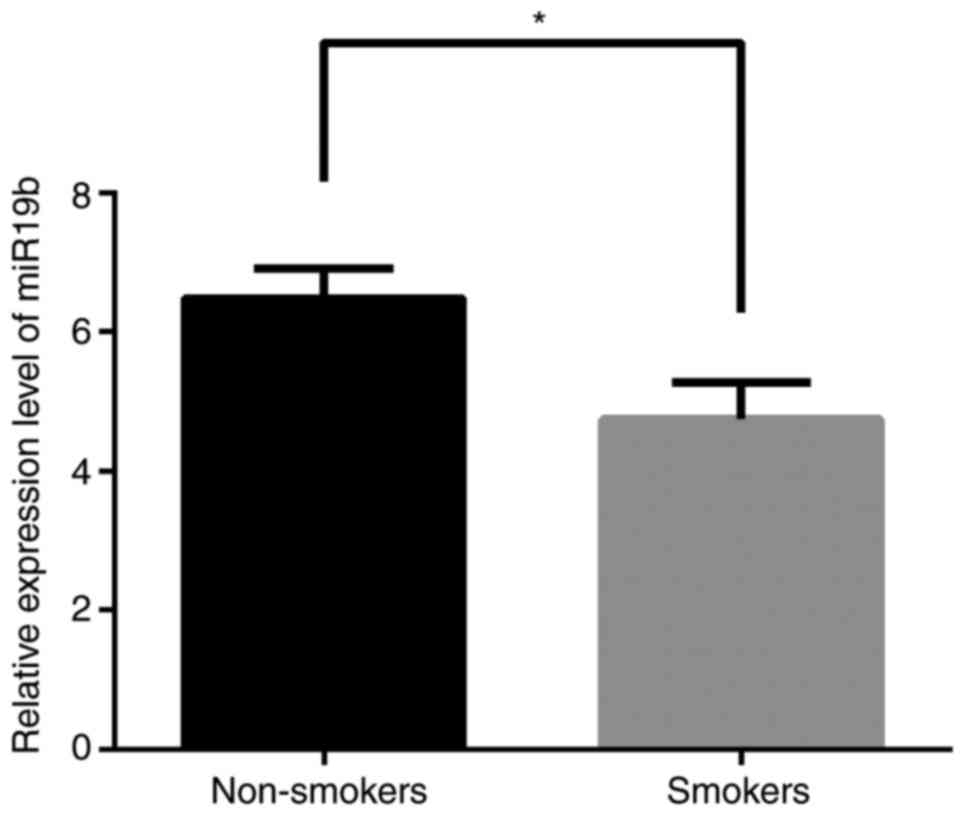
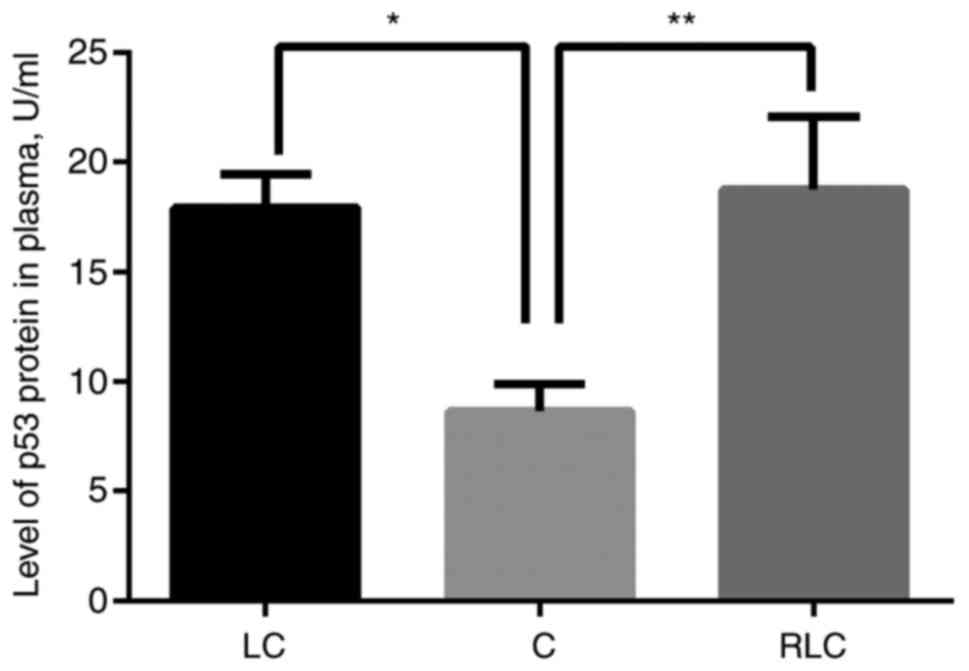
|
1
|
Amin J, Sharif M and Yasmin M:
Segmentation and classification of lung cancer: A review. Immunol
Endo Metab Age Med Chem. 16:82–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zeeb H and Shannon F: WHO handbook on
indoor radon: A public health perspectiveWorld Health Organization.
Zeeb H and Shannon F: World Health Organization; Geneva: pp. 3–21.
2009
|
|
3
|
Ahn YS and Jeong KS: Epidemiologic
characteristics of compensated occupational lung cancers among
Korean workers. J Korean Med Sci. 29:1473–1481. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Izzotti A, Carozzo S, Pulliero A,
Zhabayeva D, Ravetti JL and Bersimbaev R: Extracellular MicroRNA in
liquid biopsy: Applicability in cancer diagnosis and prevention. Am
J Cancer Res. 6:1461–1493. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anglicheau D, Muthukumar T and
Suthanthiran M: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with big effects.
Transplantation. 90:105–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishida N, Arizumi T, Hagiwara S, Ida H,
Sakurai T and Kudo M: MicroRNAs for the prediction of early
response to Sorafenib treatment in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Cancer. 6:113–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nassar FJ, Nasr R and Talhouk R: MicroRNAs
as biomarkers for early breast cancer diagnosis, prognosis and
therapy prediction. Pharmacol Ther. 172:34–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hemmatzadeh M, Mohammadi H, Karimi M,
Musavishenas MH and Baradaran B: Differential role of microRNAs in
the pathogenesis and treatment of esophageal cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 82:509–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kumar B and Lupold SE: MicroRNA expression
and function in prostate cancer: A review of current knowledge and
opportunities for discovery. Asian J Androl. 18:559–567. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taniwaki M, Daigo Y, Ishikawa N, Takano A,
Tsunoda T, Yasui W, Inai K, Kohno N and Nakamura Y: Gene expression
profiles of small-cell lung cancers: Molecular signatures of lung
cancer. Int J Oncol. 29:567–575. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu C, Cao Y, He Z, He J, Hu C, Duan H and
Jiang J: Serum levels of miR-19b and miR-146a as prognostic
biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med.
232:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Yang S, Yan W, Yang J, Qin YJ, Lin
XL, Xie RY, Wang SC, Jin W, Gao F, et al: MicroRNA-19 triggers
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells accompanied
by growth inhibition. Lab Invest. 95:1056–1070. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin Q, Chen T, Lin Q, Lin G, Lin J, Chen G
and Guo L: Serum miR-19a expression correlates with worse prognosis
of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol.
107:767–771. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chaudhry MA: Radiation-induced microRNA:
Discovery, functional analysis, and cancer radiotherapy. J Cell
Biochem. 115:436–449. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cui FM, Li JX, Chen Q, Du HB, Zhang SY,
Nie JH, Cao JP, Zhou PK, Hei TK and Tong J: Radon-induced
alterations in micro-RNA expression profiles in transformed BEAS2B
cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 76:107–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yngveson A, Williams C, Hjerpe A,
Lundeberg J, Söderkvist P and Pershagen G: p53 mutations in lung
cancer associated with residential radon exposure. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 8:433–438. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deben C, Deschoolmeester V, Lardon F,
Rolfo C and Pauwels P: TP53 and MDM2 genetic alterations in
non-small cell lung cancer: Evaluating their prognostic and
predictive value. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 99:63–73. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vähäkangas KH, Samet JM, Metcalf RA, Welsh
JA, Bennett WP, Lane DP and Harris CC: Mutations of p53 and ras
genes in radon-associated lung cancer from uranium miners. Lancet.
339:576–580. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taylor JU, Watson MA, Devereux TR, Michels
RY, Saccomanno G and Anderson M: p53 mutation hotspot in
radon-associated lung cancer. Lancet. 343:86–87. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lo YM, Darby S, Noakes L, Whitley E,
Silcocks PB, Fleming KA and Bell JI: Screening for codon 249 p53
mutation in lung cancer associated with domestic radon exposure.
Lancet. 345:601995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, Kaczorowski
AJ, Kuick R, Love RE, Zhai Y, Giordano TJ, Qin ZS, Moore BB, et al:
p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor
genes. Curr Biol. 17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Piovan C, Palmieri D, Di Leva G, Braccioli
L, Casalini P, Nuovo G, Tortoreto M, Sasso M, Plantamura I, Triulzi
T, et al: Oncosuppressive role of p53-induced miR-205 in triple
negative breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:458–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao JM, Cao B, Zhou X and Lu H: New
insights into p53 functions through its target microRNAs. J Mol
Cell Biol. 6:206–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fan Y, Yin S, Hao Y, Yang J, Zhang H, Sun
C, Ma M, Chang Q and Xi JJ: mir-19b promotes tumor growth and
metastasis via targeting TP53. RNA. 20:765–772. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang N, Wei X and Xu L: miR-150 promotes
the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting P53. FEBS Lett.
587:2346–2351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Talekar M, Trivedi M, Shah P, Ouyang Q,
Oka A, Gandham S and Amiji MM: Combination wt-p53 and MicroRNA-125b
transfection in a genetically engineered lung cancer model using
dual CD44/EGFR-targeting nanoparticles. Mol Ther. 24:759–769. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sobin LH: TNM: Principles, history, and
relation to other prognostic factors. Cancer. 91 8
Suppl:S1589–S1592. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Steele VE, Croce CM
and De Flora S: Relationships of microRNA expression in mouse lung
with age and exposure to cigarette smoke and light. FASEB J.
23:3243–3250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Quarto M, Pugliese M, La Verde G, Loffredo
F and Roca V: Radon exposure assessment and relative effective dose
estimation to inhabitants of puglia region, South Italy. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 12:14948–14957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Naeini MM and Ardekani AM: Noncoding RNAs
and cancer. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 1:55–70. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morey C and Avner P: Employment
opportunities for non-coding RNAs. FEBS Lett. 567:27–34. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rasool M, Malik A, Zahid S, Ashraf MAB,
Qazi MH, Asif M, Zaheer A, Arshad M, Raza A and Jamal MS:
Non-coding RNAs in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Non-coding RNA
Res. 1:69–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Inamura K: Major tumor suppressor and
oncogenic non-coding RNAs: Clinical relevance in lung cancer.
Cells. 6:pii: E12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Christopher AF, Kaur RP, Kaur G, Kaur A,
Gupta V and Bansa P: MicroRNA therapeutics: Discovering novel
targets and developing specific therapy. Perspect Clin Res.
7:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inamura K: Diagnostic and therapeutic
potential of MicroRNAs in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9:pii: E49.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Inamura K and Ishikawa Y: MicroRNA in lung
cancer: Novel biomarkers and potential tools for treatment. J Clin
Med. 5:pii: E36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ottman R, Levy J, Grizzle WE and
Chakrabarti R: The other face of miR-17-92a cluster, exhibiting
tumor suppressor effects in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
7:73739–73753. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Wang F, Hu S, Yang L, Shi Y
and Fan D: MiR-19b/20a/92a regulates the self-renewal and
proliferation of gastric cancer stem cells. J Cell Sci.
126:4220–4229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Yang S, Yan W, Yang J, Qin YJ, Lin
XL, Xie RY, Wang SC, Jin W, Gao F, et al: MicroRNA-19 triggers
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells accompanied
by growth inhibition. Lab Invest. 95:1056–1070. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Molinari C, Salvi S, Foca F, Teodorani N,
Saragoni L, Puccetti M, Passardi A, Tamberi S, Avanzolini A, Lucci
E and Calistri D: miR-17-92a-1 cluster host gene (MIR17HG)
evaluation and response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2735–2742. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou X, Wen W, Shan X, Zhu W, Xu J, Guo R,
Cheng W, Wang F, Qi LW, Chen Y, et al: A six-microRNA panel in
plasma was identified as a potential biomarker for lung
adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget. 8:6513–6525. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu W, Jin P, Ding C and Liu W: miR-19a/b
modulates lung cancer cells metastasis through suppression of MXD1
expression. Oncol Lett. 12:1901–1905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stayner L, Bena J, Sasco AJ, Smith R,
Steenland K, Kreuzer M and Straif K: Lung cancer risk and workplace
exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. Am J Public Health.
97:545–551. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Field RW and Withers BL: Occupational and
environmental causes of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med. 33:681–703.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Inamura K, Ninomiya H, Nomura K, Tsuchiya
E, Satoh Y, Okumura S, Nakagawa K, Takata A, Kohyama N and Ishikawa
Y: Combined effects of asbestos and cigarette smoke on the
development of lung adenocarcinoma: Different carcinogens may cause
different genomic changes. Oncol Rep. 32:475–482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bersimbaev RI and Bulgakova O: The health
effects of radon and uranium on the population of Kazakhstan. Genes
Environ. 37:182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
National Research Council: (US) Committee
on health risks of exposure to radon (BEIR VI)Health effects of
exposure to radon: BEIR VI. Washington (DC): National academies
press (US); 1999, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK233262/
|
|
50
|
Shi B, Gao H, Zhang T and Cui Q: Analysis
of plasma microRNA expression profiles revealed different cancer
susceptibility in healthy young adult smokers and middle-aged
smokers. Oncotarget. 7:21676–21685. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gross TJ, Powers LS, Boudreau RL, Brink B,
Reisetter A, Goel K, Gerke AK, Hassan IH and Monick MM: A microRNA
processing defect in smokers' macrophages is linked to SUMOylation
of the endonuclease DICER. J Biol Chem. 289:12823–12834. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Izzotti A, Balansky R, Ganchev G, Iltcheva
M, Longobardi M, Pulliero A, Geretto M, Micale RT, La Maestra S,
Miller MS, et al: Blood and lung microRNAs as biomarkers of
pulmonary tumorigenesis in cigarette smoke-exposed mice.
Oncotarget. 7:84758–84774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Izzotti A and Pulliero A: The effects of
environmental chemical carcinogens on the microRNA machinery. Int J
Hyg Environ Health. 217:601–627. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Balansky R, Izzotti A, D'Agostini F,
Longobardi M, Micale R, La Maestra S, Camoirano A, Ganchev G,
Iltcheva M, Steele VE and De Flora S: Assay of lapatinib in murine
models of cigarette smoke carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
35:2300–2307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jarry J, Schadendorf D, Greenwood C, Spatz
A and van Kempen LC: The validity of circulating microRNAs in
oncology: Five years of challenges and contradictions. Mol Oncol.
8:819–829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G,
Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J,
Shingara J, et al: The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation
pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 67:7713–7722. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mendell J: miRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–222. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM and
Hogan BL: Transgenic over-expression of the microRNA miR-17-92
cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung
epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 310:442–453. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee HJ, Guo HY, Lee SK, Jeon BH, Jun CD,
Lee SK, Park MH and Kim EC: Effects of nicotine on proliferation,
cell cycle, and differentiation in immortalized and malignant oral
keratinocytes. J Oral Pathol Med. 34:436–443. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ng TK, Huang L, Cao D, Yip YW, Tsang WM,
Yam GH, Pang CP and Cheung HS: Cigarette smoking hinders human
periodontal ligament-derived stem cell proliferation, migration,
and differentiation potentials. Sci Rep. 5:78282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fischer M: Census and evaluation of p53
target genes. Oncogene. 36:3943–3956. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Pflaum J, Schlosser S and Müller M: p53
family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, Nakata S, Ono
K, Nozoe T and Yasumoto K: Expression of the p53 family in lung
cancer. Anticancer Res. 26:1785–1790. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hasbek Z, Doğan ÖT, Sarı İ, Yücel B, Şeker
MM, Turgut B, Berk S and Siliğ Y: The diagnostic value of the
correlation between serum Anti-p53 antibody and positron emission
tomography parameters in lung cancer. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther.
25:107–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ruano-Ravina A, Pérez-Becerra R, Fraga M,
Kelsey KT and Barros-Dios JM: Analysis of the relationship between
p53 immunohistochemical expression and risk factors for lung
cancer, with special emphasis on residential radon exposure. Ann
Oncol. 19:109–114. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Schneider J, Presek P, Braun A and
Woitowitz H: Serum levels of pantropic p53 protein and
EGF-receptor, and detection of anti-p53 antibodies in former
uranium miners (SDAG Wismut). Am J Ind Med. 36:602–609. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|