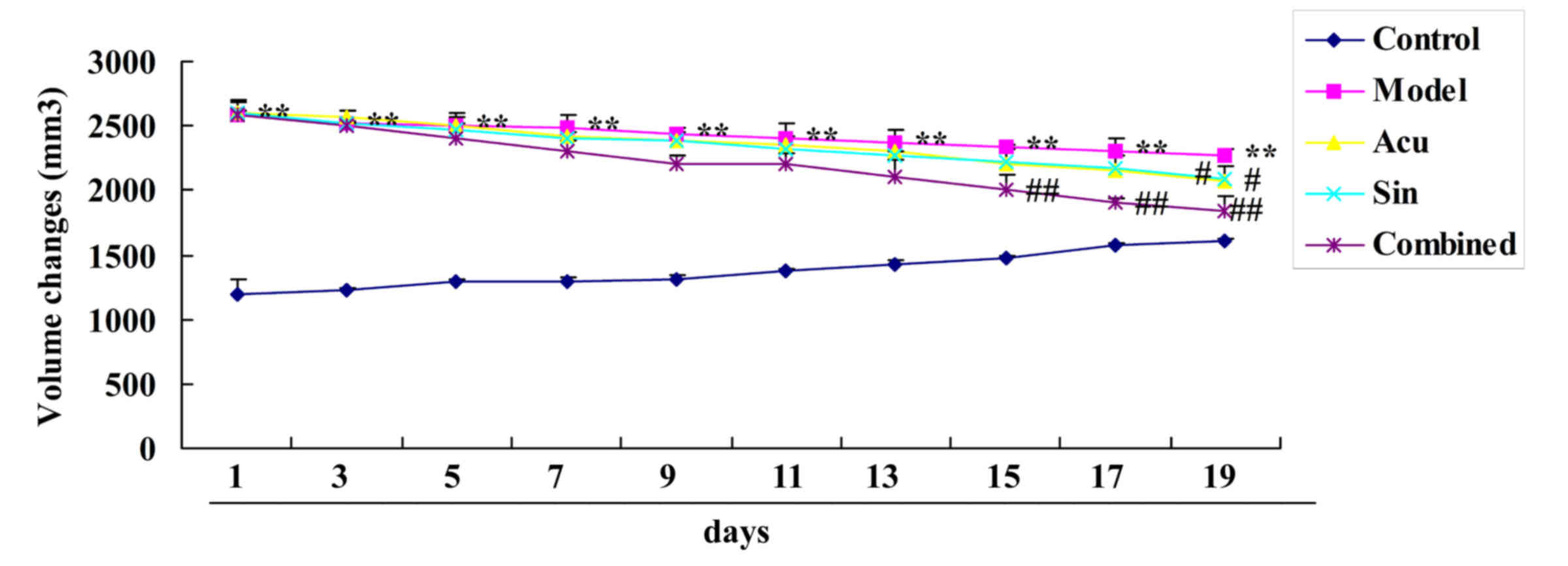
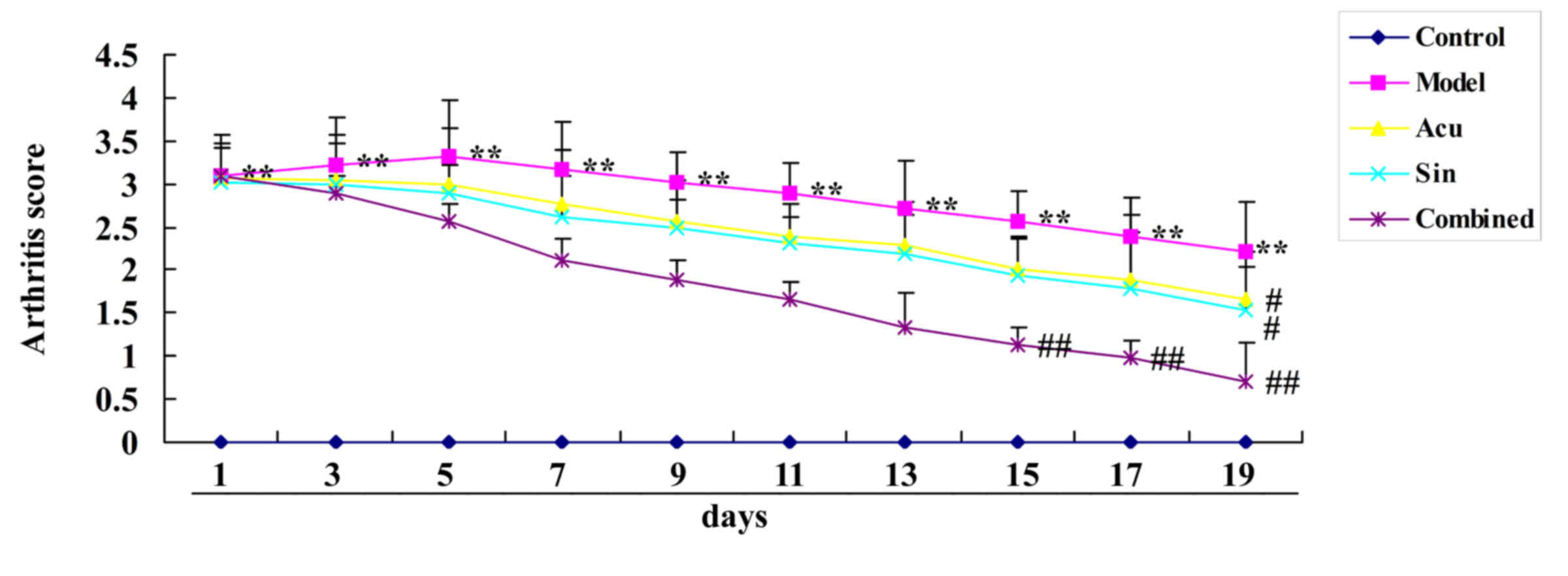
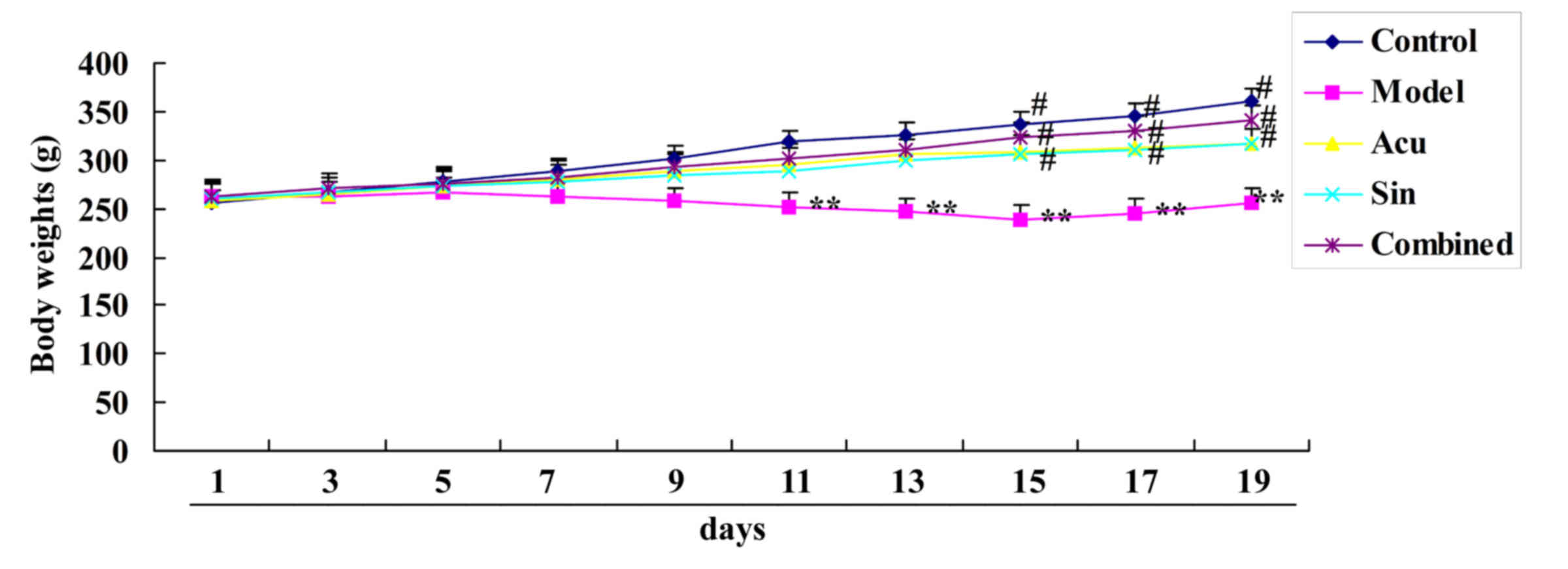
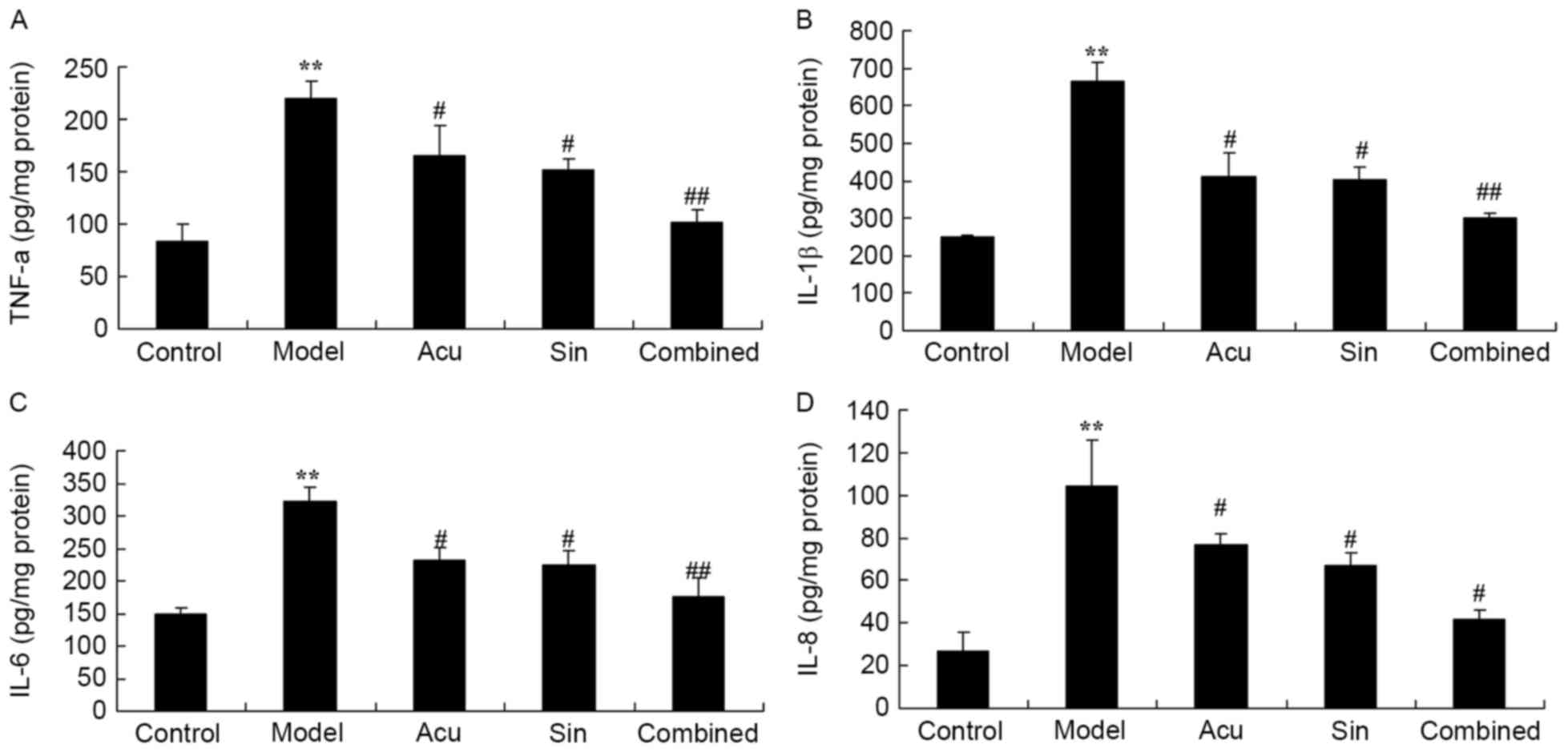
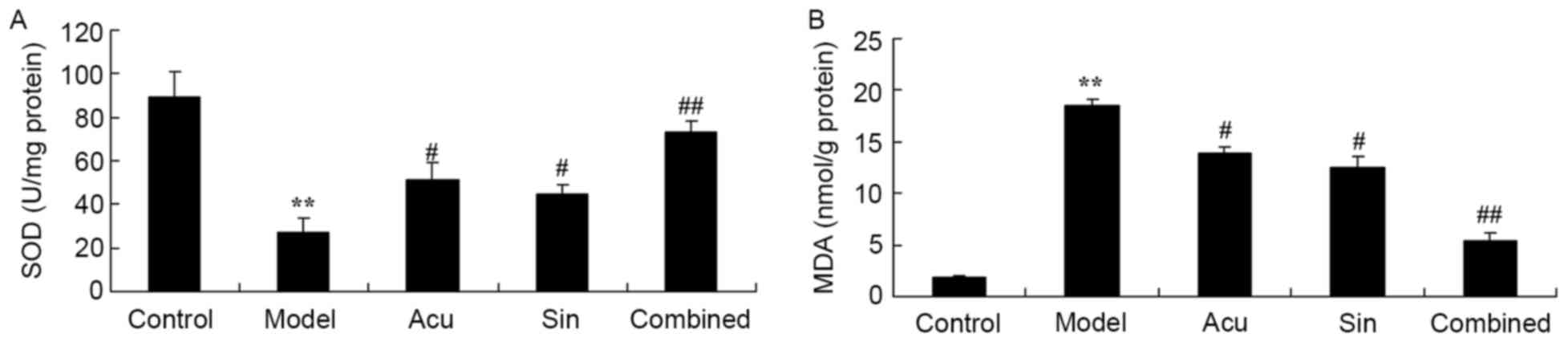
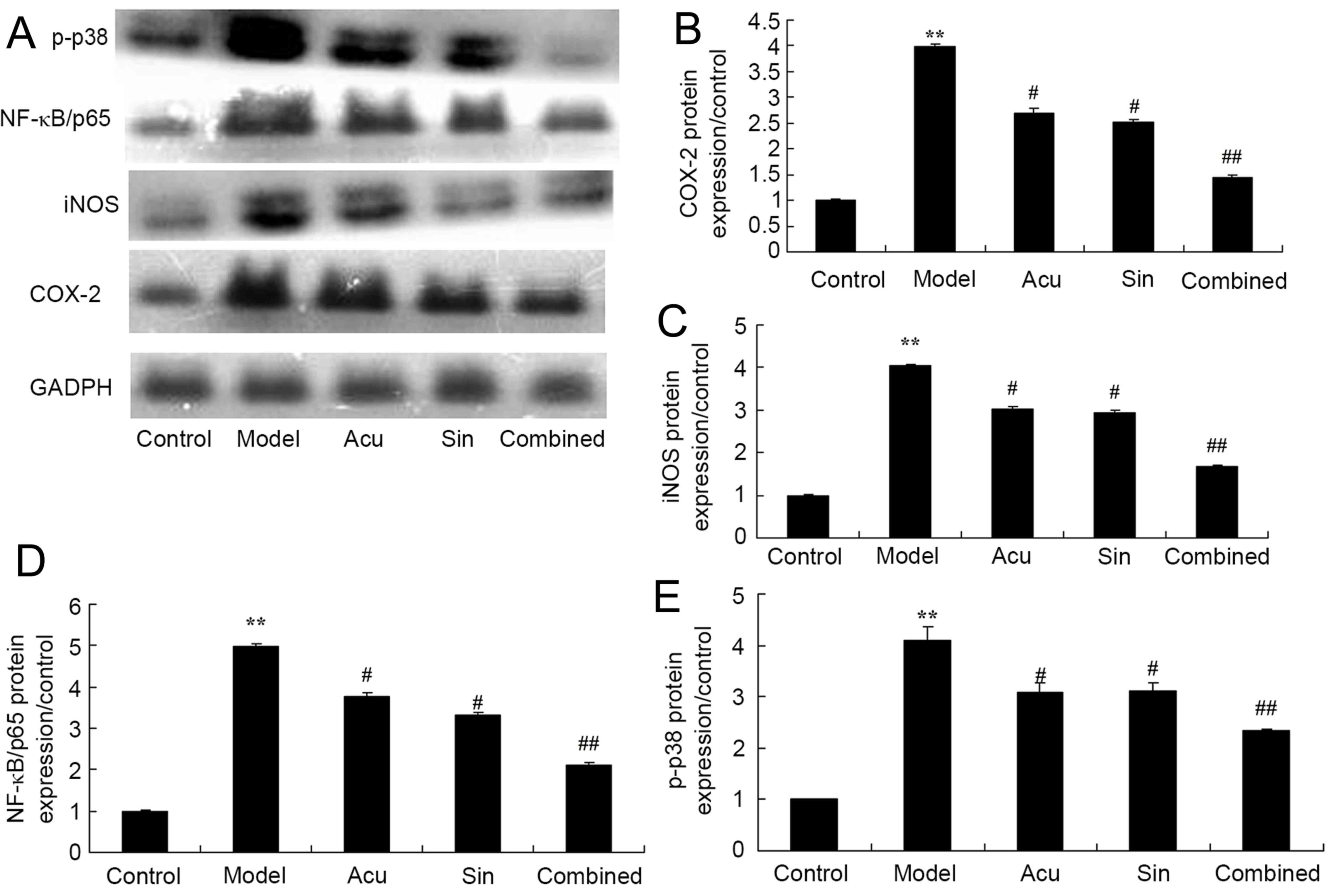
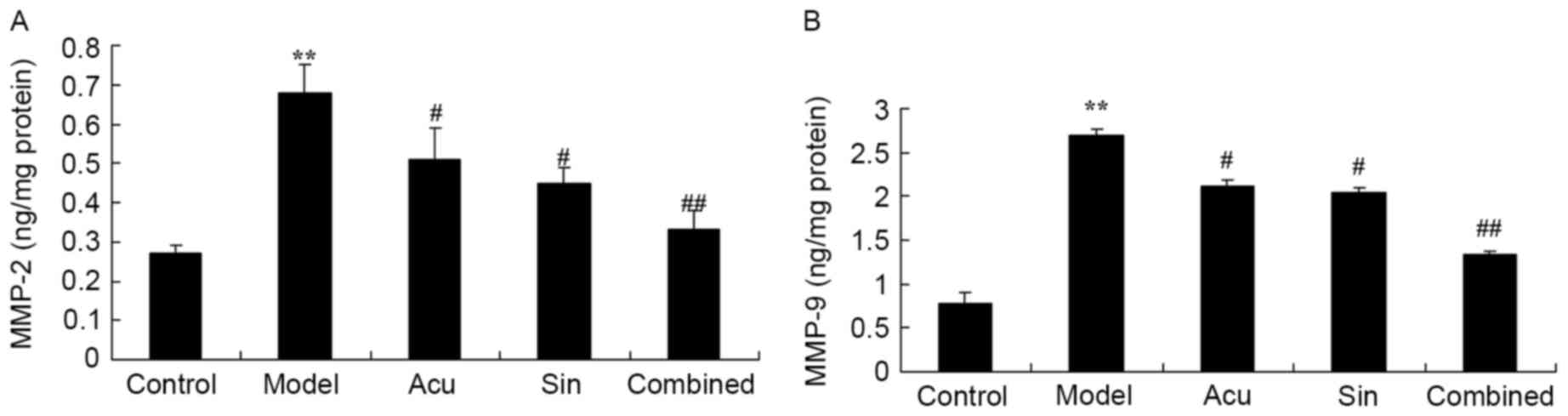
|
1
|
Kuncewitch M, Yang WL, Jacob A, Khader A,
Giangola M, Nicastro J, Coppa GF and Wang P: Stimulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway with Wnt agonist reduces organ
injury after hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
78:793–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li B, Zhang H, Zeng M, He W, Li M, Huang
X, Deng DY and Wu J: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect
alveolar macrophages from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis
partially by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Biol Int.
39:192–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gottlieb J, Zamora MR, Hodges T, Musk AW,
Sommerwerk U, Dilling D, Arcasoy S, DeVincenzo J, Karsten V, Shah
S, et al: ALN-RSV01 for prevention of bronchiolitis obliterans
syndrome after respiratory syncytial virus infection in lung
transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 35:213–221. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gerhardt SG, McDyer JF, Girgis RE, Conte
JV, Yang SC and Orens JB: Maintenance azithromycin therapy for
bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: Results of a pilot study. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 168:121–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teixeira MFC, Rodrigues JC, Leone C and
Adde FV: Acute bronchodilator responsiveness to tiotropium in
postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children. Chest.
144:974–980. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Celik S, Doesch AO, Konstandin MH, Kristen
AV, Ammon K, Sack FU, Schnabel P, Katus HA and Dengler TJ:
Increased incidence of acute graft rejection on calcineurin
inhibitor-free immunosuppression after heart transplantation.
Transplant Proc. 43:1862–1867. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao XP, Han DM, Zhao L, Guo ZK, Xiao FJ,
Zhang YK, Zhang XY, Wang LS, Wang HX and Wang H: Hepatocyte growth
factor enhances the inflammation-alleviating effect of umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a bronchiolitis
obliterans model. Cytotherapy. 18:402–412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu XY, Zhou XY, Hou JC, Zhu H, Wang Z,
Liu JX and Zheng YQ: Ginsenoside Rd promotes neurogenesis in rat
brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia via activation of
PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:421–428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu TT, Lu J, Zheng PQ, Liu SL, Wu J, Sun
W, Sun QM, Ma NX, Ding XL, Chen M and Zou X: Yiqi Huayu Jiedu
decoction inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer
cells through TGF-β/Smad pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2017:18712982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang M, Li J, Zhu D, Luo C, Li C, Zhu C,
Fan M, Yung KK and Mo Z: Effect of sinomenine on the
morphine-dependence and related neural mechanisms in mice.
Neurochem Res. 42:3587–3596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mi J, Chen X, Lin X, Guo J, Chen H, Wei L
and Hong H: Treatment of persistent allergic rhinitis via
acupuncture at the sphenopalatine acupoint: A randomized controlled
trial. Trials. 19:282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu MS, Chen KH, Chen IF, et al: The
Efficacy of Acupuncture in Post-Operative Pain Management: A
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01503672016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cui X, Zhou J, Qin Z and Liu Z:
Acupuncture for Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review. Biomed
Res Int. 2016:21719232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan Q, Chen M, Fang X, Lau WB, Xue L, Zhao
L, Zhang H, Liang YH, Bai X, Niu HY, et al: Aging might augment
reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and affect reactive
nitrogen species (RNS) level after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
in both humans and rats. Age (Dordr). 35:1017–1026. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bergeron A, Chevret S, Chagnon K, Godet C,
Bergot E, de Latour Peffault R, Dominique S, de Revel T, Juvin K,
Maillard N, et al: Budesonide/Formoterol for bronchiolitis
obliterans after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 191:1242–1249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kapila A, Baz MA, Valentine VG and Bhorade
SM: AIRSAC investigators: Reliability of diagnostic criteria for
bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation: A
survey. J Heart Lung Transplant. 34:65–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang C, Xia T, Jiang K, Qiao X, Zhang X,
Li J, Wang J and Nie J: Apoptosis of the tracheal epithelium can
increase the number of recipient bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts
in allografts and exacerbate obliterative bronchiolitis after
tracheal transplantation in mice. Transplantation. 100:1880–1888.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Walker NM, Belloli EA, Stuckey L, Chan KM,
Lin J, Lynch W, Chang A, Mazzoni SM, Fingar DC and Lama VN:
Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2 as
key signaling intermediates in mesenchymal cell activation. J Biol
Chem. 291:6262–6271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramirez AM, Shen Z, Ritzenthaler JD and
Roman J: Myofibroblast transdifferentiation in obliterative
bronchiolitis: Tgf-beta signaling through smad3-dependent and
-independent pathways. Am J Transplant. 6:2080–2088. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Königshoff M, Kneidinger N and Eickelberg
O: Tgf-beta signaling in COPD: Deciphering genetic and cellular
susceptibilities for future therapeutic regimen. Swiss Med Wkly.
139:554–563. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zarin AA, Behmanesh M, Tavallaei M,
Shohrati M and Ghanei M: Overexpression of transforming growth
factor (TGF)-beta1 and TGF-beta3 genes in lung of toxic-inhaled
patients. Exp Lung Res. 36:284–291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ladak SS, Ward C and Ali S: The potential
role of microRNAs in lung allograft rejection. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 35:550–559. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Z, Nayak D, Yang W, Baskaran G,
Ramachandran S, Sarma N, Aloush A, Trulock E, Hachem R, Patterson
GA and Mohanakumar T: Dysregulated microRNA expression and chronic
lung allograft rejection in recipients with antibodies to donor
HLA. Am J Transplant. 15:1933–1947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Li J, Yu K, Liu Y and Chen X:
Sinomenine inhibits maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells
through blocking activation of NF-kappa B. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:637–645. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Huang K, Zhong G, et al:
Acupuncture Decreases NF-kappaB p65, miR-155, and miR-21 and
Increases miR-146a Expression in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Rats.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:94046292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Z, Yang W, Steward N, Sweet SC,
Danziger-Isakov L, Heeger PS and Mohanakumar T: Role of circulating
microRNAs in the immunopathogenesis of rejection following after
pediatric lung transplantation. Transplantation. 101:2461–2468.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong M, Wang X, Zhao HL, Chen XL, Yuan JH,
Guo JY, Li KQ and Li G: Integrated analysis of transcription
factor, microRNA and lncRNA in an animal model of obliterative
bronchiolitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7050–7058. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mauad T, van Schadewijk A, Schrumpf J,
Hack CE, Fernezlian S, Garippo AL, Ejzenberg B, Hiemstra PS, Rabe
KF and Dolhnikoff M: São Paulo BO Study Group: Lymphocytic
inflammation in childhood bronchiolitis obliterans. Pediatr
Pulmonol. 38:233–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moeser A, Pletz MW, Hagel S, Kroegel C and
Stallmach A: Lung disease and ulcerative colitis-mesalazine-induced
bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia or pulmonary
manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease? Z Gastroenterol.
53:1091–1098. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fu SP, He SY, Xu B, Hu CJ, Lu SF, Shen WX,
Huang Y, Hong H, Li Q, Wang N, et al: Acupuncture promotes
angiogenesis after myocardial ischemia through H3K9 acetylation
regulation at VEGF gene. PLoS One. 9:e946042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|