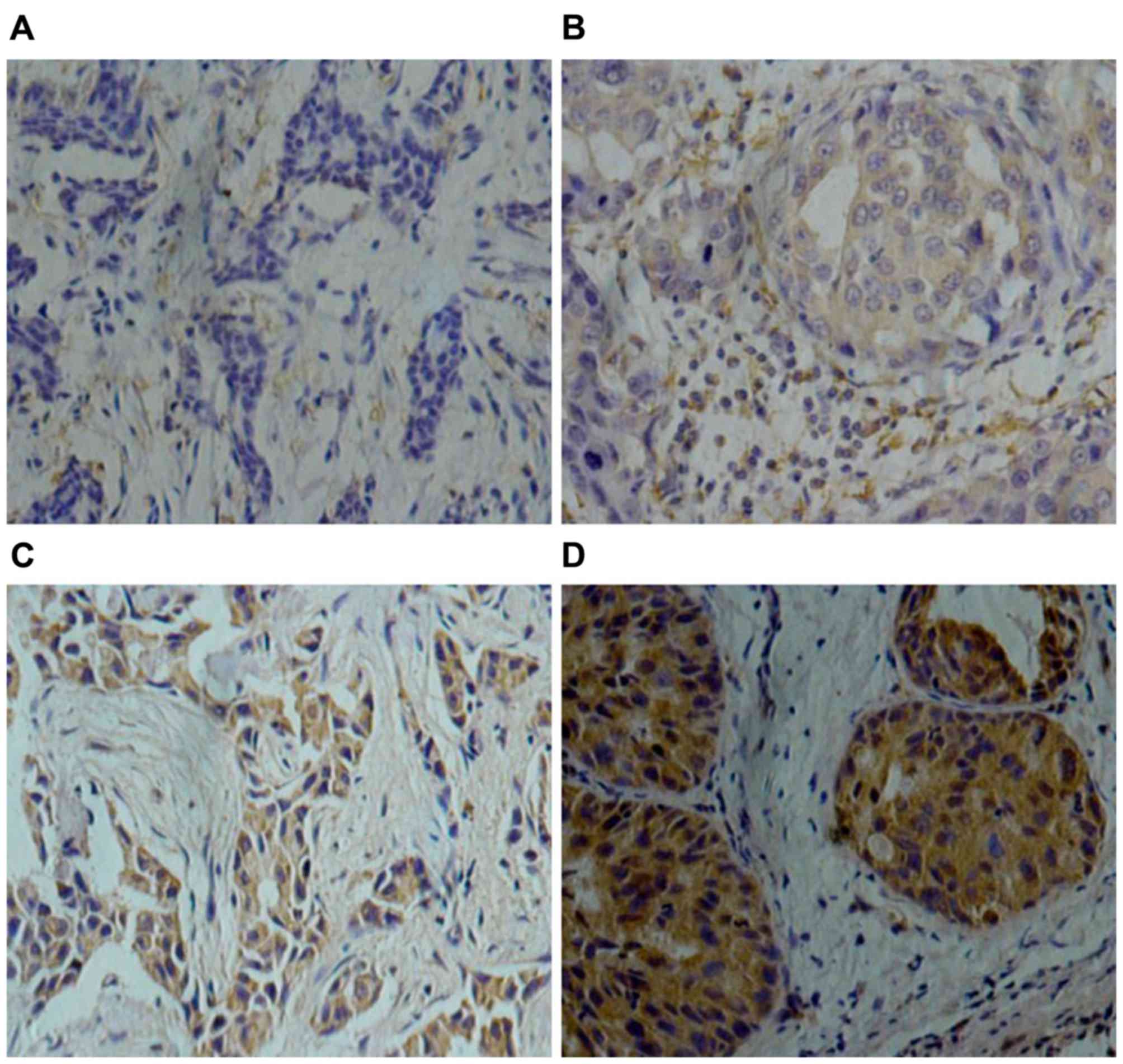
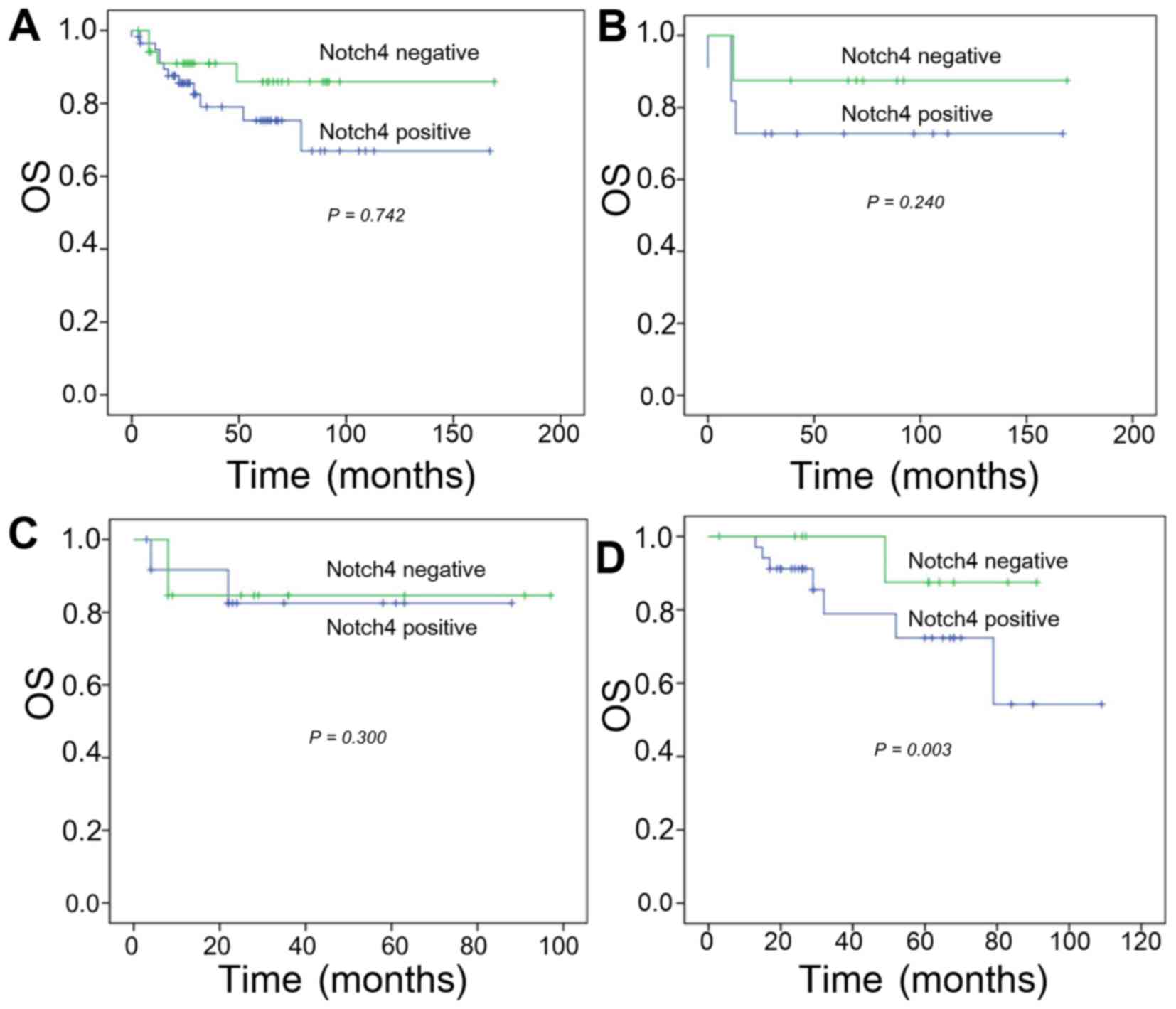
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brenton JD, Carey LA, Ahmed AA and Caldas
C: Molecular classification and molecular forecasting of breast
cancer: Ready for clinical application? J Clin Oncol. 23:7350–7360.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sotiriou C and Pusztai L: Gene-expression
signatures in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 360:790–800. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Ruijter TC, Veeck J, de Hoon JP, van
Engeland M and Tjan-Heijnen VC: Characteristics of triple-negative
breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:183–192. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hernandez-Aya LF, Chavez-MacGregor M, Lei
X, Meric-Bernstam F, Buchholz TA, Hsu L, Sahin AA, Do KA, Valero V,
Hortobagyi GN, et al: Nodal status and clinical outcomes in a large
cohort of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 29:2628–2634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Comen EA, Norton L and Massagué J: Breast
cancer tumor size, nodal status, and prognosis: Biology trumps
anatomy. J Clin Oncol. 29:2610–2612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cianfrocca M and Goldstein LJ: Prognostic
and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist.
9:606–616. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gallahan D and Callahan R: Mammary
tumorigenesis in feral mice: Identification of a new int locus in
mouse mammary tumor virus (Czech II)-induced mammary tumors. J
Virol. 61:66–74. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith GH, Gallahan D, Diella F, Jhappan C,
Merlino G and Callahan R: Constitutive expression of a truncated
INT3 gene in mouse mammary epithelium impairs differentiation and
functional development. Cell Growth Differ. 6:563–577.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uyttendaele H, Soriano JV, Montesano R and
Kitajewski J: Notch4 and Wnt-1 proteins function to regulate
branching morphogenesis of mammary epithelial cells in an opposing
fashion. Dev Biol. 196:204–217. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weijzen S, Rizzo P, Braid M, Vaishnav R,
Jonkheer SM, Zlobin A, Osborne BA, Gottipati S, Aster JC, Hahn WC,
et al: Activation of Notch-1 signaling maintains the neoplastic
phenotype in human Ras-transformed cells. Nat Med. 8:979–986. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett
LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark GM, Edge SB, Hayes DF, et
al: Staging system for breast cancer: Revisions for the 6th edition
of the AJCC cancer staging manual. Surg Clin North Am. 83:803–819.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei XL, Dou XW, Bai JW, Luo XR, Qiu SQ, Xi
DD, Huang WH, Du CW, Man K and Zhang GJ: ERα inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing Bmi1 in breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:21704–21717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK and Allred
DC: Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to
the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant
endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 17:1474–1481.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty
KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer
A, et al: American society of clinical Oncology/College of American
pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
131:18–43. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hao L, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Wang L, Luo Y, Jin
M and Zhang Y, Guo TB, Matsushima K and Zhang Y: Recombination of
CXCR4, VEGF, and MMP-9 predicting lymph node metastasis in human
breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 253:34–42. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shawber CJ, Funahashi Y, Francisco E,
Vorontchikhina M, Kitamura Y, Stowell SA, Borisenko V, Feirt N,
Podgrabinska S, Shiraishi K, et al: Notch alters VEGF
responsiveness in human and murine endothelial cells by direct
regulation of VEGFR-3 expression. J Clin Invest. 117:3369–3382.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parr C, Watkins G and Jiang WG: The
possible correlation of Notch-1 and Notch-2 with clinical outcome
and tumour clinicopathological parameters in human breast cancer.
Int J Mol Med. 14:779–786. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zardawi SJ, Zardawi I, McNeil CM, Millar
EK, McLeod D, Morey AL, Crea P, Murphy NC, Pinese M, Lopez-Knowles
E, et al: High Notch1 protein expression is an early event in
breast cancer development and is associated with the HER-2
molecular subtype. Histopathology. 56:286–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rizzo P, Miao H, D'Souza G, Osipo C, Song
LL, Yun J, Zhao H, Mascarenhas J, Wyatt D, Antico G, et al:
Cross-talk between notch and the estrogen receptor in breast cancer
suggests novel therapeutic approaches. Cancer Res. 68:5226–5235.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao K, Rizzo P, Rajan P, Albain K, Rychlik
K, Shah S and Miele L: Notch-1 and notch-4 receptors as prognostic
markers in breast cancer. Int J Surg Pathol. 19:607–613. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Magnifico A, Albano L, Campaner S, Delia
D, Castiglioni F, Gasparini P, Sozzi G, Fontanella E, Menard S and
Tagliabue E: Tumor-initiating cells of HER2-positive carcinoma cell
lines express the highest oncoprotein levels and are sensitive to
trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2010–2021. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|