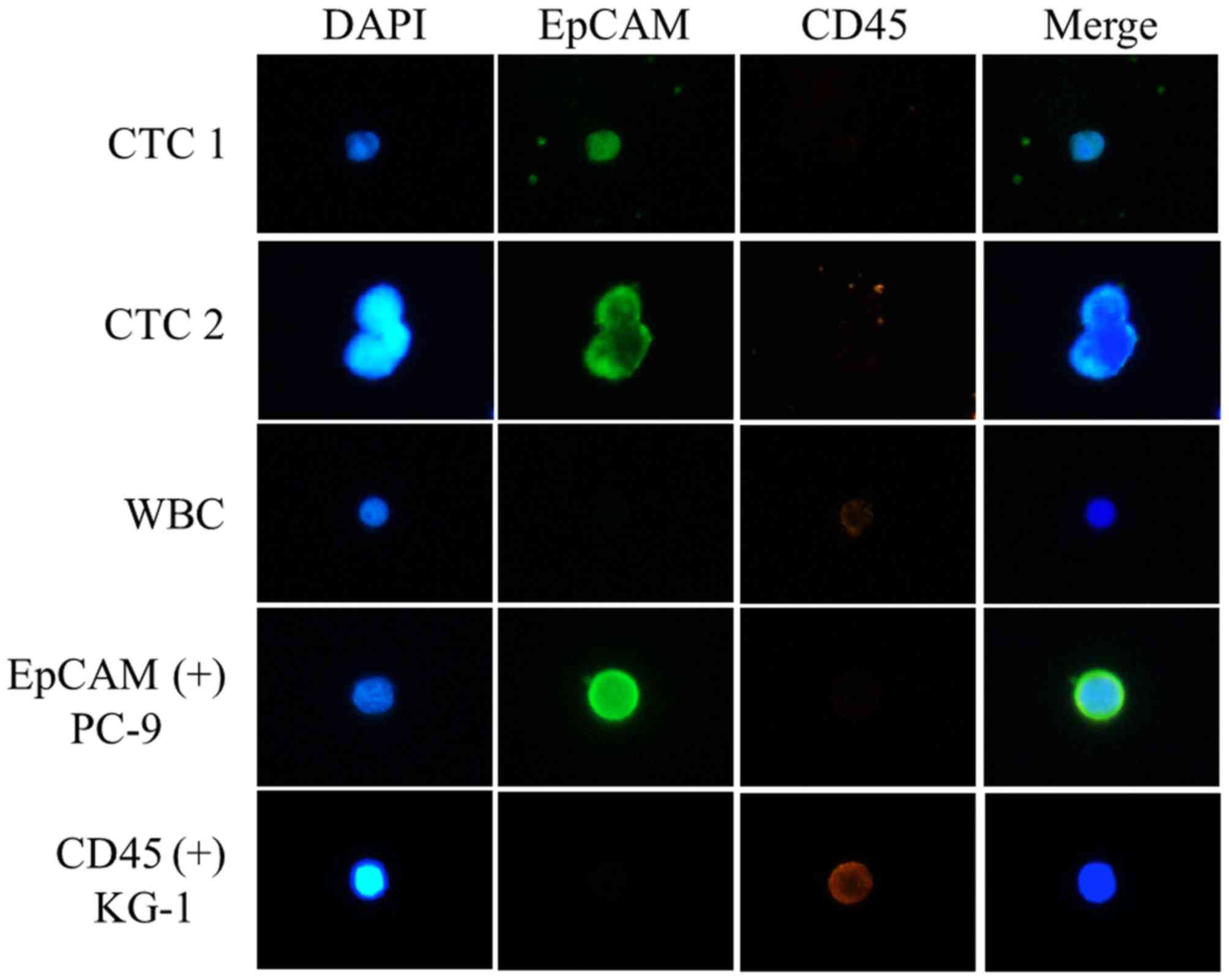
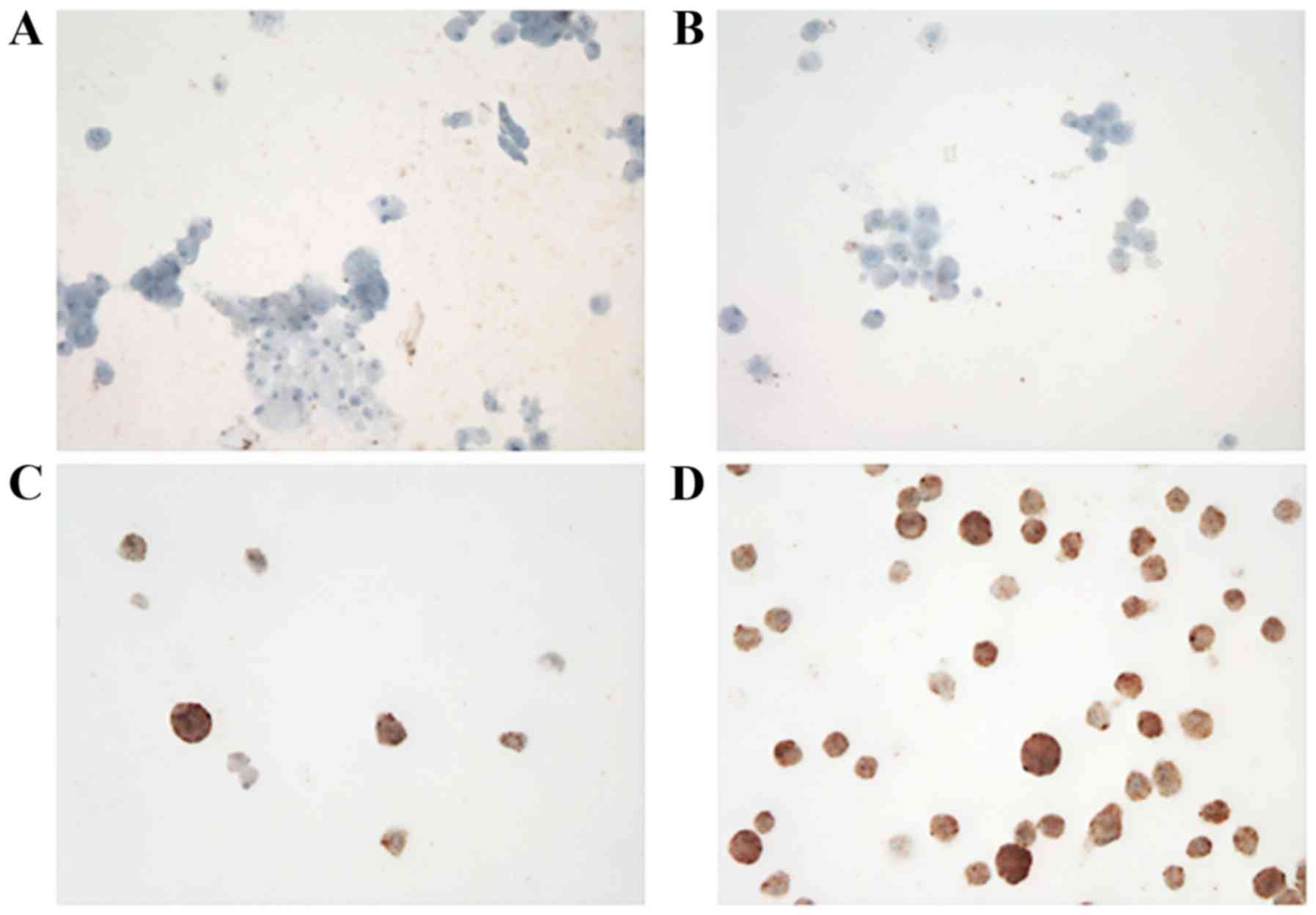
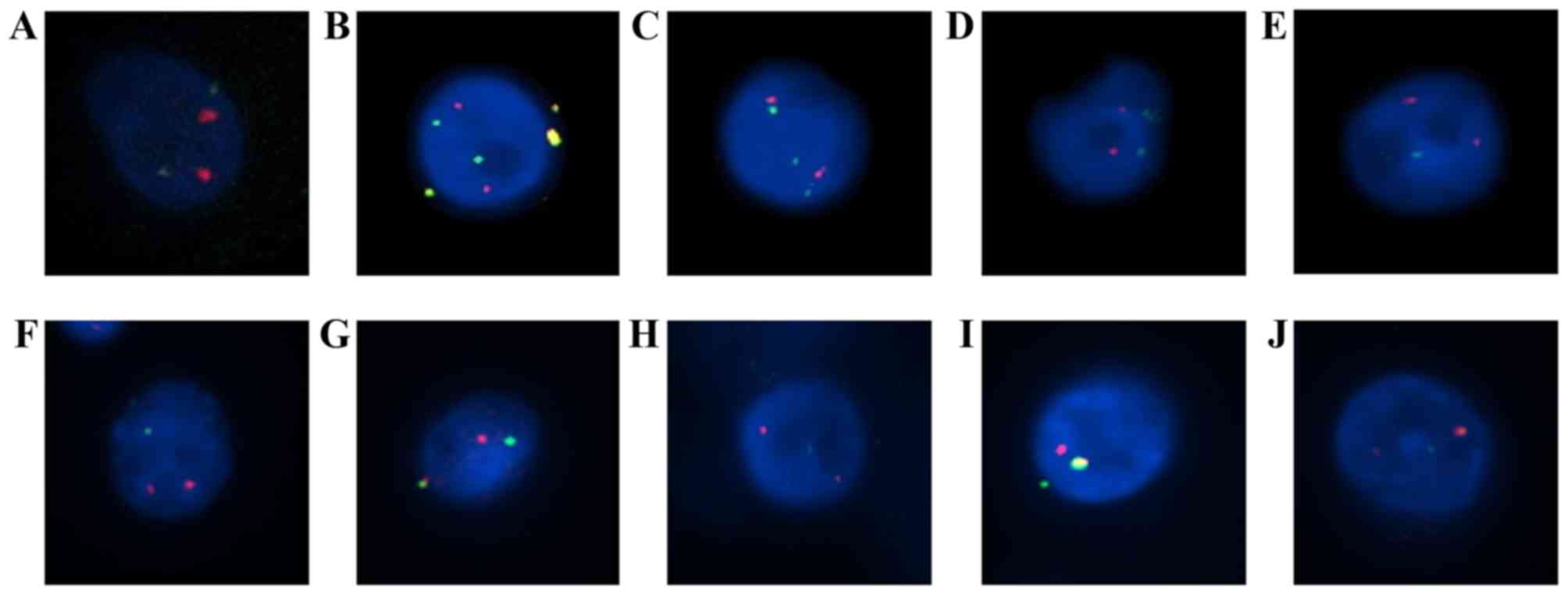
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T,
Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S,
Rischin D, et al: Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of
gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin
Oncol. 21:2237–2246. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S,
Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K,
Hatanaka H, et al: Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK
fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT,
Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Jänne PA, Costa DB, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crinó
L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, et al:
Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:2385–2394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shaw AT and Engelman JA: Ceritinib in
ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
370:2537–2539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Doebele RC, Lu X, Sumey C, Maxson DA,
Weickhardt AJ, Oton AB, Bunn PA Jr, Barón AE, Franklin WA, Aisner
DL, et al: Oncogene status predicts patterns of metastatic spread
in treatment-naive nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer.
118:4502–4511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arcila ME, Oxnard GR, Nafa K, Riely GJ,
Solomon SB, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Pao W, Miller VA and Ladanyi M:
Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR
inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a
locked nucleic acid-based assay. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1169–1180.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Faugeroux V, Pailler E, Auger N, Taylor M
and Farace F: Clinical utility of circulating tumor cells in
ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 4:2812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aceto N, Bardia A, Miyamoto DT, Donaldson
MC, Wittner BS, Spencer JA, Yu M, Pely A, Engstrom A, Zhu H, et al:
Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of
breast cancer metastasis. Cell. 158:1110–1122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cristofanilli M, Hayes DF, Budd GT, Ellis
MJ, Stopeck A, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Matera J, Allard WJ, Miller MC,
et al: Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly
diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:1420–1430.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ilie M, Long E, Butori C, Hofman V, Coelle
C, Mauro V, Zahaf K, Marquette CH, Mouroux J, Paterlini-Bréchot P
and Hofman P: ALK-gene rearrangement: A comparative analysis on
circulating tumour cells and tumour tissue from patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. Ann Oncol. 23:2907–2913. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pailler E, Adam J, Barthélémy A, Oulhen M,
Auger N, Valent A, Borget I, Planchard D, Taylor M, André F, et al:
Detection of circulating tumor cells harboring a unique ALK
rearrangement in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 31:2273–2281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan CL, Lim TH, Lim TKh, Tan DS, Chua YW,
Ang MK, Pang B, Lim CT, Takano A, Lim AS, et al: Concordance of
anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements between
circulating tumor cells and tumor in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:23251–23262. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marchetti A, Del Grammastro M, Felicioni
L, Malatesta S, Filice G, Centi I, De Pas T, Santoro A, Chella A,
Brandes AA, et al: Assessment of EGFR mutations in circulating
tumor cell preparations from NSCLC patients by next generation
sequencing: Toward a real-time liquid biopsy for treatment. PLoS
One. 9:e1038832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marrinucci D, Bethel K, Luttgen M, Bruce
RH, Nieva J and Kuhn P: Circulating tumor cells from
well-differentiated lung adenocarcinoma retain cytomorphologic
features of primary tumor type. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 133:1468–1471.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allard WJ, Matera J, Miller MC, Repollet
M, Connelly MC, Rao C, Tibbe AG, Uhr JW and Terstappen LW: Tumor
cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but
not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6897–6904. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hong B and Zu Y: Detecting circulating
tumor cells: Current challenges and new trends. Theranostics.
3:377–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Krebs MG, Metcalf RL, Carter L, Brady G,
Blackhall FH and Dive C: Molecular analysis of circulating tumour
cells-biology and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 11:129–144. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gabriel MT, Calleja LR, Chalopin A, Ory B
and Heymann D: Circulating tumor cells: A review of non-EpCAM-based
approaches for cell enrichment and isolation. Clin Chem.
62:571–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH and Brandt B:
Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of
disseminating tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:329–340. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Markou A, Strati A, Malamos N, Georgoulias
V and Lianidou ES: Molecular characterization of circulating tumor
cells in breast cancer by a liquid bead array hybridization assay.
Clin Chem. 57:421–430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang E, Lee DH, Uh Jh, Han D, Kim MS,
Choi SH, Park JK, Lee J, Jeon BH and Lee SH: Retaining ALK
rearrangement in cultured circulating tumor cells derived from lung
cancer patients. Cancer Res J. 3:11–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim EH, Lee JK, Kim BC, Rhim SH, Kim JW,
Kim KH, Jung SM, Park PS, Park HC, Lee J and Jeon BH: Enrichment of
cancer cells from whole blood using a microfabricated porous
filter. Anal Biochem. 440:114–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haber DA and Velculescu VE: Blood-based
analyses of cancer: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor
DNA. Cancer Discov. 4:650–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bidard FC, Fehm T, Ignatiadis M, Smerage
JB, Alix-Panabières C, Janni W, Messina C, Paoletti C, Müller V,
Hayes DF, et al: Clinical application of circulating tumor cells in
breast cancer: Overview of the current interventional trials.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:179–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bonnomet A, Brysse A, Tachsidis A, Waltham
M, Thompson EW, Polette M and Gilles C: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transitions and circulating tumor cells. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:261–273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hughes AD, Marshall JR, Keller E, Powderly
JD, Greene BT and King MR: Differential drug responses of
circulating tumor cells within patient blood. Cancer Lett.
352:28–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mego M, Mani SA and Cristofanilli M:
Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer-clinical
applications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:693–701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Polioudaki H, Agelaki S, Chiotaki R,
Politaki E, Mavroudis D, Matikas A, Georgoulias V and
Theodoropoulos PA: Variable expression levels of keratin and
vimentin reveal differential EMT status of circulating tumor cells
and correlation with clinical characteristics and outcome of
patients with metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:3992015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu M, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Stott SL, Smas
ME, Ting DT, Isakoff SJ, Ciciliano JC, Wells MN, Shah AM, et al:
Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in
epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science. 339:580–584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu YC, Chang IC, Wang CL, Chen TD, Chen
YT, Liu HP, Chu Y, Chiu YT, Wu TH, Chou LH, et al: Comparison of
IHC, FISH and RT-PCR methods for detection of ALK rearrangements in
312 non-small cell lung cancer patients in Taiwan. PLoS One.
8:e708392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|