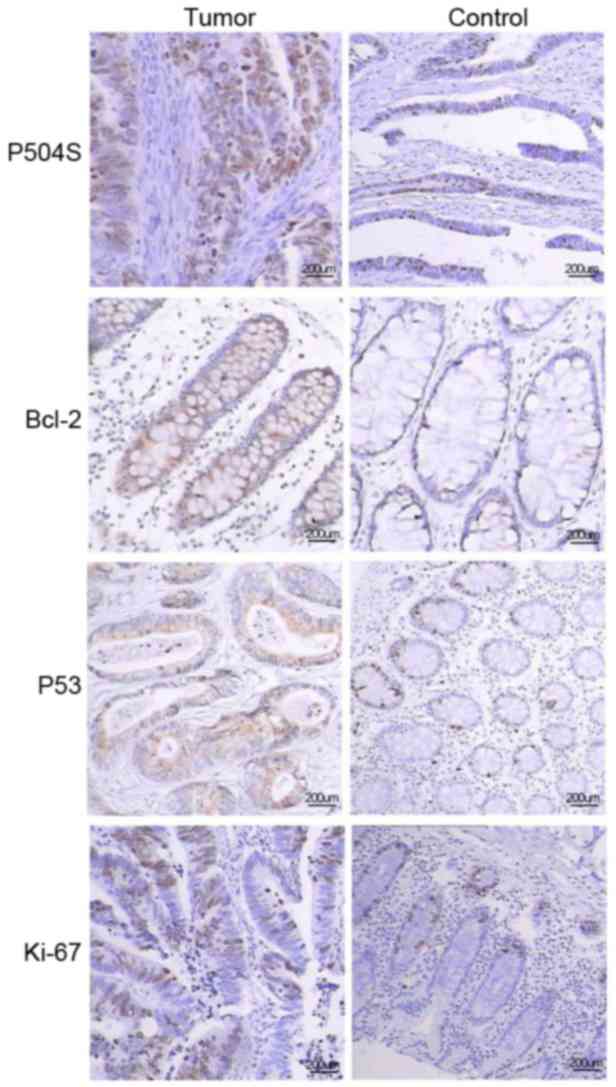
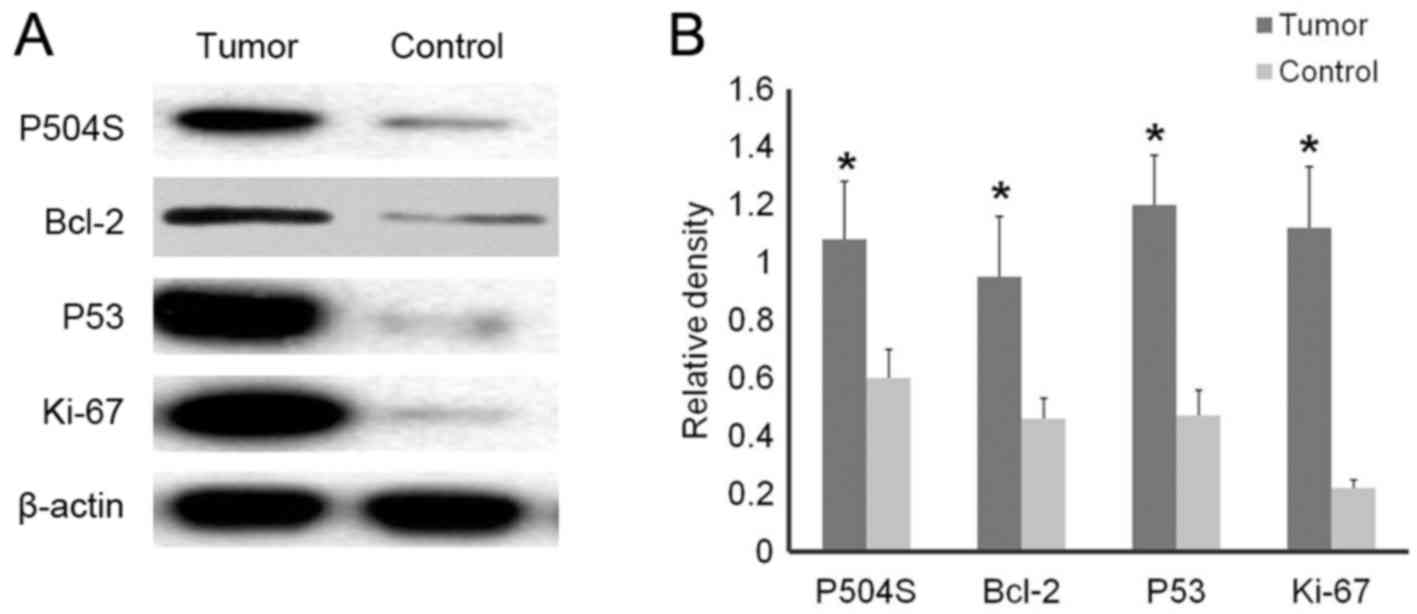
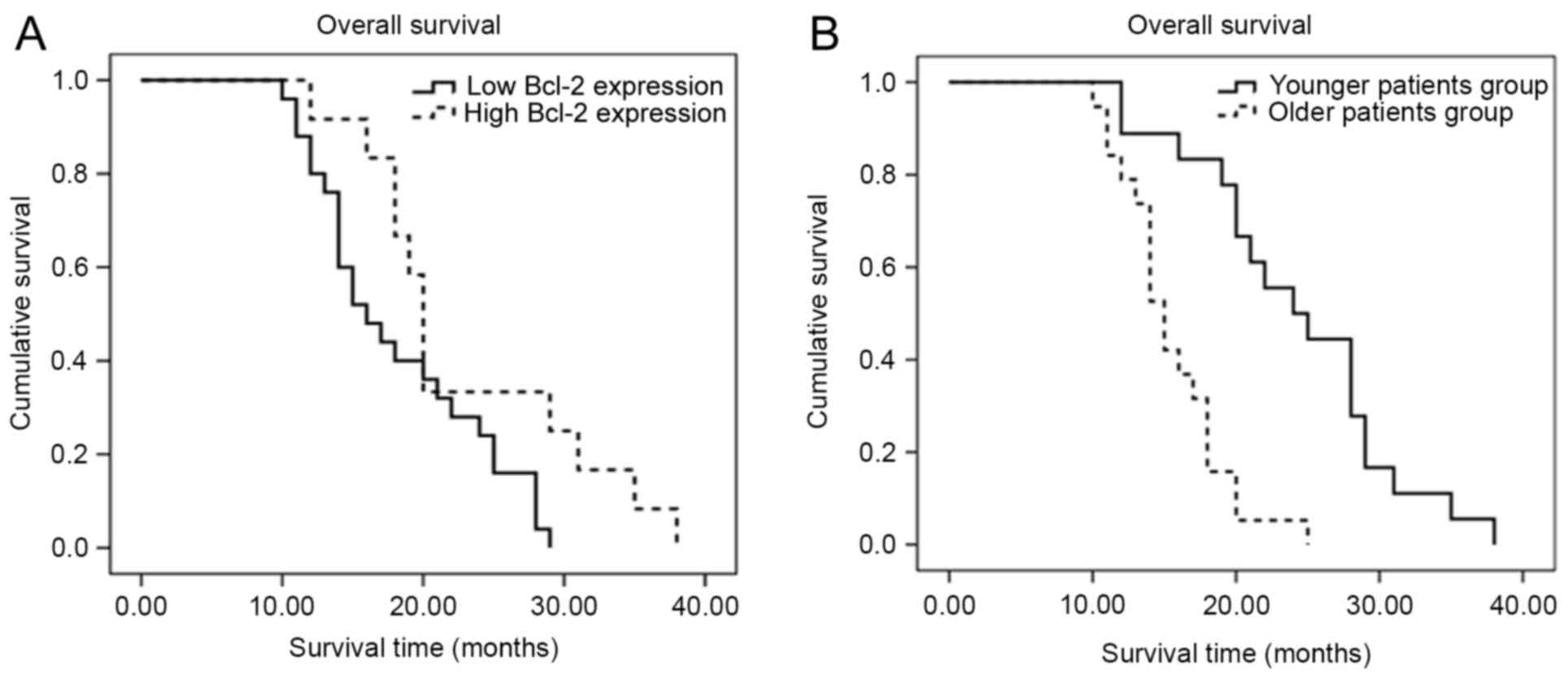
|
1
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL and Leung WK: Asia
Pacific Working Group on Colorectal Cancer: Increasing incidence of
colorectal cancer in Asia: implications for screening. Lancet
Oncol. 6:871–876. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coghlin C and Murray GI: Biomarkers of
colorectal cancer: Recent advances and future challenges.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 9:64–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coghlin C and Murray GI: Progress in the
identification of plasma biomarkers of colorectal cancer.
Proteomics. 13:2227–2228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Daugherty SE, Platz EA, Shugart YY, Fallin
MD, Isaacs WB, Chatterjee N, Welch R, Huang WY and Hayes RB:
Variants in the alpha-Methylacyl-CoA racemase gene and the
association with advanced distal colorectal adenoma. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:1536–1542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuefer R, Varambally S, Zhou M, Lucas PC,
Loeffler M, Wolter H, Mattfeldt T, Hautmann RE, Gschwend JE,
Barrette TR, et al: alpha-Methylacyl-CoA racemase: Expression
levels of this novel cancer biomarker depend on tumor
differentiation. Am J Pathol. 161:841–848. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens
LC, Lee JJ and Levin B: bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during
colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 55:237–241. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oshima CT, Iriya K and Forones NM: Ki-67
as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer but not in gastric
cancer. Neoplasma. 52:420–424. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dawson DA, Grant BF, Stinson FS and Zhou
Y: Effectiveness of the derived alcohol use disorders
identification test (AUDIT-C) in screening for alcohol use
disorders and risk drinking in the US general population. Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 29:844–854. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haining Z, Kawai N, Miyake K, Okada M,
Okubo S, Zhang X, Fei Z and Tamiya T: Relation of LAT1/4F2hc
expression with pathological grade, proliferation and angiogenesis
in human gliomas. BMC Clin Pathol. 12:42012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goel MK, Khanna P and Kishore J:
Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int J
Ayurveda Res. 1:274–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Strasser A, O'Connor L and Dixit VM:
Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:217–245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thomas S, Quinn BA, Das SK, Dash R, Emdad
L, Dasgupta S, Wang XY, Dent P, Reed JC, Pellecchia M, et al:
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:61–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hague A, Moorghen M, Hicks D, Chapman M
and Paraskeva C: BCL-2 expression in human colorectal adenomas and
carcinomas. Oncogene. 9:3367–3370. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Biden KG, Simms LA, Cummings M, Buttenshaw
R, Schoch E, Searle J, Gobe G, Jass JR, Meltzer SJ, Leggett BA and
Young J: Expression of Bcl-2 protein is decreased in colorectal
adenocarcinomas with microsatellite instability. Oncogene.
18:1245–1249. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shanmugam C, Katkoori VR, Jhala NC,
Grizzle WE, Siegal GP and Manne U: p53 Nuclear accumulation and
Bcl-2 expression in contiguous adenomatous components of colorectal
adenocarcinomas predict aggressive tumor behavior. J Histochem
Cytochem. 56:305–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ofner D, Riehemann K, Maier H, Riedmann B,
Nehoda H, Tötsch M, Böcker W, Jasani B and Schmid KW:
Immunohistochemically detectable bcl-2 expression in colorectal
carcinoma: correlation with tumour stage and patient survival. Br J
Cancer. 72:981–985. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baretton GB, Diebold J, Christoforis G,
Vogt M, Müller C, Dopfer K, Schneiderbanger K, Schmidt M and Löhrs
U: Apoptosis and immunohistochemical bcl-2 expression in colorectal
adenomas and carcinomas. Aspects of carcinogenesis and prognostic
significance. Cancer. 77:255–264. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sinicrope FA, Hart J, Michelassi F and Lee
JJ: Prognostic value of bcl-2 oncoprotein expression in stage II
colon carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 1:1103–1110. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhatavdekar JM, Patel DD, Ghosh N,
Chikhlikar PR, Trivedi TI, Suthar TP, Doctor SS, Shah NG and Balar
DB: Coexpression of Bcl-2, c-Myc, and p53 oncoproteins as
prognostic discriminants in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Dis
Colon Rectum. 40:785–790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bukholm IK and Nesland JM: Protein
expression of p53, p21 (WAF1/CIP1), bcl-2, Bax, cyclin D1 and pRb
in human colon carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 436:224–228. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bosari S, Moneghini L, Graziani D, Lee AK,
Murray JJ, Coggi G and Viale G: bcl-2 oncoprotein in colorectal
hyperplastic polyps, adenomas, and adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol.
26:534–540. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tollenaar RA, van Krieken JH, van Slooten
HJ, Bruinvels DJ, Nelemans KM, van den Broek LJ, Hermans J and van
Dierendonck JH: Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and Bcl-2 in
colorectal carcinoma: No evidence for prognostic significance. Br J
Cancer. 77:1842–1847. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kaklamanis L, Savage A, Whitehouse R,
Doussis-Anagnostopoulou I, Biddolph S, Tsiotos P, Mortensen N,
Gatter KC and Harris AL: Bcl-2 protein expression: Association with
p53 and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 77:1864–1869.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matkowskyj KA, Chen ZE, Rao MS and Yang
GY: Dysplastic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease: Molecular
pathogenesis to morphology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 137:338–350. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|