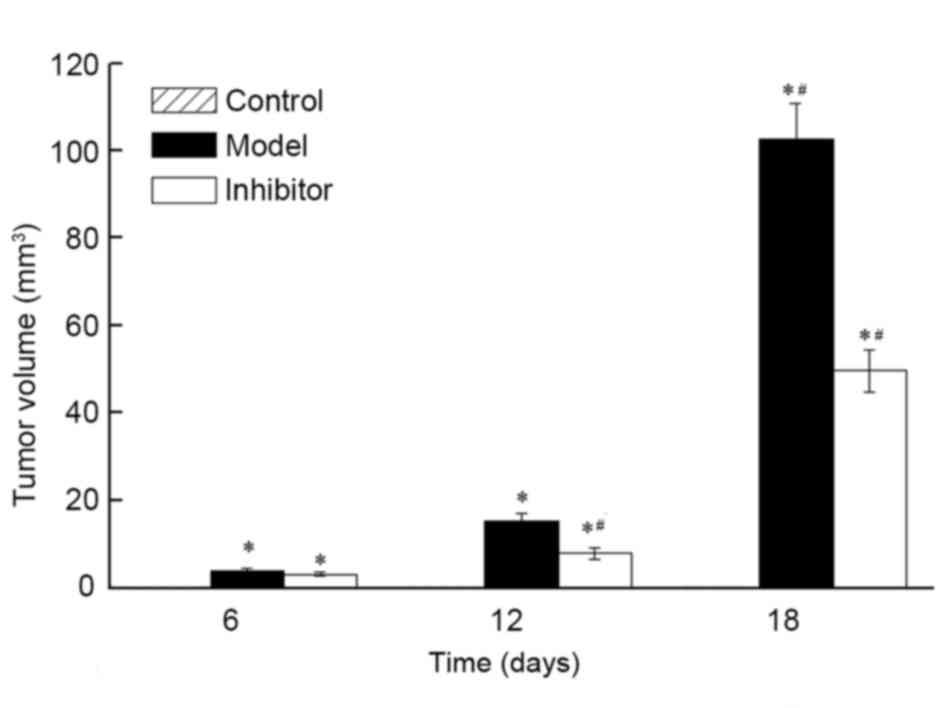
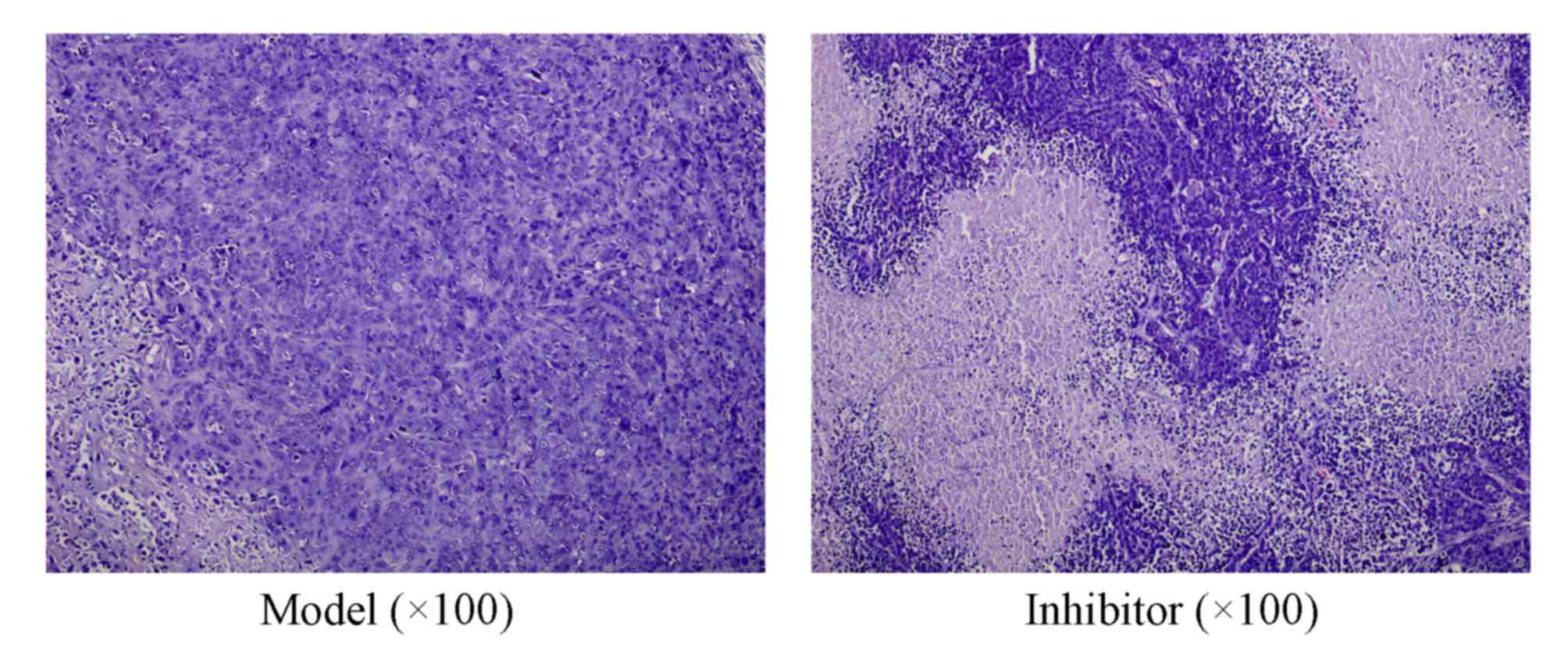
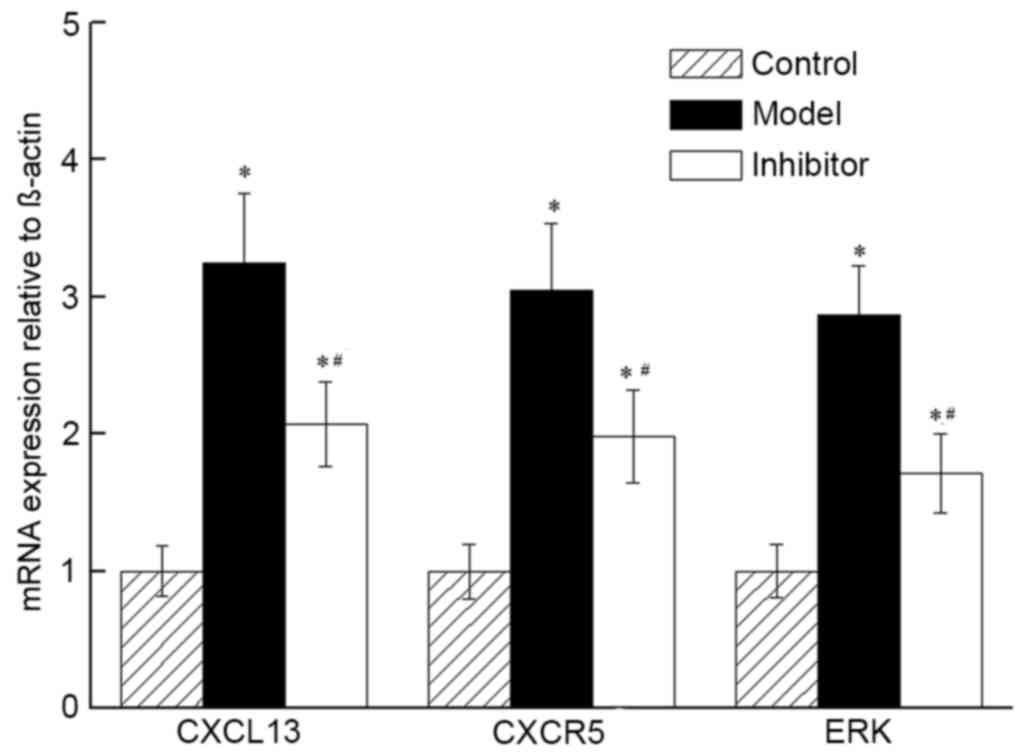
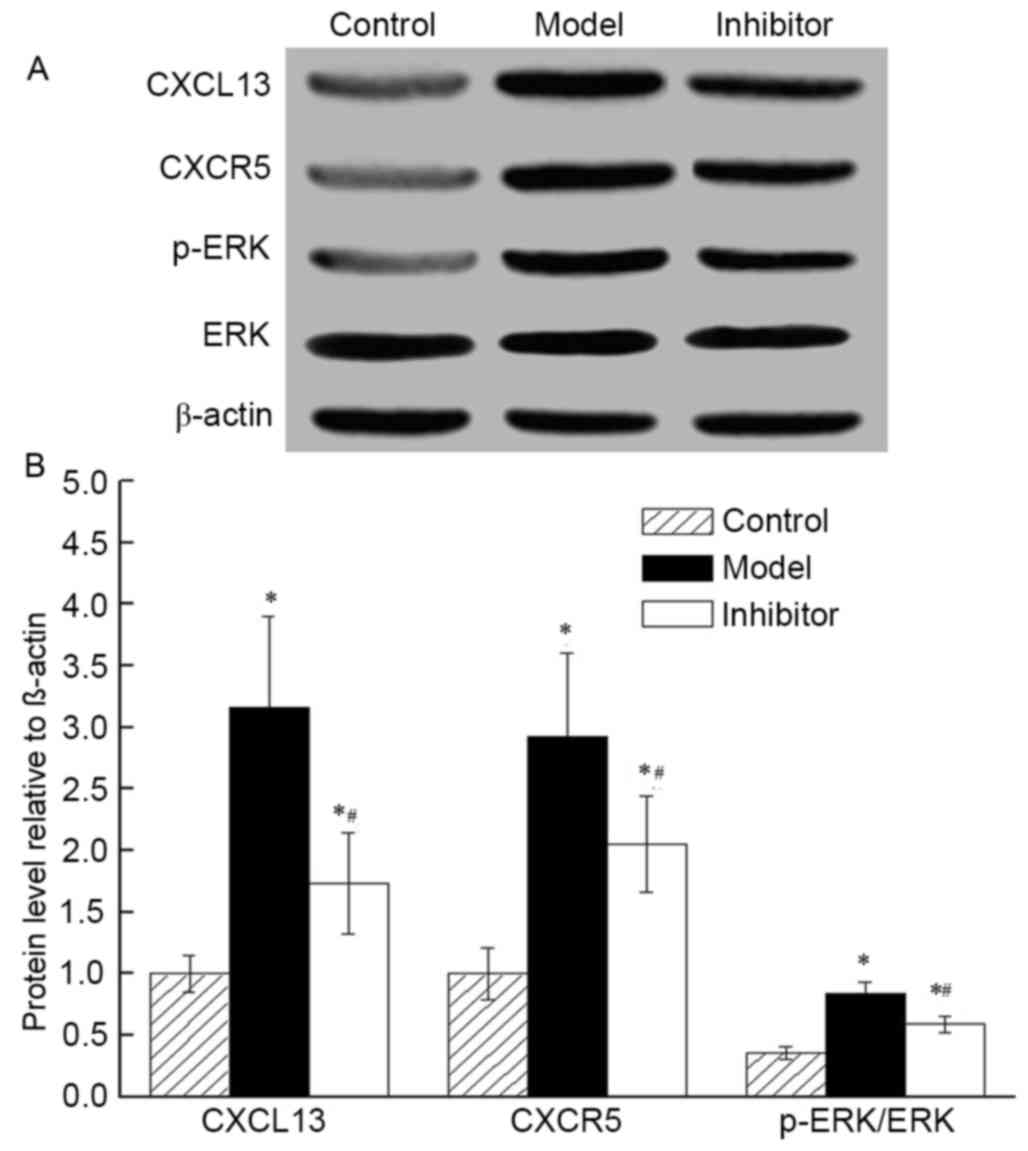
|
1
|
Soria G, Ofri-Shahak M, Haas I,
Yaal-Hahoshen N, Leider-Trejo L, Leibovich-Rivkin T, Weitzenfeld P,
Meshel T, Shabtai E, Gutman M and Ben-Baruch A: Inflammatory
mediators in breast cancer: Coordinated expression of TNF-α &
IL-1β with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. BMC Cancer. 11:1302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang F, Li L, Chen Z, Zhu M and Gu Y:
MicroRNA-214 acts as a potential oncogene in breast cancer by
targeting the PTEN-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
37:1421–1428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dauksa A, Jakstaitė A, Gasianec A and
Dambrauskas Z: Loss of proapoptotic gene Apaf-1 expression in
pancreatic cancer. Health Sci. 25:9–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li Y, Zheng Y, Li T, Wang Q, Qian J, Lu Y,
Zhang M, Bi E, Yang M, Reu F, Yi Q and Cai Z: Chemokines CCL2, 3,
14 stimulate macrophage bone marrow homing, proliferation and
polarization in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 6:24218–24229.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan KW, Evrard M, Tham M, Hong M, Huang C,
Kato M, Prevost-Blondel A, Donnadieu E, Ng LG and Abastado JP:
Tumor stroma and chemokines control T-cell migration into melanoma
following Temozolomide treatment. Oncoimmunology. 4:e9787092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bryant VL and Slade CA: Chemokines, their
receptors and human disease: The good, the bad and the itchy.
Immunol Cell Biol. 93:364–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Wang W, Tang L, He X, Yan X, Zhang
X, Zhu Y, Sun J, Shi Y, Ma X, et al: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand
13 promotes intrahepatic chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 5+
lymphocyte homing and aberrant B-cell immune responses in primary
biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 61:1998–2007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Biswas S, Sengupta S, Chowdhury Roy S,
Jana S, Mandal G, Mandal PK, Saha N, Malhotra V, Gupta A, Kuprash
DV and Bhattacharyya A: CXCL13-CXCR5 co-expression regulates
epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells during
lymph node metastasis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 143:265–276. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen L, Huang Z, Yao G, Lyu X, Li J, Hu X,
Cai Y, Li W, Li X and Ye C: The expression of CXCL13 and its
relation to unfavorable clinical characteristics in young breast
cancer. J Transl Med. 13:1682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Panse J, Friedrichs K, Marx A, Hildebrandt
Y, Luetkens T, Barrels K, Horn C, Stahl T, Cao Y, Milde-Langosch K,
et al: Chemokine CXCL13 is overexpressed in the tumour tissue and
in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
99:930–938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Huang Z, Yao G, Lyu X, Li J, Hu X,
Cai Y, Li W, Ye C and Li X: Erratum to: The expression of CXCL13
and its relation to unfavorable clinical characteristics in young
breast cancer. J Transl Med. 14:3182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dorsam RT and Gutkind JS:
G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:79–94.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
del Molino del Barrio I, Kirby J and Ali
S: The role of chemokine and glycosaminoglycan interaction in
chemokine-mediated migration in vitro and in vivo. Methods Enzymol.
570:309–333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meijer J, Zeelenberg IS, Sipos B and Roos
E: The CXCR5 chemokine receptor is expressed by carcinoma cells and
promotes growth of colon carcinoma in the liver. Cancer Res.
66:9576–9582. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Guo H, Fu L, Pan G and Sun
Y: CXCL13-CXCR5 axis promotes the growth and invasion of colon
cancer cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:287–295.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu W, Qian L, Chen X and Ding B:
Prognostic significance of CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 in patients with
breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13217–13224.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Panse J, Friedrichs K, Marx A, Hildebrandt
Y, Luetkens T, Bartels K, Horn C, Stahl T, Cao Y, Milde-Langosch K,
et al: Chemokine CXCL13 is overexpressed in the tumour tissue and
in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
99:930–938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lobenhofer EK, Huper G, Iglehart JD and
Marks JR: Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in MCF-7 cells prevents
estrogen-induced mitogenesis. Cell Growth Differ. 11:99–110.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bosch A, Li Z, Bergamaschi A, Ellis H,
Toska E, Prat A, Tao JJ, Spratt DE, Viola-Villegas NT, Castel P, et
al: PI3K inhibition results in enhanced estrogen receptor function
and dependence in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Sci
Transl Med. 7:283ra512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hindley A and Kolch W: Extracellular
signal regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen activated protein kinase
(MAPK)-independent functions of Raf kinases. J Cell Sci.
115:1575–1581. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tran DD, Koch A, Saran S, Armbrecht M,
Ewald F, Koch M, Wahlicht T, Wirth D, Braun A, Nashan B, et al:
Extracellular-signal regulated kinase (Erk1/2), mitogen-activated
protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) and tristetraprolin
(TTP) comprehensively regulate injury-induced immediate early gene
(IEG) response in in vitro liver organ culture. Cell Signal.
28:438–447. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu S, Uppal H, Demaria M, Desprez PY,
Campisi J and Kapahi P: Simvastatin suppresses breast cancer cell
proliferation induced by senescent cells. Sci Rep. 5:178952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Cao DL, Zhang ZJ, Jiang BC and
Gao YJ: Chemokine CXCL13 mediates orofacial neuropathic pain via
CXCR5/ERK pathway in the trigeminal ganglion of mice. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:1832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milde-Langosch K, Bamberger AM, Rieck G,
Grund D, Hemminger G, Müller V and Löning T: Expression and
prognostic relevance of activated extracellular-regulated kinases
(ERK1/2) in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 92:2206–2215. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Soria G and Benbaruch A: The inflammatory
chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
267:271–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aravindan BK, Prabhakar J, Somanathan T
and Subhadra L: The role of chemokine receptor 4 and its ligand
stromal cell derived factor 1 in breast cancer. Ann Transl Med.
3:232015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kitamura T and Pollard JW: Therapeutic
potential of chemokine signal inhibition for metastatic breast
cancer. Pharmacol Res. 100:266–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kudirka JC, Panupinthu N, Tesseyman MA,
Dixon SJ and Bernier SM: P2Y nucleotide receptor signaling through
MAPK/ERK is regulated by extracellular matrix: Involvement of beta3
integrins. J Cell Physiol. 213:54–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Ma L, Qi J, Shan H, Yu W and Gu
Y: MAPK/ERK signaling pathway-induced hyper-O-GlcNAcylation
enhances cancer malignancy. Mol Cell Biochem. 410:101–110. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lepen Pleić I, Secombes CJ, Bird S and
Mladineo I: Characterization of three pro-inflammatory cytokines,
TNFα1, TNFα2 and IL-1β, in cage-reared Atlantic bluefin tuna
Thunnus thynnus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 36:98–112. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|