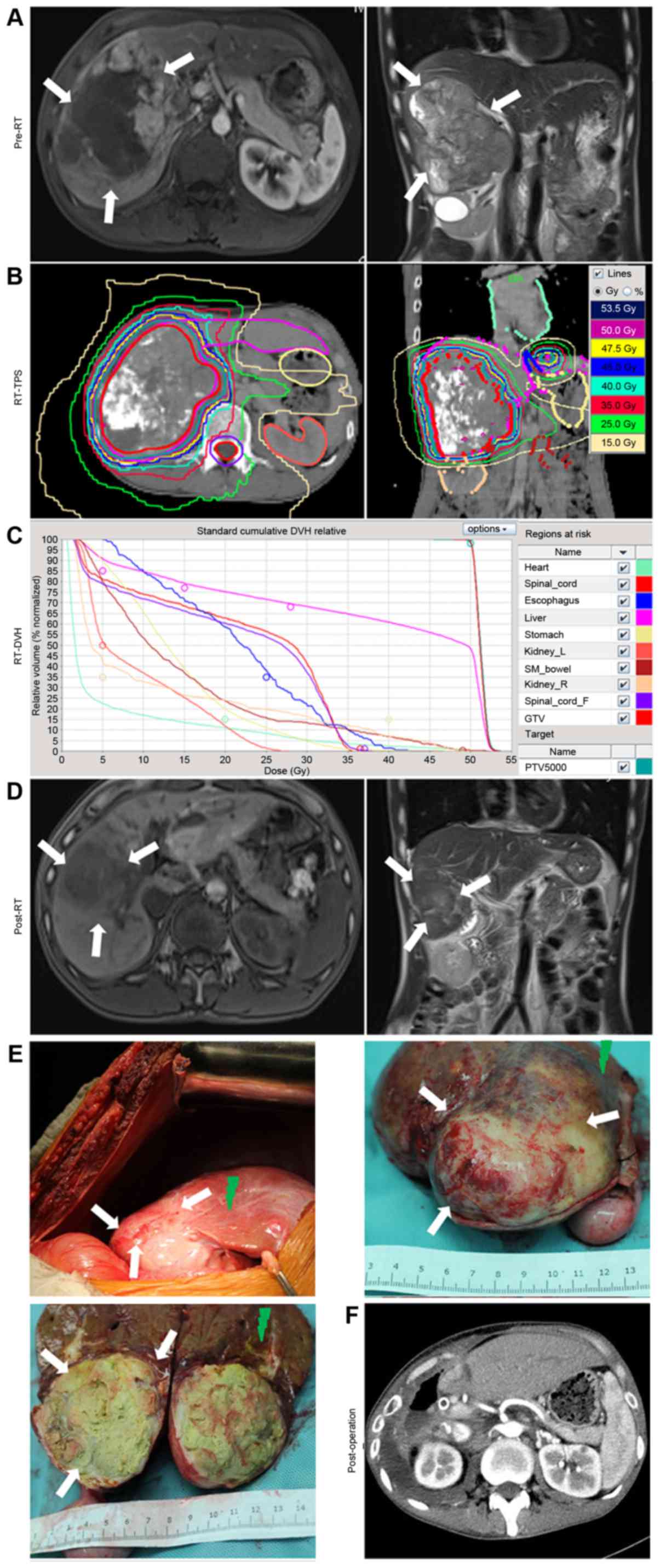
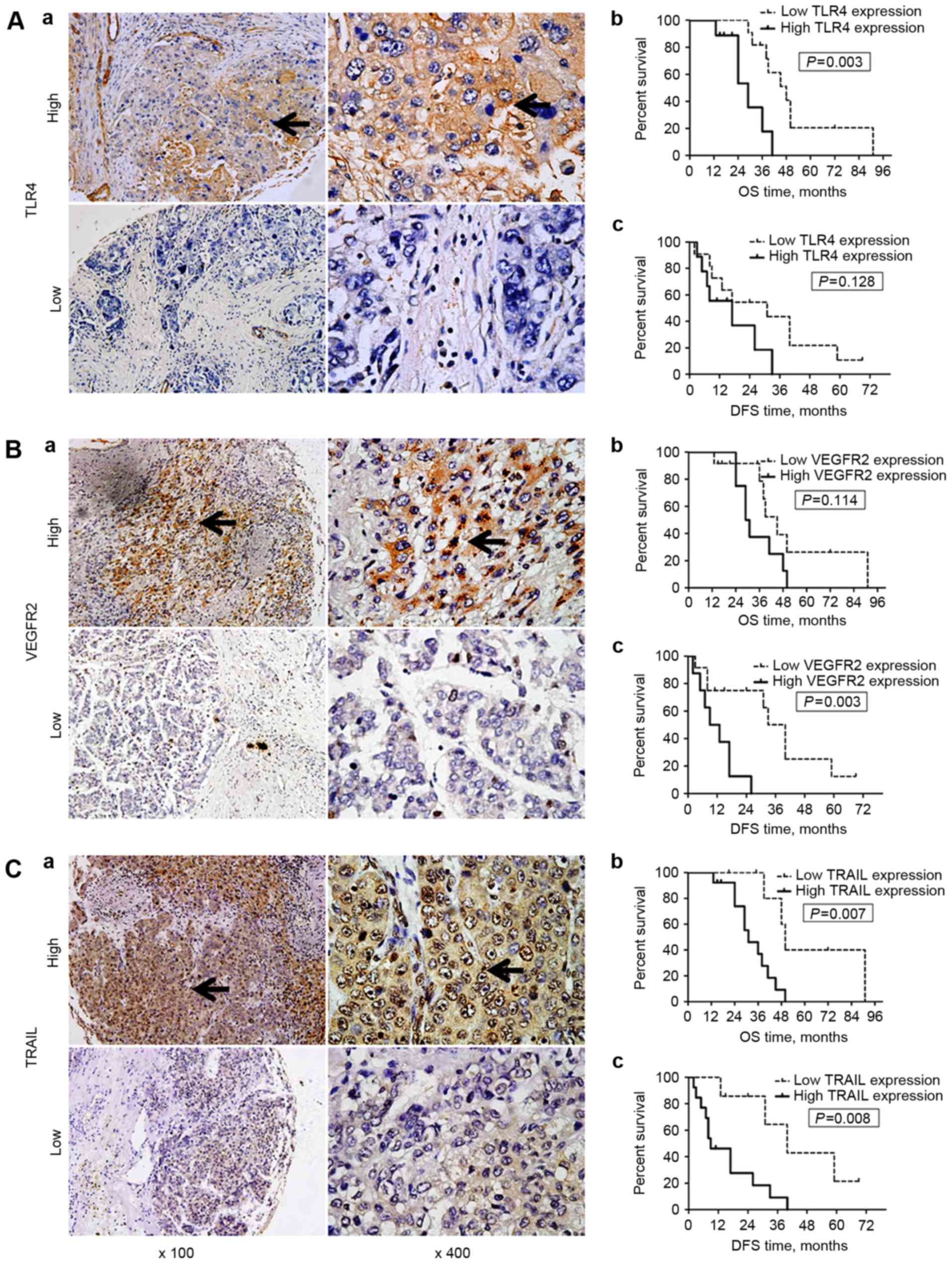
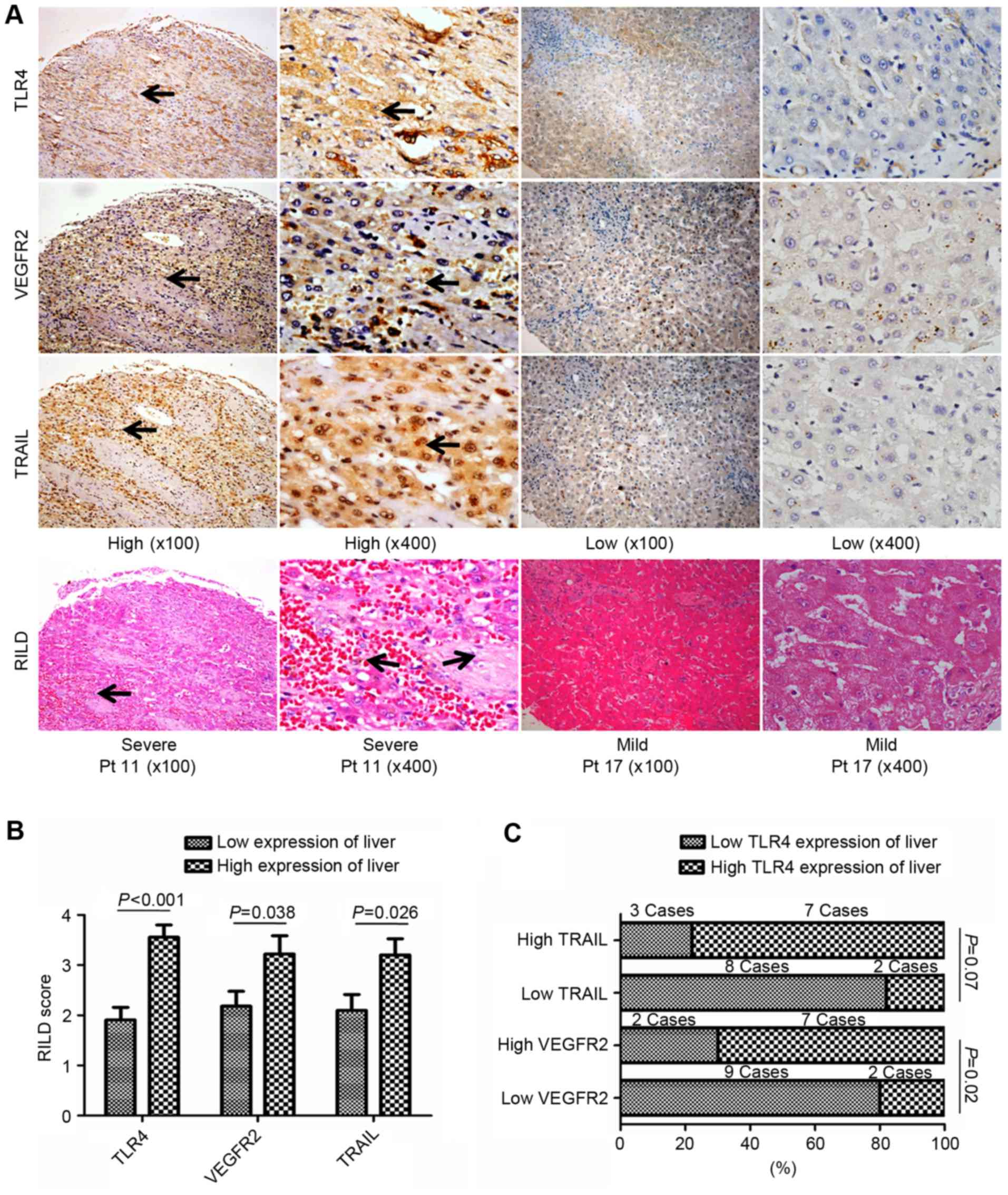
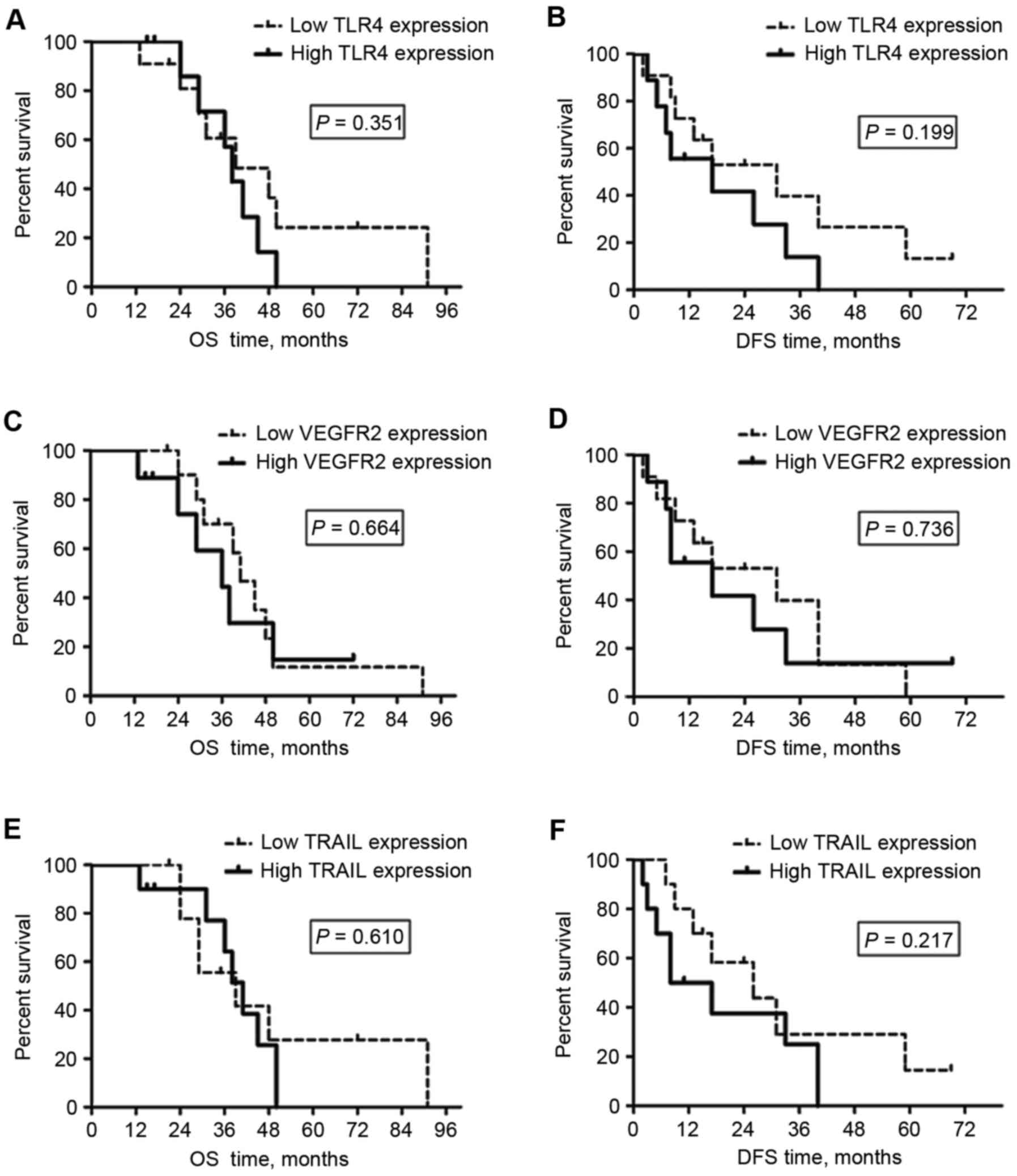
|
1
|
Stroescu C, Dragnea A, Ivanov B, Pechianu
C, Herlea V, Sgarbura O, Popescu A and Popescu I: Expression of
p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and prognostic significance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 17:411–417.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Price TR, Perkins SM, Sandrasegaran K,
Henderson MA, Maluccio MA, Zook JE, Tector AJ, Vianna RM, Johnstone
PA and Cardenes HR: Evaluation of response after stereotactic body
radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 118:3191–3198.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Law AL, Ng WT, Lee MC, Chan AT, Fung KH,
Li F, Lao WC and Lee AW: Treatment of primary liver cancer using
highly-conformal radiotherapy with kV-image guidance and
respiratory control. Radiother Oncol. 102:56–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen D, Wang R, Meng X, Yan H, Jiang S,
Feng R, Zhu K, Xu X, Dou X and Jin L: Prognostic value of serum
γ-glutamyl transferase in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
patients treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization
combined with conformal radiotherapy. Oncol Lett. 8:2298–2304.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E,
Saulnier P, et al: Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of
the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat
Med. 13:1050–1059. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seki E and Brenner DA: Toll-like receptors
and adaptor molecules in liver disease: Update. Hepatology.
48:322–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Sakurai Y,
Akashi-Takamura S, Ishibashi S, Miyake K, Shibuya M, Akira S,
Aburatani H and Maru Y: The S100A8-serum amyloid A3-TLR4 paracrine
cascade establishes a pre-metastatic phase. Nat Cell Biol.
10:1349–1355. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen
SH, Mayer L, Unkeless JC and Xiong H: Toll-like receptors on tumor
cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res.
65:5009–5014. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu ZF, Zhou XH, Hu YW, Zhou LY, Gao YB,
Peng XH, Yang XH, Zhang JY, Hu Y and Zeng ZC: TLR4-dependant immune
response, but not hepatitis B virus reactivation, is important in
radiation-induced liver disease of liver cancer radiotherapy.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:235–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhi-Feng W, Le-Yuan Z, Xiao-Hui Z, Ya-Bo
G, Jian-Ying Z, Yong H and Zhao-Chong Z: TLR4-dependent immune
response promotes radiation-induced liver disease by changing the
liver tissue interstitial microenvironment during liver cancer
radiotherapy. Radiat Res. 182:674–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ramacciato G, Mercantini P, Cautero N,
Corigliano N, Di Benedetto F, Quintini C, Ercolani G, Varotti G,
Ziparo V and Pinna AD: Prognostic evaluation of the new American
Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer
staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of 112
cirrhotic patients resected for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 12:289–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hodi FS, Ballinger M, Lyons B, Soria JC,
Nishino M, Tabernero J, Powles T, Smith D, Hoos A, McKenna C, et
al: Immune-modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors
(imRECIST): Refining guidelines to assess the clinical benefit of
cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 36:850–858. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma S, Jiao B and Liu X, Yi H, Kong D, Gao
L, Zhao G, Yang Y and Liu X: Approach to radiation therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:157–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F, Wörns MA,
Cucchetti A and Bolondi L: The treatment of intermediate stage
tumours beyond TACE: From surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol.
67:173–183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H, Wu Q, Dang S, Jin M, Xu J, Cheng Y,
Pan M, Wu Y, Zhang C and Zhang Y: Alteration of CXCR7 expression
mediated by TLR4 promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration in
human colorectal carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e273992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Long Z, Wang B, Tao D, Liu Y, Zhang J, Tan
J, Luo J, Shi F and Tao Z: Clinical research on alternating
hyperfraction radiotherapy for massive hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 10:523–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van der Schaaf A, Xu CJ, van Luijk P,
Van't Veld AA, Langendijk JA and Schilstra C: Multivariate modeling
of complications with data driven variable selection: Guarding
against overfitting and effects of data set size. Radiother Oncol.
105:115–121. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, Fan J, Zhou J, Qin LX,
Ye SL, Sun HC, Wang BL, Yu Y, Wang JH and Guo W: A comparison of
chemoembolization combination with and without radiotherapy for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J. 10:307–316. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Hoshino K,
Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Takeuchi O, Sugiyama M, Okabe M, Takeda K and
Akira S: Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like
receptor signaling pathway. Science. 301:640–643. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmidt M, Raghavan B, Müller V, Vogl T,
Fejer G, Tchaptchet S, Keck S, Kalis C, Nielsen PJ, Galanos C, et
al: Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development
of contact allergy to nickel. Nat Immunol. 11:814–819. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu FH, Yuan Y, Li D, Liao SJ, Yan B, Wei
JJ, Zhou YH, Zhu JH, Zhang GM and Feng ZH: Extracellular HSPA1A
promotes the growth of hepatocarcinoma by augmenting tumor cell
proliferation and apoptosis-resistance. Cancer Lett. 317:157–164.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu P, Cheng X, Du Y, Huang L and Dong R:
TAK-242 can be the potential agents for preventing invasion and
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Hypotheses. 81:653–655.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eiró N, Altadill A, Juárez LM, Rodríguez
M, González LO, Atienza S, Bermúdez S, Fernandez-Garcia B,
Fresno-Forcelledo MF, Rodrigo L and Vizoso FJ: Toll-like receptors
3, 4 and 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship with
clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis. Hepatol Res.
44:769–778. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Varnum SM, Springer DL, Chaffee ME, Lien
KA, Webb-Robertson BJ, Waters KM and Sacksteder CA: The effects of
low-dose irradiation on inflammatory response proteins in a 3D
reconstituted human skin tissue model. Radiat Res. 178:591–599.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gallet P, Phulpin B, Merlin JL, Leroux A,
Bravetti P, Mecellem H, Tran N and Dolivet G: Long-term alterations
of cytokines and growth factors expression in irradiated tissues
and relation with histological severity scoring. PLoS One.
6:e293992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Cheung RM, Komaki R, Fang B and
Chang JY: Radiotherapy sensitization by tumor-specific TRAIL gene
targeting improves survival of mice bearing human non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6657–6668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schenone S, Bondavalli F and Botta M:
Antiangiogenic agents: An update on small molecule VEGFR
inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 14:2495–2516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paz K and Zhu Z: Development of
angiogenesis inhibitors to vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2. Current status and future perspective. Front Biosci.
10:1415–1439. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Solberg TD, Nearman J, Mullins J, Li S and
Baranowska-Kortylewicz J: Correlation between tumor growth delay
and expression of cancer and host VEGF, VEGFR2, and osteopontin in
response to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 72:918–926.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng JC, Liu HS, Wu JK, Chung HW and Jan
GJ: Inclusion of biological factors in parallel-architecture
normal-tissue complication probability model for radiation-induced
liver disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 62:1150–1156. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang BS, Tsang NM, Lin SM, Lin DY, Lien
JM, Lin CC, Chen WT, Chen WY and Hong JH: High-dose
hypofractionated X-ray radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Tumor responses and toxicities. Oncol Lett. 6:1514–1520. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lawrence D, Shahrokh Z, Marsters S,
Achilles K, Shih D, Mounho B, Hillan K, Totpal K, DeForge L, Schow
P, et al: Differential hepatocyte toxicity of recombinant
Apo2L/TRAIL versions. Nat Med. 7:383–385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stewart M, Turley H, Cook N, Pezzella F,
Pillai G, Ogilvie D, Cartlidge S, Paterson D, Copley C, Kendrew J,
et al: The angiogenic receptor KDR is widely distributed in human
tissues and tumors and relocates intracellularly on
phosphorylation. An immunohistochemical study. Histopathology.
43:33–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hawkins MA and Dawson LA: Radiation
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: From palliation to cure.
Cancer. 106:1653–1663. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pan CC, Kavanagh BD, Dawson LA, Li XA, Das
SK, Miften M and Ten Haken RK: Radiation-associated liver injury.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76 3 Suppl:S94–S100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kondo Y, Kimura O and Shimosegawa T:
Radiation therapy has been shown to be adaptable for various stages
of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:94–101.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shim SJ, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY, Suh CO
and Lee JT: Local radiotherapy as a complement to incomplete
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in locally advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 25:1189–1196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|