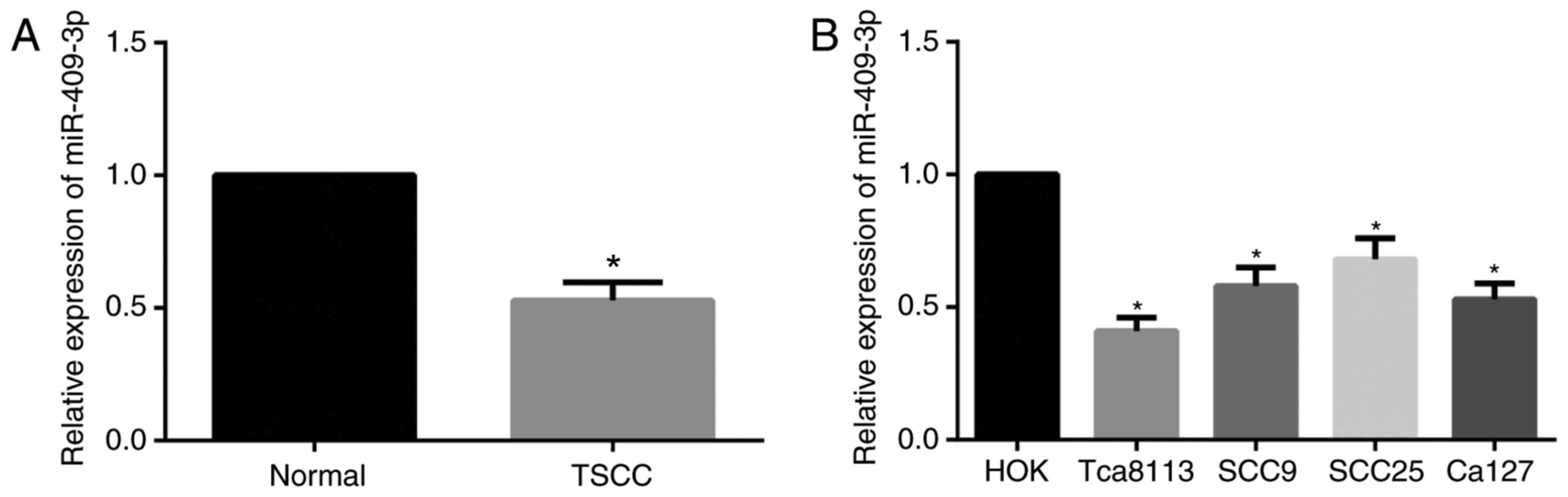
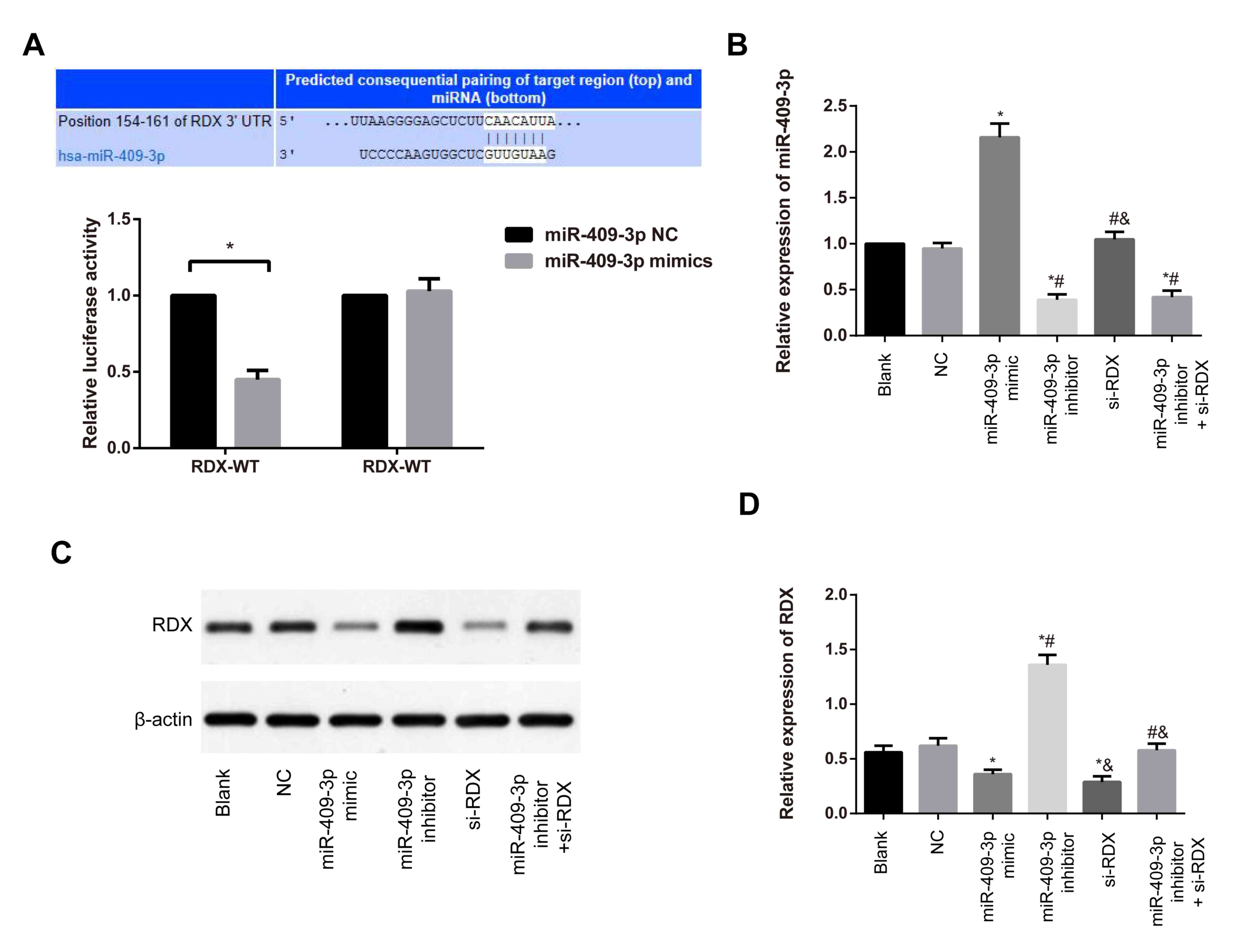
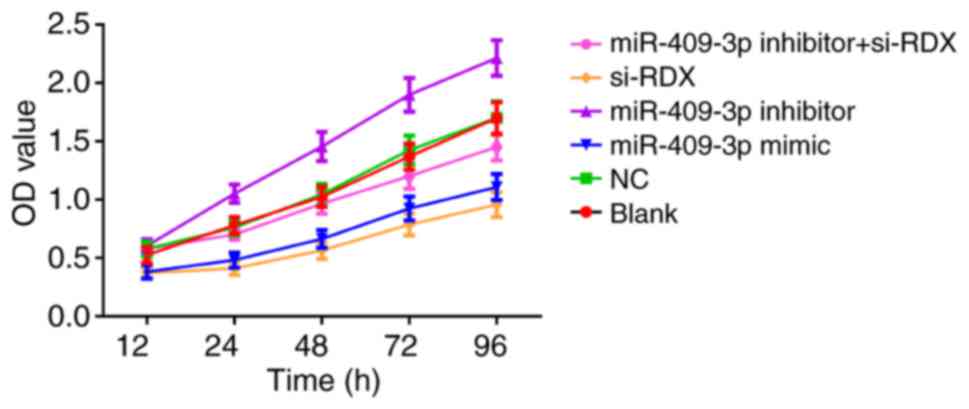
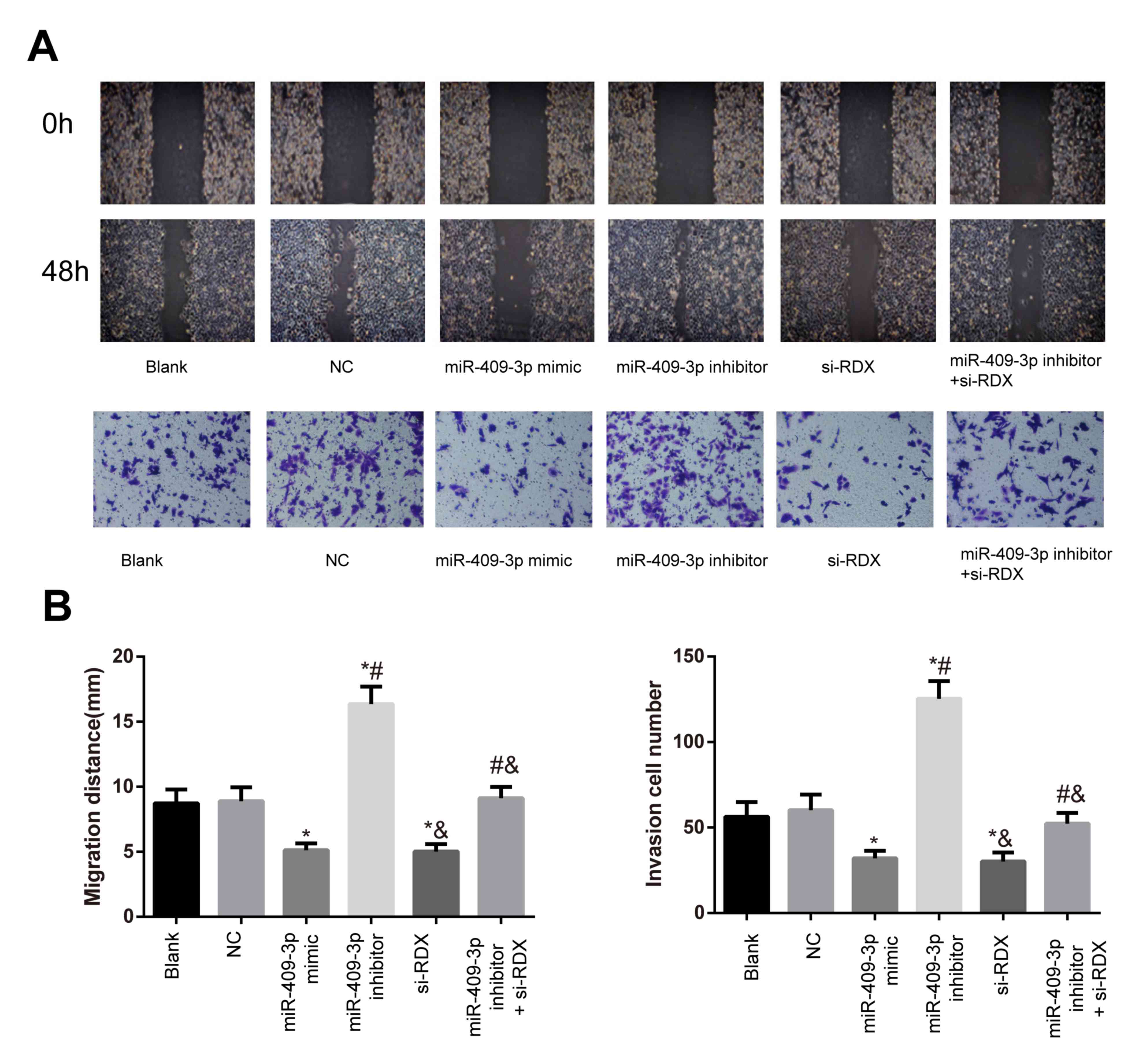
|
1
|
Khan Sannam R, Khurshid Z, Akhbar S and
Moin Faraz S: Advances of salivary proteomics in oral squamous cell
carcinoma (OSCC) detection: An update. Proteomes. 4:2016.
|
|
2
|
Kidani K, Osaki M, Tamura T, Yamaga K,
Shomori K, Ryoke K and Ito H: High expression of EZH2 is associated
with tumor proliferation and prognosis in human oral squamous cell
carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 45:39–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao W, Feng Z, Cui Z, Zhang C, Sun Z, Mao
L and Chen W: Up-regulation of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 is
associated positively with cyclin D1 overexpression and poor
clinical outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer.
118:2858–2871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mücke T, Kanatas A, Ritschl LM, Koerdt S,
Tannapfel A, Wolff KD, Loeffelbein D and Kesting M: Tumor thickness
and risk of lymph node metastasis in patients with squamous cell
carcinoma of the tongue. Oral Oncol. 53:80–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaboodkhani R, Karimi E, Ashtiani
Khorsandi MT, Kowkabi S, Firouzifar MR, Yazdani F and Yazdani N:
Evaluation of the correlation between CD44, tumor prognosis and the
5-Year survival rate in patients with oral tongue SCC. Iran J
Otorhinolaryngol. 28:407–411. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taghavi N and Yazdi I: Prognostic factors
of survival rate in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical,
histologic, genetic and molecular concepts. Arch Iran Med.
18:314–319. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McIntire M and Redston M: Targeted
therapies and predictive markers in epithelial malignancies of the
gastrointestinal tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 136:496–503. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:776–780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai R, Weng C, Dong H, Li S, Chen G and Xu
Z: MicroRNA-409-3p suppresses colorectal cancer invasion and
metastasis partly by targeting GAB1 expression. Int J Cancer.
137:2310–2322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wan L, Zhu L, Xu J, Lu B, Yang Y, Liu F
and Wang Z: MicroRNA-409-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in
human lung adenocarcinoma by targeting c-Met. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:1273–1290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu X, Chen H, Lin Y, Hu Z, Mao Y, Wu J, Xu
X, Zhu Y, Li S, Zheng X and Xie L: MicroRNA-409-3p inhibits
migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met.
Mol Cells. 36:62–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li C, Nie H, Wang M, Su L, Li J, Yu B, Wei
M, Ju J, Yu Y, Yan M, et al: MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell
proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PHF10 in gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 320:189–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Valastyan S, Chang A, Benaich N, Reinhardt
F and Weinberg RA: Concurrent suppression of integrin alpha5,
radixin, and RhoA phenocopies the effects of miR-31 on metastasis.
Cancer Res. 70:5147–5154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu G and Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA: Radixin
stimulates Rac1 and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase, CaMKII:
Cross-talk with Galpha13 signaling. J Biol Chem. 280:39042–39049.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arpin M, Chirivino D, Naba A and
Zwaenepoel I: Emerging role for ERM proteins in cell adhesion and
migration. Cell Adh Migr. 5:199–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai MM, Wang CS, Tsai CY, Chen CY, Chi
HC, Tseng YH, Chung PJ, Lin YH, Chung IH, Chen CY and Lin KH:
MicroRNA-196a/-196b promote cell metastasis via negative regulation
of radixin in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 351:222–231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng B, Liang L, Huang S, Zha R, Liu L,
Jia D, Tian Q, Wang Q, Wang C, Long Z, et al: MicroRNA-409
suppresses tumour cell invasion and metastasis by directly
targeting radixin in gastric cancers. Oncogene. 31:4509–4516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
The Helsinki Declaration of the World
Medical Association (WMA). Ethical principles of medical research
involving human subjects. polski merkuriusz lekarski: Organ
Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego. 36:298–301. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. American physiological
society. Physiologist. 39(199): 208–111. 1996.
|
|
23
|
Okuyemi OT, Piccirillo JF and Spitznagel
E: TNM staging compared with a new clinicopathological model in
predicting oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma survival. Head Neck.
36:1481–1489. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Z, Li Y, Xu J, Ren Q, Yao J and Tian X:
MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell invasion and metastasis by targeting
ZEB1 in breast cancer. IUBMB Life. 68:394–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld
W and Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in
invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 143:401–409.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao GH, Sun XL, Wu F, Chen WF, Li JQ and
Hu WC: Low expression of miR-409-3p is a prognostic marker for
breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3825–3829.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang B, Liu C, Zhang QM and Ni M:
Decreased expression of miR-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical
significance. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:246–251.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Xu H and Yang Q:
miR-409-3p suppresses breast cancer cell growth and invasion by
targeting Akt1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:189–195. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Hou W, Jia J, Zhao Y and Zhao B:
MiR-409-3p regulates cell proliferation and tumor growth by
targeting E74-like factor 2 in osteosarcoma. FEBS Open Bio.
7:348–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Neisch AL and Fehon RG: Ezrin, radixin and
moesin: Key regulators of membrane-cortex interactions and
signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 23:377–382. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Valderrama F, Thevapala S and Ridley AJ:
Radixin regulates cell migration and cell-cell adhesion through
Rac1. J Cell Sci. 125:3310–3319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yogesha SD, Sharff AJ, Giovannini M,
Bricogne G and Izard T: Unfurling of the band 4.1, ezrin, radixin,
moesin (FERM) domain of the merlin tumor suppressor. Protein Sci.
20:2113–2120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu YW, Yan JK, Li JJ, Ou YM and Yang Q:
Knockdown of radixin suppresses gastric cancer metastasis in vitro
by up-regulation of e-cadherin via NF-κB/snail pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:2509–2521. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang QH, Wang AX and Chen Y: Radixin
enhances colon cancer cell invasion by increasing MMP-7 production
via Rac1-ERK pathway. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:3402712014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Courtneidge SA: Cell migration and
invasion in human disease: The Tks adaptor proteins. Biochem Soc
Trans. 40:129–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eloy C, Santos J, Soares P and
Sobrinho-Simões M: Intratumoural lymph vessel density is related to
presence of lymph node metastases and separates encapsulated from
infiltrative papillary thyroid carcinoma. Virchows Arch.
459:595–605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jardim JF, Francisco AL, Gondak R,
Damascena A and Kowalski LP: Prognostic impact of perineural
invasion and lymphovascular invasion in advanced stage oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 44:23–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weng C, Dong H, Chen G, Zhai Y, Bai R, Hu
H, Lu L and Xu Z: miR-409-3p inhibits HT1080 cell proliferation,
vascularization and metastasis by targeting angiogenin. Cancer
Lett. 323:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen SD, Song MM, Zhong ZQ, Li N, Wang PL,
Cheng S, Bai RX and Yuan HS: Knockdown of radixin by RNA
interference suppresses the growth of human pancreatic cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:753–759. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|