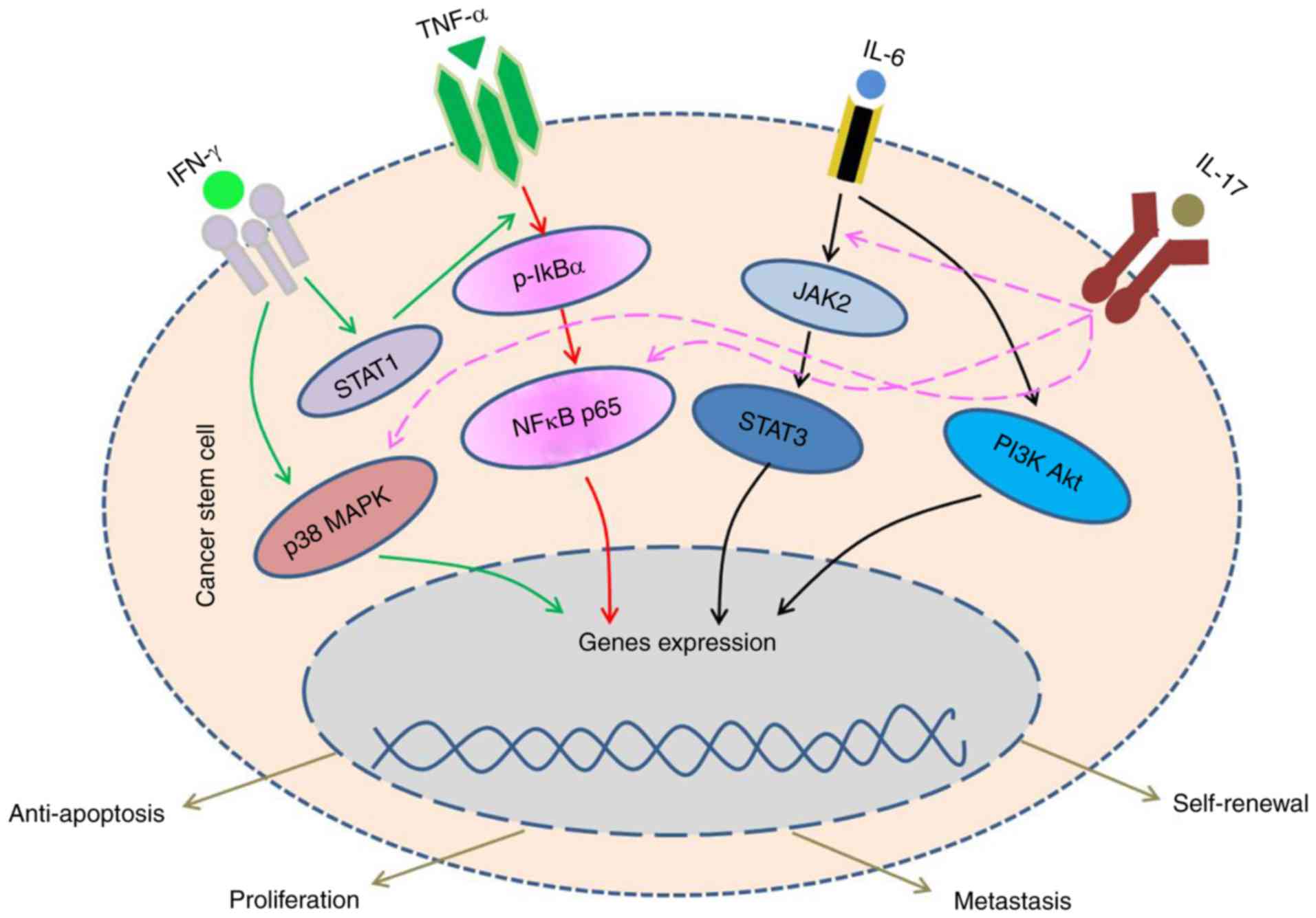
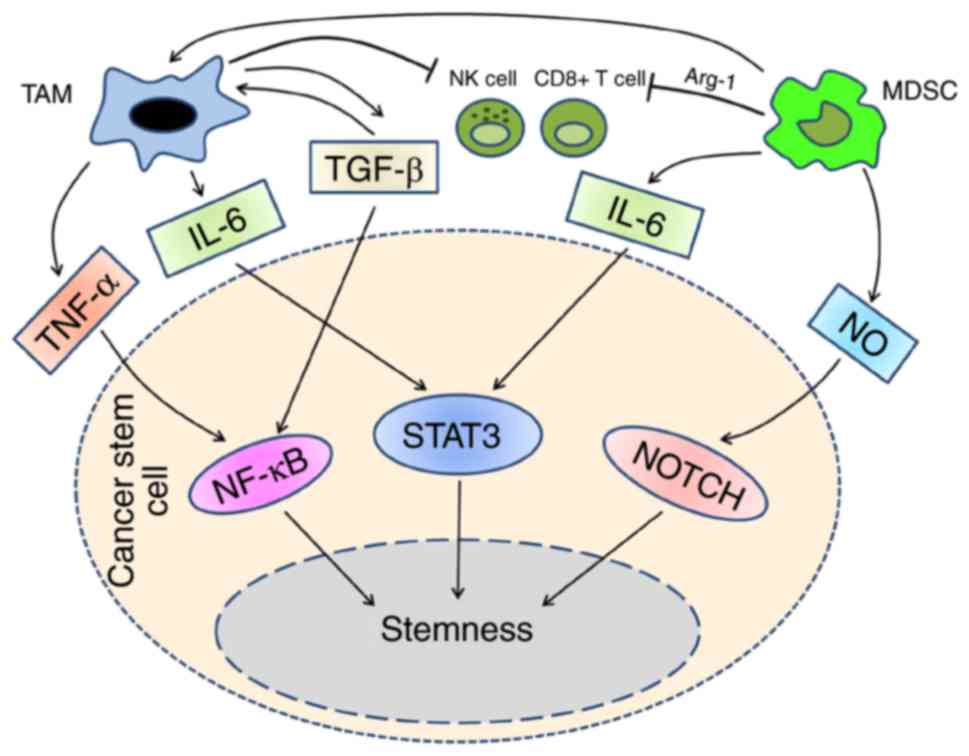
|
1
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Albini A, Bruno A, Gallo C, Pajardi G,
Noonan DM and Dallaglio K: Cancer stem cells and the tumor
microenvironment: Interplay in tumor heterogeneity. Connect Tissue
Res. 56:414–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Voog J and Jones DL: Stem cells and the
niche: A dynamic duo. Cell Stem Cell. 6:103–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kise K, Kinugasa-Katayama Y and Takakura
N: Tumor microenvironment for cancer stem cells. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 99:197–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin
C and Flavell RA: Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between
tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:759–771. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Corrales L and Gajewski TF: Molecular
pathways: Targeting the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) in
the immunotherapy of cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:4774–4779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trinchieri G: Type I interferon: Friend or
foe? J Exp Med. 207:2053–2063. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zaidi MR and Merlino G: The two faces of
interferon-γ in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6118–6124. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nardi Beyer N and da Silva Meirelles L:
Mesenchymal stem cells: Isolation, in vitro expansion and
characterization. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 249–282. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shi S and Gronthos S: Perivascular niche
of postnatal mesenchymal stem cells in human bone marrow and dental
pulp. J Bone Miner Res. 18:696–704. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sharma RR, Pollock K, Hubel A and Mckenna
D: Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: A review of clinical
applications and manufacturing practices. Transfusion.
54:1418–1437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Akiyama K, Chen C,
Qu C, Jin Y and Shi S: IFN-γ and TNF-α synergistically induce
mesenchymal stem cell impairment and tumorigenesis via NFκB
signaling. Stem Cells. 31:1383–1395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Kikuiri T, Akiyama K, Chen
C, Xu X, Yang R, Chen W, Wang S and Shi S: Mesenchymal stem
cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T
lymphocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α. Nat Med. 17:1594–1601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Trivanović D, Jauković A, Krstić J,
Nikolić S, Okić Djordjević I, Kukolj T, Obradović H, Mojsilović S,
Ilić V, Santibanez JF and Bugarski D: Inflammatory cytokines prime
adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells to enhance malignancy of
MCF-7 breast cancer cells via transforming growth factor-β1. IUBMB
Life. 68:190–200. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lv N, Gao Y, Guan H, Wu D, Ding S, Teng W
and Shan Z: Inflammatory mediators, tumor necrosis factor-α and
interferon-γ, induce EMT in human PTC cell lines. Oncol Lett.
10:2591–2597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schürch C, Riether C, Amrein MA and
Ochsenbein AF: Cytotoxic T cells induce proliferation of chronic
myeloid leukemia stem cells by secreting interferon-γ. J Exp Med.
210:605–621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu Y, Karakhanova S, Huang X, Deng SP,
Werner J and Bazhin AV: Influence of interferon-α on the expression
of the cancer stem cell markers in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Exp
Cell Res. 324:146–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamashina T, Baghdadi M, Yoneda A,
Kinoshita I, Suzu S, Dosakaakita H and Jinushi M: Cancer stem-like
cells derived from chemoresistant tumors have a unique capacity to
prime tumorigenic myeloid cells. Cancer Res. 74:2698–2709. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin X, Kim SH, Jeon HM, Beck S, Sohn YW,
Yin J, Kim JK, Lim YC, Lee JH, Kim SH, et al: Interferon regulatory
factor 7 regulates glioma stem cells via interleukin-6 and Notch
signalling. Brain. 135:1055–1069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ojha R, Singh SK and Bhattacharyya S:
JAK-mediated autophagy regulates stemness and cell survival in
cisplatin resistant bladder cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1860:2484–2497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Chen JN, Zeng TT, He F, Chen SP, Ma
S, Bi J, Zhu XF and Guan XY: CD133+ liver cancer stem cells resist
interferon-gamma-induced autophagy. BMC Cancer. 16:152016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Furuta J, Inozume T, Harada K and Shimada
S: CD271 on melanoma cell is an IFN-γ-inducible immunosuppressive
factor that mediates downregulation of melanoma antigens. J Invest
Dermatol. 134:1369–1377. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kharma B, Baba T, Matsumura N, Kang HS,
Hamanishi J, Murakami R, McConechy MM, Leung S, Yamaguchi K, Hosoe
Y, et al: STAT1 drives tumor progression in serous papillary
endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 74:6519–6530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang AM, Creasey AA, Ladner MB, Lin LS,
Strickler J, Van Arsdell JN, Yamamoto R and Mark DF: Molecular
cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor.
Science. 228:149–154. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roberts NJ, Zhou S, Diaz LA and Matthias
H: Systemic use of tumor necrosis factor alpha as an anticancer
agent. Oncotarget. 2:739–751. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Jiao M, Wu K, Li L, Zhu G, Wang
X, He D and Wu D: TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition
increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma cells. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 7:4951–4958. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Techasen A, Namwat N, Loilome W,
Bungkanjana P, Khuntikeo N, Puapairoj A, Jearanaikoon P, Saya H and
Yongvanit P: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) stimulates the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Snail in
cholangiocarcinoma. Med Oncol. 29:3083–3091. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Valizadeh A, Ahmadzadeh A, Saki G,
Khodadadi A and Teimoori A: Role of tumor necrosis factor-producing
mesenchymal stem cells on apoptosis of chronic B-lymphocytic tumor
cells resistant to fludarabine-based chemotherapy. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:8533–8539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu PF, Huang Y, Han YY, Lin LY, Sun WH,
Rabson AB, Wang Y and Shi YF: TNFα-activated mesenchymal stromal
cells promote breast cancer metastasis by recruiting CXCR2+
neutrophils. Oncogene. 36:482–490. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Katanov C, Lerrer S, Liubomirski Y,
Leider-Trejo L, Meshel T, Bar J, Feniger-Barish R, Kamer I,
Soria-Artzi G, Kahani H, et al: Regulation of the inflammatory
profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: Prominent roles
for TNF-α and the NF-κB pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:872015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee SH, Hong HS, Liu ZX, Kim RH, Kang MK,
Park NH and Shin KH: TNFα enhances cancer stem cell-like phenotype
via Notch-Hes1 activation in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:58–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Storci G, Sansone P, Mari S, D'Uva G,
Tavolari S, Guarnieri T, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D,
Chieco P, et al: TNFalpha up-regulates SLUG via the
NF-kappaB/HIF1alpha axis, which imparts breast cancer cells with a
stem cell-like phenotype. J Cell Physiol. 225:682–691. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ostyn P, El Machhour R, Begard S, Kotecki
N, Vandomme J, Flamenco P, Segard P, Masselot B, Formstecher P,
Touil Y and Polakowska R: Transient TNF regulates the self-renewing
capacity of stem-like label-retaining cells in sphere and skin
equivalent models of melanoma. Cell Commun Signal. 12:522014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fukushima K, Tsuchiya K, Kano Y, Horita N,
Hibiya S, Hayashi R, Kitagaki K, Negi M, Itoh E, Akashi T, et al:
Atonal homolog 1 protein stabilized by tumor necrosis factor α
induces high malignant potential in colon cancer cell line. Cancer
Sci. 106:1000–1007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gallipoli P, Pellicano F, Morrison H,
Laidlaw K, Allan EK, Bhatia R, Copland M, Jørgensen HG and Holyoake
TL: Autocrine TNF-α production supports CML stem and progenitor
cell survival and enhances their proliferation. Blood.
122:3335–3339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou X, Zhou S, Li B, Li Q, Gao L, Li D,
Gong Q, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang N, et al: Transmembrane TNF-α
preferentially expressed by leukemia stem cells and blasts is a
potent target for antibody therapy. Blood. 126:1433–1442. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sheng YH, He Y, Hasnain SZ, Wang R, Tong
H, Clarke DT, Lourie R, Oancea I, Wong KY, Lumley JW, et al: MUC13
protects colorectal cancer cells from death by activating the NF-κB
pathway and is a potential therapeutic target. Oncogene.
36:700–713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nenu I, Tudor D, Filip AG and Baldea I:
Current position of TNF-α in melanomagenesis. Tumor Biol.
36:6589–6602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bromberg J and Wang TC: Inflammation and
cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell. 15:79–80.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Smith PC, Hobisch A, Lin DL, Culig Z and
Keller ET: Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer progression. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 12:33–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yao X, Huang J, Zhong H, Shen N, Faggioni
R, Fung M and Yao Y: Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory
autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther. 141:125–139. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hideshima T, Nakamura N, Chauhan D and
Anderson KC: Biologic sequelae of interleukin-6 induced PI3-K/Akt
signaling in multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 20:5991–6000. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A and Bhatt
AN: Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic
resistance. Tumor Biol. 37:11553–11572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen Y, Zhang F, Tsai Y, Yang X, Yang L,
Duan S, Wang X, Keng P and Lee SO: IL-6 signaling promotes DNA
repair and prevents apoptosis in CD133+ stem-like cells of lung
cancer after radiation. Radiat Oncol. 10:2272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Altundag O, Altundag K and Gunduz E:
Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 23:1044–1045. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Knüpfer H and Preiß R: Significance of
interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 102:129–135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ok LS, Yang X, Duan S, Ying T, Strojny LR,
Peter K, et al: IL-6 promotes growth and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of CD133+ cells of non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:6626–6638. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang F, Duan S, Ying T, Keng PC and Chen
Y, Lee SO and Chen Y: Cisplatin treatment increases stemness
through upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factors by interleukin-6
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 107:746–754. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu CC, Lin JH, Hsu TW, Su K, Li AF, Hsu
HS and Hung SC: IL-6 enriched lung cancer stem-like cell population
by inhibition of cell cycle regulators via DNMT1 upregulation. Int
J Cancer. 136:547–559. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hsu HS, Lin JH, Hsu TW, Su K, Wang CW,
Yang KY, Chiou SH and Hung SC: Mesenchymal stem cells enhance lung
cancer initiation through activation of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
Lung Cancer. 75:167–177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lu JH, Wei HJ, Peng BY, Chou HH, Chen WH,
Liu HY and Deng WP: Adipose-derived stem cells enhance cancer stem
cell property and tumor formation capacity in lewis lung carcinoma
cells through an interleukin-6 paracrine circuit. Stem Cells Dev.
25:1833–1842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
a Dzaye OD, Hu F, Derkow K, Haage V,
Euskirchen P, Harms C, Lehnardt S, Synowitz M, Wolf SA and
Kettenmann H: Glioma stem cells but not bulk glioma cells
upregulate IL-6 secretion in microglia/brain macrophages via
toll-like receptor 4 signaling. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
75:429–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ding DC, Liu HW and Chu TY: Interleukin-6
from ovarian mesenchymal stem cells promotes proliferation, sphere
and colony formation and tumorigenesis of an ovarian cancer cell
line SKOV3. J Cancer. 7:1815–1823. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huynh PT, Beswick EJ, Yun AC, Johnson P,
O'Connell MR, Watts T, Singh P, Qiu S, Morris K, Powell DW and
Pinchuk IV: CD90(+) stromal cells are the major source of IL-6,
which supports cancer stem-like cells and inflammation in
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:1971–1981. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang X, Sun W, Shen W, Xia M, Chen C,
Xiang D, Ning B, Cui X, Li H, Li X, et al: Long non-coding RNA DILC
regulates liver cancer stem cells via IL-6/STAT3 axis. J Hepatol.
64:1283–1294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mcnee G, Eales KL, Wei W, Williams DS,
Barkhuizen A, Bartlett DB, Essex S, Anandram S, Filer A, Moss PA,
et al: Citrullination of histone H3 drives IL-6 production by bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells in MGUS and multiple myeloma.
Leukemia. 31:373–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kolls JK and Lindén A: Interleukin-17
family members and inflammation. Immunity. 21:467–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Guéry L and Hugues S: Th17 cell plasticity
and functions in cancer immunity. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3146202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang B, Fung A, Zhao H, Wang T and Ma D:
The Role of Interleukin 17 in Tumour Proliferation, Angiogenesis
and Metastasis. Mediators of Inflammation. 2014:390–392. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yang S, Wang B, Guan C, Wu B, Cai C, Wang
M, Zhang B, Liu T and Yang P: Foxp3+IL-17+ T cells promote
development of cancer-initiating cells in colorectal cancer. J
Leukoc Biol. 89:85–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wei S, Zhao E, Kryczek I and Zou W: Th17
cells have stem cell-like features and promote long-term immunity.
Oncoimmunology. 1:516–519. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lotti F, Jarrar AM, Pai RK, Hitomi M,
Lathia J, Mace A, Gantt GA Jr, Sukhdeo K, DeVecchio J, Vasanji A,
et al: Chemotherapy activates cancer-associated fibroblasts to
maintain colorectal cancer-initiating cells by IL-17A. J Exp Med.
210:2851–2872. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiang T, Long H, He L, Han X, Lin K, Liang
Z, Zhuo W, Xie R and Zhu B: Interleukin-17 produced by tumor
microenvironment promotes self-renewal of CD133+ cancer stem-like
cells in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 34:165–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Luo Y, Yang Z, Su L, Shan J, Xu H, Xu Y,
Liu L, Zhu W, Chen X, Liu C, et al: Non-CSCs nourish CSCs through
interleukin-17E-mediated activation of NF-κB and JAK/STAT3
signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
375:390–399. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Parajuli P, Anand R, Mandalaparty C,
Suryadevara R, Sriranga PU, Michelhaugh SK, Cazacu S, Finniss S,
Thakur A, Lum LG, et al: Preferential expression of functional
IL-17R in glioma stem cells: Potential role in self-renewal.
Oncotarget. 7:6121–6135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jiang YX, Yang SW, Li PA, Luo X, Li ZY,
Hao YX and Yu PW: The promotion of the transformation of quiescent
gastric cancer stem cells by IL-17 and the underlying mechanisms.
Oncogene. 36:1256–1264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Condamine T and Gabrilovich DI: Molecular
mechanisms regulating myeloid-derived suppressor cell
differentiation and function. Trends Immunol. 32:19–25. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Medina-Echeverz J, Aranda F and Berraondo
P: Myeloid-derived cells are key targets of tumor immunotherapy.
Oncoimmunology. 3:e283982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chikamatsu K, Okamoto A, Sakakura K,
Hatsushika K, Takahashi G and Masuyama K: P3.14. Immunoregulatory
properties of CD44+ cancer stem-like cells in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol Suppl. 3:205–206. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Otvos B, Finke J, Vogelbaum M and Lathia
JD: Interrogating the interactions between myeloid derived
suppressor cells and cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. J Immuno
Ther Cancer. 1:2682013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Gao L, Yu S and Zhang X: Hypothesis:
Tim-3/galectin-9, a new pathway for leukemia stem cells survival by
promoting expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and
differentiating into tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 70:273–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Otvos B, Silver DJ, Mulkearns-Hubert EE,
Alvarado AG, Turaga SM, Sorensen MD, Rayman P, Flavahan WA, Hale
JS, Stoltz K, et al: Cancer stem cell-secreted macrophage migration
inhibitory factor stimulates myeloid derived suppressor cell
function and facilitates glioblastoma immune evasion. Stem Cells.
34:2026–2039. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cui TX, Kryczek I, Zhao L, Zhao E, Kuick
R, Roh MH, Vatan L, Szeliga W, Mao Y, Thomas DG, et al:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells enhance stemness of cancer cells
by inducing microRNA101 and suppressing the corepressor CtBP2.
Immunity. 39:611–621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Panni RZ, Sanford DE, Belt BA, Mitchem JB,
Worley LA, Goetz BD, Mukherjee P, Wang-Gillam A, Link DC, Denardo
DG, et al: Tumor-induced STAT3 activation in monocytic
myeloid-derived suppressor cells enhances stemness and mesenchymal
properties in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
63:513–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Peng D, Tanikawa T, Li W, Zhao L, Vatan L,
Szeliga W, Wan S, Wei S, Wang Y, Liu Y, et al: Myeloid-derived
suppressor cells endow stem-like qualities to breast cancer cells
through IL6/STAT3 and NO/NOTCH cross-talk signaling. Cancer Res.
76:3156–3165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shih JY, Yuan A, Chen JW and Yang PC:
Tumor-associated macrophage: Its role in cancer invasion and
metastasis. J Cancer Mol. 2:101–106. 2006.
|
|
78
|
Allavena P, Sica A, Solinas G, Porta C and
Mantovani A: The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor
progression: The role of tumor-associated macrophages. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 66:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Franklin RA, Liao W, Sarkar A, Kim MV,
Bivona MR, Liu K, Pamer EG and Li MO: The cellular and molecular
origin of tumor-associated macrophages. Science. 344:921–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Raggi C, Mousa HS, Correnti M, Sica A and
Invernizzi P: Cancer stem cells and tumor-associated macrophages: A
roadmap for multitargeting strategies. Oncogene. 35:671–682. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jinushi M, Chiba S, Yoshiyama H, Masutomi
K, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Yagita H, Takaoka A and Tahara H:
Tumor-associated macrophages regulate tumorigenicity and anticancer
drug responses of cancer stem/initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:12425–12430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ding J, Jin W, Chen C, Shao Z and Wu J:
Tumor associated macrophage × cancer cell hybrids may acquire
cancer stem cell properties in breast cancer. PLoS One.
7:e419422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ye XZ, Xu SL, Xin YH, Yu SC, Ping YF, Chen
L, Xiao HL, Wang B, Yi L, Wang QL, et al: Tumor-associated
microglia/macrophages enhance the invasion of glioma stem-like
cells via TGF-β1 signaling pathway. J Immunol. 189:444–453. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fan QM, Jing YY, Yu GF, Kou XR, Ye F, Gao
L, Li R, Zhao QD, Yang Y, Lu ZH and Wei LX: Tumor-associated
macrophages promote cancer stem cell-like properties via
transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 352:160–168.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yang J, Liao D, Chen C, Liu Y, Chuang TH,
Xiang R, Markowitz D, Reisfeld RA and Luo Y: Tumor-associated
macrophages regulate murine breast cancer stem cells through a
novel paracrine EGFR/Stat3/Sox-2 signaling pathway. Stem Cells.
31:248–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhou N, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Lei Z, Hu R, Li
H, Mao Y, Wang X, Irwin DM, Niu G and Tan H: Exposure of
tumor-associated macrophages to apoptotic MCF-7 cells promotes
breast cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:11966–11982.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wan S, Zhao E, Kryczek I, Vatan L,
Sadovskaya A, Ludema G, Simeone DM, Zou W and Welling TH:
Tumor-associated macrophages produce interleukin 6 and signal via
STAT3 to promote expansion of human hepatocellular carcinoma stem
cells. Gastroenterology. 147:1393–1404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Tham M, Tan KW, Keeble J, Wang X, Hubert
S, Barron L, Tan NS, Kato M, Prevost-Blondel A, Angeli V and
Abastado JP: Melanoma-initiating cells exploit M2 macrophage TGFβ
and arginase pathway for survival and proliferation. Oncotarget.
5:12027–12042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhou W, Ke SQ, Huang Z, Flavahan W, Fang
X, Paul J, Wu L, Sloan AE, McLendon RE, Li X, et al: Periostin
secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated
macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat Cell Biol.
17:170–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shi Y, Ping Y, Zhang X and Bian XW:
Hostile takeover: Glioma stem cells recruit TAMs to support tumor
progression. Cell Stem Cell. 16:219–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
He KF, Zhang L, Huang CF, Ma SR, Wang YF,
Wang WM, Zhao ZL, Liu B, Zhao YF, Zhang WF and Sun ZJ: CD163+
tumor-associated macrophages correlated with poor prognosis and
cancer stem cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int.
2014:8386322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hou YC, Chao YJ, Tung HL, Wang HC and Shan
YS: Coexpression of CD44-positive/CD133-positive cancer stem cells
and CD204-positive tumor-associated macrophages is a predictor of
survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer.
120:2766–2777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|