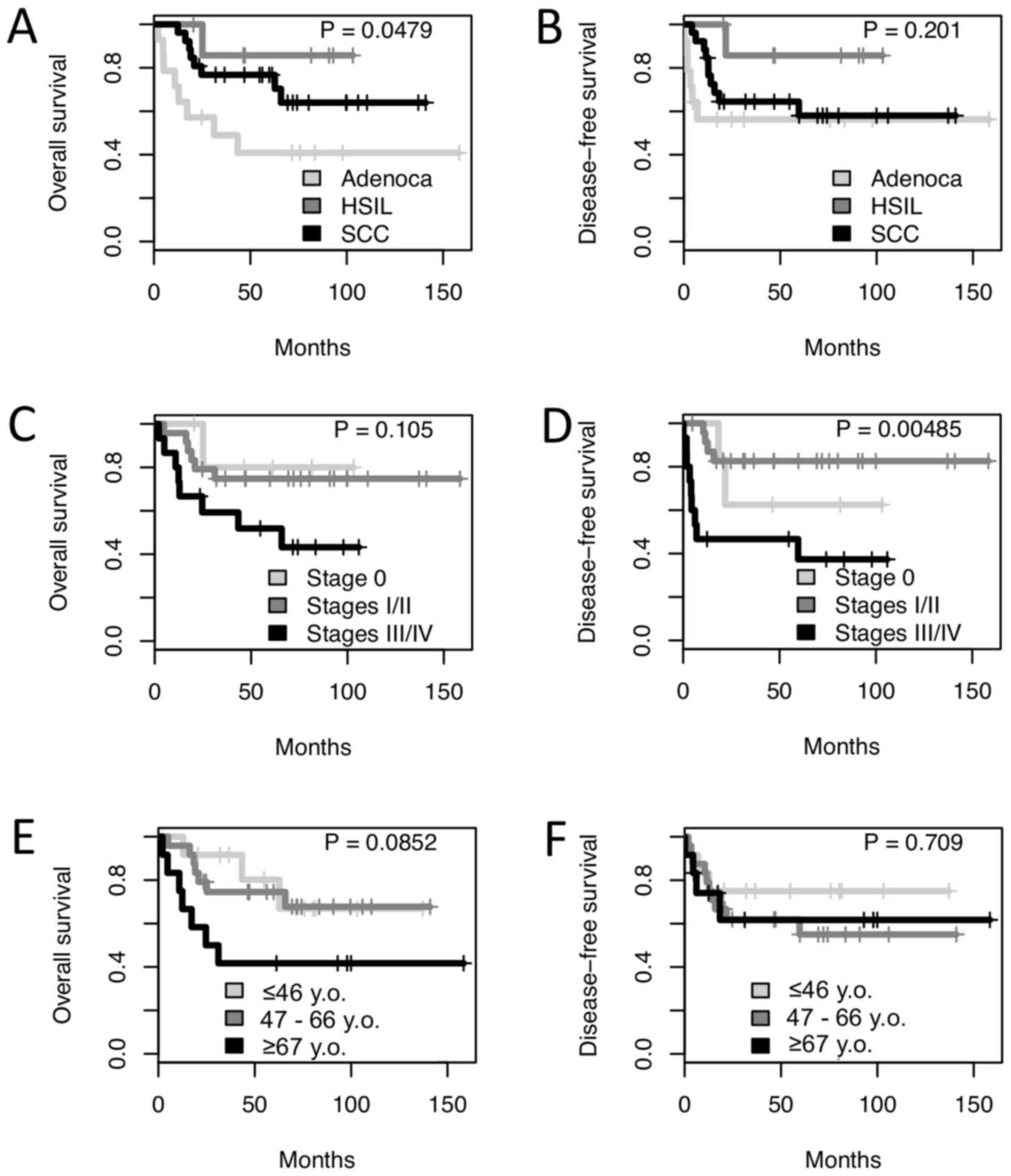
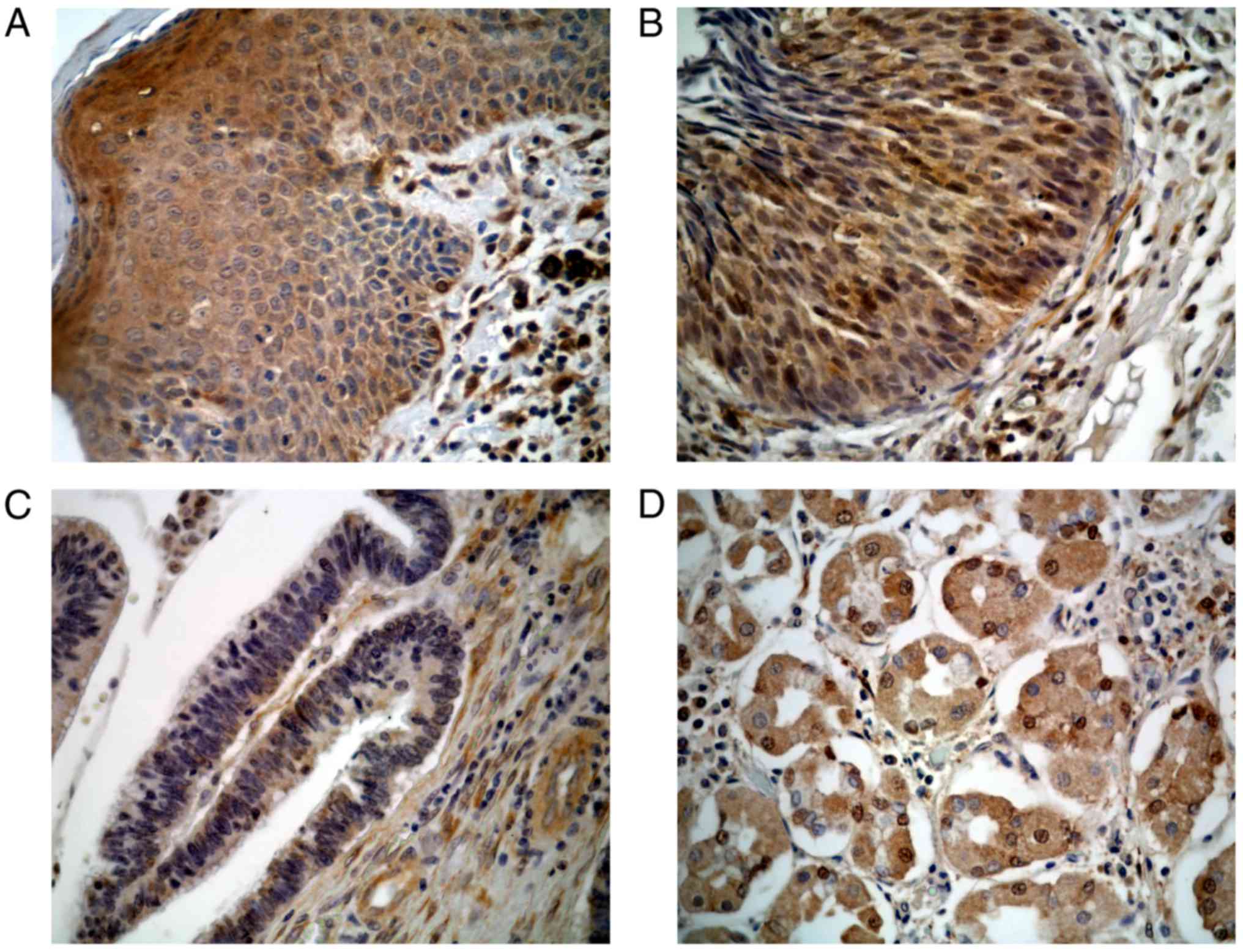
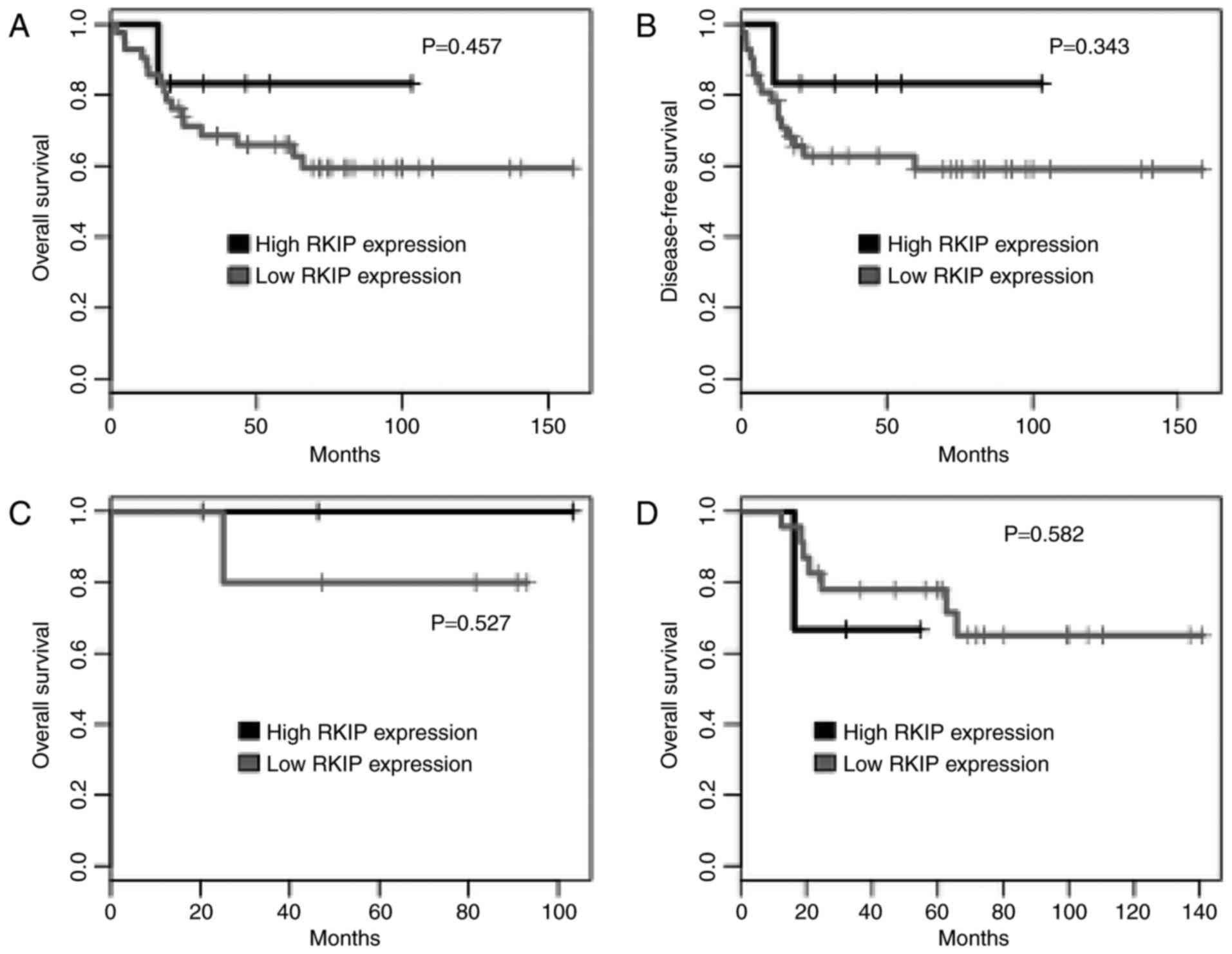
|
1
|
Nelson RA, Levine AM, Bernstein L, Smith
DD and Lai LL: Changing patterns of anal canal carcinoma in the
United States. J Clin Oncol. 31:1569–1575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deans GT, McAleer JJ and Spence RA:
Malignant anal tumours. Br J Surg. 81:500–508. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bosman FT: World Health Organization and
International Agency for Research on Cancer: WHO classification of
tumours of the digestive system. IARC Press; Lyon; 2010
|
|
5
|
Leonard D, Beddy D and Dozois EJ:
Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg.
24:54–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Serup-Hansen E, Linnemann D,
Skovrider-Ruminski W, Høgdall E, Geertsen PF and Havsteen H: Human
papillomavirus genotyping and p16 expression as prognostic factors
for patients with American joint committee on cancer stages I to
III carcinoma of the anal canal. J Clin Oncol. 32:1812–1817. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burgos J, Curran A, Tallada N, Guelar A,
Navarro J, Landolfi S, Villar J, Crespo M, Ribera E and Falcó V:
Risk of progression to high-grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia in
HIV-infected MSM. AIDS. 29:695–702. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stier EA, Sebring MC, Mendez AE, Ba FS,
Trimble DD and Chiao EY: Prevalence of anal human papillomavirus
infection and anal HPV-related disorders in women: A systematic
review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213:278–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doorbar J: Molecular biology of human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci (Lond).
110:525–541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doorbar J: Model systems of human
papillomavirus-associated disease. J Pathol. 238:166–179. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ajiro M and Zheng ZM: Oncogenes and RNA
splicing of human tumor viruses. Emerg Microbes Infect. 3:e632014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ajani JA, Wang X, Izzo JG, Crane CH, Eng
C, Skibber JM, Das P and Rashid A: Molecular biomarkers correlate
with disease-free survival in patients with anal canal carcinoma
treated with chemoradiation. Dig Dis Sci. 55:1098–1105. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D,
Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, McFerran B, Wyche J, Kolch W and Sedivy
JM: Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing
kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol.
21:7207–7217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P,
McFerran B, Kaiser C, Fee F, Katsanakis KD, Rose DW, Mischak H, et
al: Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling
by RKIP. Nature. 401:173–177. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lorenz K, Lohse MJ and Quitterer U:
Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to
GRK-2. Nature. 426:574–579. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Odabaei G, Chatterjee D, Jazirehi AR,
Goodglick L, Yeung K and Bonavida B: Raf-1 kinase inhibitor
protein: Structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and
pivotal role in apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res. 91:169–200. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wang LY, Feng F, Zhao Y, Huang MY,
Shao Q, Chen C, Sheng H, Chen DL, Zeng ZL, et al: Effect of Raf
kinase inhibitor protein expression on malignant biological
behavior and progression of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep.
34:2106–2114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martinho O, Gouveia A, Silva P, Pimenta A,
Reis RM and Lopes JM: Loss of RKIP expression is associated with
poor survival in GISTs. Virchows Arch. 455:277–284. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martinho O, Simões K, Longatto-Filho A,
Jacob CE, Zilberstein B, Bresciani C, Gama-Rodrigues J, Cecconello
I, Alves V and Reis RM: Absence of RKIP expression is an
independent prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer patients. Oncol
Rep. 29:690–696. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mai S, Welzel G, Ottstadt M, Lohr F,
Severa S, Prigge ES, Wentzensen N, Trunk MJ, Wenz F, von
Knebel-Doeberitz M and Reuschenbach M: Prognostic relevance of HPV
infection and p16 overexpression in squamous cell anal cancer. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 93:819–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meulendijks D, Tomasoa NB, Dewit L, Smits
PH, Bakker R, van Velthuysen ML, Rosenberg EH, Beijnen JH,
Schellens JH and Cats A: HPV-negative squamous cell carcinoma of
the anal canal is unresponsive to standard treatment and frequently
carries disruptive mutations in TP53. Br J Cancer. 112:1358–1366.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smaglo BG, Tesfaye A, Halfdanarson TR,
Meyer JE, Wang J, Gatalica Z, Reddy S, Arguello D and Boland PM:
Comprehensive multiplatform biomarker analysis of 199 anal squamous
cell carcinomas. Oncotarget. 6:43594–43604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, de
Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, Kalogeras KT, Kotoula V,
Papamichael D, Laurent-Puig P, et al: Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS,
and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy
in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A
retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 11:753–762. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bidinotto LT, Véo CA, Loaiza EA, de França
AP, Lorenzi AT, Rosa LA, de Oliveira CM, Levi JE, Scapulatempo-Neto
C, Longatto-Filho A and Reis RM: Low mutation percentage of KRAS
and BRAF genes in Brazilian anal tumors. Mol Med Rep. 14:3791–3797.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scapulatempo-Neto C, Veo C, Fregnani JHTG,
Lorenzi A, Mafra A, Melani AGF, Loaiza EAA, Rosa LAR, de Oliveira
CM, Levi JE and Longatto-Filho A: Characterization of topoisomerase
II α and minichromosome maintenance protein 2 expression in anal
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 13:1891–1898. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martinho O, Campos M, Ribeiro G, Penna V,
Curcelli EC, Olivieri MV, Morini S, Scapulatempo C, Abrahão-Machado
LF and Reis RM: Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression and
prognostic value in soft tissue sarcomas. Pathobiology. 83:41–46.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matalon SA, Mamon HJ, Fuchs CS, Doyle LA,
Tirumani SH, Ramaiya NH and Rosenthal MH: Anorectal cancer:
Critical anatomic and staging distinctions that affect use of
radiation therapy. Radiographics. 35:2090–2107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Franklin RA, Giri S, Valasareddy P, Lands
LT and Martin MG: Comparative survival of patients with anal
adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the anus, and rectal
adenocarcinoma. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 15:47–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Rock CE, Stewart
AK, Ko CY and Halverson A: Outcomes and prognostic factors for
squamous-cell carcinoma of the anal canal: Analysis of patients
from the national cancer data base. Dis Colon Rectum. 52:624–631.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vandamme D, Herrero A, Al-Mulla F and
Kolch W: Regulation of the MAPK pathway by raf kinase inhibitory
protein. Crit Rev Oncog. 19:405–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fedchenko N and Reifenrath J: Different
approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry
analysis results in the bone tissue-a review. Diagn Pathol.
9:2212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu CJ, Zhou L, Zhang J, Huang C and Zhang
GM: Immunohistochemical detection of Raf kinase inhibitor protein
in normal cervical tissue and cervical cancer tissue. J Int Med
Res. 39:229–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|