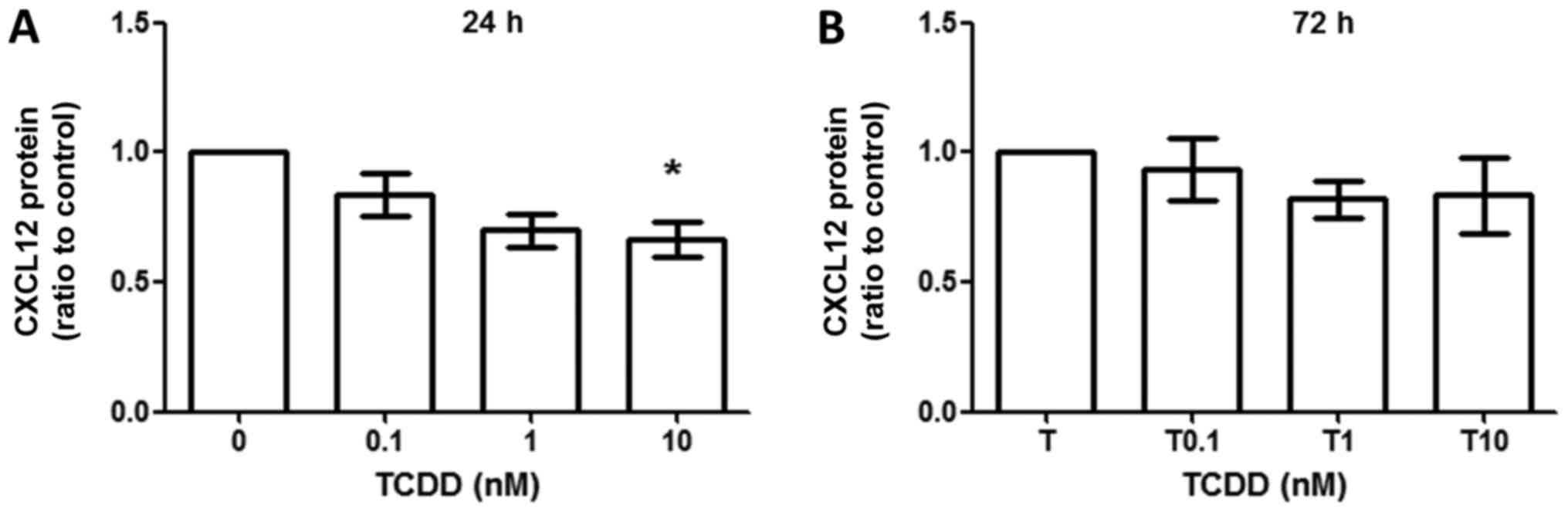
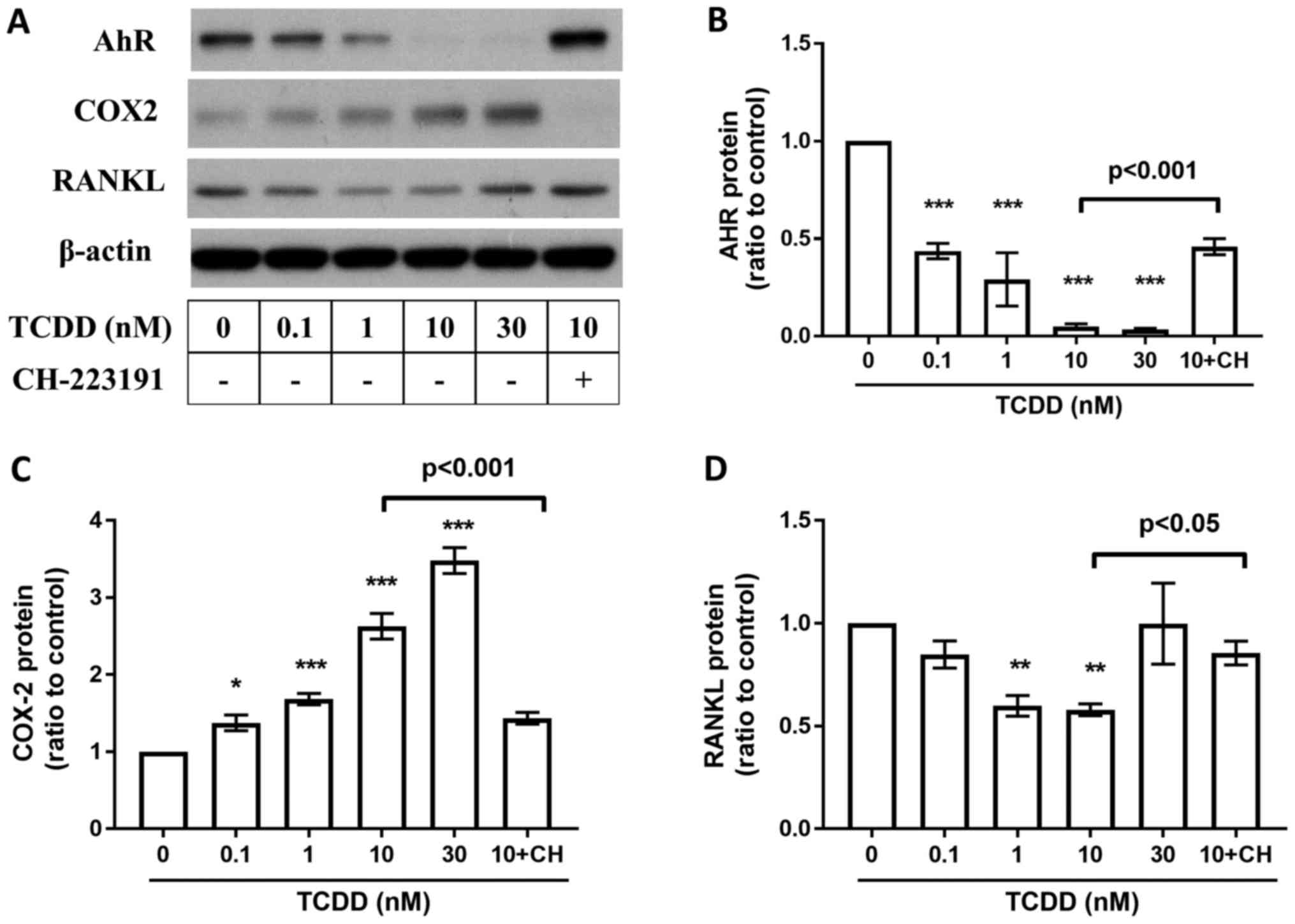
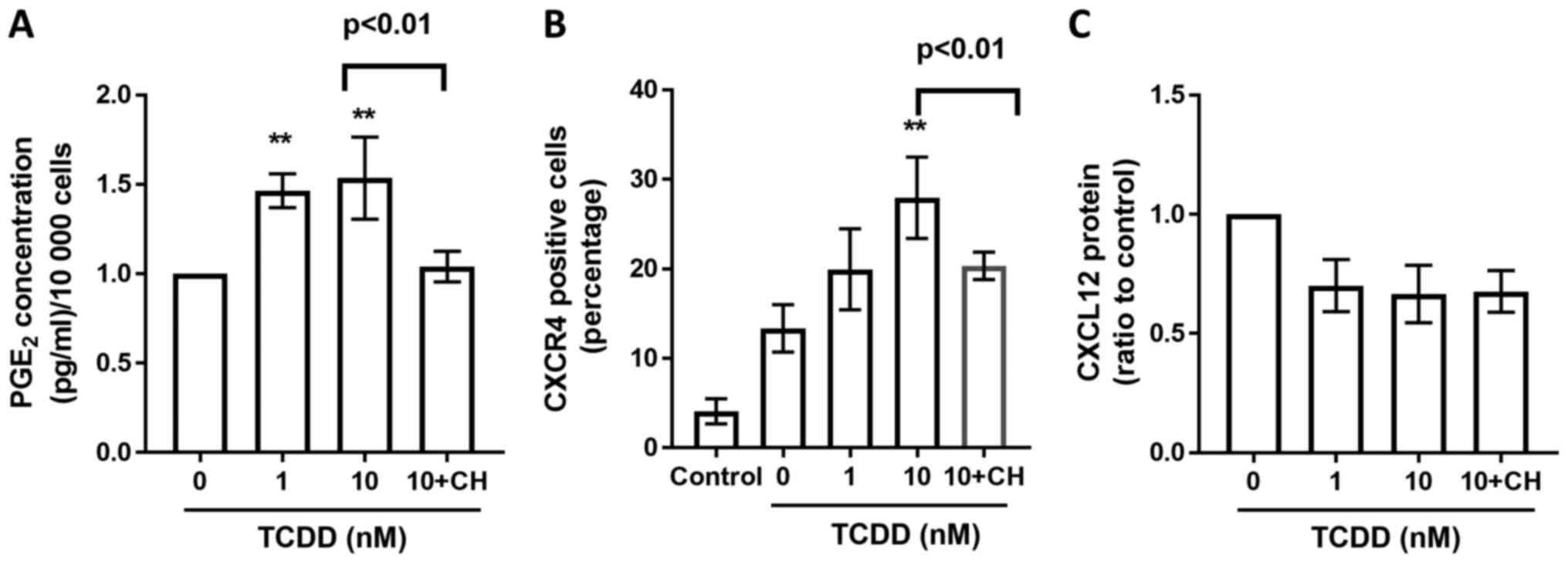
|
1
|
Harada S and Rodan GA: Control of
osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature.
423:349–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Trieb K and Windhager R: Receptor
activator of nuclear factor κB expression is a prognostic factor in
human osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 10:1813–1815. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Caetano-Lopes J, Canhão H and Fonseca JE:
Osteoblasts and bone formation. Acta Reumatol Port. 32:103–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yellowley C: CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling and
other recruitment and homing pathways in fracture repair. Bonekey
Rep. 2:3002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shahnazari M, Chu V, Wronski TJ, Nissenson
RA and Halloran BP: CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in the osteoblast
regulates the mesenchymal stem cell and osteoclast lineage
populations. FASEB J. 27:3505–3513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu C, Fuertes E, Flexeder C, Hofbauer LC,
Berdel D, Hoffmann B, Kratzsch J, von Berg A and Heinrich J:
GINIplus Study Group; LISAplus Study Group: Associations between
ambient air pollution and bone turnover markers in 10-year old
children: Results from the GINIplus and LISAplus studies. Int J Hyg
Environ Health. 218:58–65. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qi H, Aguiar DJ, Williams SM, La Pean A,
Pan W and Verfaillie CM: Identification of genes responsible for
osteoblast differentiation from human mesodermal progenitor cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:3305–3310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ray S and Swanson HI: Activation of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor by TCDD inhibits senescence: A tumor
promoting event? Biochem Pharmacol. 77:681–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barouki R, Coumoul X and
Fernandez-Salguero PM: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor, more than a
xenobiotic-interacting protein. FEBS Lett. 581:3608–3615. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Veldhoen M, Hirota K, Westendorf AM, Buer
J, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC and Stockinger B: The aryl hydrocarbon
receptor links TH17-cell-mediated autoimmunity to environmental
toxins. Nature. 453:106–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mimura J and Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Functional
role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1619:263–268. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harvey WA, Jurgensen K, Pu X, Lamb CL,
Cornell KA, Clark RJ, Klocke C and Mitchell KA: Exposure to
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases human hepatic
stellate cell activation. Toxicology. 344–346:26–33. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Herlin M, Finnilä MA, Zioupos P, Aula A,
Risteli J, Miettinen HM, Jämsä T, Tuukkanen J, Korkalainen M,
Håkansson H, et al: New insights to the role of aryl hydrocarbon
receptor in bone phenotype and in dioxin-induced modulation of bone
microarchitecture and material properties. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
273:219–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Korkalainen M, Kallio E, Olkku A, Nelo K,
Ilvesaro J, Tuukkanen J, Mahonen A and Viluksela M: Dioxins
interfere with differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Bone. 44:1134–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schwarz M and Appel KE: Carcinogenic risks
of dioxin: Mechanistic considerations. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
43:19–34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Garcia-Moure M, Martinez-Vélez N,
Patiño-García A and Alonso MM: Oncolytic adenoviruses as a
therapeutic approach for osteosarcoma: A new hope. J Bone Oncol.
9:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ and Thomas
DM: Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer.
14:722–735. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dalla-Torre CA, de Toledo SRC, Yoshimoto
M, Petrilli AS, Andrade JA, Chilton-MacNeill S, Squire JA and
Zielenska M: Expression of major vault protein gene in osteosarcoma
patients. J Orthop Res. 25:958–963. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Le Vu B, de Vathaire F, Shamsaldin A,
Hawkins MM, Grimaud E, Hardiman C, Diallo I, Vassal G, Bessa E,
Campbell S, et al: Radiation dose, chemotherapy and risk of
osteosarcoma after solid tumours during childhood. Int J Cancer.
77:370–377. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang YY, Huang HL, Chen YC, Hsu JT, Shieh
TM and Tsai MT: Biological characteristics of the MG-63 human
osteosarcoma cells on composite tantalum carbide/amorphous carbon
films. PLoS One. 9:e955902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Svec D, Tichopad A, Novosadova V, Pfaffl
MW and Kubista M: How good is a PCR efficiency estimate:
Recommendations for precise and robust qPCR efficiency assessments.
Biomol Detect Quantif. 3:9–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Q and Baldwin KT:
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced degradation of aryl
hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Role of the transcription activaton and DNA binding of AhR. J Biol
Chem. 275:8432–8438. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Benayahu D, Shur I, Marom R, Meller I and
Issakov J: Cellular and molecular properties associated with
osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 84:108–114. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bilbe G, Roberts E, Birch M and Evans DB:
PCR phenotyping of cytokines, growth factors and their receptors
and bone matrix proteins in human osteoblast-like cell lines. Bone.
19:437–445. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pautke C, Schieker M, Tischer T, Kolk A,
Neth P, Mutschler W and Milz S: Characterization of osteosarcoma
cell lines MG-63, Saos-2 and U-2 OS in comparison to human
osteoblasts. Anticancer Res. 24:3743–3748. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miki Y, Hata S, Ono K, Suzuki T, Ito K,
Kumamoto H and Sasano H: Roles of Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
aromatase-dependent cell proliferation in human osteoblasts. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:pii: E2159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Denison MS and Nagy SR: Activation of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and
endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:309–334. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Denison MS, Soshilov AA, He G, DeGroot DE
and Zhao B: Exactly the same but different: Promiscuity and
diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the Aryl
hydrocarbon (Dioxin) receptor. Toxicol Sci. 124:1–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Walker NJ: Unraveling the complexities of
the mechanism of action of dioxins. Toxicol Sci. 95:297–299. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huff J, Lucier G and Tritscher A:
Carcinogenicity of TCDD: Experimental, mechanistic, and
epidemiologic evidence. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 34:343–372.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eskenazi B, Warner M, Sirtori M, Fuerst T,
Rauch SA, Brambilla P, Mocarelli P and Rubinacci A: Serum dioxin
concentrations and bone density and structure in the Seveso Women's
Health Study. Environ Health Perspect. 122:51–57. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clohisy JC, Frazier E, Hirayama T and
Abu-Amer Y: RANKL is an essential cytokine mediator of
polymethylmethacrylate particle-induced osteoclastogenesis. J
Orthop Res. 21:202–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qu L and Liu B: Cyclooxygeanse-2 promotes
metastasis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int. 15:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rezzonico R, Schmid-Alliana A, Romey G,
Bourget-Ponzio I, Breuil V, Breittmayer V, Tartare-Deckert S, Rossi
B and Schmid-Antomarchi H: Prostaglandin E2 induces interaction
between hSlo potassium channel and Syk tyrosine kinase in
osteosarcoma cells. J Bone Miner Res. 17:869–878. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu Y, Liu Q, Guo S, Zhang Q, Tang J, Liu
G, Kong D, Li J, Yan S, Wang R, et al: 2, 3, 7,
8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin promotes endothelial cell apoptosis
through activation of EP3/p38MAPK/Bcl-2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3540–3551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts
HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C and Kaidi A: The COX-2/PGE2 pathway:
Key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour
microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Obermajer N, Muthuswamy R, Odunsi K,
Edwards RP and Kalinski P: PGE2-induced CXCL12 production and CXCR4
expression controls the accumulation of human MDSCs in ovarian
cancer environment. Cancer Res. 71:7463–7470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Y, Guan GF, Chen J, Hu B, Sun C, Ma Q,
Wen YH, Qiu XC and Zhou Y: Aberrant CXCR4 and β-catenin expression
in osteosarcoma correlates with patient survival. Oncol Lett.
10:2123–2129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hsu EL, Yoon D, Choi HH, Wang F, Taylor
RT, Chen N, Zhang R and Hankinson O: A proposed mechanism for the
protective effect of dioxin against breast cancer. Toxicol Sci.
98:436–444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yun C, Katchko KM, Schallmo MS, Jeong S,
Yun J, Chen CH, Weiner JA, Park C, George A, Stupp SI, et al: Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor antagonists mitigate the effects of dioxin on
critical cellular functions in differentiating human
osteoblast-like cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19:pii: E225. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Branstetter D, Rohrbach K, Huang LY,
Soriano R, Tometsko M, Blake M, Jacob AP and Dougall WC: RANK and
RANK ligand expression in primary human osteosarcoma. J Bone Oncol.
4:59–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen Y, Di Grappa MA, Molyneux SD, McKee
TD, Waterhouse P, Penninger JM and Khokha R: RANKL blockade
prevents and treats aggressive osteosarcomas. Sci Transl Med.
7:317ra1972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|