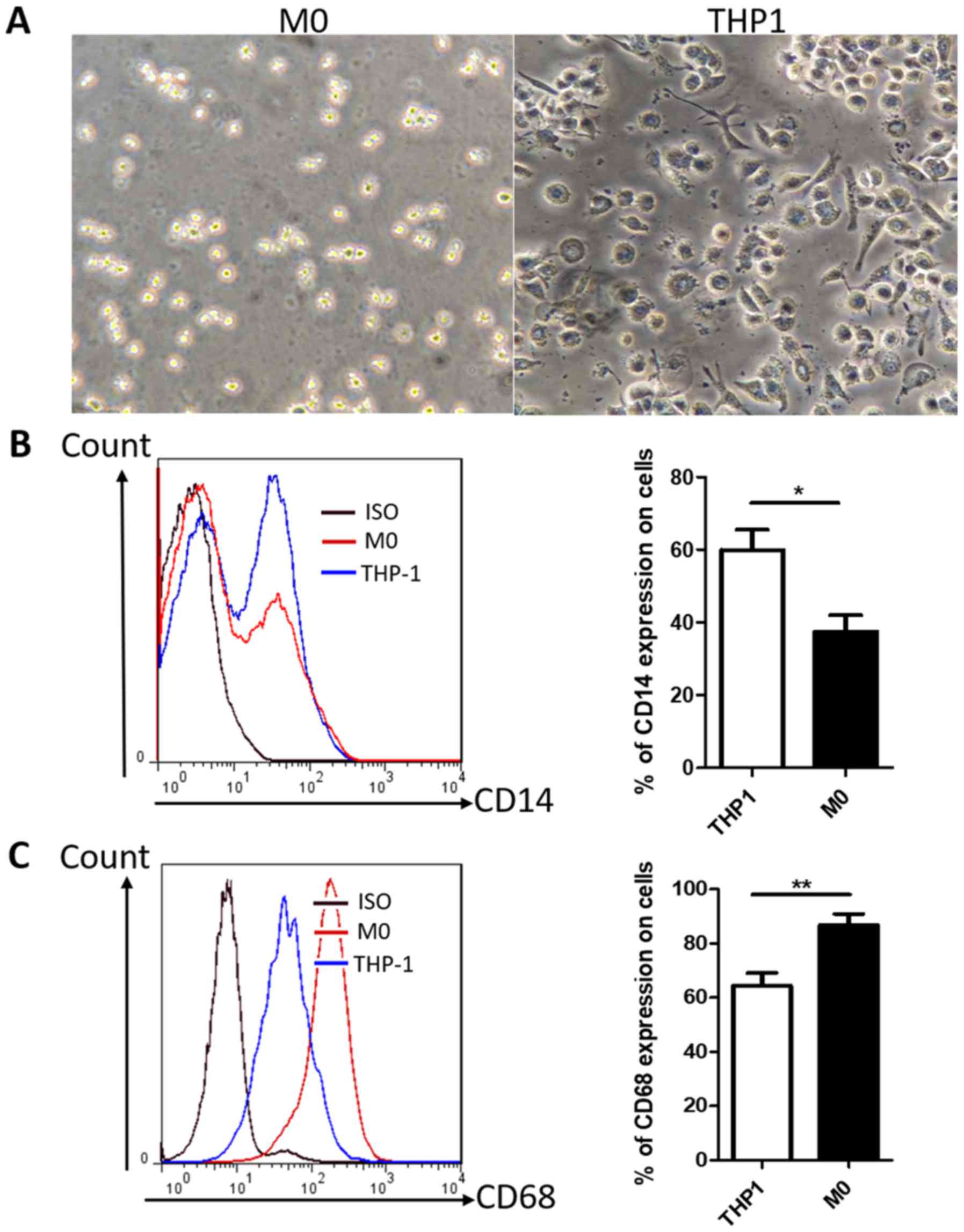
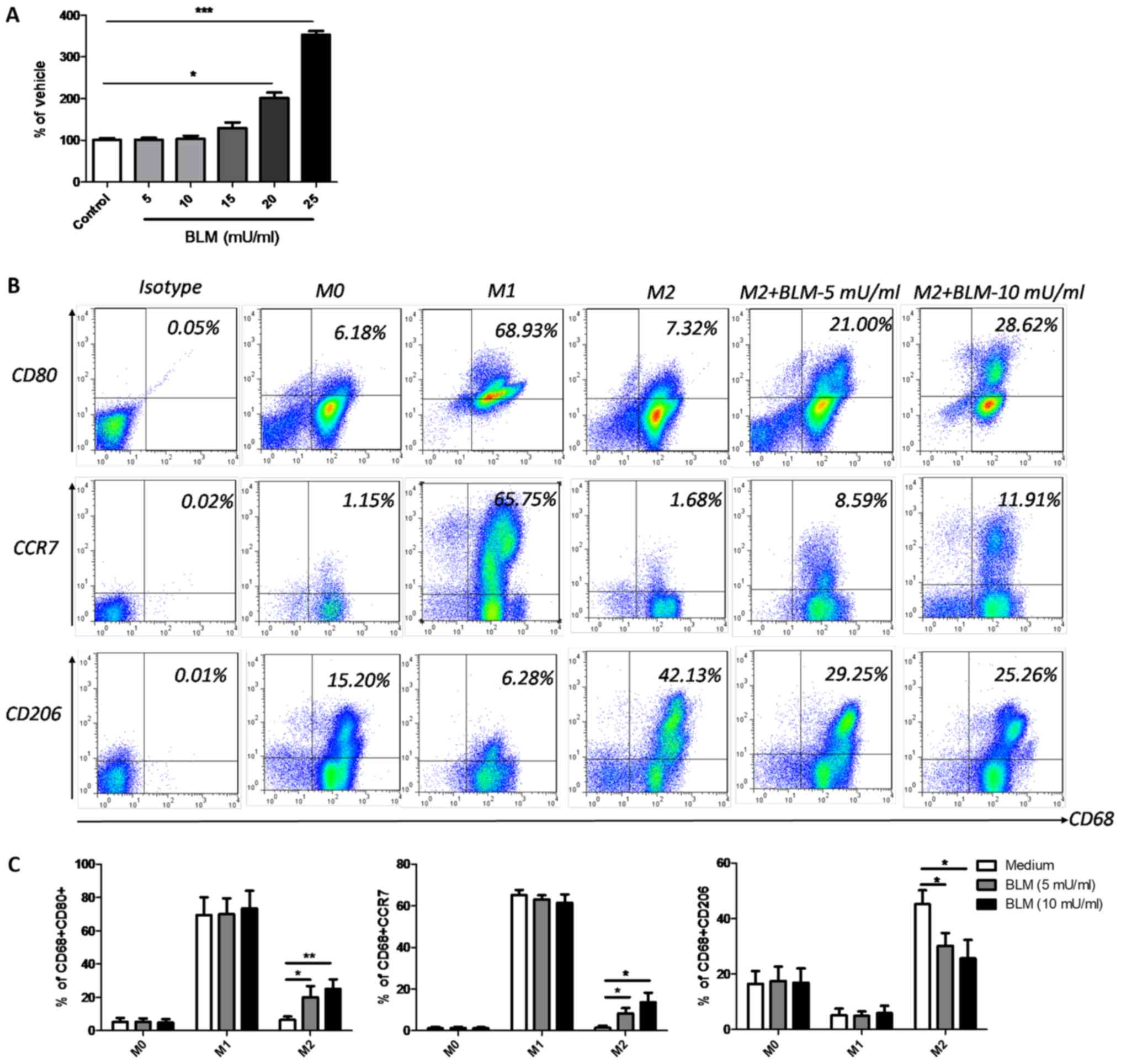
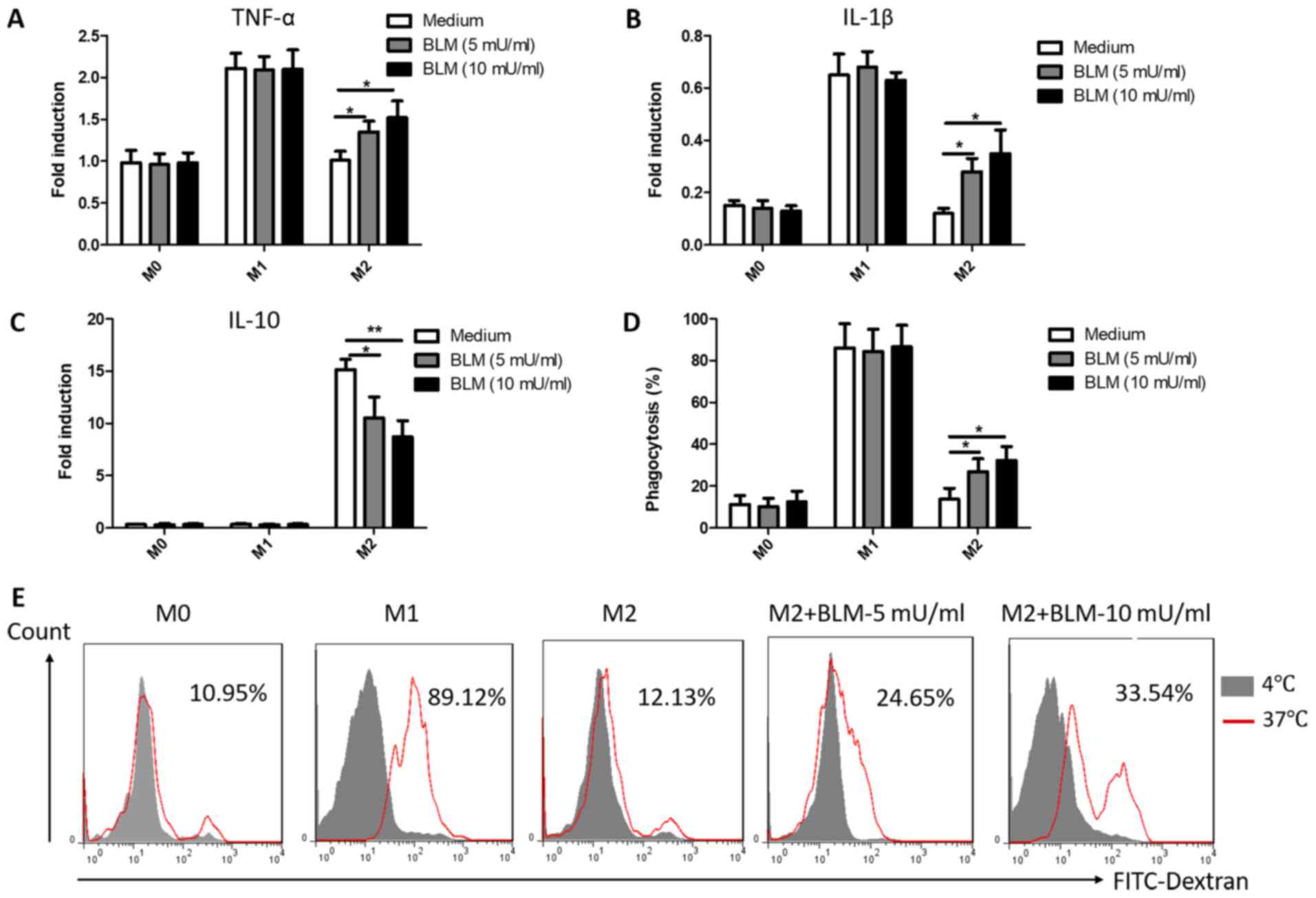
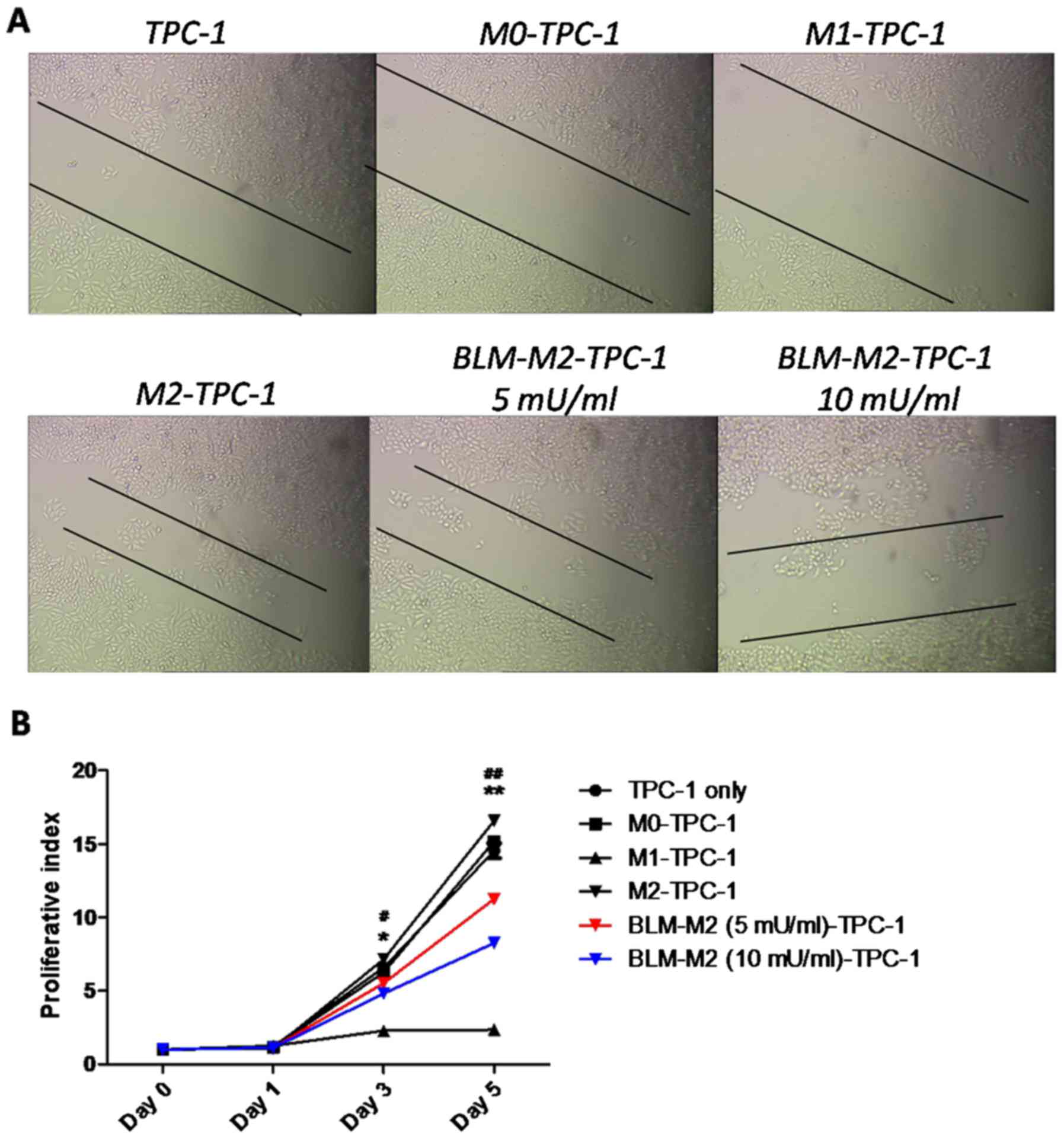
|
1
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Integrated
genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell.
159:676–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Walker S: Immunotherapy and the treatment
of non-small cell lung cancer. J Adv Pract Oncol. 7:304–306.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pusztaszeri MP, Faquin WC and Sadow PM:
Tumor-associated inflammatory cells in thyroid carcinomas. Surg
Pathol Clin. 7:501–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qing W, Fang WY, Ye L, Shen LY, Zhang XF,
Fei XC, Chen X, Wang WQ, Li XY, Xiao JC and Ning G: Density of
tumor-associated macrophages correlate with lymph node metastasis
in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 22:905–910. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quatromoni JG and Eruslanov E:
Tumor-associated macrophages: Function, phenotype and link to
prognosis in human Lung Cancer. Am J Transl Res. 4:376–389.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Allavena P, Sica A, Solinas G, Porta C and
Mantovani A: The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor
progression: The role of tumor-associated macrophages. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 66:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Can NY, Ayturk S, Celik M, Sezer YA,
Ozyilmaz F, Tastekin E, Sut N, Ustun F, Bulbul BY, Puyan FO and
Guldiken S: Histological perspective on the effects of
tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment
surrounding papillary thyroid carcinoma. Pol J Pathol. 67:332–344.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang W, Ye L, Shen L, Cai J, Huang F, Wei
Q, Fei X, Chen X, Guan H, Wang W, et al: Tumor-associated
macrophages promote the metastatic potential of thyroid papillary
cancer by releasing CXCL8. Carcinogenesis. 35:1780–1787. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang WC, Chen JY, Lee CH and Yang AH:
Expression of decoy receptor 3 in diffuse sclerosing variant of
papillary thyroid carcinoma: Correlation with M2 macrophage
differentiation and lymphatic invasion. Thyroid. 23:720–726. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lopez-Gonzalez JS, Avila-Moreno F,
Prado-Garcia H, Aguilar-Cazares D, Mandoki JJ and Meneses-Flores M:
Lung carcinomas decrease the number of monocytes/macrophages (CD14+
cells) that produce TNF-alpha. Clin Immunol. 122:323–329. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohri CM, Shikotra A, Green RH, Waller DA
and Bradding P: Macrophages within NSCLC tumour islets are
predominantly of a cytotoxic M1 phenotype associated with extended
survival. Eur Respir J. 33:118–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Redente EF, Dwyer-Nield LD, Merrick DT,
Raina K, Agarwal R, Pao W, Rice PL, Shroyer KR and Malkinson AM:
Tumor progression stage and anatomical site regulate
tumor-associated macrophage and bone marrow-derived monocyte
polarization. Am J Pathol. 176:2972–2985. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zea AH, Rodriguez PC, Atkins MB, Hernandez
C, Signoretti S, Zabaleta J, McDermott D, Quiceno D, Youmans A,
O'Neill A, et al: Arginase-producing myeloid suppressor cells in
renal cell carcinoma patients: A mechanism of tumor evasion. Cancer
Res. 65:3044–3048. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang CI, Liao JC and Kuo L: Macrophage
arginase promotes tumor cell growth and suppresses nitric
oxide-mediated tumor cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 61:1100–1106.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biswas SK, Sica A and Lewis CE: Plasticity
of macrophage function during tumor progression: Regulation by
distinct molecular mechanisms. J Immunol. 180:2011–2057. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qian BZ and Pollard JW: Macrophage
diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell.
141:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mehrpour M, Esclatine A, Beau I and
Codogno P: Overview of macroautophagy regulation in mammalian
cells. Cell Res. 20:748–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ruffell B, Affara NI and Coussens LM:
Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment.
Trends Immunol. 33:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Batschinski K, Dervisis N, Kitchell B,
Newman R and Erfourth T: Combination of bleomycin and cytosine
arabinoside chemotherapy for relapsed canine lymphoma. J Am Anim
Hosp Assoc. 54:150–155. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ng K, Duncan S, Shamash J and Alifrangis
C: Dose intense chemotherapy in the management of poor prognosis
and relapsed testicular cancer: Experiences and controversies.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:431–436. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Porwal PK, Dubey KP, Morey A, Singh H,
Pooja S and Bose A: Bleomycin sclerotherapy in lymphangiomas of
head and neck: prospective study of 8 cases. Indian J Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 70:145–148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Racnik J, Svara T, Zadravec M, Gombac M,
Cemazar M, Sersa G and Tozon N: Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin
of different types of cutaneous tumours in a ferret (Mustela
Putorius Furo). Radiol Oncol. 52:98–104. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai Y, Sun R, Wang R, Ren JG, Zhang W,
Zhao YF and Zhao JH: The activation of Akt/mTOR pathway by
bleomycin in Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human
submandibular gland cells: A treatment mechanism of bleomycin for
mucoceles of the salivary glands. Biomed Pharmacother. 90:109–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mouratis MA and Aidinis V: Modeling
pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 17:355–361.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weng D, Chen JX, Li HH, Liu F, Zhou LD,
Liu HP, Zheng RJ, Jiang Y, Liu ZH and Ge B: 2-aminopurine
suppresses the TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Discov.
4:172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung WJ, Lee SY, Choi SI, Kim BK, Lee EJ,
In KH and Lee MG: Toll-like receptor expression in pulmonary
sensory neurons in the bleomycin-induced fibrosis model. PLoS One.
13:e01931172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bolzan AD and Bianchi MS: DNA and
chromosome damage induced by bleomycin in mammalian cells: An
update. Mutat Res. 775:51–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Massonneau J, Ouellet C, Lucien F, Dubois
CM, Tyler J and Boissonneault G: Suboptimal extracellular pH values
alter DNA damage response to induced double-strand breaks. FEBS
Open Bio. 8:416–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang W, Wang G, Phelps DS, Al-Mondhiry H
and Floros J: Combined SP-A-bleomycin effect on cytokines by THP-1
cells: Impact of surfactant lipids on this effect. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 283:L94–L102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Razonable RR, Henault M and Paya CV:
Stimulation of toll-like receptor 2 with bleomycin results in
cellular activation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and
chemokines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 210:181–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Sakazaki Y, Kato S,
Young HA and Aizawa H: Role of proinflammatory cytokines IL-18 and
IL-1beta in bleomycin-induced lung injury in humans and mice. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 41:661–670. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Genin M, Clement F, Fattaccioli A, Raes M
and Michiels C: M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells
differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide.
BMC Cancer. 15:5772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Steinbach F and Thiele B: Phenotypic
investigation of mononuclear phagocytes by flow cytometry. J
Immunol Methods. 174:109–122. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB and Lewis
CE: The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour
angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:618–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan A, Hsiao YJ, Chen HY, Chen HW, Ho CC,
Chen YY, Liu YC, Hong TH, Yu SL, Chen JJ and Yang PC: Opposite
effects of M1 and M2 macrophage subtypes on lung cancer
progression. Sci Rep. 5:142732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Reeves AR, Spiller KL, Freytes DO,
Vunjak-Novakovic G and Kaplan DL: Controlled release of cytokines
using silk-biomaterials for macrophage polarization. Biomaterials.
73:272–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pang L, Han S, Jiao Y, Jiang S, He X and
Li P: Bu Fei Decoction attenuates the tumor associated macrophage
stimulated proliferation, migration, invasion and immunosuppression
of non-small cell Lung Cancer, partially via IL-10 and PD-L1
regulation. Int J Oncol. 51:25–38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kang H, Zhang J, Wang B, Liu M, Zhao J,
Yang M and Li Y: Puerarin inhibits M2 polarization and metastasis
of tumor-associated macrophages from NSCLC xenograft model via
inactivating MEK/ERK 1/2 pathway. Int J Oncol. 50:545–554. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho SW, Kim YA, Sun HJ, Kim YA, Oh BC, Yi
KH, Park DJ and Park YJ: CXCL16 signaling mediated macrophage
effects on tumor invasion of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 23:113–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Komohara Y, Fujiwara Y, Ohnishi K and
Takeya M: Tumor-associated macrophages: Potential therapeutic
targets for anti-cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:180–185.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gocheva V, Wang HW, Gadea BB, Shree T,
Hunter KE, Garfall AL, Berman T and Joyce JA: IL-4 induces
cathepsin protease activity in tumor-associated macrophages to
promote cancer growth and invasion. Genes Dev. 24:241–255. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang R, Zhang J, Chen S, Lu M, Luo X, Yao
S, Liu S, Qin Y and Chen H: Tumor-associated macrophages provide a
suitable microenvironment for non-small Lung Cancer invasion and
progression. Lung Cancer. 74:188–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Komohara Y, Jinushi M and Takeya M:
Clinical significance of macrophage heterogeneity in human
malignant tumors. Cancer Sci. 105:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rolny C, Mazzone M, Tugues S, Laoui D,
Johansson I, Coulon C, Squadrito ML, Segura I, Li X, Knevels E, et
al: HRG inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by inducing macrophage
polarization and vessel normalization through downregulation of
PlGF. Cancer Cell. 19:31–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Almatroodi SA, McDonald CF, Darby IA and
Pouniotis DS: Characterization of M1/M2 tumour-associated
macrophages (TAMs) and Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with
NSCLC. Cancer Microenviron. 9:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Muraille E, Leo O and Moser M: TH1/TH2
paradigm extended: Macrophage polarization as an unappreciated
pathogen-driven escape mechanism. Front Immunol. 5:6032014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim S, Cho SW, Min HS, Kim KM, Yeom GJ,
Kim EY, Lee KE, Yun YG, Park DJ and Park YJ: The expression of
tumor-associated macrophages in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 28:192–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mellor AL and Munn DH: Creating immune
privilege: Active local suppression that benefits friends, but
protects foes. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:74–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A and
Allavena P: Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2
polarised population promoting tumour progression: Potential
targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer. 42:717–727. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu CP, Zhang X, Tan QL, Xu WX, Zhou CY,
Luo M, Li X, Huang RY and Zeng X: NF-κB pathways are involved in M1
polarization of RAW 264.7 macrophage by polyporus polysaccharide in
the tumor microenvironment. PLoS One. 12:e01883172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gong H, Cao Y, Han G, Zhang Y, You Q, Wang
Y and Pan Y: p53/microRNA-374b/AKT1 regulates colorectal cancer
cell apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Int J Oncol.
50:1785–1791. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang L, Zhao W, Wei P, Zuo W and Zhu S:
Tumor suppressor p53 induces miR-15a processing to inhibit neuronal
apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP) in the apoptotic response DNA
damage in breast cancer cell. Am J Transl Res. 9:683–691.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu JF, Nie XC, Shao YC, Su WH and Ma HY:
Bleomycin suppresses the proliferation and the mobility of human
gastric cancer cells through the smad signaling pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 40:1401–1409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao N, Shang B, Zhang X, Shen C, Xu R,
Chen R and He Q: Potent antitumor actions of the new antibiotic
boningmycin through induction of apoptosis and cellular senescence.
Anticancer Drugs. 22:166–175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Uchida R, Yokota S and Tomoda H: Structure
elucidation of meroterpenoid habiterpenol, a novel abrogator of
bleomycin-induced G2 arrest in Jurkat cells, produced by
Phytohabitans suffuscus 3787_5. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 67:783–786.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang Q, Cui K, Espin-Garcia O, Cheng D,
Qiu X, Chen Z, Moore M, Bristow RG, Xu W, Der S and Liu G:
Resistance to bleomycin in cancer cell lines is characterized by
prolonged doubling time, reduced DNA damage and evasion of G2/M
arrest and apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e823632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lofdahl A, Rydell-Tormanen K,
Larsson-Callerfelt AK, AUID- and Wenglen Oho C: Pulmonary fibrosis
in vivo displays increased p21 expression reduced by 5-HT2B
receptor antagonists in vitro-a potential pathway affecting
proliferation. Sci Rep. 8:19272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Park HR, Lee EJ, Moon SC, Chung TW and Kim
KJ: Inhibition of lung cancer growth by HangAmDan-B is mediated by
macrophage activation to M1 subtype. Oncol Lett. 13:2330–2336.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Poppoe F, Chen J, Yu L and Deng F:
Macrophages polarized by expression of toxoGRA15II inhibit growth
of hepatic carcinoma. Front Immunol. 8:1372017.PubMed/NCBI
|