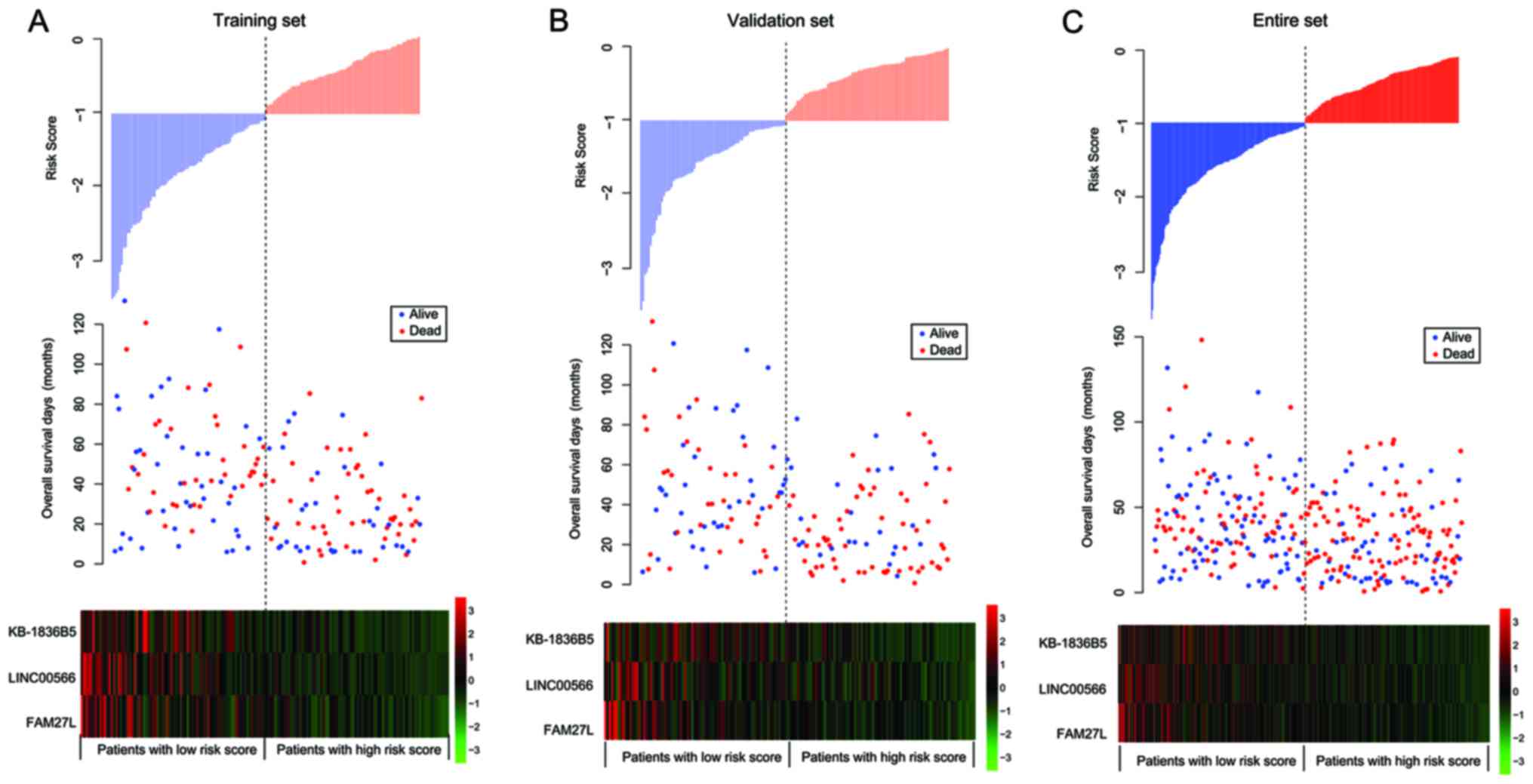
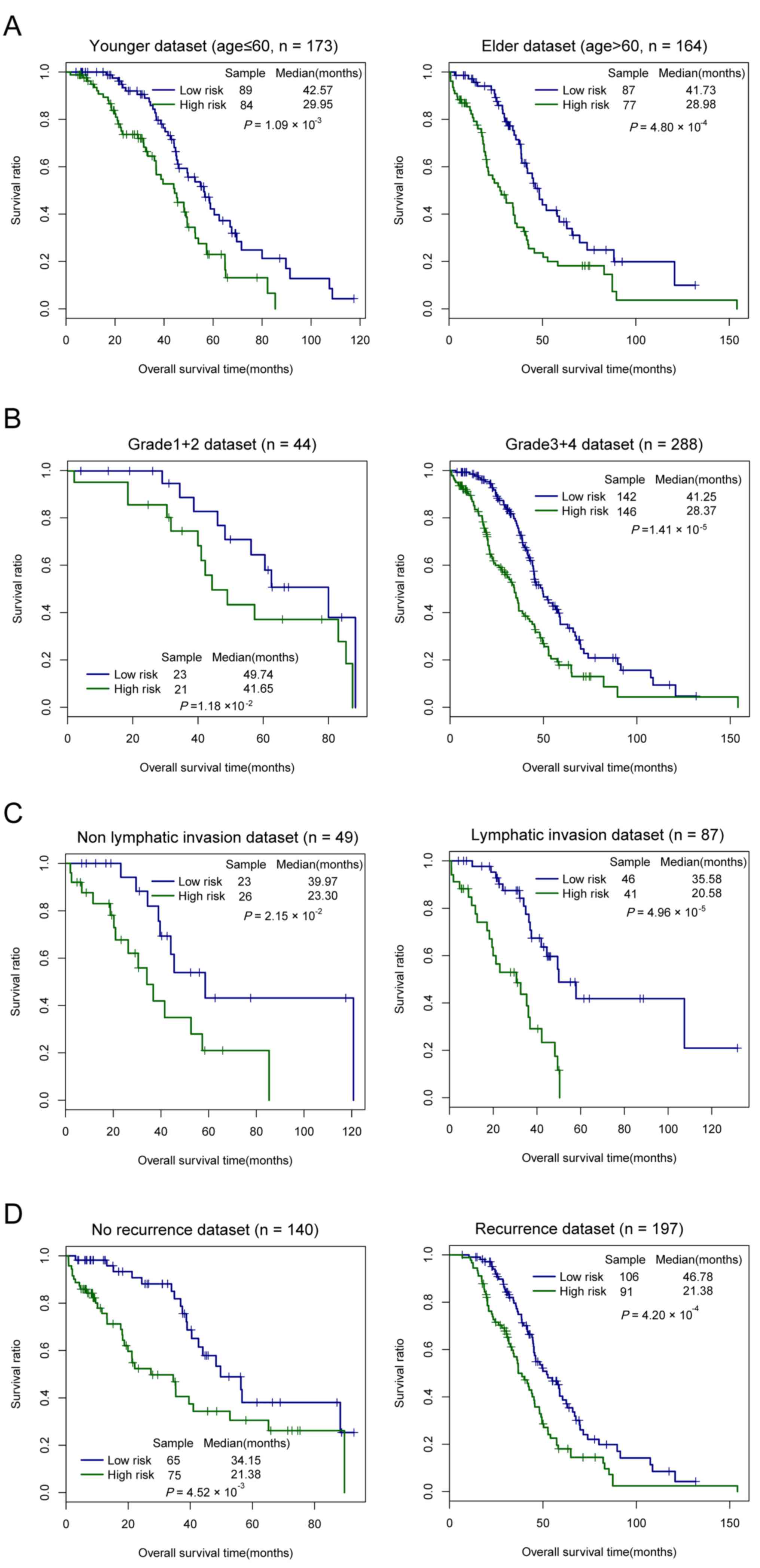
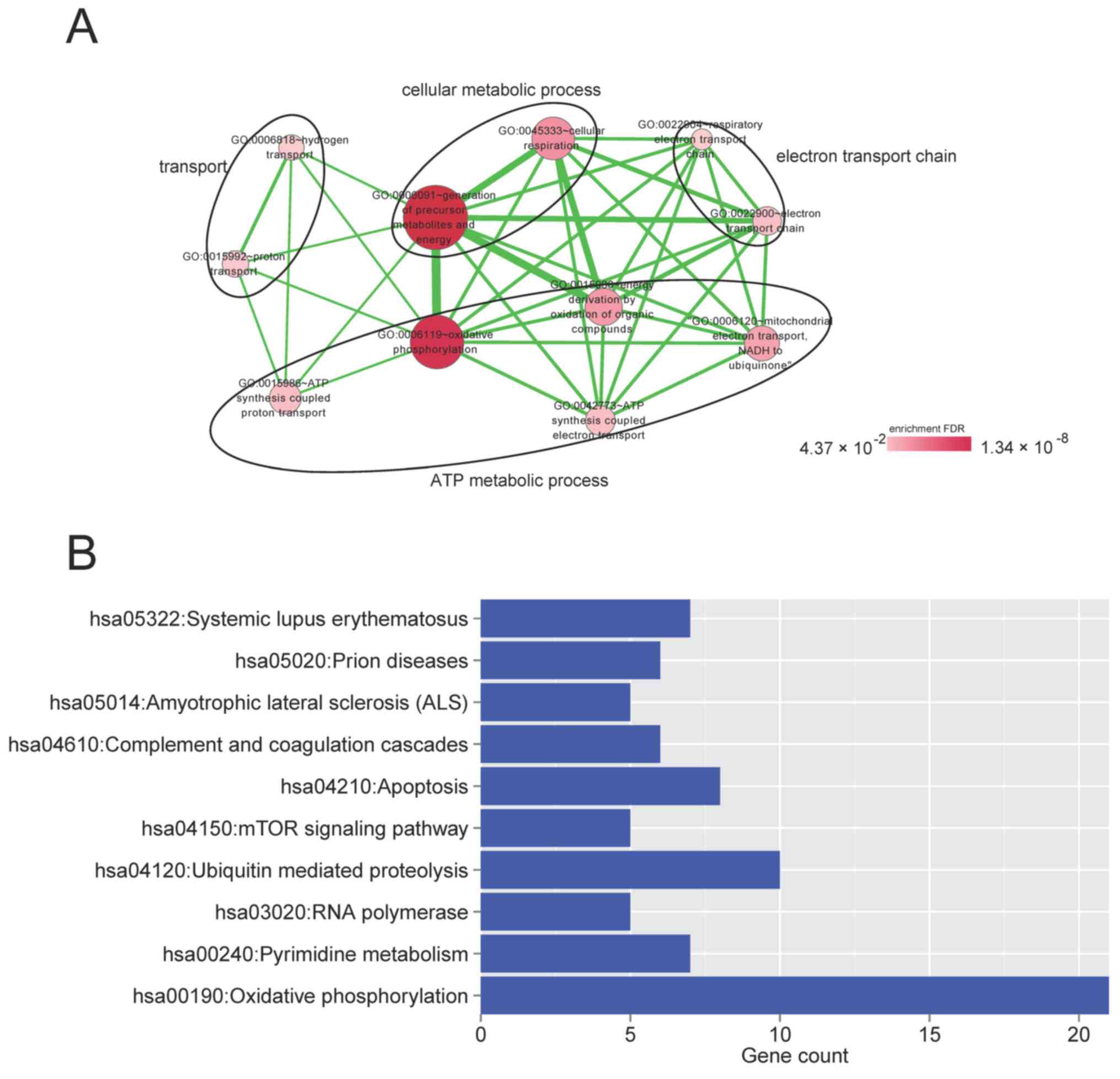
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. Ca A Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Baldwin LA, Huang B, Miller RW, Tucker T,
Goodrich ST, Podzielinski I, DeSimone CP, Ueland FR, van Nagell JR
and Seamon LG: Ten-year relative survival for epithelial ovarian
cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 120:612–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dey BK, Mueller AC and Dutta A: Long
non-coding RNAs as emerging regulators of differentiation,
development, and disease. Transcription. 5:e9440142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang G, Lu X and Yuan L: LncRNA: A link
between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul Mech.
1839:1097–1109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:12532015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren C, Li X, Wang T, Zhao C, Liang T, Zhu
Y, Li M, Yang C, Zhao Y and Zhang GM: Functions and mechanisms of
long noncoding RNAs in ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
25:566–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng Z, Guo J, Chen L, Luo N, Yang W and
Qu X: A long noncoding RNA AB073614 promotes tumorigenesis and
predicts poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
6:25381–25389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yim GW, Kim HJ, Kim LK, Kim SW, Kim S, Nam
EJ and Kim YT: Long non-coding RNA HOXA11 antisense promotes cell
proliferation and invasion and predicts patient prognosis in serous
ovarian cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 49:656–668. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen ZJ, Zhang Z, Xie BB and Zhang HY:
Clinical significance of up-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 in prognosis of
ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3373–3377.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou M, Wang X, Shi H, Cheng L, Wang Z,
Zhao H, Yang L and Sun J: Characterization of long non-coding
RNA-associated ceRNA network to reveal potential prognostic lncRNA
biomarkers in human ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 7:12598–12611.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bristow RE, Palis BE, Chi DS and Cliby WA:
The national cancer database report on advanced-stage epithelial
ovarian cancer: Impact of hospital surgical case volume on overall
survival and surgical treatment paradigm. Gynecol Oncol.
118:262–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression of RNA-Seq data at the gene level-the DESeq package.
Embl. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Robinson MD, Mccarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang P, Wang Y, Bo H, Zou X and Mao JH: A
novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict
survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55343–55351.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hanley JA: The robustness of the
‘binormal’ assumptions used in fitting ROC curves. Med Decis
Making. 8:197–203. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID bioinformatics resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:169–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Consortium GO: Gene ontology consortium:
Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:1049–1056. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Minoru K, Yoko S, Masayuki K, Miho F and
Mao T: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:457–462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qi L, Liu C, Yuan X, Kang S, Miao R, Xiao
H, Zhao G, Luo H, Bu D, Zhao H, et al: Large-scale prediction of
long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene
co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3864–3878. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nina H and Damjan G: Long non-coding RNA
in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:4655–4669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rooth C: Ovarian cancer: Risk factors,
treatment and management. Br J Nurs. 22:S23–S30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hunn J and Rodriguez GC: Ovarian cancer:
Etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology. Clin Obstet Gynecol.
55:3–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nature
Rev Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP and
Pauler FM: Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA
transcription. BMC Biol. 11:592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dello Russo C, Lisi L, Feinstein DL and
Navarra P: mTOR kinase, a key player in the regulation of glial
functions: Relevance for the therapy of multiple sclerosis. Glia.
61:301–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
at a glance. J Cell Sci. 122:3589–3594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mabuchi S, Kuroda H, Takahashi R and
Sasano T: The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 137:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Zeng J and Shen K: PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 290:1067–1078. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dobbin ZC and Landen CN: The importance of
the PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway in the progression of ovarian cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 14:8213–8227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bassermann F, Eichner R and Pagano M: The
ubiquitin proteasome system-implications for cell cycle control and
the targeted treatment of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1843:150–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson DE: The ubiquitin-proteasome
system: Opportunities for therapeutic intervention in solid tumors.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Varela JC and Tomlinson S: Complement: An
overview for the clinician. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am.
29:409–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Afshar-Kharghan V: The role of the
complement system in cancer. J Clin Invest. 127:780–789. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pio R, Corrales L and Lambris JD: The role
of complement in tumor growth. Tumor Microenviron Cell Stress.
229–262. 2013.
|