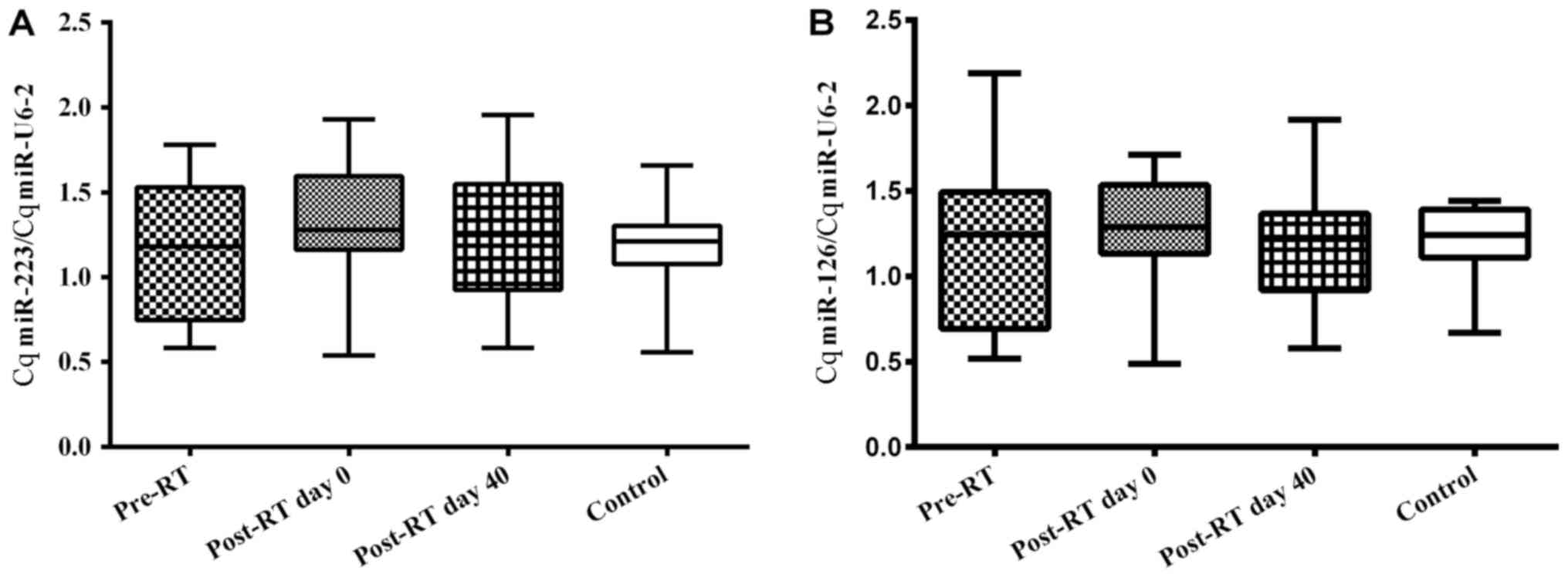
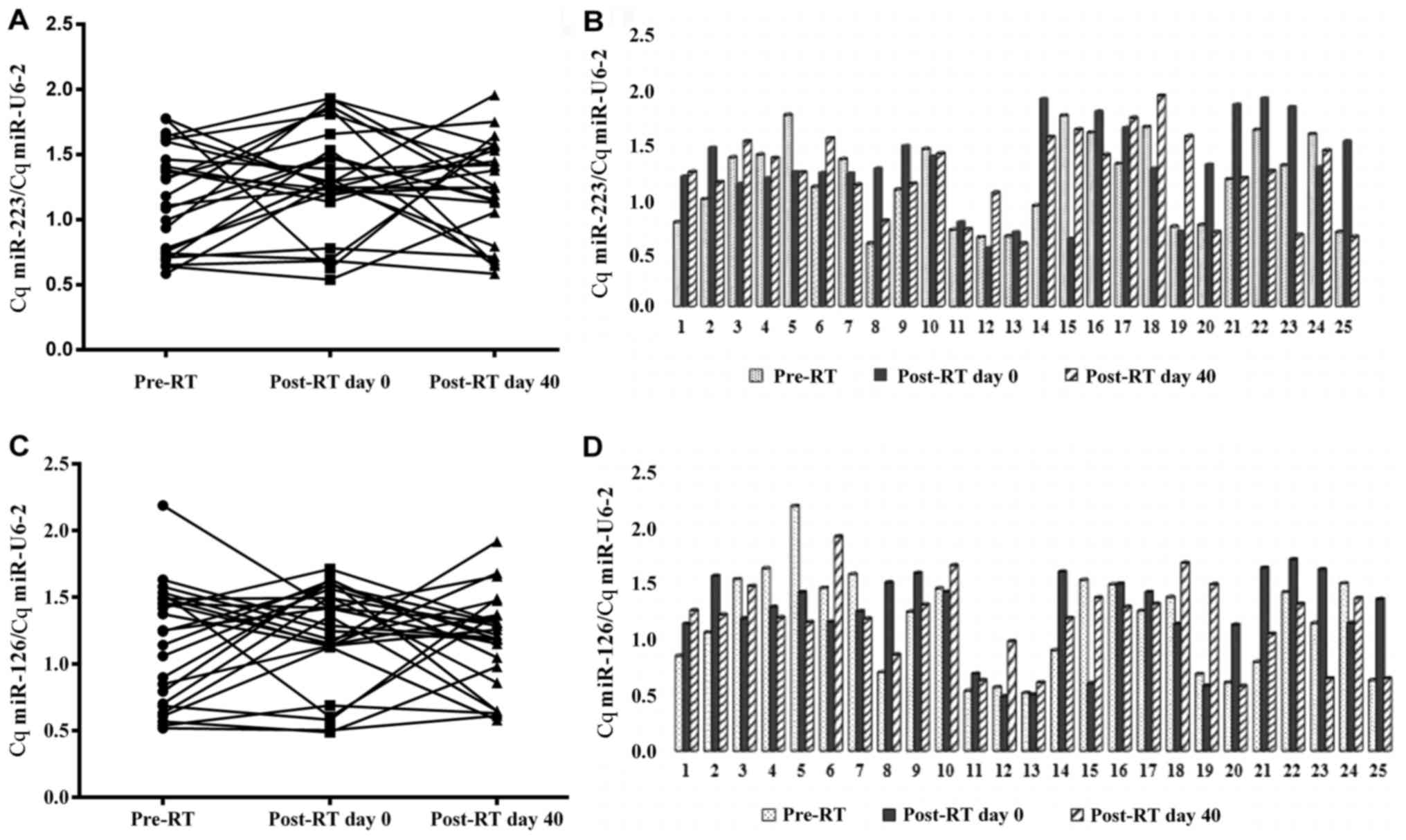
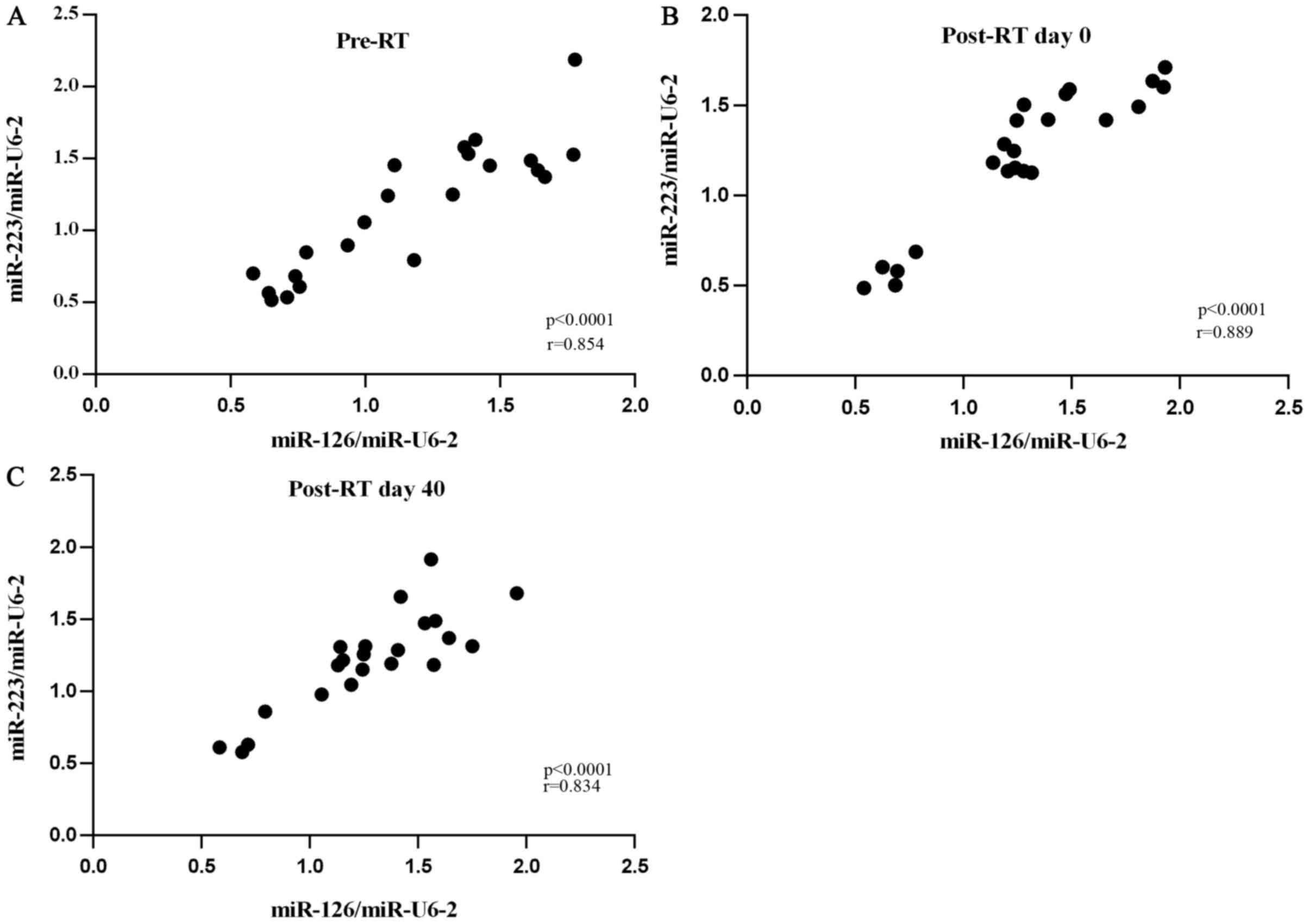
|
1
|
Sun X, Liu Z, Yang Z, Xiao L, Wang F, He
Y, Su P, Wang J and Jing B: Association of microRNA-126 expression
with clinicopathological features and the risk of biochemical
recurrence in prostate cancer patients undergoing radical
prostatectomy. Diagn Pathol. 8:2082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He J, Hua J, Ding N, Xu S, Sun R, Zhou G,
Xie X and Wang J: Modulation of microRNAs by ionizing radiation in
human gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:787–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li M, Li GF, Hou XY, Gao H, Xu YG and Zhao
T: A dosimetric comparison between conventional fractionated and
hypofractionated image-guided radiation therapies for localized
prostate cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:1447–1454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayden AJ, Catton C and Pickles T:
Radiation therapy in prostate cancer: A risk-adapted strategy. Curr
Oncol. 17 Suppl 2:S18–S24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E,
Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fossati N, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau
S, et al: EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer Part 1:
Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur
Urol. 71:618–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang FE, Vaida F, Ignacio L, Houghton A,
Nauityal J, Halpern H, Sutton H and Vijayakumar S: Analysis of
weekly complete blood counts in patients receiving standard
fractionated partial body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 33:6171995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Verheij M, Dewit LG, Boomgaard MN,
Brinkman HJ and van Mourik JA: Ionizing radiation enhances platelet
adhesion to the extracellular matrix of human endothelial cells by
an increase in the release of von Willebrand factor. Radiat Res.
137:202–207. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hallahan DE, Chen AY, Teng M and Cmelak
AJ: Drug-radiation interactions in tumor blood vessels. Oncology
(Williston Park). 13 10 Suppl 5:S71–S77. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Sørensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Olsen JH and
Baron JA: Prognosis of cancers associated with venous
thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 343:1846–1850. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kroll MH, Hellums JD, McIntire LV, Schafer
AI and Moake JL: Platelets and shear stress. Blood. 88:1525–1541.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ni H and Freedman J: Platelets in
hemostasis and thrombosis: Role of integrins and their ligands.
Transfus Apher Sci. 28:257–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arcangeli S and Greco C: Hypofractionated
radiotherapy for organ-confined prostate cancer: Is less more? Nat
Rev Urol. 13:400–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zachariah B, Jacob SS, Gwede C, Cantor A,
Patil J, Casey L and Zachariah AB: Effect of fractionated regional
external beam radiotherapy on peripheral blood cell count. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 50:465–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lundgren MSFS, Cavalcanti MSM and Sampaio
DA: Weekly monitoring of the effects of conventional external beam
radiation therapy on patients with head and neck, chest, and pelvis
cancer by means of blood cells count. Radiol Bras. 41:29–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ampil FL, Burton GV and Li BD: ‘Routine’
weekly blood counts during breast irradiation for early stage
cancer: Are they really necessary? Breast J. 7:450–452. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kalovidouris AE and Papayannis AG: Effect
of ionizing radiation on platelet function in vitro. Acta Radiol
Oncol. 20:333–336. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mihaescu A, Thornberg C, Santén S,
Mattsson S, Jeppsson B and Thorlacius H: Radiation-induced
platelet-endothelial cell interactions are mediated by P-selectin
and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 in the colonic
microcirculation. Surgery. 151:606–611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zekanowska E, Rystok-Grabska D, Wisniewski
T, Ziolkowska E, Slomka A, Giemza-Kucharska P and Rosc D: C0141
Radiotherapy and platelets activation in patients with prostate
cancer. Thromb Res. 130:S163–S164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lewinski A, Brona A, Lewandowski KC,
Jedrzejuk D, Bohdanowicz-Pawlak A, Skowronska-Jozwiak E,
Bienkiewicz M and Milewicz A: Effects of radioiodine administration
on serum concentrations of matrix metalloproteinases, adiponectin
and thrombospondin-1. Thyroid Res. 6:92013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lambert MP, Xiao L, Nguyen Y, Kowalska MA
and Poncz M: The role of platelet factor 4 in radiation-induced
thrombocytopenia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:1533–1540. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Willeit P, Zampetaki A, Dudek K, Kaudewitz
D, King A, Kirkby NS, Crosby-Nwaobi R, Prokopi M, Drozdov I,
Langley SR, et al: Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for
trombosit activation. Circ Res. 112:595–600. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nagalla S, Shaw C, Kong X, Kondkar AA,
Edelstein LC, Ma L, Chen J, McKnight GS, López JA, Yang L, et al:
Platelet microRNA-mRNA coexpression profiles correlate with
platelet reactivity. Blood. 117:5189–5197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Boer HC, van Solingen C, Prins J, Duijs
JM, Huisman MV, Rabelink TJ and van Zonneveld AJ: Aspirin treatment
hampers the use of plasma microRNA-126 as a biomarker for the
progression of vascular disease. Eur Heart J. 34:3451–3457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian HS, Zhou QG and Shao F: Relationship
between arterial atheromatous plaque morphology and
platelet-associated miR-126 and miR-223 expressions. Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 8:309–314. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu XY, Chen JY, Zheng ZW, Wu H, Li LW,
Zhang ZW, Chen ZH, Lin QX, Han YL and Zhong SL: Plasma miR-126 as a
potential marker predicting major adverse cardiac events in dual
antiplatelet-treated patients after percutaneous coronary
intervention. EuroIntervention. 9:546–554. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang YY, Zhou X, Ji WJ, Shi R, Lu RY, Li
JL, Yang GH, Luo T, Zhang JQ, Zhao JH, et al: Decreased circulating
microRNA-223 level predicts high on-treatment platelet reactivity
in patients with troponin-negative non-ST elevation acute coronary
syndrome. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 38:65–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Angiolillo DJ, Fernandez-Ortiz A, Bernardo
E, Ramírez C, Cavallari U, Trabetti E, Sabaté M, Jimenez-Quevedo P,
Hernández R, Moreno R, et al: Lack of association between the P2Y12
receptor gene polymorphism and platelet response to clopidogrel in
patients with coronary artery disease. Thromb Res. 116:491–497.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruggeri ZM: New insights into the
mechanisms of platelet adhesion and aggregation. Semin Hematol.
31:229–239. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta DeltaC (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Burdak-Rothkamm S and Prise KM: New
molecular targets in radiotherapy: DNA damage signalling and repair
in targeted and non-targeted cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 625:151–155.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mouthon MA, Vereycken-Holler V, Van der
Meeren A and Gaugler MH: Irradiation increases the interactions of
platelets with the endothelium in vivo: Analysis by intravital
microscopy. Radiat Res. 160:593–599. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hallahan DE, Staba-Hogan MJ, Virudachalam
S and Kolchinsky A: X-ray-induced P-selectin localization to the
lumen of tumor blood vessels. Cancer Res. 58:5216–5220.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hallahan DE and Virudachalam S:
Accumulation of P-selectin in the lumen of irradiated blood
vessels. Radiat Re. 152:6–13. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Otto K: Volumetric modulated arc therapy:
IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 35:310–317. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cozzi L, Dinshaw KA, Shrivastava SK,
Mahantshetty U, Engineer R, Deshpande DD, Jamema SV, Vanetti E,
Clivio A, Nicolini G and Fogliata A: A treatment planning study
comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field
IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 89:180–191.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nabavizadeh N, Simeonova AO, Waller JG,
Romer JL, Monaco DL, Elliott DA, Tanyi JA, Fuss M, Thomas CR Jr and
Holland JM: Volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy for pancreatic
malignancies: Dosimetric comparison with sliding-window
intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal
radiotherapy. Med Dosim. 39:256–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Blank KR, Cascardi MA and Kao GD: The
utility of serial complete blood count monitoring in patients
receiving radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 44:317–321. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pinkawa M, Djukic V, Klotz J, Petz D,
Piroth MD, Holy R and Eble MJ: Hematologic changes during prostate
cancer radiation therapy are dependent on the treatment volume.
Future Oncol. 10:835–843. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kennedy AR, Maity A and Sanzari JK: A
review of radiation-induced coagulopathy and new findings to
support potential prevention strategies and treatments. Radiat Res.
186:121–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mutlu H, Berk V, Karaca H, Erden A, Aslan
T and Akca Z: Treatment regimen with bevacizumab decreases mean
platelet volume in patients with metastatic colon cancer. Clin Appl
Thromb Hemost. 18:546–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Khode V, Sindhur J, Kanbur K, Ruikar K and
Nallulwar S: Mean platelet volume and other platelet volume indices
in patients with stable coronary artery disease and acute
myocardial infarction: A case control study. J Cardiovasc Dis Res.
3:272–275. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Riedl J, Kaider A, Reitter EM, Marosi C,
Jäger U, Schwarzinger I, Zielinski C, Pabinger I and Ay C:
Association of mean platelet volume with risk of venous
thromboembolism and mortality in patients with cancer. Results from
the vienna cancer and thrombosis study (CATS). Thromb Haemost.
111:670–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Inagaki N, Kibata K, Tamaki T, Shimizu T
and Nomura S: Prognostic impact of the mean platelet
volume/platelet count ratio in terms of survival in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 83:97–101. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cooke NM, Egan K, McFadden S, Grogan L,
Breathnach OS, O'Leary J, Hennessy BT and Kenny D: Increased
platelet reactivity in patients with late-stage metastatic cancer.
Cancer Med. 2:564–570. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Johnson RC, Mayadas TN, Frenette PS,
Mebius RE, Subramaniam M, Lacasce A, Hynes RO and Wagner DD: Blood
cell dynamics in P-selectin-deficient mice. Blood. 86:1106–1114.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Esemuede N, Lee T, Pierre-Paul D, Sumpio
BE and Gahtan V: The role of thrombospondin-1 in human disease. J
Surg Res. 122:135–142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sachais BS, Higazi AA, Cines DB, Poncz M
and Kowalska MA: Interactions of platelet factor 4 with the vessel
wall. Semin Thromb Hemost. 30:351–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weiss K, Palumbo B, Palumbo I, Palumbo R,
Granegger S, Hiltunen J and Sinzinger H: Platelet function after
single [153Sm]EDTMP therapy in prostate cancer. Q J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 50:330–333. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
El Kaffas A, Smith K, Pradhan P, Machtaler
S, Wang H, von Eyben R, Willmann JK and Hristov D: Molecular
contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of radiation-induced
P-Selectin expression in healthy mice colon. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 97:581–585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rofstad EK, Henriksen K, Galappathi K and
Mathiesen B: Antiangiogenic treatment with thrombospondin-1
enhances primary tumor radiation response and prevents growth of
dormant pulmonary micrometastases after curative radiation therapy
in human melanoma xenografts. Cancer Res. 63:4055–4061.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rofstad EK, Galappathi K and Mathiesen B:
Thrombospondin-1 treatment prevents growth of dormant lung
micrometastases after surgical resection and curative radiation
therapy of the primary tumor in human melanoma xenografts. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 58:493–499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wiesner T, Bugl S, Mayer F, Hartmann JT
and Kopp HG: Differential changes in platelet VEGF, Tsp, CXCL12,
and CXCL4 in patients with metastatic cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis.
27:141–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Poruk KE, Firpo MA, Huerter LM, Scaife CL,
Emerson LL, Boucher KM, Jones KA and Mulvihill SJ: Serum platelet
factor 4 is an independent predictor of survival and venous
thromboembolism in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:2605–2610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lam YW, Mobley JA, Evans JE, Carmody JF
and Ho SM: Mass profiling-directed isolation and identification of
a stage-specific serologic protein biomarker of advanced prostate
cancer. Proteomics. 5:2927–2938. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen JJ, Gao Y, Tian Q, Liang YM and Yang
L: Platelet factor 4 protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
from acute radiation injury. Br J Radiol. 87:201401842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gatsiou A, Boeckel JN, Randriamboavonjy V
and Stellos K: MicroRNAs in platelet biogenesis and function:
Implications in vascular homeostasis and inflammation. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 10:524–531. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Edelstein LC, McKenzie SE, Shaw C,
Holinstat MA, Kunapuli SP and Bray PF: MicroRNAs in platelet
production and activation. J Thromb Haemost. 11 Suppl 1:S340–S350.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Corsten MF, Dennert R, Jochems S,
Kuznetsova T, Devaux Y, Hofstra L, Wagner DR, Staessen JA, Heymans
S and Schroen B: Circulating MicroRNA-208b and MicroRNA-499 reflect
myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
3:499–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, Li Q, Li Y, He
J, Qin YW and Jing Q: Circulating microRNA: A novel potential
biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in
humans. Eur Heart J. 31:659–666. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li
M, Sun L, Ji G, Shi Y, Han Z, et al: miRNA-223 promotes gastric
cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor
EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res. 9:824–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Iuliano
R, Cimmino A, Aqeilan R, Volinia S, Bhatt D, Alder H, Marcucci G,
et al: MicroRNA fingerprints during human megakaryocytopoiesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 5078–5083. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Templin T, Paul S, Amundson SA, Young EF,
Barker CA, Wolden SL and Smilenov LB: Radiation-induced micro-RNA
expression changes in peripheral blood cells of radiotherapy
patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:549–557. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cui W, Ma J, Wang Y and Biswal S: Plasma
miRNA as biomarkers for assessment of total-body radiation exposure
dosimetry. PLoS One. 6:e229882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jin L, Wang R, Jiang S, Yue J, Liu T, Dou
X, Zhu K, Feng R, Xu X, Chen D and Yin Y: Dosimetric and clinical
toxicity comparison of critical organ preservation with
three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated
radiotherapy, and RapidArc for the treatment of locally advanced
cancer of the pancreatic head. Curr Oncol. 23:e41–e48. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ponomaryova AA, Morozkin ES, Rykova EY,
Zaporozhchenko IA, Skvortsova TE, Dobrodeev АY, Zavyalov AA,
Tuzikov SA, Vlassov VV, Cherdyntseva NV, et al: Dynamic changes in
circulating miRNA levels in response to antitumor therapy of lung
cancer. Exp Lung Res. 42:95–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Smirnov DA, Brady L, Halasa K, Morley M,
Solomon S and Cheung VG: Genetic variation in radiation-induced
cell death. Genome Res. 22:332–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Foray N, Bourguignon M and Hamada N:
Individual response to ionizing radiation. Mutat Res. 770:369–386.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mei N, Imada H, Nomoto S, Kunugita N and
Norimura T: Individual variation and age dependency in the
radiosensitivity of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes from normal
donors. J Radiat Res. 37:235–245. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Barber JB, West CM, Kiltie AE, Roberts SA
and Scott D: Detection of individual differences in
radiation-induced apoptosis of peripheral blood lymphocytes in
normal individuals, ataxia telangiectasia homozygotes and
heterozygotes, and breast cancer patients after radiotherapy.
Radiat Res. 153:570–578. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|