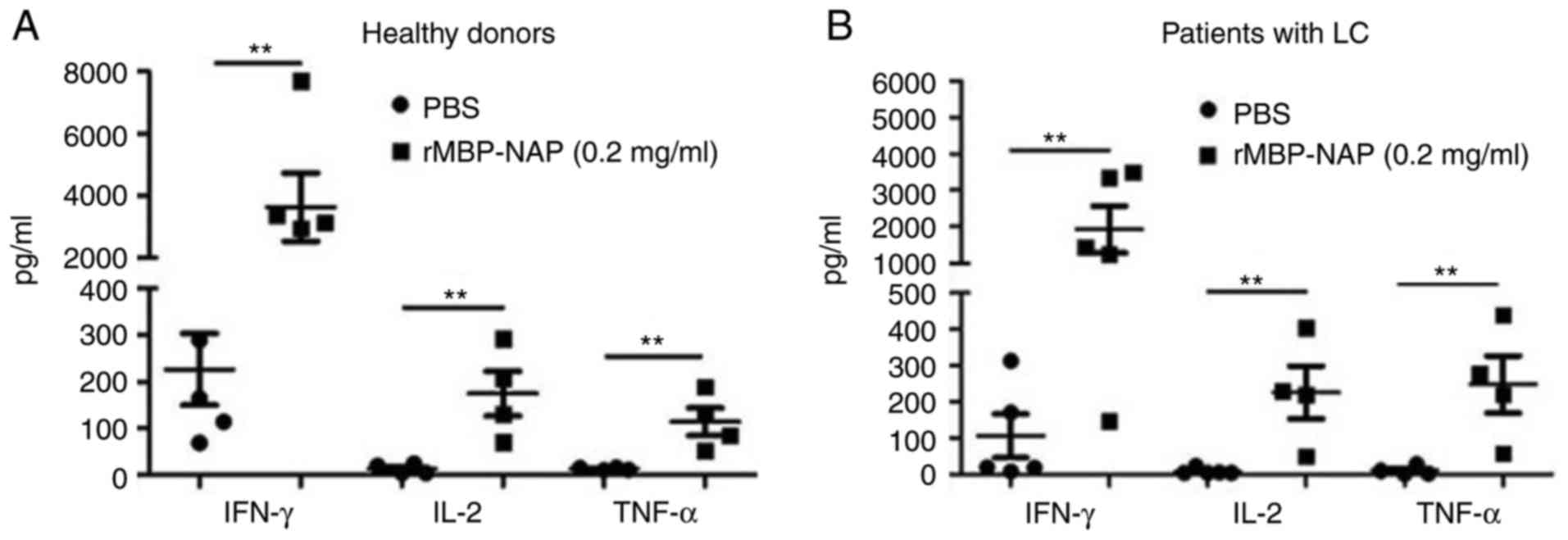
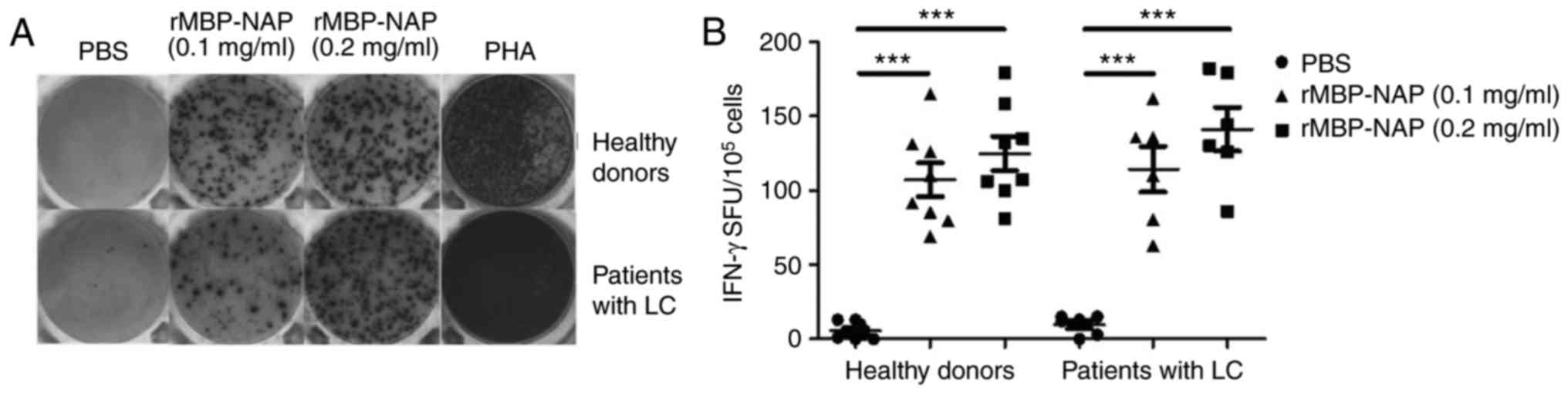
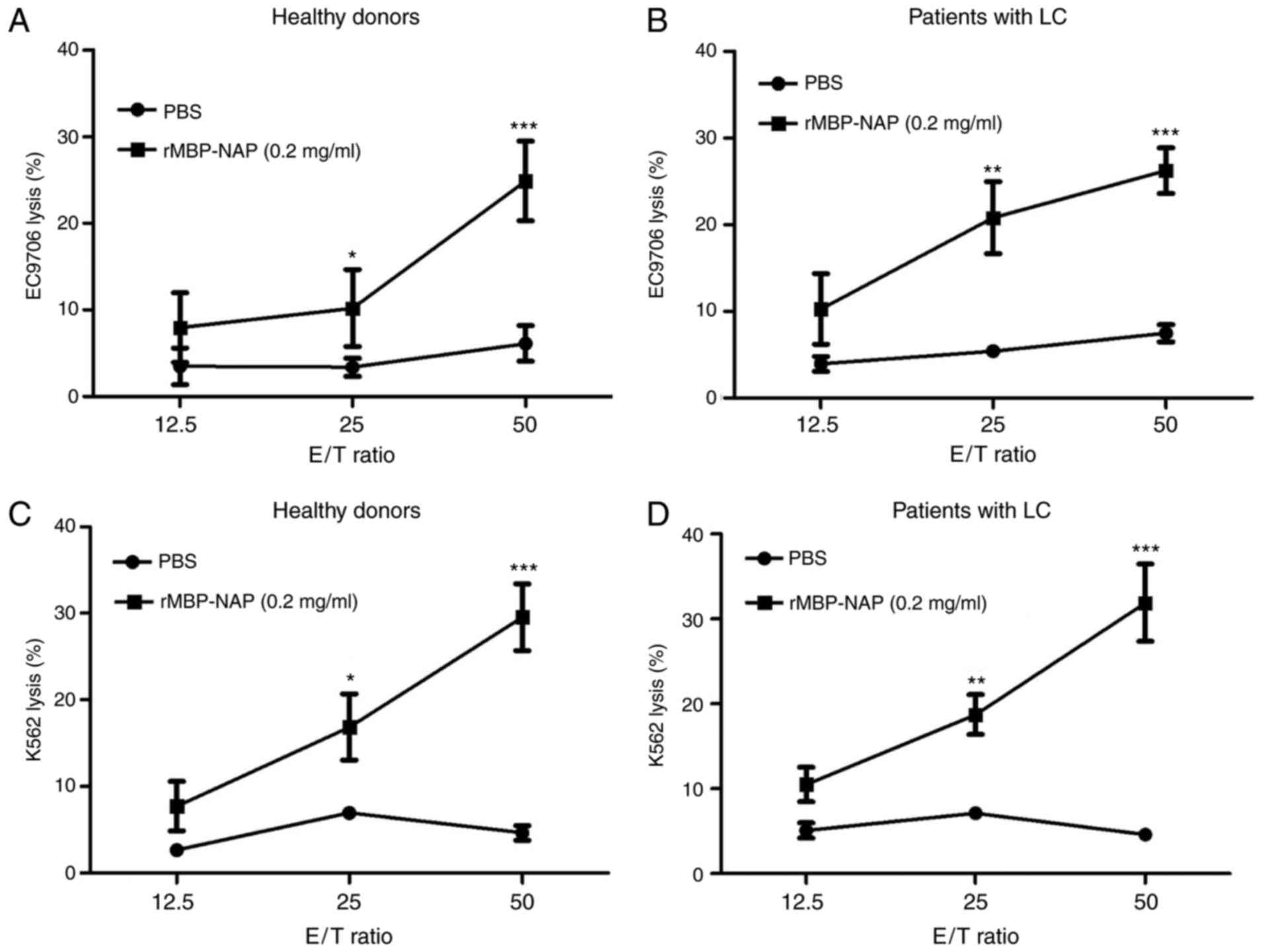
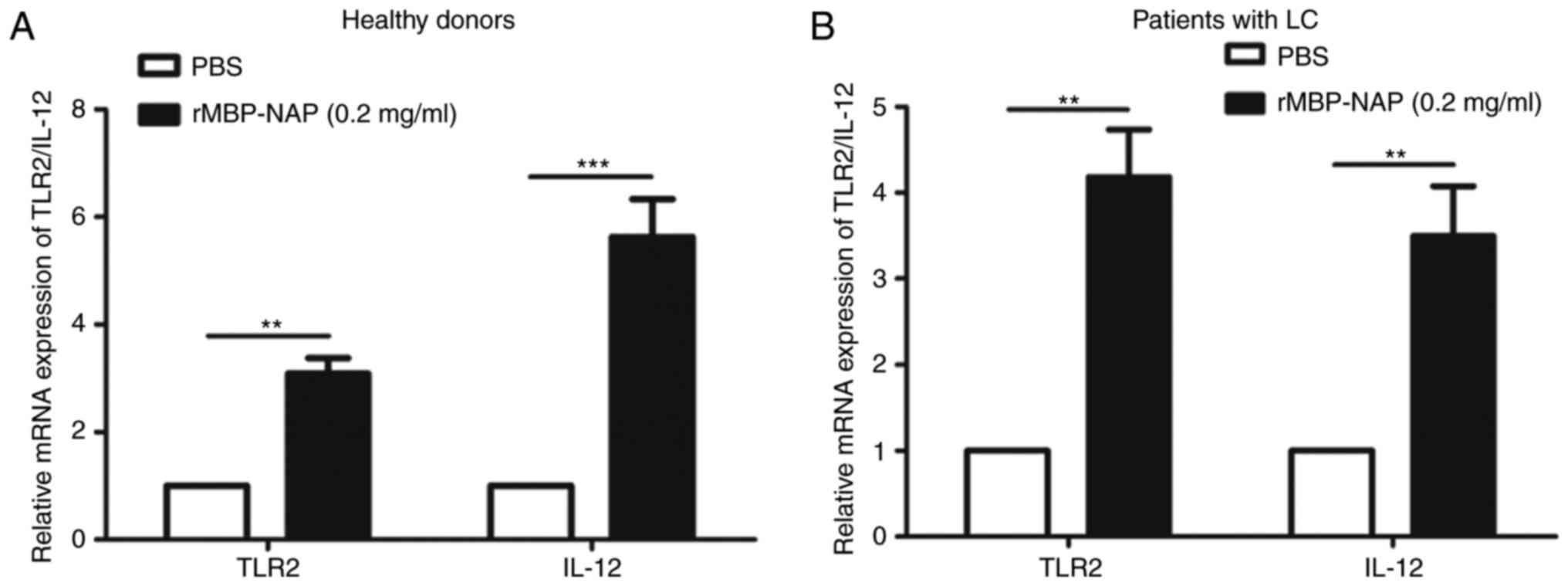
|
1
|
Adams S: Toll-like receptor agonists in
cancer therapy. Immunother. 1:949–964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol.
5:987–995. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Husek P, Pacovsky J, Chmelarova M, Podhola
M and Brodak M: Methylation status as a predictor of intravesical
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) immunotherapy response of high grade
non-muscle invasive bladder tumor. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky
Olomouc Czech Repub. 161:210–216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhuang X, Wu T, Zhao Y, Hu X, Bao Y, Guo
Y, Song Q, Li G, Tan S and Zhang Z: Lipid-enveloped zinc phosphate
hybrid nanoparticles for codelivery of H-2K(b) and
H-2D(b)-restricted antigenic peptides and monophosphoryl lipid A to
induce antitumor immunity against melanoma. J Control Release.
228:26–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho JH, Lee HJ, Ko HJ, Yoon BI, Choe J,
Kim KC, Hahn TW, Han JA, Choi SS, Jung YM, et al: The TLR7 agonist
imiquimod induces anti-cancer effects via autophagic cell death and
enhances anti-tumoral and systemic immunity during radiotherapy for
melanoma. Oncotarget. 8:24932–24948. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guha M: Anticancer TLR agonists on the
ropes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:503–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rakoff-Nahoum S and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:57–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shuang Chen, Wong MH, Schulte DJ, Arditi M
and Michelsen KS: Differential expression of Toll-like receptor 2
(TLR2) and responses to TLR2 ligands between human and murine
vascular endothelial cells. J Endotoxin Res. 13:281–296. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Santegoets SJ, Welters MJ and van der Burg
SH: Monitoring of the immune dysfunction in cancer patients.
Vaccines (Basel). 4:E92016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang QZ, Duan GC, Fan QT and Xi YL: Fusion
expression of helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein in
E. coli. World J Gastroenterol. 11:454–456. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu HW: Helicobacter pylori
neutrophil-activating protein: From molecular pathogenesis to
clinical applications. World J Gastroenterol. 20:5294–5301. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang F, Ma J, Ni W, Wang F, Sun X, Li Y,
Li Q, Xie F, Wang J, Zhai R, et al: MUC1 and maltose binding
protein recombinant fusion protein combined with Bacillus
CalmetteGuerin induces MUC1specific and nonspecific antitumor
immunity in mice. Mol Med Rep. 10:1056–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang T, Liu X, Ji Z, Men Y, Du M, Ding C,
Wu Y, Liu X and Kang Q: Antitumor and immunomodulatory effects of
recombinant fusion protein rMBP-NAP through TLR-2 dependent
mechanism in tumor bearing mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:876–883.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang T, Du M, Ji Z, Ding C, Wang C, Men Y,
Liu S, Liang T, Liu X and Kang Q: Recombinant protein rMBP-NAP
restricts tumor progression by triggering antitumor immunity in
mouse metastatic lung cancer. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 9:113–119.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu QY, Zhou T, Zhao YY, Chen L, Gong MW,
Xia QW, Ying MG, Zheng QH and Zhang QQ: Antitumor effects and
related mechanisms of Penicitrinine A, a novel alkaloid with a
unique spiro skeleton from the marine fungus penicillium citrinum.
Mar Drugs. 13:4733–4753. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Horibe T, Kawamoto M, Kohno M and Kawakami
K: Cytotoxic activity to acute myeloid leukemia cells by Antp-TPR
hybrid peptide targeting Hsp90. J Biosci Bioeng. 114:96–103. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Motohashi S and Nakayama T: Clinical
applications of natural killer T cell-based immunotherapy for
cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:638–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roychowdhury S and Caligiuri MA: Cytokine
therapy for cancer: Antigen presentation. Cancer Treat Res.
123:49–266. 2005.
|
|
20
|
Baxevanis CN, Perez SA and Papamichail M:
Cancer immunotherapy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 46:167–189. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miller CH, Maher SG and Young HA: Clinical
use of interferon-gamma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1182:69–79. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Minor DR, Moores SP and Chan JK: Prolonged
survival after intraperitoneal interleukin-2 immunotherapy for
recurrent ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 22:43–44. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeon H, Kim D, Choi M, Kang S, Kim JY, Kim
S and Jon S: Targeted cancer therapy using fusion protein of TNFα
and tumor-associated fibronectin-specific aptide. Mol Pharm.
14:3772–3779. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang K, Ren Y, Liu Y, Zhang J and He JJ:
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced protein 8-like-2 (TIPE2)
inhibits proliferation and tumorigenesis in breast cancer cells.
Oncol Res. 25:55–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aranda F, Vacchelli E, Obrist F, Eggermont
A, Galon J, Sautes-Fridman C, Cremer I, Henrik Ter Meulen J,
Zitvogel L, Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Trial watch: Toll-like
receptor agonists in oncological indications. Oncoimmunology.
3:e291792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ren T, Wen ZK, Liu ZM, Qian C, Liang YJ,
Jin ML, Cai YY and Xu L: Targeting toll-like receptor 9 with CpG
oligodeoxynucleotides enhances anti-tumor responses of peripheral
blood mononuclear cells from human lung cancer patients. Cancer
Invest. 26:448–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thanhäuser A, Böhle A, Flad HD, Ernst M,
Mattern T and Ulmer AJ: Induction of
bacillus-Calmette-Guérin-activated killer cells from human
peripheral blood mononuclear cells against human bladder carcinoma
cell lines in vitro. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 37:105–111. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
De Nardo D: Toll-like receptors:
Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine.
74:181–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bollard CM and Barrett AJ: CytotoxicT
lymphocytes for leukemia and lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol
Educ Program. 2014:565–569. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martorelli D, Muraro E, Merlo A, Turrini
R, Rosato A and Dolcetti R: Role of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in
the control of viral diseases and cancer. Int Rev Immunol.
29:371–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weigelin B, Krause M and Friedl P:
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte migration and effector function in the tumor
microenvironment. Immunol Lett. 138:19–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mempel TR and Bauer CA: Intravital imaging
of CD8+ T cell function in cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 26:311–327.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Reynolds JM and Dong C: Toll-like receptor
regulation of effector T lymphocyte function. Trends Immunol.
34:511–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu W, O'Donnell MA, Chen X, Han R and Luo
Y: Recombinant bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) expressing
interferon-alpha 2B enhances human mononuclear cell cytotoxicity
against bladder cancer cell lines in vitro. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 58:1647–1655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|