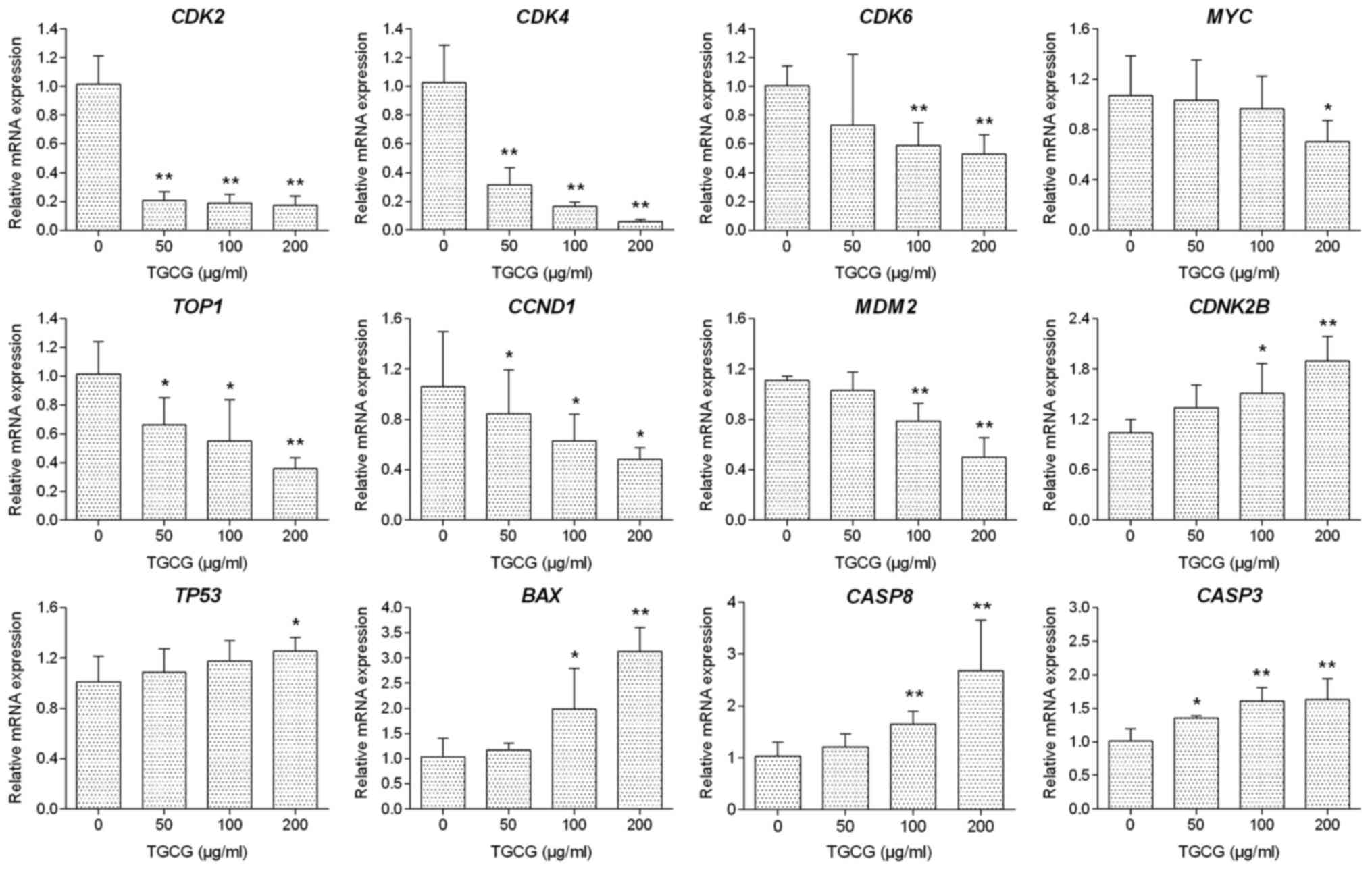
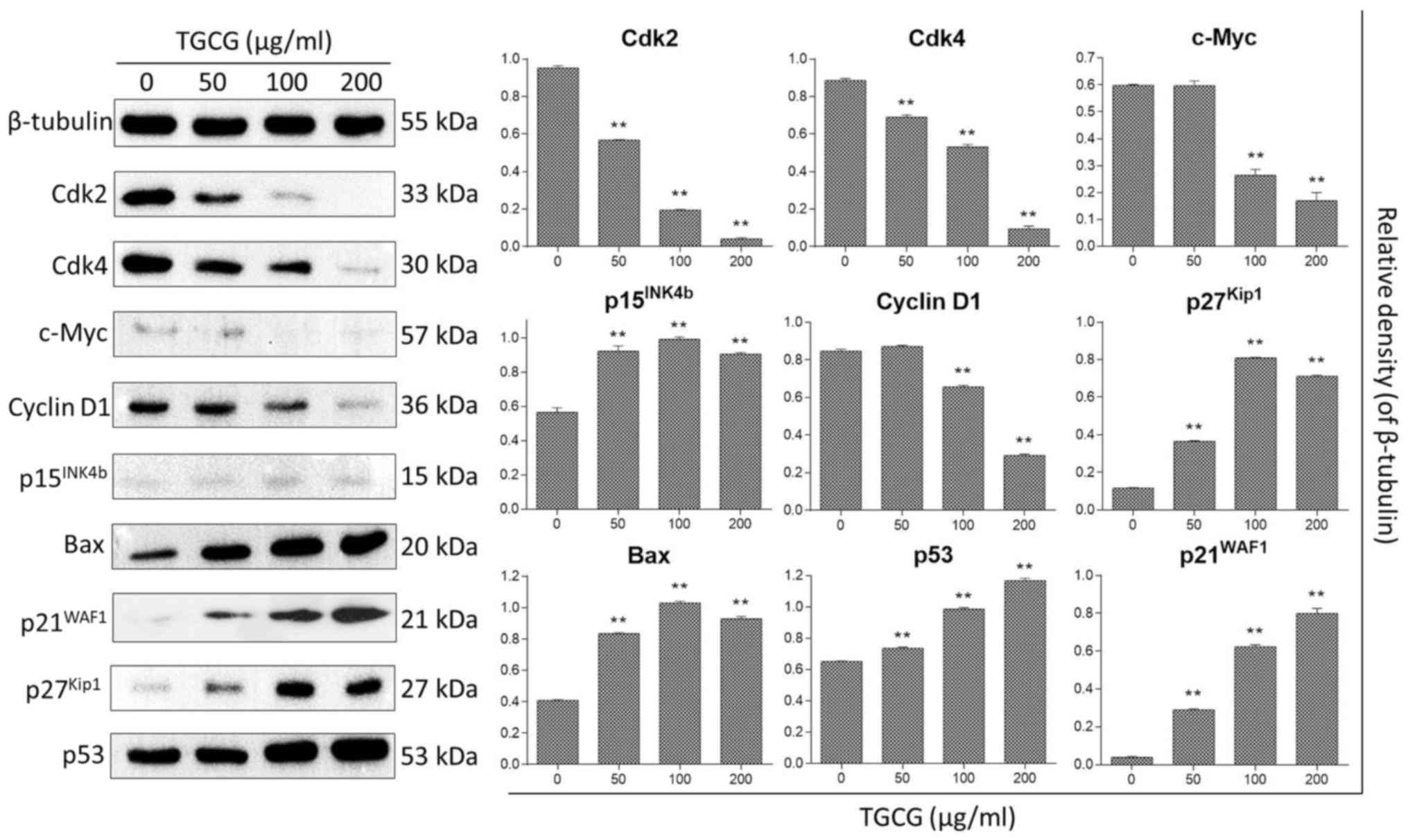
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kolligs FT: Diagnostics and epidemiology
of colorectal cancer. Visc Med. 32:158–164. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Center MM, Jemal A and Ward E:
International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1688–1694. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Platz EA, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Rimm EB,
Spiegelman D and Giovannucci E: Proportion of colon cancer risk
that might be preventable in a cohort of middle-aged US men. Cancer
Causes Control. 11:579–588. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baak JP, Gyllenhaal C, Liu L, Guo H and
Block KI: Prognostic proof and possible therapeutic mechanisms of
herbal medicine in patients with metastatic lung and colon cancer.
Integr Cancer Ther. 10:NP1–NP11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mano MS and Duhoux F: Colon cancer: Update
on adjuvant therapy. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 7:178–183. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iwamoto T: Clinical application of drug
delivery systems in cancer chemotherapy: Review of the efficacy and
side effects of approved drugs. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:715–718. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ades S: Adjuvant chemotherapy for colon
cancer in the elderly: Moving from evidence to practice. Oncology
(Williston Park). 23:162–167. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin AR, Carides AD, Pearson JD, Horgan
K, Elmer M, Schmidt C, Cai B, Chawla SP and Grunberg SM: Functional
relevance of antiemetic control. Experience using the FLIE
questionnaire in a randomised study of the NK-1 antagonist
aprepitant. Eur J Cancer. 39:1395–1401. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chien TJ, Liu CY, Lu RH, Kuo CW, Lin YC
and Hsu CH: Therapeutic efficacy of Traditional Chinese medicine,
‘Kuan-Sin-Yin’, in patients undergoing chemotherapy for advanced
colon cancer-A controlled trial. Complement Ther Med. 29:204–212.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin YY, Lee IY, Huang WS, Lin YS, Kuan FC,
Shu LH, Cheng YC, Yang YH and Wu CY: Danshen improves survival of
patients with colon cancer and dihydroisotanshinone I inhibit the
proliferation of colon cancer cells via apoptosis and skp2
signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 209:305–316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Su Z, Zhou C, Qin S, Jia E and Wu Z: The
significant pathways and genes underlying the colon cancer
treatment by the traditional Chinese medicine PHY906. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2017:87538152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Li XM, Bai Z, Chi BX, Wei Y and
Chen X: Curcumol induces cell cycle arrest in colon cancer cells
via reactive oxygen species and Akt/GSK3β/cyclin D1 pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 210:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin H, Liu J and Zhang Y: Developments in
cancer prevention and treatment using traditional Chinese medicine.
Front Med. 5:127–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baeg IH and So SH: The world ginseng
market and the ginseng (Korea). J Ginseng Res. 37:1–7. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dai D, Zhang CF, Williams S, Yuan CS and
Wang CZ: Ginseng on cancer: Potential role in modulating
inflammation-mediated angiogenesis. Am J Chin Med. 45:13–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang CZ, Zhang Z, Wan JY, Zhang CF,
Anderson S, He X, Yu C, He TC, Qi LW and Yuan CS: Protopanaxadiol,
an active ginseng metabolite, significantly enhances the effects of
fluorouracil on colon cancer. Nutrients. 7:799–814. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JG, McKinney KQ, Pavlopoulos AJ, Park
JH and Hwang S: Data supporting the identification of
anti-metastatic drug and natural compound targets in isogenic
colorectal cancer cells. Data Brief. 1:73–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang CZ, Xie JT, Zhang B, Ni M, Fishbein
A, Aung HH, Mehendale SR, Du W, He TC and Yuan CS: Chemopreventive
effects of Panax notoginseng and its major constituents on
SW480 human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 31:1149–1156.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu C, Liu F, Qian W, Zhang T and Li F:
Combined effect of sodium selenite and ginsenoside Rh2 on HCT116
human colorectal carcinoma cells. Arch Iran Med. 19:23–29.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee JG, McKinney KQ, Pavlopoulos AJ, Park
JH and Hwang S: Identification of anti-metastatic drug and natural
compound targets in isogenic colorectal cancer cells. J Proteomics.
113:326–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen L, Meng Y, Sun Q, Zhang Z, Guo X,
Sheng X, Tai G, Cheng H and Zhou Y: Ginsenoside compound K
sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via
autophagy-dependent and -independent DR5 upregulation. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e23342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang QY and Feng MG: DPS data processing
system: Experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining.
Beijing Science Press; Beijing, China: 2007
|
|
25
|
Yun TK, Choi SY and Yun HY:
Epidemiological study on cancer prevention by ginseng: Are all
kinds of cancers preventable by ginseng? J Korean Med Sci. 16
Suppl:S19–S27. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng H, Li S, Fan Y, Gao X, Hao M, Wang
J, Zhang X, Tai G and Zhou Y: Comparative studies of the
antiproliferative effects of ginseng polysaccharides on HT-29 human
colon cancer cells. Med Oncol. 28:175–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li B, Wang CZ, He TC, Yuan CS and Du W:
Antioxidants potentiate American ginseng-induced killing of
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 289:62–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim SE, Lee YH, Park JH and Lee SK:
Ginsenoside-Rs4, a new type of ginseng saponin concurrently induces
apoptosis and selectively elevates protein levels of p53 and
p21WAF1 in human hepatoma SK-HEP-1 cells. Eur J Cancer. 35:507–511.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi S, Kim TW and Singh SV: Ginsenoside
Rh2-mediated G1 phase cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer
cells is caused by p15 Ink4B and p27 Kip1-dependent inhibition of
cyclin-dependent kinases. Pharm Res. 26:2280–2288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao JL, Lv GY, He BC, Zhang BQ, Zhang H,
Wang N, Wang CZ, Du W, Yuan CS and He TC: Ginseng saponin
metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol inhibits tumor growth by targeting
multiple cancer signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 30:292–298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park HM, Kim SJ, Kim JS and Kang HS:
Reactive oxygen species mediated ginsenoside Rg3- and Rh2-induced
apoptosis in hepatoma cells through mitochondrial signaling
pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2736–2741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Wu X, Zhang CF, Calway T,
He TC, Du W, Chen J, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: TRAIL pathway is
associated with inhibition of colon cancer by protopanaxadiol. J
Pharmacol Sci. 127:83–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dang CV: c-Myc target genes involved in
cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 19:1–11.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP and
Eisenman RN: The Myc/Max/Mad network and the transcriptional
control of cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 16:653–699. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shao Q, Kannan A, Lin Z, Stack BC Jr, Suen
JY and Gao L: BET protein inhibitor JQ1 attenuates Myc-amplified
MCC tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 74:7090–7102. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu J, Cui CF, Yang L, Wang L and Jiang XH:
Emodin inhibits colon cancer cell invasion and migration by
suppressing epithelialmesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Oncol Res. Jan 4–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Jiang J, Zhao M, Luo X, Liang Z,
Zhen Y, Fu Q, Deng X, Lin X, Li L, et al: microRNA-374a suppresses
colon cancer progression by directly reducing CCND1 to inactivate
the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 7:41306–41319. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Izutani Y, Yogosawa S, Sowa Y and Sakai T:
Brassinin induces G1 phase arrest through increase of p21 and p27
by inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
pathway in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 40:816–824.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Z, Li C, Wang X, Zhai C, Yi Z, Wang
L, Liu B, Du B, Wu H, Guo X, et al: Dauricine induces apoptosis,
inhibits proliferation and invasion through inhibiting NF-kappaB
signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
225:266–275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mehendale S, Aung H, Wang A, Yin JJ, Wang
CZ, Xie JT and Yuan CS: American ginseng berry extract and
ginsenoside Re attenuate cisplatin-induced kaolin intake in rats.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 56:63–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fishbein AB, Wang CZ, Li XL, Mehendale SR,
Sun S, Aung HH and Yuan CS: Asian ginseng enhances the
anti-proliferative effect of 5-fluorouracil on human colorectal
cancer: Comparison between white and red ginseng. Arch Pharm Res.
32:505–513. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gu C, Qiao J, Zhu M, Du J, Shang W, Yin W,
Wang W, Han M and Lu W: Preliminary evaluation of the interactions
of Panax ginseng and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge with
5-fluorouracil on pharmacokinetics in rats and pharmacodynamics in
human cells. Am J Chin Med. 41:443–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pagliara V, Saide A, Mitidieri E, di Villa
Bianca d'Emmanuele R, Sorrentino R, Russo G and Russo A: 5-FU
targets rpL3 to induce mitochondrial apoptosis via
cystathionine-β-synthase in colon cancer cells lacking p53.
Oncotarget. 7:50333–50348. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Russo A, Saide A, Cagliani R, Cantile M,
Botti G and Russo G: rpL3 promotes the apoptosis of p53 mutated
lung cancer cells by down-regulating CBS and NFκB upon 5-FU
treatment. Sci Rep. 6:383692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Holden JA: DNA topoisomerases as
anticancer drug targets: From the laboratory to the clinic. Curr
Med Chem Anti-Canc Agents. 1:1–25. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cheng MH, Yang YC, Wong YH, Chen TR, Lee
CY, Yang CC, Chen SH, Yang IN, Yang YS, Huang HS, et al: B1, a
novel topoisomerase II inhibitor, induces apoptosis and cell cycle
G1 arrest in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Anticancer Drugs.
23:191–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Surget S, Khoury MP and Bourdon JC:
Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: A
clinical perspective. Onco Targets Ther. 7:57–68. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Levine AJ and Oren M: The first 30 years
of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:749–758. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang X, Arooz T, Siu WY, Chiu CH, Lau A,
Yamashita K and Poon RY: MDM2 and MDMX can interact differently
with ARF and members of the p53 family. FEBS Lett. 490:202–208.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Weng C, Li Y, Xu D, Shi Y and Tang H:
Specific cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspase-3 in tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis
in Jurkat leukemia T cells. J Biol Chem. 280:10491–10500. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Salvesen GS: Caspases: Opening the boxes
and interpreting the arrows. Cell Death Differ. 9:3–5. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|