|
1
|
Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S,
Reifenberger G and von Deimling A: Glioblastoma: Pathology,
molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 129:829–848.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Agnihotri S, Burrell KE, Wolf A, Jalali S,
Hawkins C, Rutka JT and Zadeh G: Glioblastoma, a brief review of
history, molecular genetics, animal models and novel therapeutic
strategies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 61:25–41. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tully PA, Gogos AJ, Love C, Liew D,
Drummond KJ and Morokoff AP: Reoperation for recurrent glioblastoma
and its association with survival benefit. Neurosurgery.
79:678–689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Desbaillets I, Diserens AC, Tribolet N,
Hamou MF and Van Meir EG: Upregulation of interleukin 8 by
oxygen-deprived cells in glioblastoma suggests a role in leukocyte
activation, chemotaxis, and angiogenesis. J Exp Med. 186:1201–1212.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shan Y, He X, Song W, Han D, Niu J and
Wang J: Role of IL-6 in the invasiveness and prognosis of glioma.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:9114–9120. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jarnicki A, Putoczki T and Ernst M: Stat3:
Linking inflammation to epithelial cancer-more than a ‘gut’
feeling? Cell Div. 5:142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A and Bhatt
AN: Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11553–11572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA and Struhl K: An
epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and
IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell. 139:693–706.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akira S and Kishimoto T: IL-6 and NF-IL6
in acute-phase response and viral infection. Immunol Rev.
127:25–50. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu CT, Chen MF, Chen WC and Hsieh CC: The
role of IL-6 in the radiation response of prostate cancer. Radiat
Oncol. 8:1592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang R, Lin Q, Gao HB and Zhang P:
Stress-related hormone norepinephrine induces interleukin-6
expression in GES-1 cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:101–109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D
and Rose-John S: The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the
cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:878–888. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
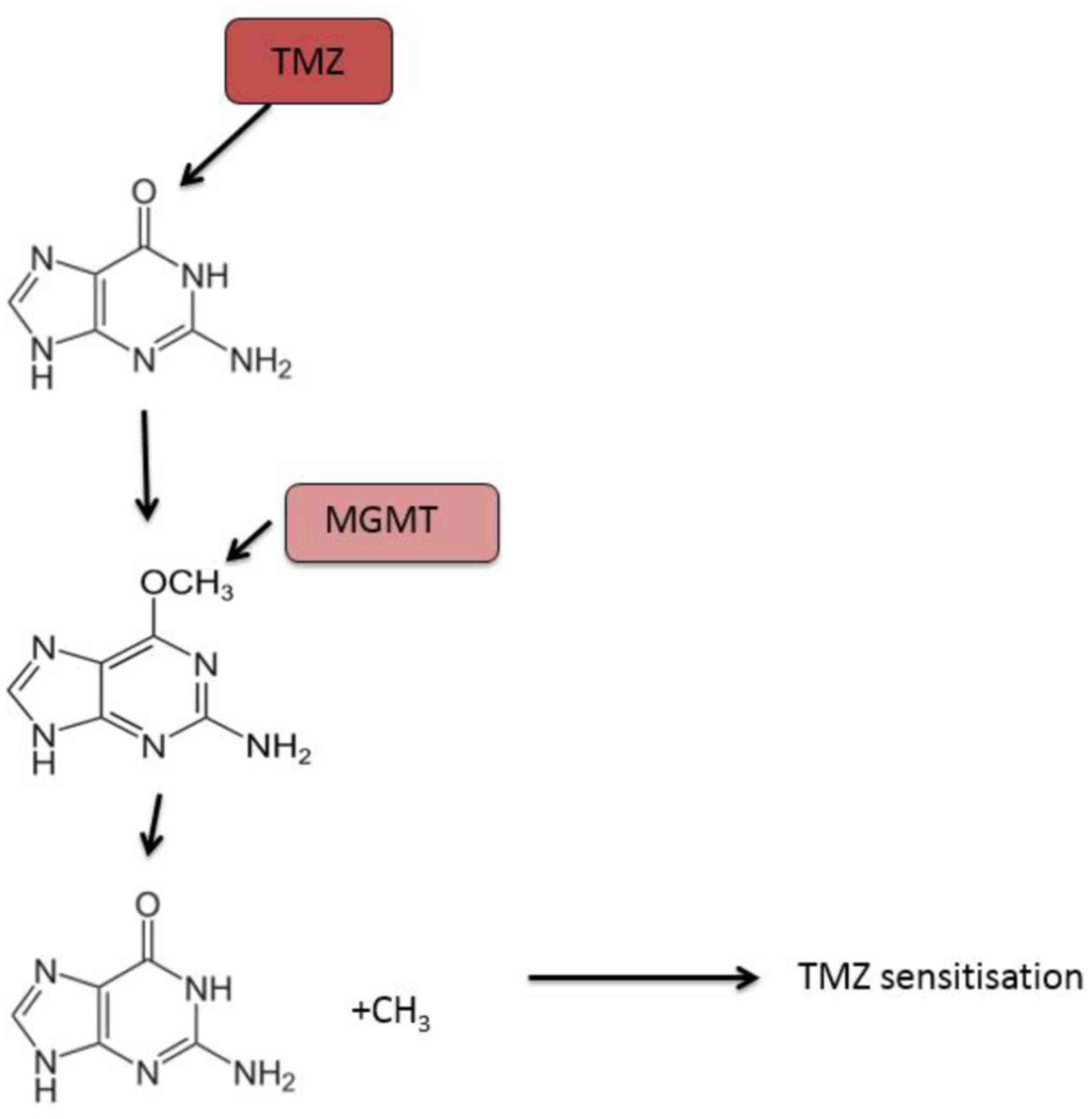
|
Gruys E, Toussaint MJ, Niewold TA and
Koopmans SJ: Acute phase reaction and acute phase proteins. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 6:1045–1056. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tilg H, Trehu E, Atkins MB, Dinarello CA
and Mier JW: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as an anti-inflammatory cytokine:
Induction of circulating IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor
necrosis factor receptor p55. Blood. 83:113–118. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aderka D, Le JM and Vilcek J: IL-6
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor
production in cultured human monocytes, U937 cells, and in mice. J
Immunol. 143:3517–3523. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jones SA, Scheller J and Rose-John S:
Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130
signaling. J Clin Invest. 121:3375–3383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mihara M, Hashizume M, Yoshida H, Suzuki M
and Shiina M: IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in
physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond).
122:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goswami S, Gupta A and Sharma SK:
Interleukin-6-mediated autocrine growth promotion in human
glioblastoma multiforme cell line U87MG. J Neurochem. 71:1837–1845.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taga T and Kishimoto T: Gp130 and the
interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 15:797–819.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rabe B, Rose-John S
and Scheller J: The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and
role in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cell Biol. 90:484–494. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jones SA, Horiuchi S, Topley N, Yamamoto N
and Fuller GM: The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: Mechanisms of
production and implications in disease. FASEB J. 15:43–58. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoshida K, Taga T, Saito M, Suematsu S,
Kumanogoh A, Tanaka T, Fujiwara H, Hirata M, Yamagami T, Nakahata
T, et al: Targeted disruption of gp130, a common signal transducer
for the interleukin 6 family of cytokines, leads to myocardial and
hematological disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:pp. 407–411.
1996; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yeung YT, McDonald KL, Grewal T and Munoz
L: Interleukins in glioblastoma pathophysiology: Implications for
therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 168:591–606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rolhion C, Penault-Llorca F, Kémény JL,
Lemaire JJ, Jullien C, Labit-Bouvier C, Finat-Duclos F and Verrelle
P: Interleukin-6 overexpression as a marker of malignancy in human
gliomas. J Neurosurg. 94:97–101. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tchirkov A, Khalil T, Chautard E, Mokhtari
K, Véronèse L, Irthum B, Vago P, Kémény JL and Verrelle P:
Interleukin-6 gene amplification and shortened survival in
glioblastoma patients. Br J Cancer. 96:474–476. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kudo M, Jono H, Shinriki S, Yano S,
Nakamura H, Makino K, Hide T, Muta D, Ueda M, Ota K, et al:
Antitumor effect of humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody
(tocilizumab) on glioma cell proliferation. Laboratory
investigation. J Neurosurg. 111:219–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Meir E, Sawamura Y, Diserens AC, Hamou
MF and de Tribolet N: Human glioblastoma cells release interleukin
6 in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 50:6683–6688. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ashizawa T, Miyata H, Iizuka A, Komiyama
M, Oshita C, Kume A, Nogami M, Yagoto M, Ito I, Oishi T, et al:
Effect of the STAT3 inhibitor STX-0119 on the proliferation of
cancer stem-like cells derived from recurrent glioblastoma. Int J
Oncol. 43:219–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3
and Stat4: Members of the family of signal transducers and
activators of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:pp.
4806–4810. 1994; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem
WW and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 activation is required for cellular
transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 18:2553–2558. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ouédraogo ZG, Biau J, Kemeny JL, Morel L,
Verrelle P and Chautard E: Role of STAT3 in genesis and progression
of human malignant gliomas. Mol Neurobiol. 54:5780–5797. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smilowitz HM, Weissenberger J, Weis J,
Brown JD, O'Neill RJ and Laissue JA: Orthotopic transplantation of
v-src-expressing glioma cell lines into immunocompetent mice:
Establishment of a new transplantable in vivo model for malignant
glioma. J Neurosurg. 106:652–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dechow TN, Pedranzini L, Leitch A, Leslie
K, Gerald WL, Linkov I and Bromberg JF: Requirement of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 for the transformation of human mammary
epithelial cells by Stat3-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp.
10602–10607. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven
E, De Groot RP and Jove R: Stat3 activation by Src induces specific
gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell
Biol. 18:2545–2552. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro
MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L,
Fernández-Luna JL, Nuñez G, et al: Constitutive activation of Stat3
signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma
cells. Immunity. 10:105–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Chakraborty A,
Zhou MY, Zeng Q, Pitt AS and Tweardy DJ: Requirement of Stat3 but
not Stat1 activation for epidermal growth factor receptor- mediated
cell growth in vitro. J Clin Invest. 102:1385–1392. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rahaman SO, Harbor PC, Chernova O, Barnett
GH, Vogelbaum MA and Haque SJ: Inhibition of constitutively active
Stat3 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene. 21:8404–8413. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sherry MM, Reeves A, Wu JK and Cochran BH:
STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency
in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells. 27:2383–2392. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kohsaka S, Wang L, Yachi K, Mahabir R,
Narita T, Itoh T, Tanino M, Kimura T, Nishihara H and Tanaka S:
STAT3 inhibition overcomes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma
by downregulating MGMT expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1289–1299.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heimberger AB: The therapeutic potential
of inhibitors of the signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 for central nervous system malignancies. Surg
Neurol Int. 2:1632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Waldner MJ, Foersch S and Neurath MF:
Interleukin-6-a key regulator of colorectal cancer development. Int
J Biol Sci. 8:1248–1253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Culig Z and Puhr M: Interleukin-6: A
multifunctional targetable cytokine in human prostate cancer. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 360:52–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dethlefsen C, Højfeldt G and Hojman P: The
role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 138:657–664. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Macciò A and Madeddu C: The role of
interleukin-6 in the evolution of ovarian cancer: Clinical and
prognostic implications-a review. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:1355–1368.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miura T, Mitsunaga S, Ikeda M, Shimizu S,
Ohno I, Takahashi H, Furuse J, Inagaki M, Higashi S, Kato H, et al:
Characterization of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer and
high serum interleukin-6 levels. Pancreas. 44:756–763. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chang CH, Hsiao CF, Yeh YM, Chang GC, Tsai
YH, Chen YM, Huang MS, Chen HL, Li YJ, Yang PC, et al: Circulating
interleukin-6 level is a prognostic marker for survival in advanced
nonsmall cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Int J
Cancer. 132:1977–1985. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Lai KB,
Lee CN and Hsieh CY: Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth
by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene.
22:1517–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Weissenberger J, Loeffler S, Kappeler A,
Kopf M, Lukes A, Afanasieva TA, Aguzzi A and Weis J: IL-6 is
required for glioma development in a mouse model. Oncogene.
23:3308–3316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu Q, Li G, Li R, Shen J, He Q, Deng L,
Zhang C and Zhang J: IL-6 promotion of glioblastoma cell invasion
and angiogenesis in U251 and T98G cell lines. J Neurooncol.
100:165–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li R, Li G, Deng L, Liu Q, Dai J, Shen J
and Zhang J: IL-6 augments the invasiveness of U87MG human
glioblastoma multiforme cells via up-regulation of MMP-2 and
fascin-1. Oncol Rep. 23:1553–1559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Anton K, Banerjee D and Glod J:
Macrophage-associated mesenchymal stem cells assume an activated,
migratory, pro-inflammatory phenotype with increased IL-6 and
CXCL10 secretion. PLoS One. 7:e350362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Garonna E, Botham KM, Birdsey GM, Randi
AM, Gonzalez-Perez RR and Wheeler-Jones CP: Vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor-2 couples cyclo-oxygenase-2 with
pro-angiogenic actions of leptin on human endothelial cells. PLoS
One. 6:e188232011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shibuya M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and its receptor system: Physiological functions in
angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J Biochem.
153:13–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Labussière M, Cheneau C, Prahst C, Gállego
Pérez-Larraya J, Farina P, Lombardi G, Mokhtari K, Rahimian A,
Delattre JY, Eichmann A and Sanson M: Angiopoietin-2 may be
involved in the resistance to bevacizumab in recurrent
glioblastoma. Cancer Invest. 34:39–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou YH, Tan F, Hess KR and Yung WK: The
expression of PAX6, PTEN, vascular endothelial growth factor, and
epidermal growth factor receptor in gliomas: relationship to tumor
grade and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 9:3369–3375. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Modes of
resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:592–603.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Takano S: Glioblastoma angiogenesis: VEGF
resistance solutions and new strategies based on molecular
mechanisms of tumor vessel formation. Brain Tumor Pathol. 29:73–86.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li JL, Sainson RC, Oon CE, Turley H, Leek
R, Sheldon H, Bridges E, Shi W, Snell C, Bowden ET, et al:
DLL4-Notch signaling mediates tumor resistance to anti-VEGF therapy
in vivo. Cancer Res. 71:6073–6083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Peterson TE, Kirkpatrick ND, Huang Y,
Farrar CT, Marijt KA, Kloepper J, Datta M, Amoozgar Z, Seano G,
Jung K, et al: Dual inhibition of Ang-2 and VEGF receptors
normalizes tumor vasculature and prolongs survival in glioblastoma
by altering macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:pp. 4470–4475.
2016; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tabouret E, Denicolai E, Delfino C,
Graillon T, Boucard C, Nanni I, Padovani L, Figarella-Branger D and
Chinot O: Changes in PlGF and MET-HGF expressions in paired initial
and recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 130:431–437. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Piao Y, Liang J, Holmes L, Henry V, Sulman
E and de Groot JF: Acquired resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in
glioblastoma is associated with a mesenchymal transition. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:4392–4403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wesche J, Haglund K and Haugsten EM:
Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem J.
437:199–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fu Z, Chen X, Guan S, Yan Y, Lin H and Hua
ZC: Curcumin inhibits angiogenesis and improves defective
hematopoiesis induced by tumor-derived VEGF in tumor model through
modulating VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
6:19469–19482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wu XY, Xu H, Wu ZF, Chen C, Liu JY, Wu GN,
Yao XQ, Liu FK, Li G and Shen L: Formononetin, a novel FGFR2
inhibitor, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in
preclinical models. Oncotarget. 6:44563–44578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Waxman AB and Kolliputi N: IL-6 protects
against hyperoxia-induced mitochondrial damage via Bcl-2-induced
Bak interactions with mitofusins. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
41:385–396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hirano T, Ishihara K and Hibi M: Roles of
STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival
signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors.
Oncogene. 19:2548–2556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gritsko T, Williams A, Turkson J, Kaneko
S, Bowman T, Huang M, Nam S, Eweis I, Diaz N, Sullivan D, et al:
Persistent activation of stat3 signaling induces survivin gene
expression and confers resistance to apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:11–19. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Clarke MF and Fuller M: Stem cells and
cancer: Two faces of eve. Cell. 124:1111–1115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B,
Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA and
Dick JE: A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after
transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 367:645–648. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Magee JA, Piskounova E and Morrison SJ:
Cancer stem cells: Impact, heterogeneity, and uncertainty. Cancer
Cell. 21:283–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Willyard C: Stem cells: Bad seeds. Nature.
498:S12–S13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti
B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F and Vescovi
A: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hossain A, Gumin J, Gao F, Figueroa J,
Shinojima N, Takezaki T, Priebe W, Villarreal D, Kang SG, Joyce C,
et al: Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human gliomas increase
proliferation and maintain stemness of glioma stem cells through
the IL-6/gp130/STAT3 pathway. Stem Cells. 33:2400–2415. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jafri NF, Clarke JL, Weinberg V, Barani IJ
and Cha S: Relationship of glioblastoma multiforme to the
subventricular zone is associated with survival. Neuro Oncol.
15:91–96. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Young GS, Macklin EA, Setayesh K, Lawson
JD, Wen PY, Norden AD, Drappatz J and Kesari S: Longitudinal MRI
evidence for decreased survival among periventricular glioblastoma.
J Neurooncol. 104:261–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kroon P, Berry PA, Stower MJ, Rodrigues G,
Mann VM, Simms M, Bhasin D, Chettiar S, Li C, Li PK, et al:
JAK-STAT blockade inhibits tumor initiation and clonogenic recovery
of prostate cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 73:5288–5298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A,
Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ,
Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, et al: The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
is required for growth of CD44+CD24stem cell-like breast
cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest. 121:2723–2735. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Schroeder A, Herrmann A, Cherryholmes G,
Kowolik C, Buettner R, Pal S, Yu H, Müller-Newen G and Jove R: Loss
of androgen receptor expression promotes a stem-like cell phenotype
in prostate cancer through STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res.
74:1227–1237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhou B, Damrauer JS, Bailey ST, Hadzic T,
Jeong Y, Clark K, Fan C, Murphy L, Lee CY, Troester MA, et al:
Erythropoietin promotes breast tumorigenesis through
tumor-initiating cell self-renewal. J Clin Invest. 124:553–563.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Guo X, Qiu J, Tu T, Yang X, Deng L, Anders
RA, Zhou L and Fu YX: Induction of innate lymphoid cell-derived
interleukin-22 by the transcription factor STAT3 mediates
protection against intestinal infection. Immunity. 40:25–39. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang H, Lathia JD, Wu Q, Wang J, Li Z,
Heddleston JM, Eyler CE, Elderbroom J, Gallagher J, Schuschu J, et
al: Targeting interleukin 6 signaling suppresses glioma stem cell
survival and tumor growth. Stem Cells. 27:2393–2404. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Giladi ND, Ziv-Av A, Lee HK, Finniss S,
Cazacu S, Xiang C, Waldman Ben-Asher H, deCarvalho A, Mikkelsen T,
Poisson L and Brodie C: RTVP-1 promotes mesenchymal transformation
of glioma via a STAT-3/IL-6-dependent positive feedback loop.
Oncotarget. 6:22680–22697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li GH, Wei H, Lv SQ, Ji H and Wang DL:
Knockdown of STAT3 expression by RNAi suppresses growth and induces
apoptosis and differentiation in glioblastoma stem cells. Int J
Oncol. 37:103–110. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jackson C, Ruzevick J, Amin AG and Lim M:
Potential role for STAT3 inhibitors in glioblastoma. Neurosurg Clin
N Am. 23:379–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chang Q, Bournazou E, Sansone P, Berishaj
M, Gao SP, Daly L, Wels J, Theilen T, Granitto S, Zhang X, et al:
The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Neoplasia. 15:848–862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Liang Q, Ma C, Zhao Y, Gao G and Ma J:
Inhibition of STAT3 reduces astrocytoma cell invasion and
constitutive activation of STAT3 predicts poor prognosis in human
astrocytoma. PLoS One. 8:e847232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bowman T, Broome MA, Sinibaldi D, Wharton
W, Pledger WJ, Sedivy JM, Irby R, Yeatman T, Courtneidge SA and
Jove R: Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src
transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 98:pp. 7319–7324. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hodge DR, Hurt EM and Farrar WL: The role
of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2502–2512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kortylewski M and Yu H: Stat3 as a
potential target for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother.
30:131–139. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS, Larner AC,
Carter-Su C, Schwartz J and Jove R: Enhanced DNA-binding activity
of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src
oncoprotein. Science. 269:81–83. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3: A
STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in
response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science.
264:95–98. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Elliott LH, Brooks WH and Roszman TL:
Inability of mitogen-activated lymphocytes obtained from patients
with malignant primary intracranial tumors to express high affinity
interleukin 2 receptors. J Clin Invest. 86:80–86. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fletcher S, Drewry JA, Shahani VM, Page BD
and Gunning PT: Molecular disruption of oncogenic signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein. Biochem Cell
Biol. 87:825–833. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jing N and Tweardy DJ: Targeting Stat3 in
cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs. 16:601–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Leeman RJ, Lui VW and Grandis JR: STAT3 as
a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 6:231–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Müller-Newen G,
Schaper F and Graeve L: Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling
through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J. 334:297–314. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kim SR, Bae MK, Kim JY, Wee HJ, Yoo MA and
Bae SK: Aspirin induces apoptosis through the blockade of
IL-6-STAT3 signaling pathway in human glioblastoma A172 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 387:342–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Shao H, Cheng HY, Cook RG and Tweardy DJ:
Identification and characterization of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 recruitment sites within the epidermal
growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 63:3923–3930. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Abou-Ghazal M, Yang DS, Qiao W,
Reina-Ortiz C, Wei J, Kong LY, Fuller GN, Hiraoka N, Priebe W,
Sawaya R and Heimberger AB: The incidence, correlation with
tumor-infiltrating inflammation, and prognosis of phosphorylated
STAT3 expression in human gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 14:8228–8235.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Tu Y, Zhong Y, Fu J, Cao Y, Fu G, Tian X
and Wang B: Activation of JAK/STAT signal pathway predicts poor
prognosis of patients with gliomas. Med Oncol. 28:15–23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Minniti G, Muni R, Lanzetta G, Marchetti P
and Enrici RM: Chemotherapy for glioblastoma: Current treatment and
future perspectives for cytotoxic and targeted agents. Anticancer
Res. 29:5171–5184. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Baer JC, Freeman AA, Newlands ES, Watson
AJ, Rafferty JA and Margison GP: Depletion of O6-alkylguanine-DNA
alkyltransferase correlates with potentiation of temozolomide and
CCNU toxicity in human tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 67:1299–1302.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang G, Weiss C, Sheng P and Bresnick E:
Retrovirus-mediated transfer of the human O6-methylguanine-DNA
methyltransferase gene into a murine hematopoietic stem cell line
and resistance to the toxic effects of certain alkylating agents.
Biochem Pharmacol. 51:1221–1218. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF,
de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani
L, et al: MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Piperi C, Themistocleous MS, Papavassiliou
GA, Farmaki E, Levidou G, Korkolopoulou P, Adamopoulos C and
Papavassiliou AG: High incidence of MGMT and RARbeta promoter
methylation in primary glioblastomas: Association with
histopathological characteristics, inflammatory mediators and
clinical outcome. Mol Med. 16:1–9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Giometto B, Bozza F, Faresin F, Alessio L,
Mingrino S and Tavolato B: Immune infiltrates and cytokines in
gliomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 138:50–56. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Chang CY, Li MC, Liao SL, Huang YL, Shen
CC and Pan HC: Prognostic and clinical implication of IL-6
expression in glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Neurosci. 12:930–933.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Sasaki A, Ishiuchi S, Kanda T, Hasegawa M
and Nakazato Y: Analysis of interleukin-6 gene expression in
primary human gliomas, glioblastoma xenografts, and glioblastoma
cell lines. Brain Tumor Pathol. 18:13–21. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Hussain SF, Kong LY, Jordan J, Conrad C,
Madden T, Fokt I, Priebe W and Heimberger AB: A novel small
molecule inhibitor of signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 reverses immune tolerance in malignant glioma
patients. Cancer Res. 67:9630–9636. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, Aoki H,
Yokoyama T, Fokt I, Hess K, Conrad C, Madden T, Sawaya R, et al: A
novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant
glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 26:2435–2444.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Stechishin OD, Luchman HA, Ruan Y, Blough
MD, Nguyen SA, Kelly JJ, Cairncross JG and Weiss S: On-target
JAK2/STAT3 inhibition slows disease progression in orthotopic
xenografts of human glioblastoma brain tumor stem cells. Neuro
Oncol. 15:198–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
McFarland BC, Ma JY, Langford CP,
Gillespie GY, Yu H, Zheng Y, Nozell SE, Huszar D and Benveniste EN:
Therapeutic potential of AZD1480 for the treatment of human
glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:2384–2393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
He K, Qi Q, Chan CB, Xiao G, Liu X,
Tucker-Burden C, Wang L, Mao H, Lu X, McDonald FE, et al: Blockade
of glioma proliferation through allosteric inhibition of JAK2. Sci
Signal. 6:ra552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Senft C, Priester M, Polacin M, Schröder
K, Seifert V, Kögel D and Weissenberger J: Inhibition of the
JAK-2/STAT3 signaling pathway impedes the migratory and invasive
potential of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 101:393–403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Lo HW, Cao X, Zhu H and Ali-Osman F:
Constitutively activated STAT3 frequently coexpresses with
epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas and
targeting STAT3 sensitizes them to Iressa and alkylators. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:6042–6054. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Mukthavaram R, Ouyang X, Saklecha R, Jiang
P, Nomura N, Pingle SC, Guo F, Makale M and Kesari S: Effect of the
JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor SAR317461 on human glioblastoma tumorspheres.
J Transl Med. 13:2692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fuh B, Sobo M, Cen L, Josiah D, Hutzen B,
Cisek K, Bhasin D, Regan N, Lin L, Chan C, et al: LLL-3 inhibits
STAT3 activity, suppresses glioblastoma cell growth and prolongs
survival in a mouse glioblastoma model. Br J Cancer. 100:106–112.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Ball S, Li C, Li PK and Lin J: The small
molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and induces
apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells. PLoS One.
6:e188202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sai K, Wang S, Balasubramaniyan V, Conrad
C, Lang FF, Aldape K, Szymanski S, Fokt I, Dasgupta A, Madden T, et
al: Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma
stem-like cells by WP1193, a novel small molecule inhibitor of the
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Neurooncol. 107:487–501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Han TJ, Cho BJ, Choi EJ, Kim DH, Song SH,
Paek SH and Kim IA: Inhibition of STAT3 enhances the
radiosensitizing effect of temozolomide in glioblastoma cells in
vitro and in vivo. J Neurooncol. 130:89–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|